The Accumulation of Visceral Fat and Preventive Measures among the Elderly
lsrael Oluwasegun Ayenigbara*
1 School Health and Community Health Unit,Department of Health Education,University of Ibadan,Ibadan,Nigeria
Abstract
Keywords:visceral fat;prevention;healthy diet;exercise;stress management
lntroduction
Visceral fat is a specific fat that is produced in the body,transformed into cholesterol,and circulated in the blood to other parts of the body [1].Importantly,these types of cholesterol are not good for health as they are made up of low- density fats,and are often low-density lipoproteins (LDLs),which form plaque on the walls of the arteries,thereby constricting and blocking them and preventing the free flow of nutrients in the body [1].The fats in the body can be categorized into two types:cutaneous fat and extremely deleterious visceral fat,which is usually found in the region of the abdomen that houses vital organs such as the liver,pancreas,and digestive tract [1].Importantly,visceral fat is usually stored in the stomach cavity,and it affects the normal functioning of hormones in the body [1,2].Hence,high storage of visceral fat and high levels of the constituents of visceral fat in the body,especially in the abdominal region,predispose an individual to deleterious health conditions,as visceral fat is a predisposing factor for other noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) [2].
In an elderly person,having some muscle or cutaneous fat is good for health;however,a high amount of visceral fat is a factor that causes complex health and medical conditions,such as type 2 diabetes and coronary diseases,in an elderly person [2- 4].Importantly,intra-abdominal fat is the depot that conveys the greatest risk to health and well-being in the elderly population [5].The connection between overall body fat and the risk of morbidity and death increases with age [5,6].For instance,overweight or obese middle-aged adults are predisposed to an increased risk of morbidity and death from NCDs [6].Over the years,it has been established that there is a substantial connection and association between high levels of intraabdominal fat,visceral fat,and cardiac visceral fat and morbidity and death from some NCDs in the general population [7].Globally,15 million people die of NCDs between the age of 30 years and the age of 69 years annually,with cardiovascular diseases,cancers,respiratory diseases,and diabetes accounting for more 80% of all NCDrelated deaths [8,9].Furthermore,there is an increase in NCD morbidity among people older than 70 years [8,9].This review presents the current evidence on the causes of visceral fat,a risk factor for the onset of different types of NCDs,with the main emphasis on its prevention,with a focus on elderly people.
Sources of lnformation
A literature review was performed with the PubMed and Springer Link databases.Specifically,the types of studies included in this review are clinical trials,meta-analyses,randomized controlled trials,and systematic and review articles.Furthermore,major international and national health agency databases were searched to obtain valuable information for the review,and careful screening was done to ensure that significant data were incorporated into this review.
Causes of Visceral Fat
Significantly,the health risks that are generally associated with the excessive accumulation of visceral fat in the body are different types of NCDs,which include cardiovascular diseases,type 2 diabetes,hypertension,stroke,breast and colorectal cancer,and Alzheimer disease [1,2]( Table1).Additionally,high accumulation of visceral fat inthe body can cause glucose intolerance due to elevated insulin resistance [2].

Table1 Waist Circumferences and Risk Levels According to Sex.
Many studies have affirmed that visceral fat adiposity,in combination with lipid dysregulation and diminished insulin sensitivity,is associated with high consumption of sugar and sugar-laden foods [10- 13].Furthermore,high consumption of diary products causes overweight and abdominal obesity [14,15].Likewise,other environmental variables,for example,maternal smoking,estrogenic compounds in food,and endocrine-disrupting chemicals,might be significant risk factors in the accumulation of visceral fat [16].Additionally,quality protein consumption during the day and the number of times the essential amino acid intake of approximately 10 g has been achieved are inversely associated with the level of central abdominal fat [17,18].Specifically,a study revealed that long-term alcohol consumption is a major cause of large abdomen circumference and an increase in the risk of abdominal weight gain and obesity in adult men [19].Importantly,the degree and frequency of abdominal obesity are rising among the Western population,potentially because of the combination of inactivity and unhealthy diet (e.g.,high-calorie diets),and also in developing nations,where it is associated with the urbanization of the population [20].
