Trichosporon asahii ankle cavity effusion infection in a patient with severe aplastic anemia
Peng Zhang, Zhenghai Yang, Jie Li, Xiaoning Li
Department of Clinical Laboratory, Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu, Anhui, China
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS:Trichosporon asahii, Ankle cavity effusion, Aplastic anemia
1. Introduction
Trichosporon species are widespread and have been isolated from a wide range of substances, including soil, cheese, cabbage, parrot droppings, human hair and nails, and scarab beetles[1]. Trichosporon infections have been the subject of clinical research in association with cancer, organ transplants, hypoimmunity, burns, peritoneal dialysis, and prolonged use of antibiotics[2]. Poor prognosis of the infection was well illustrated by the report of a fatal outbreak of trichosporonosis in neonates under antifungal therapy[3]. However,Trichsponorn (T.) asahii infection in the presence of aplastic anemia has rarely been reported[4]. We therefore report a case of a 38-yearold man who presented with severe aplastic anemia and T. asahii ankle cavity effusion infection at our tertiary care institution. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College (Protocol No.: WF2019016).
2. Case report
A 38-year-old man from Anhui Province presented with right ankle swelling for 1 year after having undergone allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation were admitted to our hospital. In January 2018, he presented with a 10-day history of dizziness and fatigue. Bone marrow evaluation verified the diagnosis of severe aplastic anemia. Afterwards he underwent sibling-donated allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without complication. Subsequently, he was diagnosed with Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus infections for which he was treated with rituximab, γ-globulin, and ganciclovir. Five months later, he presented with chills and fever accompanied by mid-upper abdominal pain. Clinical laboratory results showed procalcitonin:0.16 ng/mL, C-reactive protein: 34.53 mg/L, white blood cell count:3.0×109/L, neutrophils: 85.1%, and platelets: 29×109/L. He was treated with aztreonam combined with amikacin. Eight months later,he presented with poor appetite and gastrointestinal complaints.As graft-versus-host disease was possible, he was given tacrolimus and methylprednisolone. In January 2019, after long-term use of antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents, he complained of pain in multiple joints, especially the right ankle and knee. MRI indicated right ankle swelling with exudation of surrounding soft tissue.Considering a possible ankle cavity infection, we extracted effusion for microorganism culture and identification.
硫酸氢氯吡格雷片仿制药对比原研药治疗冠心病的疗效、安全性与经济性的系统评价 ………………… 边 妍等(21):2980
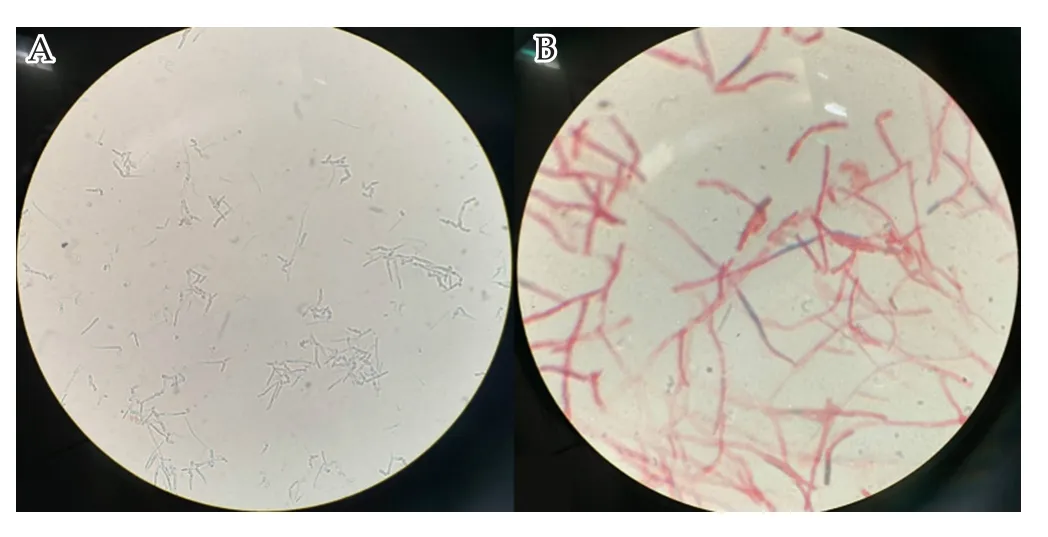
Figure 1. Routine microscopy (A) and Gram stain (B) of Trichosporon asahii isolated from ankle cavity effusion from a 38-year-old male with severe aplastic anemia and multiple joint show, respectively, yeast cells without budding but with septate hyaline hyphae with arthroconidia. Magnification:10 × 40 (A) and 10 × 100 (B).
