不同生物药剂对茶炭疽病菌和茶轮斑病菌的室内毒力测定
郭迟鸣 林文珍 汪文华 郭莺 刘黎卿 林志楷

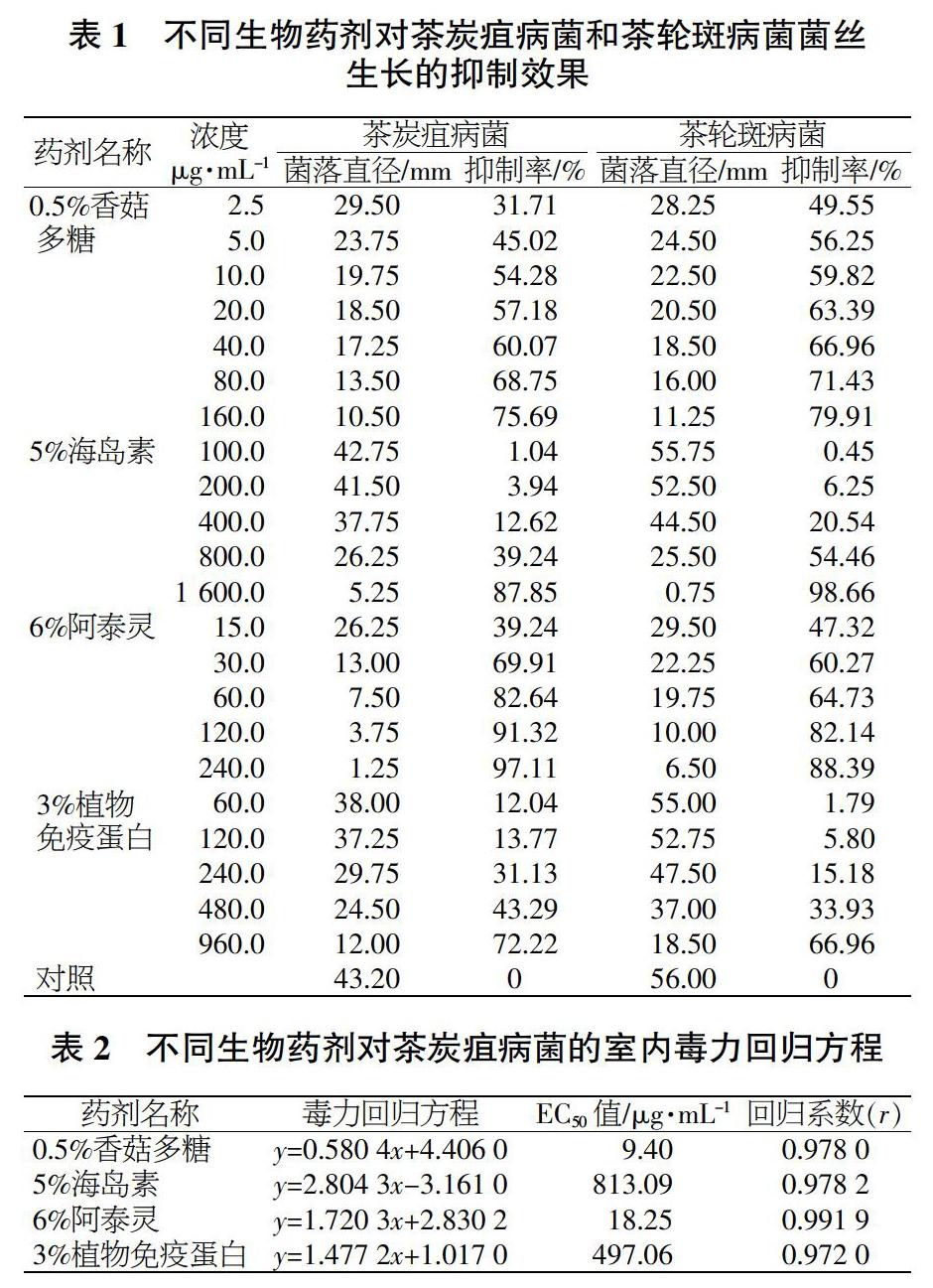
摘要 茶树是我国重要的经济作物,但是由于其主要生长在温暖、湿润的环境,造成了茶树病害的滋生。茶炭疽病和茶轮斑病是茶树的重要病害,目前主要利用化学方法防治,而生物防治方法仍十分有限。本研究利用菌丝生长速率法测定了4种生物药剂对茶炭疽病菌和茶轮斑病菌的室内抑菌活性。结果表明,0.5%香菇多糖对茶炭疽病菌和茶轮斑病菌菌丝生长的抑制作用较好,EC50值分别为9.40 μg/mL和2.68 μg/mL;其次为6%阿泰灵,EC50值分别为18.25 μg/mL和18.63 μg/mL,而5%海岛素和3%植物免疫蛋白效果较差。
关键词 茶炭疽病菌;茶轮斑病菌;生物药剂;毒力测定
中图分类号 S435.711 文献标识码 A
文章编号 1007-5739(2020)12-0116-02 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
Toxicity Measurement of Different Biological Reagents on Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Pseudopestalotiopsis
camelliae-sinensis
GUO Chi-ming 1,2 LIN Wen-zhen 1,2 WANG Wen-hua 1,2 GUO Ying 1,2 LIU Li-qing 1,2 LIN Zhi-kai 1,2
(1 Fujian Institute of Subtropical Botany,Xiamen Fujian 361006; 2 Fujian Key Laboratory of Physiology and Biochemistry for Subtropical Plant)
Abstract Tea plant is one of the important economic plants in China, it mainly grows in warm and humid environment, which resulting in the disease propagation. Anthracnose and gray leaf blight leaf spot are two important diseases in tea plants.At present, controlling the two diseases mainly relies on chemical fungicides, but biological control methods are still very limited. The paper used the mycelium growth rate method to determine inhibitory effect of 4 different biological reagents against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Pseudopestalotiopsis camelliae-sinensis. The results showed that 0.5% lentinan had the strongest anitfungal activity on the mycelial growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Pseudopestalotiopsis camelliae-sinensis, and the EC50 values were 9.40 μg/mL and 2.68 μg/mL, respectively; 6% Atailing also showed good inhibitory activity on the two fungus, the EC50 values were 18.25 μg/mL and 18.63 μg/mL, respectively. While 5% Haidaosu and 3% plant immune protein showed poor inhibitory activity.
Key words Colletotrichum gloeosporioides;Pseudopestalotiopsis camelliae-sinensis;biological reagent;toxicity measurement
茶樹作为一种重要的经济作物,广泛种植于热带和亚热带地区。我国是茶树的原产地,茶叶更是我国对外贸易的重要农产品之一[1]。茶叶品质及农残是制约茶叶生产出口的重要因素,因而筛选和使用高效、低残留的农药对有效合理防治茶树病害具有重要意义。

