Determination of the Contents of Seven Chemical Components in Vidal Grape by Quantitative Analysis of Multi-components by Single Marker (QAMS)
Shizhao XU Fei QI Yalin XI Ling WU Weijia SUN


Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to establish a method of quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS) for the simultaneous determination of such seven chemical components as gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin and caffeic acid in Vidal grape. [Methods] The high performance liquid chromatography was carried out using a COSMOSIL C18-MS-II column (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm) with the mobile phase acetonitrile-2% acetic acid aqueous solution (gradient elution) at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min. The detection wavelength was 280 nm, and the column temperature was 25 ℃. Using caffeic acid as an internal reference, the relative correction factors between it and other six to-be-detected components, and the contents of the seven components were calculated using the correction factors. The established was compared the results with the external standard method to verify the feasibility and accuracy of the method. [Results] The seven components had a good linear relationship in the ranges of 1.060-10.60, 1.419-14.19, 1.062-10.62, 0.295 0-2.950, 0.101 9-1.019, 0.201 4-2.014, and 0.149 8-1.498 μg, respectively, and the relative correction factors of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid and rutin were 0.976 0, 0.780 6, 0.327 7, 1.640, 1.161, 2.778, respectively. There was no significant difference between the results of the QAMS method and the external standard method. [Conclusions] The QAMS method using caffeic acid as an internal reference is accurate and feasible, and provides a reliable method for the quality evaluation of Vidal ice grape.
Key words High performance liquid chromatography; Vidal grape; Content determination; Polyphenol compounds
Received: July 29, 2020 Accepted: September 28, 2020
Supported by Natural Science Foundation Project of Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Department (20180550846).
Shizhao XU (1988-), male, P. R. China, pharmacist-in-charge, PhD, devoted to research about Chinese medicine chemistry, Chinese medicine chemical analysis and Chinese medicine processing mechanism.
*Corresponding author. E-mail: dazhao666@163.com.
Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) is a woody vine of the genus Vitis in Vitaceae. According to the Compendium of Materia Medica, grapes, also known as Caolongzhu, have a sweet taste and neutral nature and are non-toxic. It has the effects of reducing fluid retention, inducing urination, and regulating middle energizer[1], and is mainly used for treating dampness of muscles and bones. It can also replenish qi and strengthen the spirit, and makes people endure hunger and cold. After long-term consumption, it can achieve the effects of reducing weight, delaying aging and prolonging life. It can also used for making wine[1].
Vidal is a hybrid of Μgni blanc and Sebel blanc, and was introduced from Canada in 1996 to Beidianzi Town, Huanren Manchu Autonomous County, Liaoning Province[2]. At present, the planting base has reached more than 13 333 hm2, and the output value of Vidal ice grape and related industries has reached 20 billion yuan, which promotes the rapid development of modern agriculture and health industries[3].
The main components in grapes are phenolic acids and flavonoids, which exist in the flesh, skin, and seeds[4-5]. Because grapes are nutritious, juicy and acidic, they are now widely used in the brewing industry and are called "liquid gold"[3]. Therefore, it is of great significance to research, develop and utilize ice grape. Some researchers have used the ion exchange resin method to study the adsorption kinetics of total acids and total phenols in Vidal grapes[6], but there are few studies on the determination of the main components of Vidal grapes. Therefore, it is particularly important to determine the content of the main ingredients in Vidal grapes and establish quality standards. The quantitative analysis of multi-component by single marker (QAMS) is proposed to realize the simultaneous detection of multiple index components, solving some of the difficulties in the component index detection due to the difficulties in supply of reference substances, also providing a new analytical method for the quality evaluation of Chinese medicine[7]. In this study, we used caffeic acid as a single reference substance to realize the quantitative analysis of phenolic acids and flavonoids, and established the application of the QAMS method in the quality control of the chemical components of Vidal grapes.
Instruments and Materials
Instruments
Agilent 1100 high performance liquid chromatograph (including quaternary gradient pump, online degasser, VWD detector, Agilent HP-1100 workstation); AR224CN electronic balance (Shanghai Ohaus Instrument Co., Ltd.); METTQE-200 high-speed Chinese medicine pulverizer (Wuyi County Yili Tools Co., Ltd.); KQ5200DB CNC ultrasonic cleaner (Kunshan Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Ltd.); type 101 electric thermostatic drying oven; RE-52C rotary evaporator (Shanghai Yarong Biochemical Instrument Factory).