The effusion sample underwent routine microscopy, gram stain,and subculture. Routine microscopy revealed yeast cells without budding, and Gram stain revealed septate hyaline hyphae with arthroconidia (Figure 1). On Sabouraud’s dextrose agar at 37 ℃,the fungal colonies appeared curdy, white, and cottony (Figure 2).VITEK 2 compact automated system and VITEK MS (bioMérieux SA, Marcy l’Etoile, France) identified T. asahii (Supplementary Figure 1). Antifungal susceptibility was tested using ATBTM FUNGUS 3 (bioMérieux, La Baime-les Grottes, France) for 5-fluorocytosine, amphotericin B, fluconazole, itraconazole,and voriconazole. Minimum inhibitory concentration for 5-fluorocytosine, amphotericin B, fluconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole were 4.0, 0.5, 2.0, 0.25, and 0.125 mg/L, respectively.Prompt treatment with amphotericin B liposomes (55 mg/24 h i.v.) and voriconazole (200 mg/12 h p.o.) for 8 days decreased the patient’s ankle symptoms, with negative effusion culture results for T. asahii.
3. Discussion
According to the National China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net program, 133 Trichosporon isolates were identified by sequencing the IGS1 region. The results showed that the most common species was T. asahii (108, 81.2%), followed by T.dermatis (7, 5.3%), T. asteroides (5, 3.8%), T. inkin (5, 3.8%), and T.dohaense (3, 2.3%)[5]. Although invasive trichosporonosis has been studied for many years, there are no standard guidelines for clinical interpretation of Trichosporon infection. Commonly, infections occur in patients who have hematologic malignancies with neutropenia and other risk factors such as a tumor, use of an immunosuppressor,antibiotics, uremia, chronic respiratory failure, and diabetes-related foot problems. Trichosporon is the second next to Candida species as the the most frequent cause of fungemia in patients with hematologic malignancies.
The invasive trichosporonosis diagnosis is of two types: proven and probable. A proven diagnosis requires (1) trichosporon organism growth in blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid cultures, or biopsy specimen cultures; and (2) related symptoms. Probable diagnosis requires the patient to have a predisposing host factor and clinical evidence of fungal disease. In our case, the patient’s ankle was swollen, and his MRI indicated right ankle swelling and exudation of the surrounding soft tissue. Subsequent cavity effusion cultured on Sabouraud’s dextrose agar displayed T. asahii via the VITEK 2 compact automated system and VITEK MS. The culture affirming T. asahii and the associated symptoms met the criteria for a proven diagnosis.
Upon treatment, most Trichosporon cases occur as an accidental infection despite standard prophylactic antifungal regimens.Mortality rates are reportedly >80%[6]. In a small-case study,only 23% of patients with hematologic malignancies and invasive trichosporonosis treated with amphotericin B therapy survived.Flucytosine did not offer additional benefit. The echinocandins have little effect on Trichosporon species and are not recommended for treating these infections. Despite some contradictory evidence about Trichosporon treatment, amphotericin B is commonly considered the initial management. To date, however, the treatment and management of invasive trichosporonosis has begun to shift from amphotericin to azoles. Suzuki et al. reported that, among hematologic malignancy patients infected with Trichosporon, those treated with azoles (versus those who were not) exhibited significantly better survival[7]. Clinical practice pattern data supported the use of azoles as well. Azoles such as voriconazole, posaconazole, and fluconazole may be effective[8].Amphotericin B combined with azoles may also be effective[9]. Our patient’s antifungal susceptibility test showed five antifungal drugs with sensitivity. Therefore, we prescribed amphotericin B liposomes combined with voriconazole. Eight days later, after repeated isolation and effusion fluid cultures, no T. asahii were evident, and the patient’s ankle symptoms were alleviated. Thus, we believe that management and therapy of trichosporonosis infection must include an azole[10].
4. Conclusion
This case of T. asahii infection in ankle cavity of the male patient with severe aplastic anemia presented questions about this rare fungus and its ability to invade the immunosuppressed host.Dedicated efforts by clinicians and microbiologists to target fungal infections are suggested, as well as further studies to manage and control Trichosporon infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年6期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine2020年6期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine的其它文章
- Non-Iranian travelers may threaten malaria elimination in Iran
- Immunized camels and COVID-19
- Structural biology oriented predicative analysis of immunogenic epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 viral sequence by variable algorithms
- Analysis of temporal trends of human brucellosis between 2013 and 2018 in Yazd Province, Iran to predict future trends in incidence: A time-series study using ARIMA model
- Effect of ABCB1 3435C>T transporter gene polymorphism on plasma efavirenz concentration in HIV-1 infected Thai adults
- Knowledge and attitude toward COVID-19 among healthcare workers at District 2 Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City
