基于Walsh函数调制的单帧远场波前反演方法
孔庆峰,王 帅,杨 平,林海奇,刘 永,许 冰
基于Walsh函数调制的单帧远场波前反演方法
孔庆峰1,2,3,4,王 帅1,3*,杨 平1,3*,林海奇1,3,4,刘 永2,许 冰1,3
1中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209;2电子科技大学光电科学与工程学院,四川 成都 610054;3中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209;4中国科学院大学,北京 100049
单帧远场图像重构波前像差的方法在结构简便性方面有独特的优势。然而,传统的基于单帧远场图像的波前重构算法存在多解问题,算法收敛过程容易陷入停滞。本文在分析单帧相位反演方法的多解问题成因的基础上,提出了一种基于Walsh函数的二维离散相位调制的波前重构方法。此种方法可以有效地打破近场波前的对称性,解决多解问题。仿真结果表明,该方法只需一个远场图像就可以精确地重建波前像差。
相位反演;像差;远场;二维离散调制
1 引 言
相位反演技术(Phase retrieval,PR)是一种通过已知的二维光强分布来恢复波前像差的方法。由于其检测精度高、环境要求低,它被广泛应用于激光质量评价[1]、自适应光学[2-3]、X射线相位对比成像[4-5]、天文观测[6-8]等领域。
Gerchberg-Saxton(GS)算法是经典的利用远场图像重构波前的复原算法,其结构简单,易于实现[9]。GS算法利用远场和近场强度间的傅里叶变换关系来计算波前像差,但其算法在迭代过程容易陷入停滞。这种迭代停滞是由于实际的近场复振幅和它的旋转180°共轭复振幅在远场上具有相同的光强分布而产生的[10]。因此,GS算法很容易收敛到局部最小伪解或两个全局最小模糊解之一[11]。