Materials and Reagents
Gallic acid reference substance, epicatechin reference substance, catechin reference substance, ferulic acid reference substance, chlorogenic acid reference substance, rutin reference substance (National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, purity (high performance liquid chromatography)≥98%, with batch numbers of 11083-200302, 878-200102, 877-200001, 0773-9910, 110753-200413, and 080-9303, respectively); caffeic acid reference substance (Shanghai Yuanye Biological Co., Ltd., purity (high performance liquid chromatography)≥98%, with a batch number of Y17D6C7672); Wahaha purified water; acetonitrile, phosphoric acid, acetic acid and methanol, all chromatographically pure.
Vidal grapes were collected from Beidianzi, Huanren County, Benxi City, Liaoning Province. Fresh grapes were taken and dried at 50 ℃ for 72 h, crushed, and sieved with a 40-mesh sieve for use.
Experimental methods
Chromatographic conditions
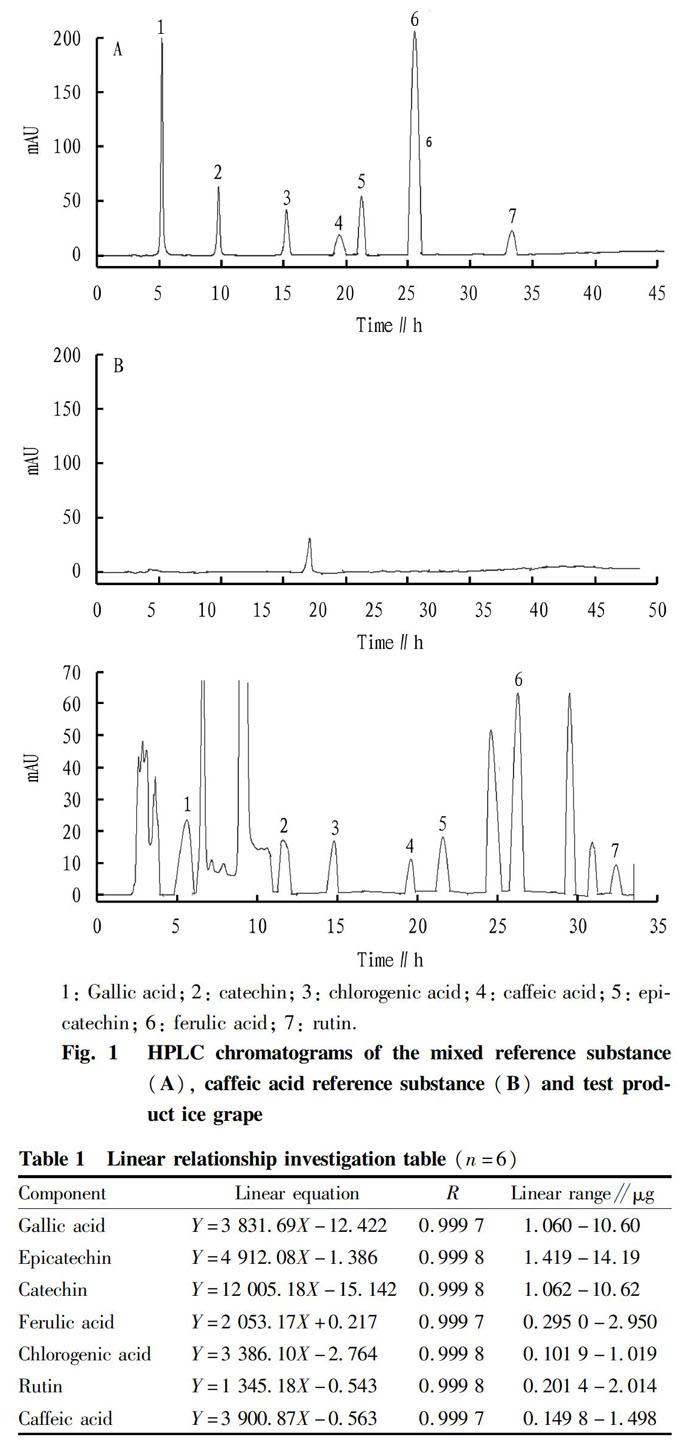
Cosmosil C18-MS-II column (4.6 mm×250 mm, 5 μm) was used, and the mobile phase was acetonitrile (A)-2% acetic acid aqueous solution (B). The gradient elution program was carried out at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min as follows: 0-14 min, 6%→12%A; 14-30 min, 12%→20% A; 30-40 min, 20%→40%A. The detection wavelength was 280 nm, and the injection volume was 10 μl[ 8]. Under these conditions, the resolution of the chemical components in the sample was good. The chromatogram is shown in Fig. 1.