Preventive Measures against the Accumulation of Visceral Fat
A high quantity of fat in the body predisposes an individual to deleterious health consequences,as it is related to elevated levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides,thereby causing a reduction in the quantity of high-density lipoproteins [1,2].Furthermore,a high amount of fat impedes the body’ s normal ability to act on insulin,hence raising glucose and insulin levels [1,2].Also,a high amount of fat in the body is a significant predisposing factor for morbidity and death from numerous NCDs,such as stroke,myocardial infarction,hypertension,malignant growth,diabetes,osteoarthritis,fatty liver,and depression [21].The health risk of a high amount of visceral fat can be great,and therefore it is of upmost importance to make diet and lifestyle modification changes,as reduction in body weight enables an individual to lessen visceral fat production and reduce the quantity of visceral fat stored in the body [2].Importantly,the best proactive ways for elderly people to reduce the amount of and lessen the accumulation of excessive visceral fat in the body is through the combination of healthy eating,adequate and frequent exercise,and proper stress management [2]( Figure1).These are discussed extensively in the following sections.
Regular Physical Exercise
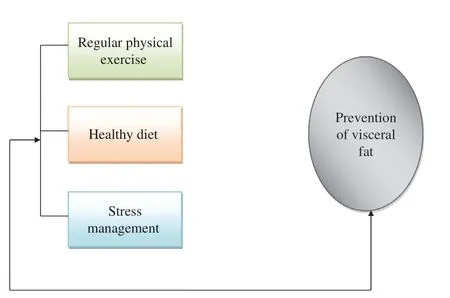
Figure1:Methods for the Prevention of Visceral Fat.
Physical exercise is a good method to decrease drastically the accumulation of visceral fat in the body [1,2,21].For better results,elderly people ought to incorporate both cardiovascular exercise and strength training,which raise the heart rate and increase muscle mass,respectively,into their exercise schedules and sessions [2].For instance,as little as 80 min of either aerobic or resistance training per week had significant positive effects on preventing weight regain following a diet-induced weight loss [22].More importantly,both aerobic and resistance training prevented regain of potentially harmful visceral fat [22].Furthermore,according to a randomized controlled trial on the effect of aerobic exercise training dose on liver fat and visceral adiposity,there was no difference in the degree of liver fat reduction by either aerobic exercise dose or intensity as all of the aerobic exercise regimens studied reduced the levels of liver fat and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) [23].Also,with regard to the effect of aerobic versus resistance exercise training on visceral fat,a systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that aerobic exercise is an important exercise program for reducing VAT levels,and that aerobic exercise below current recommendations for overweight/obesity management may be sufficient for beneficial VAT level reduction as well [24].Furthermore,a systematic review and metaanalysis on exercise and ectopic fat in type 2 diabetes suggests that exercise effectively reduces the level of visceral fat and perhaps that of liver adipose tissue and that aerobic exercise should be a key feature of exercise programs aimed at reducing the level of visceral fat in obesity-related type 2 diabetes [25].Importantly,regular aerobic exercise reduces the levels of hepatic lipids in obesity even in the absence of body weight reduction [26].Hence,physical activity should be strongly promoted for the management of fatty liver,the benefits of which are not exclusively contingent on weight loss [26].