Gonsalves提出了相位差(phase difference,PD)算法来克服GS算法的多解问题[2],该算法通过添加一副离焦面光强分布信息来提高波前恢复的精度。然而,此方法需要使用两个CCD相机,牺牲了光学结构的简便性。
2008年,李敏、李新阳提出了一种基于线性相位反演的方法来解决单帧相位反演的问题,此方法对较小的像差有效[12-13]。2010年,Meimon提出了一种基于单个图像重建波前的线性焦面反演算法,但该算法仅对低阶像差复原有效[14]。Greenbaum在2016年提出了一种引入非冗余掩模(non-redundant mask,NRM)打破相位的符号不确定性的方法来重建单帧焦面图像的近场波前[11]。然而,NRM进出光路的精度和探测装置的复杂性限制了该算法在实际波前探测中的应用。
为解决传统单帧反演算法的上述问题,本文提出了一种基于Walsh函数的二维离散相位调制的反演方法,打破了近场像差的旋转翻转对称性,通过调制后的特殊光强分布,可以快速恢复出原始波前的准确相位信息。
本文的结构如下:第二节着重分析了传统单帧相位反演方法的像差多解问题,并介绍了基于Walsh函数的二维离散相位片调制的波前复原算法的基本原理和限定条件;在第三节中,通过仿真实验,比较了基于不同Walsh函数相位调制的复原结果;并在第四节对本文工作进行了总结。
2 基本原理
2.1 传统单帧相位反演方法的像差多解问题
当两组波前像差具有互为旋转180°复共轭关系时(类似于奇函数),它们将具有相同的远场光斑分布,即两个不同近场对应同一个远场光强分布。下面用数学表达式来分析此问题。
均匀光波入射下,通过振幅归一化,入射平面波复振幅可以表示为
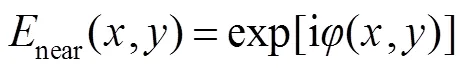
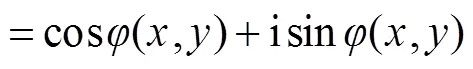
远场复振幅可以通过近场复振幅的傅里叶变换获得,在忽略系数的情况下,可以表示如下:
