腹腔镜下保留肾单位手术对肾癌患者sCD44v6、sICAM-1、β-EP水平的影响
刘佳生
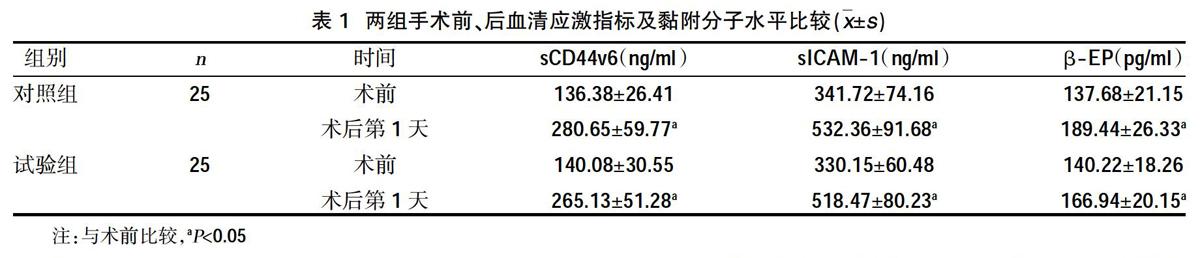
摘要:目的 探討腹腔镜下保留肾单位手术(RLNSS)对肾癌患者血清应激指标[β内啡肽(β-EP)]及黏附分子水平[可溶性分化抗原44拼接变异体6(sCD44v6)、可溶性细胞间黏附分子-1(sICAM-1)]的影响。方法 回顾性分析2017年2月~2019年10月我院收治的50例肾癌患者的临床资料,依照不同手术方法将其分为对照组与试验组,各25例。对照组实施开放性肾癌根治术,试验组实施RLNSS手术治疗,比较两组血清应激指标(β-EP)及黏附分子水平(sCD44v6、sICAM-1)。结果 术后第1天,试验组血清sCD44v6水平为(265.13±51.28)ng/ml、sICAM-1为(518.47±80.23)ng/ml,低于对照组的(280.65±59.77)ng/ml、(532.36±91.68)ng/ml,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后第1天,试验组β-EP水平为(166.94±20.15)pg/ml,低于对照组的(189.44±26.33)pg/ml,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 肾癌患者实施RLNSS手术治疗可减轻患者应激反应程度,对血清黏附分子水平影响较小。
关键词:肾癌;腹腔镜下保留肾单位手术;应激激素;黏附分子
中图分类号:R737.11 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.14.035
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)14-0117-02
Effect of Laparoscopic Nephron-sparing Operation on the Levels of sCD44v6,sICAM-1
and β-EP in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma
LIU Jia-sheng
(Urology Department,Jiamusi Central Hospital,Jiamusi 154002,Heilongjiang,China)
Abstract:Objective To explore the serum stress index [β endorphin (β-EP)] and the level of adhesion molecules [soluble differentiation antigen 44 splicing variant 6 (sCD44v6), soluble cells] in laparoscopic nephron-sparing surgery (RLNSS) Inter-adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1)].Methods The clinical data of 50 kidney cancer patients admitted to our hospital from February 2017 to October 2019 were retrospectively analyzed, and they were divided into a control group and a test group according to different surgical methods, 25 cases each.The control group underwent radical resection of renal cell carcinoma, and the experimental group underwent RNLSS surgery to compare the serum stress index (β-EP) and the level of adhesion molecules (sCD44v6, sICAM-1) between the two groups.Results On the first postoperative day, the serum sCD44v6 level in the experimental group was (265.13±51.28) ng/ml and sICAM-1 was (518.47±80.23) ng/ml, which was lower than that in the control group (280.65±59.77) ng/ml and (532.36) ±91.68) ng/ml, but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); on the first postoperative day, the β-EP level of the test group was (166.94±20.15) pg/ml, which was lower than that of the control group (189.44±26.33) pg/ml, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The operation of RNLSS in patients with renal cell carcinoma can reduce the degree of stress response of patients and have little effect on the level of serum adhesion molecules.