Furthermore,a study on the effect of a 12-week aerobic exercise program on hepatic fat accumulation and insulin resistance in obese Hispanic adolescents revealed that a controlled aerobic exercise program,without weight loss,reduced hepatic and visceral fat accumulation and decreased insulin resistance in obese adolescents [27].In addition,aerobic training of moderate or high intensity has the highest potential to reduce VAT levels in overweight males and females [28].Also,an aerobic exercise program,without a hypocaloric diet,shows beneficial effects to reduce VAT levels by more than 30 cm2(on CT analysis) in women and more than 40 cm2in men,even after 12 weeks [28].For overweight and obese adults who wish to reduce the amounts of visceral fat and fatty liver infiltration and reduce insulin resistance as measured by homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) and alanine aminotransferase levels,a moderate amount of aerobic exercise is the most time- efficient and effective exercise mode,as aerobic training led to signifi-cant reductions in the levels of liver fat,visceral fat,alanine aminotransferase,insulin resistance as measured by HOMA,and total and subcutaneous abdominal fat [29].In obese adolescent girls,aerobic exercise is effective in reducing the levels of liver fat and VAT and increasing insulin sensitivity independently of weight loss or calorie restriction [30].At least 10 metabolic equivalent hours per week of aerobic exercise,such as brisk walking,light jogging,or stationary ergometer use,is required for reduction of the amount of visceral fat,and there is a dose-response relationship between aerobic exercise and reduction of the amount of visceral fat in obese individuals without metabolicrelated disorders [31].
Healthy Diet
Healthy diets with reduced amounts of sugar- and fat-laden foods will enable elderly people to reduce body weight and lessen the accumulation of visceral fat [1,2].The components of healthy diets should include natural fruits and vegetables and complex carbohydrates (e.g.,potatoes,beans,and natural grains) [2].Also,rather than frying,it is important to boil,steam,bake,and grill foods as this will make the diet healthier with reduced fat content [2].Furthermore,a high-fat diet,rather than a 60% high-sugar diet,will lead to obesity and macrophage infiltration in adipose tissues [32].According to a study on the effects of a very low calorie ketogenic diet at 2 years on visceral fat and on the burden of obesity,a very low calorie ketogenic diet was effective,with a decrease in the amount of VAT and a reduction in the individual burden of obesity [33].There is evidence in humans indicating that dietary fat quality influences insulin sensitivity and associated metabolic abnormalities [34].Therefore,prevention of metabolic syndrome has to be targeted:(1) to correct overweight by reducing the energy density of the habitual diet (i.e.,fat intake) and (2) to increase insulin sensitivity and reduce associated metabolic abnormalities through a reduction of the amount of dietary saturated fat,partially replaced,when appropriate,by monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats [34].Furthermore,with regard to the effects of dietary sugar restriction on liver fat,de novo lipogenesis (DNL),and insulin kinetics in children with obesity,it was found that short-term (9 days) isocaloric fructose restriction decreased the levels of liver fat,VAT,and DNL and improved insulin kinetics in children with obesity;hence,these findings support the need for efforts to reduce sugar consumption across all age groups [35].In addition,a fast food diet,which includes fructose and fats,produces a gene expression signature of increased hepatic fibrosis,inflammation,endoplasmic reticulum stress,and lipoapoptosis [36].Hepatic DNL (fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis) is increased in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [36].Furthermore,stable-isotope studies showed that increased DNL in patients with NAFLD contributed to fat accumulation in the liver and the development of NAFLD [36].
Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption is associated with abdominal fat partitioning in healthy adults as daily consumers of sugar-sweetened beverages had a 10% higher absolute VAT volume and a 15% greater VAT to subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) ratio compared with nonconsumers,whereas consumption of diet soda was not associated with either the volume or the distribution of VAT [37].Also,whole grain is beneficial in the reduction of the level of VAT in adults [38].In affirmation of this,a study on the effects of whole-grain and refined-grain intakes on abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adiposity in healthy adults revealed that increased whole-grain intake is associated with lower VAT levels in adults,whereas higher intakes of refined grains are associated with higher VAT levels [38].Additionally,adherence to recommended dietary guidelines and physical activity are associated with lower SAT and VAT volumes [39].With regard to the association between food consumption and the total volumes of VAT and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue (SAAT),it was found that intakes of potatoes and cakes were positively and inversely,respectively,associated with both VAT and SAAT [40].By contrast,intake of cereals was negatively associated with VAT only,whereas intakes of eggs and nonalcoholic beverages were positively associated with SAAT only [40].The association between eggs and nonalcoholic beverages and SAAT remained significant after further consideration of VAT;intake of nonalcoholic beverages was also inversely associated with VAT [40].Hence,it can be deduced that diet and foods are independently associated with VAT or SAAT volumes [40].