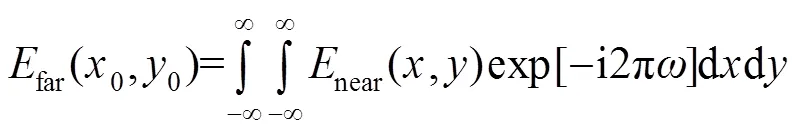

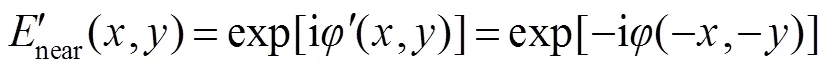


比较式(2)和式(4),根据积分对称性,两者实部相等、虚部符号相反,光强值为振幅的平方。因此,两组具有旋转180°复共轭关系的波前具有相同的远场光斑分布,即:
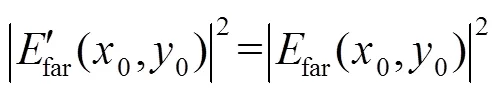
因此,利用单个远场光斑反演近场波前像差,算法就可能由于多解问题陷入停滞,得不到准确的波前相位信息。
2.2 二维离散像差调制
为了解决基于单帧焦面图像的相位反演算法的多解问题,一种可行的方法是打破近场波前相位的旋转对称性。如果采用连续像差进行波前调制,则相当于在待测波前的基础上叠加了一个波面,虽然可能对原来的两组旋转对称像差的远场光强一致性起到了破坏,但并不能解决多解问题。
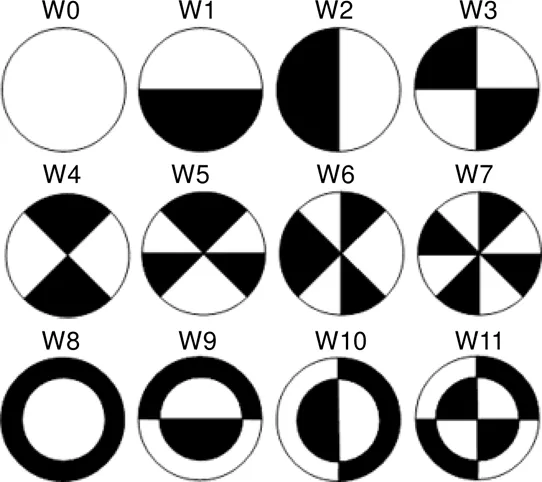
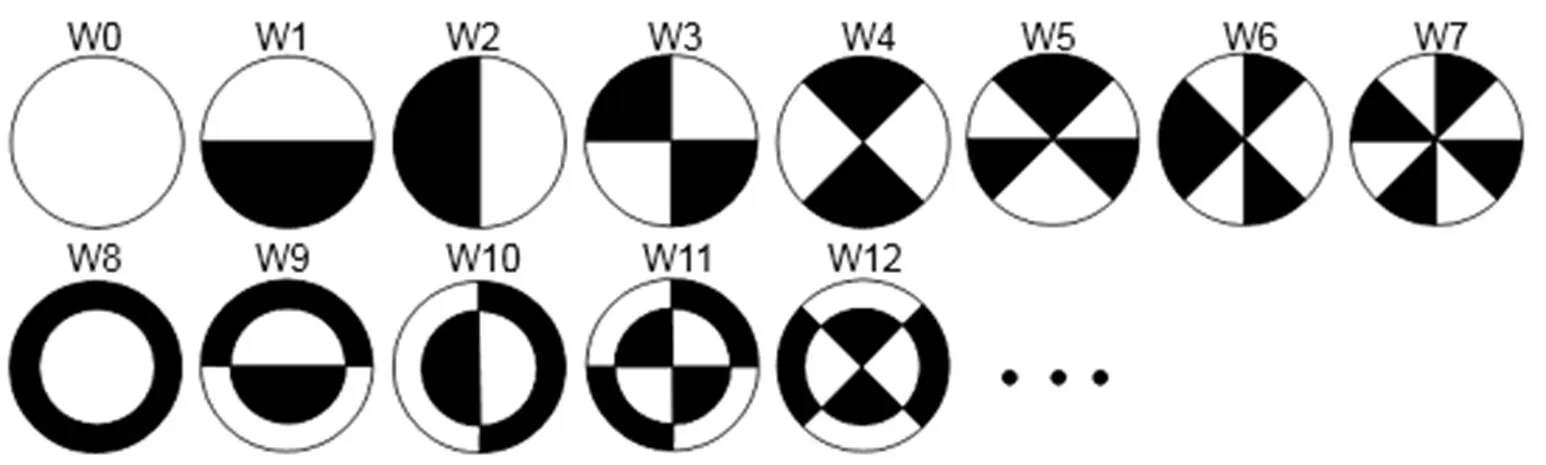
Wang于2009年首次提出了利用Walsh函数来表征离散二元像差的模式,如图1所示[15-16],此组函数的黑白区间总面积相等。这些图案与传统连续像差具有明显不同的分布方式。
如果以这些离散图案制作成相位片,即黑色区域相对白色区域具有相位台阶,将其置于光路中,则有可能打破原有近场相位的旋转对称性。由此本文提出了一种基于Walsh函数调制的波前复原方法,其光路系统如图2所示。在近场插入一片带有相位台阶的相位片,其具有类似图1的空间分布方式。通过此相位片的空间调制后,波前经过透镜聚焦到相机靶面。
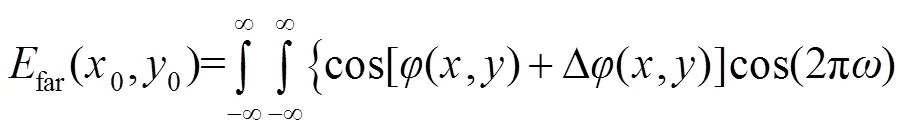
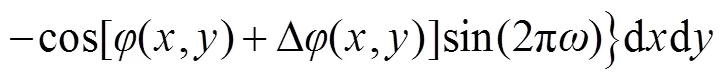

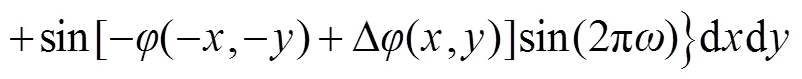