Preparation of mixed reference solution
Appropriate amounts of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, and caffeic acid reference substances were accurately weighed, and added with methanol, obtaining a mixed reference solution with mass concentrations of 529.9, 709.7, 531.2, 147.5, 50.94, 100.7 and 74.92 μg/ml, respectively, which was stored at 4 ℃ for later use.
Preparation of test solution
A certain amount of sample powder (1.0 g) was accurately weighed and added with 80% ethanol according to a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:16. The mixture was ultrasonically treated for 60 min, followed by standing and filtration. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness, dissolved in methanol and transferred to a 100 ml volumetric flask, and diluted with methanol to constant weight and shaken to mix well. The solution was filtered with a 0.45 μm microporous membrane, obtaining the subsequent filtrate for testing[9].
Results and Analysis
Linear relationship investigation
Certain amounts of the mixed reference solution (2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 20 μl) prepared under "Preparation of mixed reference solution" were precisely pipetted, respectively, and measured for the peak area according to the chromatographic condition method under "Chromatographic conditions", and the chromatograms were recorded. With the injection volume X (μg) as the abscissa and the peak area Y as the ordinate, a standard curve was drawn, and the regression equation, correlation coefficient and linear range were calculated. The results are shown in Table 1.
Correction factor calculation
In the linear range, the amount of each component was directly proportional to the peak area of the component to be tested. When the quality control of the seven components in Vidal ice grape, caffeic acid was used as the internal standard, and the fs/k values between caffeic acid and gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, and rutin were calculated by the following formula:
fs/k= fs/fk=Wk×Ak/Ws×Ak
Wherein As is the peak area of the internal standard substance; Ws is the concentration (or mass) of the internal standard substance; Ak is the peak area of the component to be measured; and Wk is the concentration (or mass) of the component k to be tested.
Finally, the contents of the six components were calculated through the calculation formula of fs/k[10].
Results of precision test
The reference solutions (10 μl) prepared under "Preparation of mixed reference solution" were injected for 5 times under "Chromatographic conditions", respectively, and determined for the component contents. The RSD values of the injection volumes of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, and caffeic acid were 1.6%, 0.5%, 0.7%, 1.4%, 1.8%, 0.6%, and 1.4%, respectively, indicating that the precision of each instrument was good. The results are shown in Table 3.
Stability test
The reference solutions prepared under "Preparation of mixed reference solution" were taken, stood at room temperature, and injected at a volume of 20 μl at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h and determined for component contents, respectively. The RSDs of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, and caffeic acid contents were 1.8%, 0.2%, 1.0%, 0.2%, 1.8%, 0.3% and 1.8 %, indicating that each sample was stable within 24 h. The results are shown in Table 4.
Repeatability test
An appropriate amount of ice grape sample powder was taken, and six test sample solutions were prepared according to the method under "Preparation of test solution". Parallel operation was performed to determine the contents of the components according to the content determination method. The RSDs of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, and caffeic acid in the sample were 1.1%, 1.3%, 1.3%, 1.5%, 1.8%, 1.8% and 1.8%, respectively. 1.8%, indicating that the method had good repeatability. The results are shown in Table 5.
Recovery test
Five parts of the Vidal grape sample powder (1 g each) with a known content were precisely weighed in parallel. Each part of the sample was added with a certain amount of the gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin and caffeic acid reference substance solution, and prepared into a test solution according to the treatment method of the test solution under "Preparation of test solution". The test solutions were injected and determined, and the chromatograms were recorded. The sample recovery and RSD of each component were calculated. The sample recoveries of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin, and caffeic acid were 100.4%, 99.7%, 100.3%, 100.5%, 99.5%, 100.7% and 99.5%, respectively, and the RSDs were 0.2%, 0.7%, 0.8%, 2.2%, 0.9%, 2.4% and 1.0%, respectively, indicating that the accuracy of the method was good. The results are shown in Table 6.