Stress Management
Stress also has a vital role in the accumulation of excess visceral fat [2].This is possible because when an individual is stressed,cortisol is released in the body,which increases the amount of visceral fat the body stores [2].Furthermore,chronic stress,mainly through hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation,promotes the accumulation of visceral fat [41].Similarly to job stress in adults,school-related stress in children may contribute to central adiposity,especially for girls with a high cortisol awakening response [42].As high stress levels predispose an individual to VAT,individuals with increased levels of visceral fat should reduce their stress levels [2].Important to the realization of this are relaxation methods;for example,meditation,deep breathing,and other stress management means could be of great benefit in helping an individual shed visceral fat [2].For instance,meditation has shown positive effects in reducing physical and emotional symptoms such as psychological stress,depression,anxiety,fatigue,fear of recurrence,and rumination,representing an efficient strategy for coping with breast cancer and improving quality of life in the elderly [43].Furthermore,with regard to the effectiveness of traditional meditation retreats,it was revealed that meditation retreats are moderately effective in reducing depression,anxiety,and stress and in improving the quality of life of participants [44].Also,poor sleep quality is associated with greater visceral adiposity and leptin levels,and hence good and quality sleep is advised for elderly people to reduce visceral adiposity fat secretion [45,46].
Conclusions
Visceral fat is a specific fat that is produced in the body,transformed into cholesterol,and circulated in the blood to other parts of the body.These types of cholesterol are not good for health as they are made up of low-density fats,and are often LDLs,which form plaque on the walls of the arteries,thereby constricting and blocking them and preventing the free flow of nutrients in the body.Visceral fat is deleterious to the health of elderly people because it is linked morbidity and death associated with numerous NCDs.Importantly,elderly people are often prone to the accumulation of visceral fat as a result of physiological and behavioral changes that come with aging,thereby causing inactivity and making healthy food choices less attractive.An extensive literature review was conduced on the prevention of the accumulation of visceral fat,and it was found that regular physical exercise,healthy food choices,and proper stress management are imperative for the prevention of excessive visceral fat in elderly people and the general population.
Recommendations
Subsequent to the literature review,the following recommendations are made:
1.Regular physical exercise,especially aerobic exercises,should be practiced by elderly people.Examples of such activities include brisk walking,light jogging,dancing,swimming,water aerobics,bicycle riding,canoeing,doing minor chores at home,and stationary ergometer use.However,adequate safety measures should be put in place,and health conditions should be certified by a physician before elderly people participate in any form of physical exercise.
2.Healthy diets low in sugars and fats but high in natural fruits and vegetables and complex carbohydrates (e.g.,potatoes,beans,and natural grains) should be consumed more by elderly people.Furthermore,rather than frying,it is important to boil,steam,bake,and grill foods as this will make the diet healthier with a reduced fat content.
3.Proper stress management that includes meditation,adequate rest,sleep,and deep breathing is recommended for elderly people to reduce the rate of cortisol secretion in the body,and also to reduce depression,anxiety,stress,and fatigue and to improve the quality of life.
Acknowledgments
Great thanks are given to unknown reviewers for valuable comments.Furthermore,I thank researchers who over the years have contributed to the ideas discussed in this article.
Confiict of interest
The author declares no potential conflict of interest.
Funding
The work was self-funded by the author.
Dedication
The article is dedicated to all senior citizens around the world.
 Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications2020年2期
Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications2020年2期
- Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications的其它文章
- Development of Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention as a National Reperfusion Strategy for Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Assessment of Its Use in Egypt
- Discovery of Digenic Mutation,KCNH2 c.1898A > C and JUP c.916dupA,in a Chinese Family with Long QT Syndrome via Whole-Exome Sequencing
- Association of Serum Chemerin Levels with Coronary Artery Disease:Pathogenesis and Clinical Research
- Identification of Novel TTN Mutations in Three Chinese Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy Pedigrees by Whole Exome Sequencing
- Chronic Effusive Pericarditis and Chronic Constrictive Pericarditis
- Some Issues Related to STEMI and NSTEMI