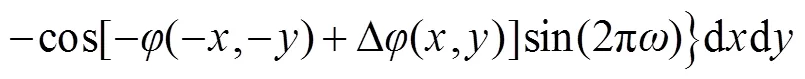
比较式(6)和式(7),两者具有明显差别,一般情况下:
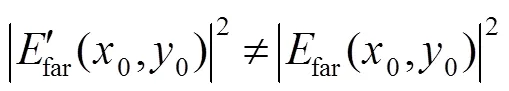
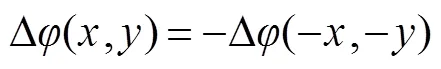
将式(9)代入式(7),可得:
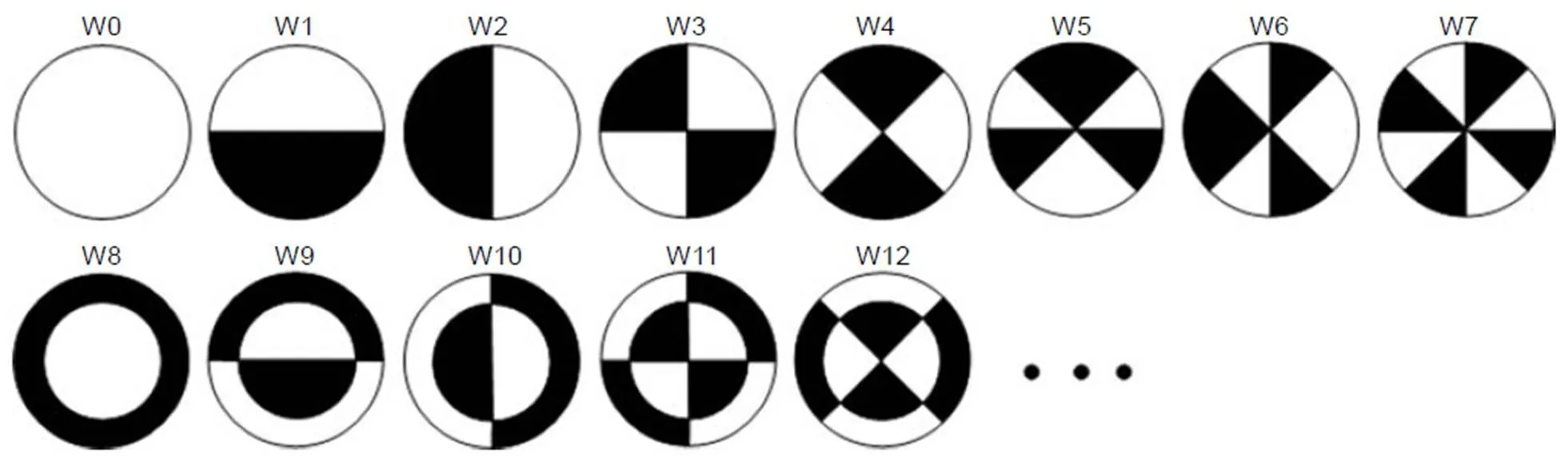
图1 Walsh函数分布
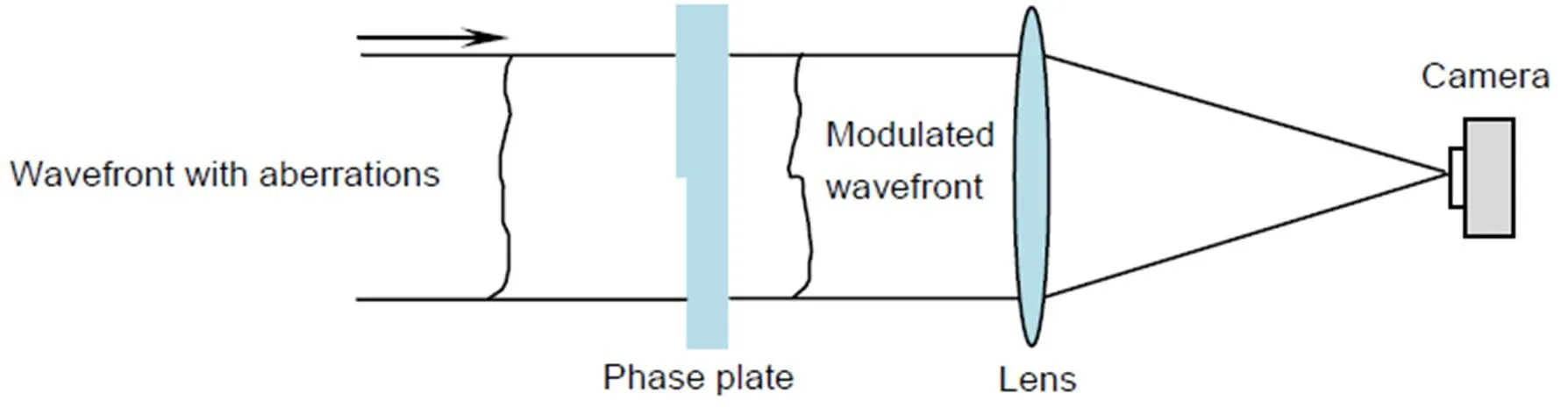
图2 光学系统模型
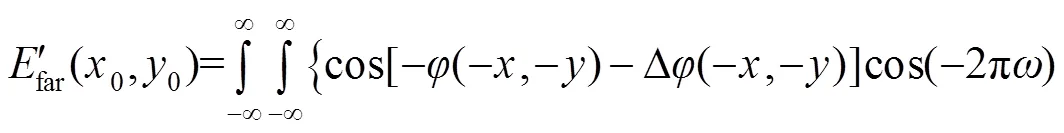
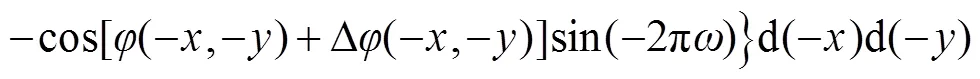
比较式(6)和式(10),两者实部相等,虚部符号相反,即同样可以得到:
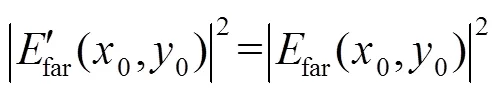
分别用正、负离焦像差和一对随机旋转复共轭随机像差为例,来验证以上结论。其中正、负离焦像差可以看作为特殊的旋转复共轭对。仿真模拟中,透镜焦距为500 mm,波长625 nm,光束半径为2 mm,CCD像素尺寸为10mm,相位片的相位台阶为p/2。
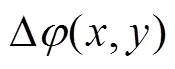
2.3 基于Walsh函数二维离散调制的相位反演算法
由式(1)可知,远场复振幅可以近似看成近场复振幅的傅里叶变换:
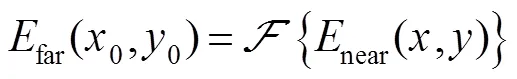
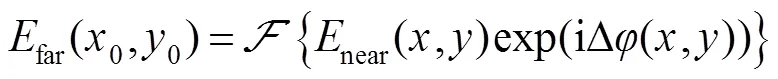
对上式进行逆傅里叶变换,可以得到:
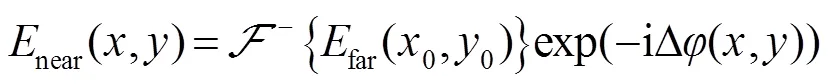