Experimental results
The mixed reference solution and single reference solution (caffeic acid) and the test solution (10 μl each) were precisely injected to the high performance liquid chromatograph to determine the peak area. The results are shown in Fig. 1. The contents of gallic acid, epicatechin, catechin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, rutin and caffeic acid in ice grapes were calculated by the QAMS method and the one-point external standard method, respectively, as shown in Table 7.
Conclusions and Discussion
In the QAMS method, according to the experimental requirements of QAMS, caffeic acid was selected as the internal standard, the correction factors of caffeic acid with other components were determined, and the internal standard and the correction factors were used to determine the contents of the components.
The chemical composition of Vidal ice grape is complicated, and it is not very convincing to evaluate its quality with a single component. The QAMS method using ice grapes own components as internal reference materials to achieve simultaneous determination of multiple components not only solves the problem of diversification of reference materials in the determination, but also saves time and testing costs in the testing process. Compared with other methods, the QAMS method not only reduces the amount of reference substance used, but also simplifies the sample inspection procedure. The QAMS method is a novel mode of multi-index quality control of traditional Chinese medicine, which can realize the overall quality control of traditional Chinese medicine. This is the advantage of the QAMS method. However, there are few applicable medicinal materials, and reasonable internal standards are difficult to find, which is the shortcoming of the QAMS method.
References
[1] QIAN CC, ZHANG QC. Detailed translation of "Compendium of Materia Medica"[M]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese)
[2] YIN ZB, CUI LH, LIU YC, et al. Introduction and cultivation test of Vidal ice grape[J]. Hebei Fruits, 2007(3): 5-6, 9. (in Chinese)
[3] YAO ZK. From Huanren remote poor township to the worlds golden ice valley——Enlightenment from the development of ice grape industry in Beidianzi Township[J]. Agricultural Science&Technology and Equipment, 2010(9): 44-45. (in Chinese)
[4] WANG CM, GUO TJ, WANG J, et al. Studies on aroma components in juice of grape Vidal from different collecting time[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2014, 36(2): 158-163. (in Chinese)
[5] CHEN F, ZHANG XX, YANG X, et al. The changes of free terpenoid compounds in vidal grape during the ripening and post-ripening stages[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2010, 10(6): 187-192. (in Chinese)
[6] TIAN JH, JIANG DQ, LI JM, et al. Static adsorption kinetics of total acid and total phenol in ice grape juice with ion exchange resin[J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(6): 119-124. (in Chinese)
[7] WANG ZM, GAO HM, FU XT, et al. Multi-components quantitation by one marker new method for quality evaluation of Chinese herbal medicine[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2006, 31(23): 1925-1928. (in Chinese)
[8] LIANG N, CHU DH, ZHANG ZQ. Determination of seven components of ice grape by HPLC[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 45(11): 2372-2375. (in Chinese)
[9] MOU P, WANG ZS, FAN Q, et al. Progress in physiological activities and extraction methods of grape polyphenols[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable, 2018, 38(12): 30-35, 45. (in Chinese)
[10] WEI LJ, YI Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Determination of six phenolic components in quinoa by quantitative analysis of multi-component by single marker (QAMS)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(19): 232-242. (in Chinese)
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Effects of LPS on the Gene Expression of NMB and Its Receptor in the Hypothalamic-pituitary-testicul
- Comparative Nutritional Analysis on Fish Meal and Meat and Bone Meal of Harmless Treatment of Dead Pig Carcass
- A Monophyletic Status of Axis Genus in Subfamily Cervinae Supported by the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Chinese Hog Deer (Axis porcinus)
- Prevention and Control Measures of the Occurrence of Ceracris kiangsu Tsai in Sugarcane Areas of Yunnan Province
- Study on the Accuracy of Different CASA Systems in the Quality Detection of Fresh Boar Semen
- Evaluation and Selection of Appropriate Tobacco Varieties for Badong Hubei Province