具体的基于Walsh函数二维离散调制的相位反演算法流程如图4所示。首先设定待测波前初始值为0,之后通过二维调制,计算得到远场光强,比较计算所得光强与实际测得光强是否足够接近,可用误差平方和(sum of squares due to error,SSE,用SSE表示)来评价,其公式表达式如下:
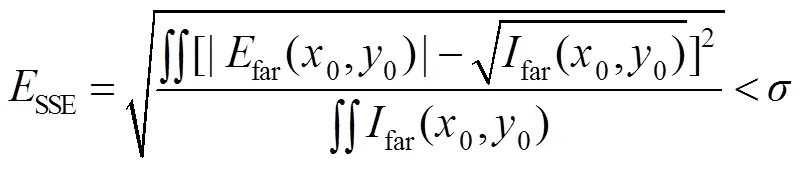
3 仿真实验
在本节中,对基于Walsh函数二维调制波前复原方法的有效性和测量精度进行了数值仿真。与传统GS算法之间的对比仿真实验也被阐述。
仿真参数如下:透镜焦距为500 mm,波长625 nm,光束半径为2 mm,CCD像素尺寸为10mm,相位片的相位台阶为p/2。评估标准SSE被设置为小于10-6。如果300次迭代后不能达到判定标准,程序循环将终止。
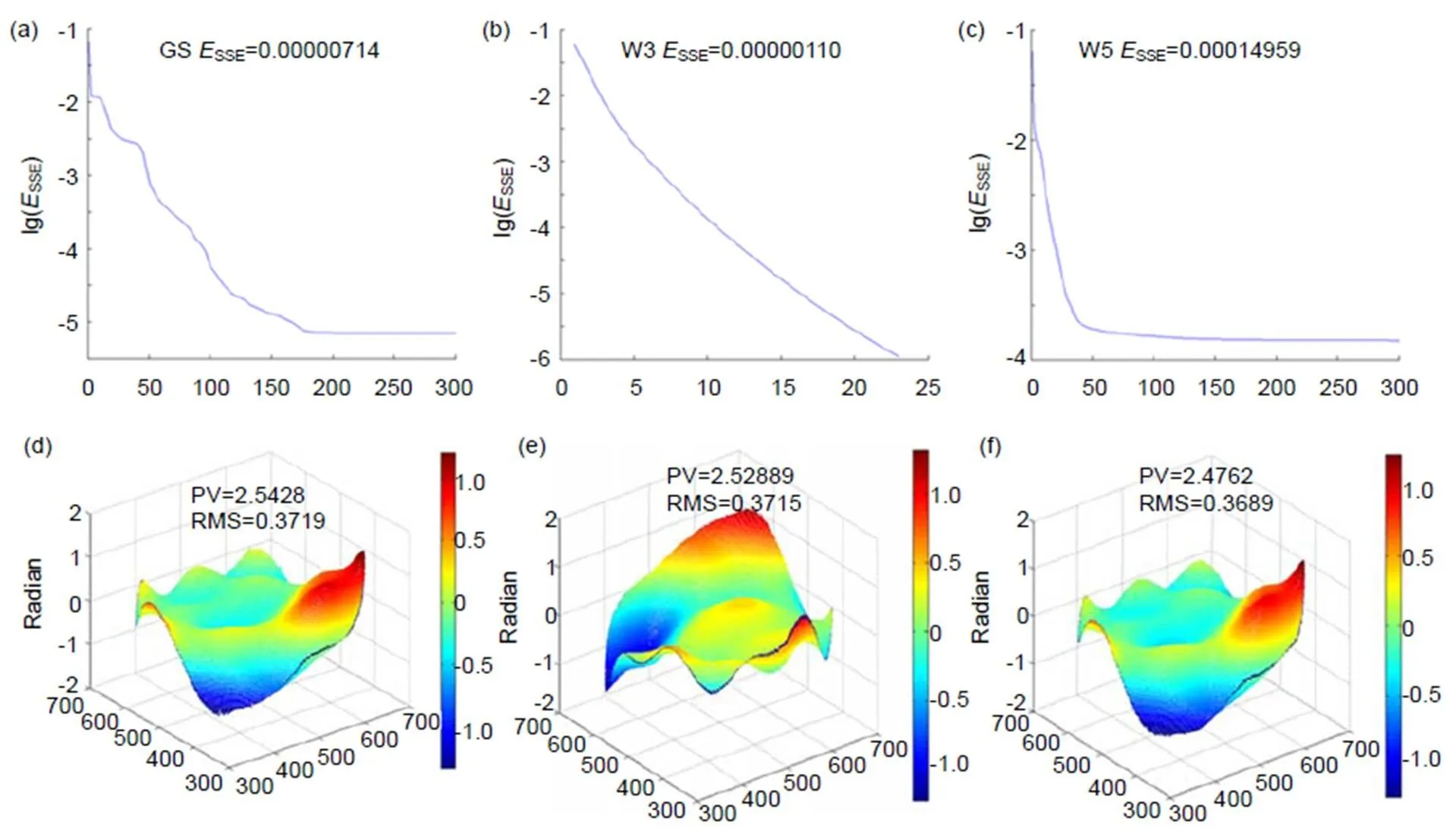
首先,利用前65阶Zernike多项式生成了PV值为2.5218 rad和RMS值为0.3719 rad的随机波前像差,如图5所示。
使用传统GS算法、基于Walsh函数W3的调制反演算法、基于Walsh函数W5的调制反演算法分别重构上述随机入射波前。
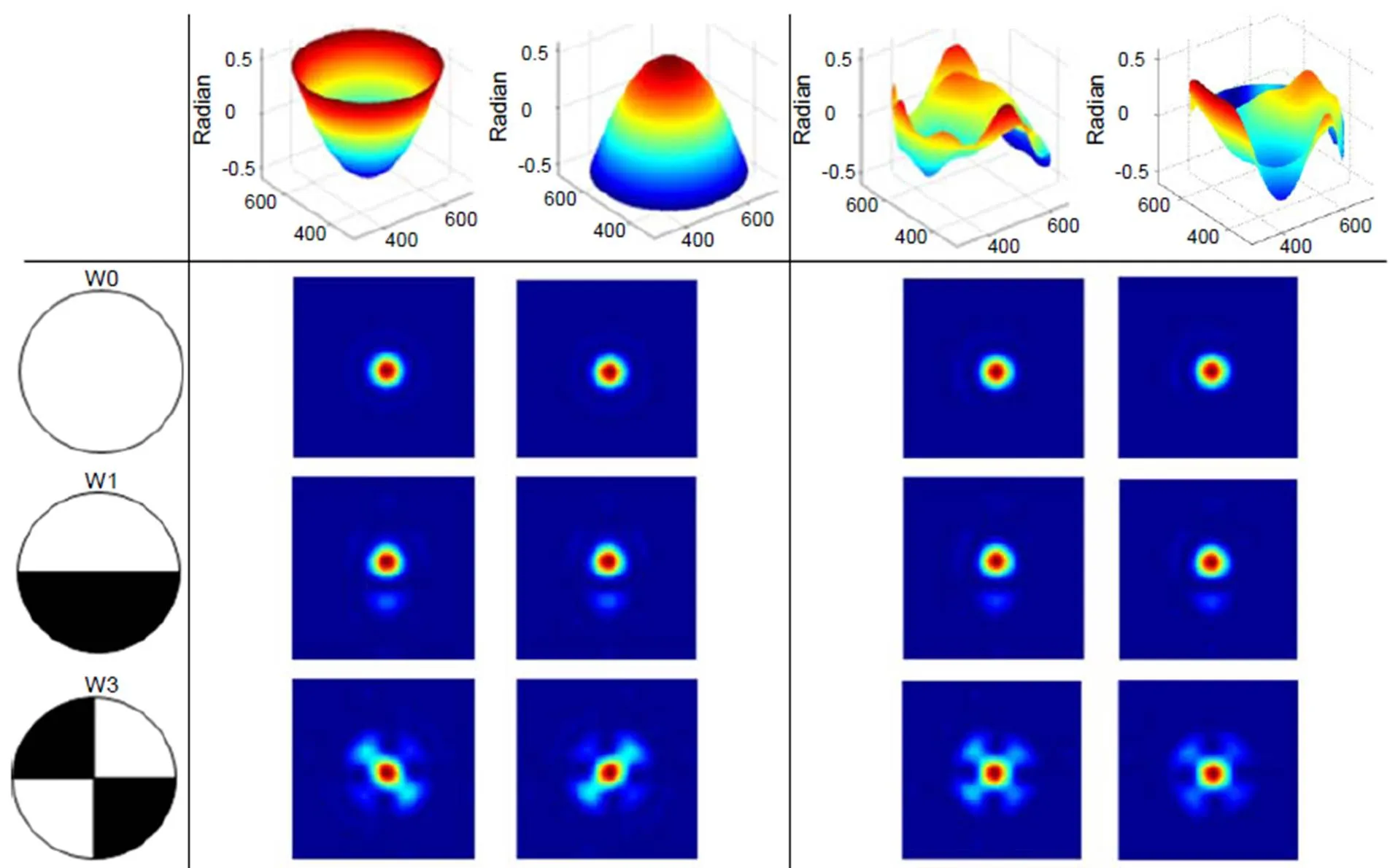
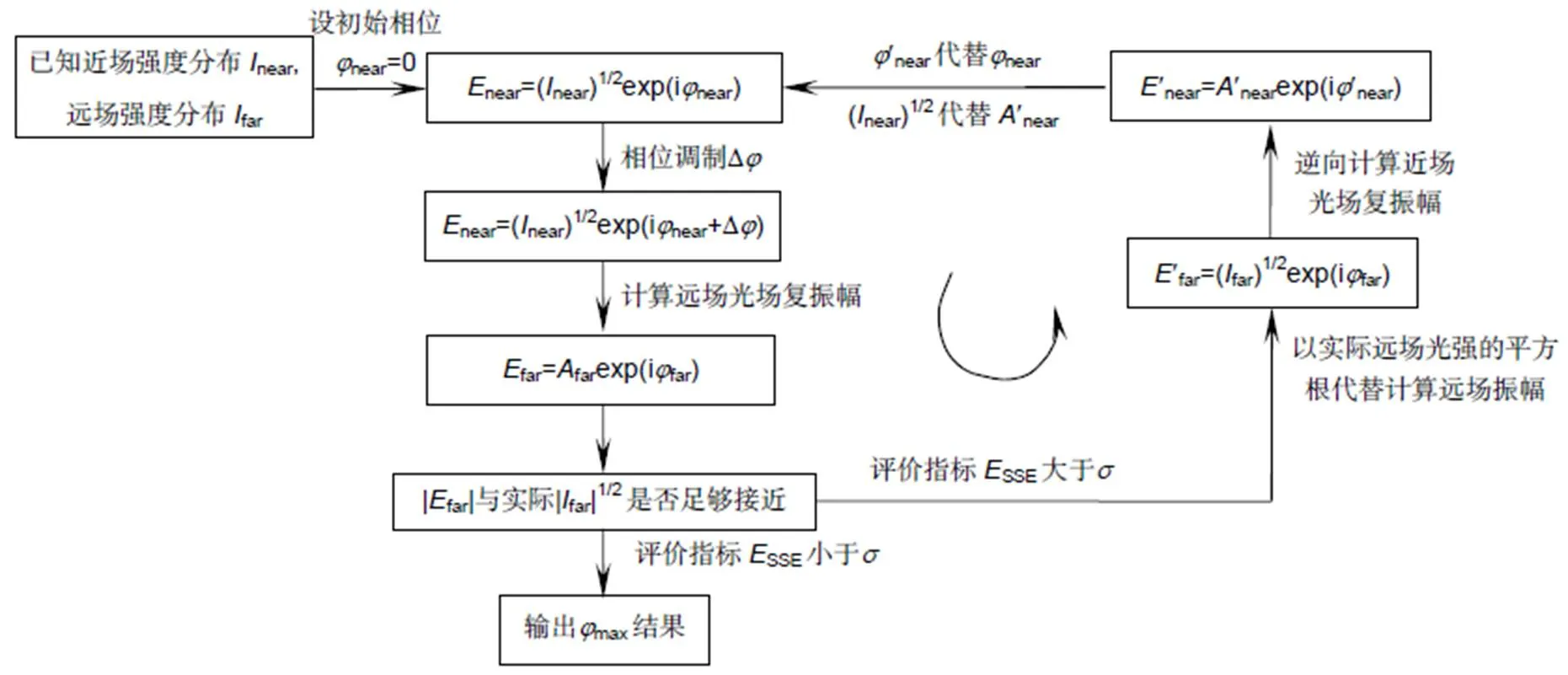
图4 基于Walsh函数调制的相位反演算法流程图
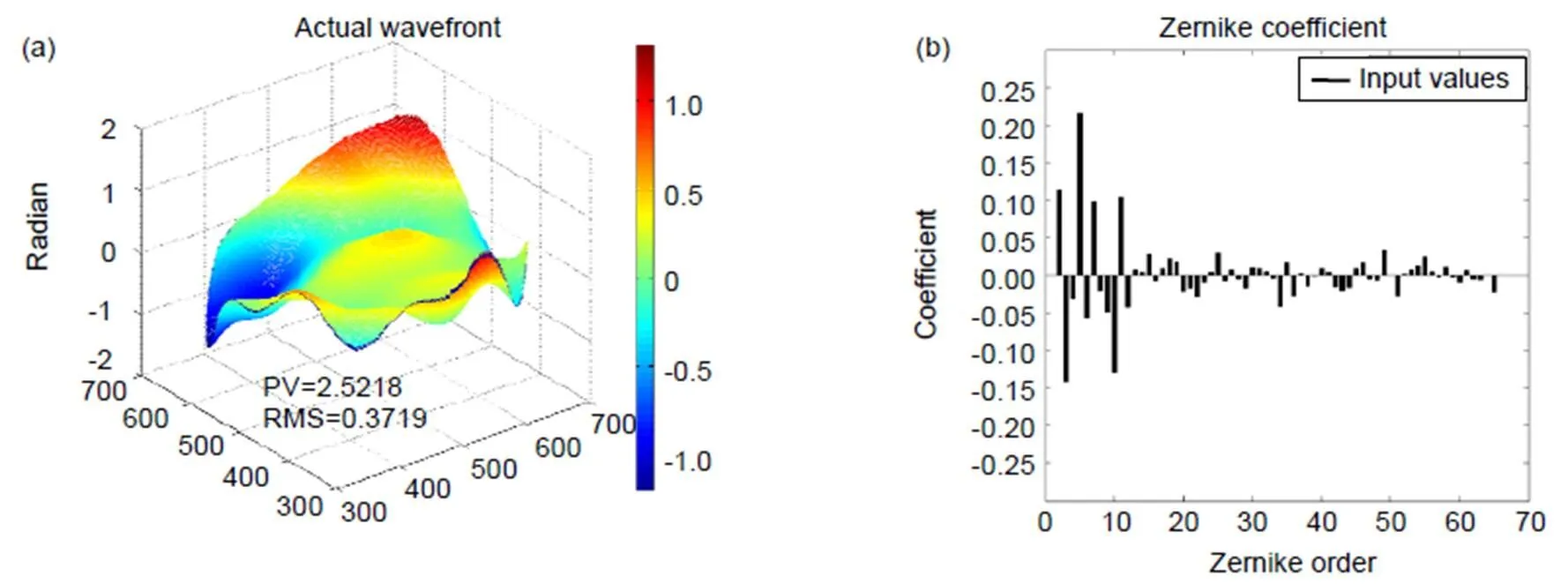
图5 待测波前。(a) 波形;(b) Zernike系数
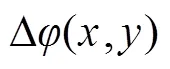
为了验证不同相位台阶对二维离散调制方法的影响,以四象限结构W3为例,进行仿真,评价指标为10E-7,相位台阶深度分别是p/5、p/2和7p/10。对应的波前复原迭代曲线如图9所示,可以看出在p/2的相位台阶下,整体复原效果最好,p/5效果稍好,而绿色曲线7p/10效果稍差一些,但都能准确复原波前。相位台阶过小时,调制效果不够明显;过大时,台阶效应较大,不利于复原波面。
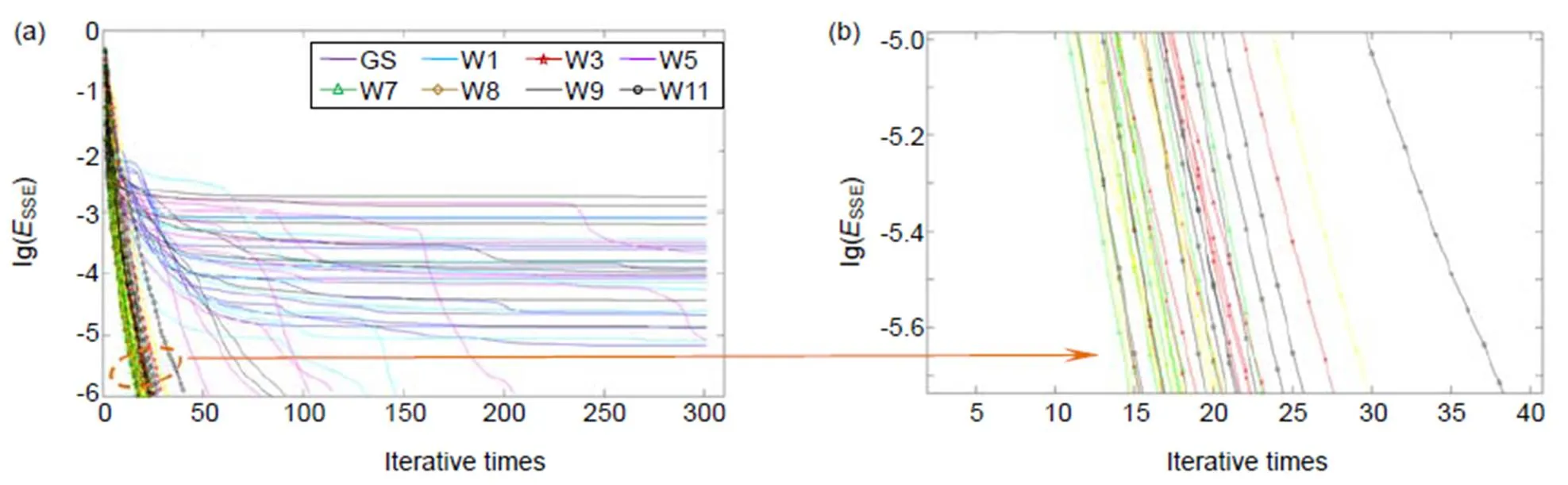
图7 传统GS算法和Walsh函数调制算法的迭代曲线
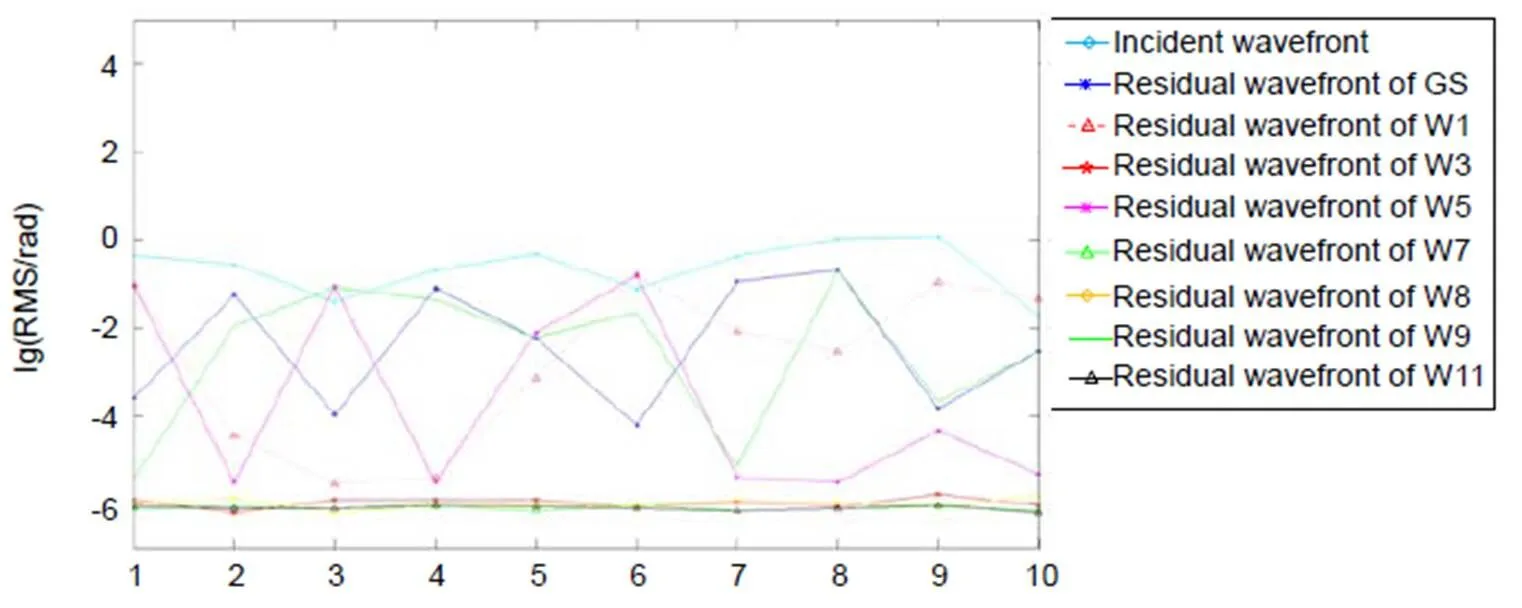
图8 不同相位反演方法的残余波前RMS值比较图

图9 不同相位台阶下评价指标ESSE的收敛曲线
4 结 论
本文详细分析了传统单帧反演算法的多解问题,提出了一种基于Walsh函数调制的波前重构方法。介绍了该方法的基本原理和限定条件,即调制相位本身应不具备180°旋转翻转对称性。通过仿真实验,比较了提出算法和传统GS算法的波前复原精度。结果表明,基于Walsh函数相位调制的波前反演算法在单帧远场图像条件下可以精确地复原出待测波前像差。当然,从相位调制片制作工艺难度和对波前尺寸的普适性角度来讲,实际应用中基于W3的四象限调制方式将更有优势。
[1] Védrenne N, Mugnier L M, Michau V,. Laser beam complex amplitude measurement by phase diversity[J]., 2014, 22(4): 4575–4589.
[2] Gonsalves R A. Phase retrieval and diversity in adaptive optics[J]., 1982, 21(5): 215829.
[3] Jiang W H. Overview of adaptive optics development[J]., 2018, 45(3): 170489.
姜文汉. 自适应光学发展综述[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170489.
[4] Wu J, Chen J B. A phase retrieval algorithm for X-ray phase contrast imaging[J]., 2013, 124(9): 864–866.
[5] Wu X Z, Yan A M. Phase retrieval from one single phase contrast X-ray image[J]., 2009, 17(13): 11187–11196.
[6] Fienup J R, Marron J C, Schulz T J,. Hubble Space Telescope characterized by using phase-retrieval algorithms[J]., 1993, 32(10): 1747–1767.
[7] Hartung M, Blanc A, Fusco T,. Calibration of NAOS and CONICA static aberrations experimental results[J]., 2003, 399(1): 386–394.
[8] Bao H, Rao C H, Tian Y,. Research progress on adaptive optical image post reconstruction[J]., 2018, 45(3): 170730.
鲍华, 饶长辉, 田雨, 等. 自适应光学图像事后重建技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(3): 170730.
[9] Gerchberg R W, Saxton W O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures[J]., 1972, 35(2): 237–246.
[10] Fienup J R, Wackerman C C. Phase-retrieval stagnation problems and solutions[J]., 1986, 3(11): 1897–1907.
[11] Greenbaum A Z, Sivaramakrishnan A. In-focus wavefront sensing using non-redundant mask-induced pupil diversity[J]., 2016, 24(14): 15506–15521.
[12] Li M, Li X Y, Jiang W H. Small-phase retrieval with a single far-field image[J]., 2008, 16(11): 8190–8197.
[13] Li M, Li X Y. Linear phase retrieval with a single far-field image based on Zernike polynomials[J]., 2009, 17(17): 15257–15263.
[14] Meimon S, Fusco T, Mugnier L M. LIFT: a focal-plane wavefront sensor for real-time low-order sensing on faint sources[J]., 2010, 35(18): 3036–3038.
[15] Wang F L. Wavefront sensing through measurements of binary aberration modes[J]., 2009, 48(15): 2865–2870.
[16] Wang S, Yang P, Ao M W,. Wavefront sensing by means of binary intensity modulation[J]., 2014, 53(35): 8342–8349.
Single-frame far-field wavefront retrieval method based on Walsh function modulation
Kong Qingfeng1,2,3,4, Wang Shuai1,3*, Yang Ping1,3*, Lin Haiqi1,3,4, Liu Yong2, Xu Bing1,3
1Key Laboratory of Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan 610054, China;3Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;4University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Distribution of Walsh functions
Overview:Phase retrieval (PR) is an iterative process of wavefront recovering from known intensity distribution. Owing to high detection accuracy and lower environment requirement, PR has become an attractive candidate to the wavefront sensor (WFS) in adaptive optics. With the development of computer speed, PR will have greater potentiality in active optic systems.
Gerchberg and Saxton proposed firstly the GS algorithm to recover the wavefront aberration. This algorithm can achieve typical convergence, but its iterative process easily falls into stagnation. For instance, the true pupil field(,) and its twin*(-, -) have the same Fourier modulus, so the algorithm tries to recover both together and goes nowhere. For overcoming the two-fold ambiguity of GS algorithm, phase diversity (PD) algorithm was proposed by Gonsalves in 1979. However, this method introduces a defocused plane to increase the constrained intensity information to reconstruct the wavefront, which will sacrifice the simplicity. Löfdahl proposed PD sensor with a beam splitter to make the focus and defocused images be captured by one CCD. For the same purpose a PD sensor with a distorted diffraction grating was presented by Blanchard in 2000. Nevertheless, more complex structure, interaction of high frequency information and dynamic range of CCD limit the practical application of these methods in the PD.
In 2008, Min Li and Xinyang Li proposed a method based on the linear phase retrieval (LPR) to reconstruct small aberrations from a single far field image. In 2010, the linearized focal plane technique (LIFT) was presented by Serge Meimon, which is only effective for lower order aberration. Bing Dong et al demonstrated a hybrid phase retrieval algorithm using a combination of LPR and GS in 2015. The estimation result of LPR is used as a prior knowledge to speed convergence of GS. In this way, the higher order aberrations are basically recovered, but the problem of multiple solutions remains unsolved.
In order to solve the problems mentioned above in traditional single-frame phase retrieval algorithm, a feasible method is proposed to break the rotational symmetry of near-field wavefront phase. If continuous aberration is used for wavefront modulation, it is equivalent to adding a wavefront on the measured wavefront. This cannot solve the problem of multiple solutions.
A wavefront reconstruction method based on Walsh function two-dimensional discrete phase modulation is proposed in this paper. This method can effectively break the symmetry of near-field wavefront and overcome problem of PR multiple solutions. The basic principle and limitation of this method are introduced. The wavefront retrieval accuracy of the proposed algorithm is compared to the traditional GS algorithm through simulations and experiments. The results show that the wavefront retrieval algorithm based on phase modulation of Walsh function can accurately reconstruct the wavefront aberration under the condition of single far-field image.
Citation: Kong Q F, Wang S, Yang P,Single-frame far-field wavefront retrieval method based on Walsh function modulation[J]., 2020, 47(6): 190323
Single-frame far-field wavefront retrieval method based on Walsh function modulation
Kong Qingfeng1,2,3,4, Wang Shuai1,3*, Yang Ping1,3*, Lin Haiqi1,3,4, Liu Yong2, Xu Bing1,3
1Key Laboratory of Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;2School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan 610054, China;3Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, Sichuan 610209, China;4University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The reconstruction of wavefront from single far-field image data has unique advantages in simplicity of structure. However, the traditional wavefront reconstruction algorithm has multiple solutions based on single far-field image, its iterative process easily falls into stagnation. In this paper, based on the analysis of the multi-solution problem of single-frame phase retrieval method, a wavefront reconstruction method based on Walsh function two-dimensional discrete phase modulation is proposed. This method can effectively break the symmetry of near-field wavefront and overcome problem of multiple solutions. The simulation results show that the method can accurately reconstruct wavefront aberration with only one far-field image.
phase retrieval; aberration; far-field; two-dimensional discrete modulation
10.12086/oee.2020.190323
TN247
A
: Kong Q F, Wang S, Yang P,. Single-frame far-field wavefront retrieval method based on Walsh function modulation[J]., 2020,47(6): 190323
孔庆峰,王帅,杨平,等. 基于Walsh函数调制的单帧远场波前反演方法[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(6): 190323
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61805251) and Chinese Academy of Sciences Youth Innovation Promotion Agency (2017429)
* E-mail: wangshuai@ioe.ac.cn; pingyang2516@163.com
2019-06-12;
2019-09-16
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61805251);中国科学院青年创新促进会资助项目(2017429)
孔庆峰(1983-),男,博士研究生,主要从事波前复原技术的研究。E-mail:kqfengxx@sina.com
王帅(1988-),男,博士,副研究员,主要从事新型波前探测技术的研究。E-mail:wangshuai@ioe.ac.cn杨平(1980-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事自适应光学系统的研究。E-mail:pingyang2516@163.com

