Breeding of Rice Restorer Line Haihui 818 of Multi-resistant Gene Pyramiding
Xiaowei YAN Qingjie TANG Yisheng HAN Huijian WANG Jing XU Funeng XING


Abstract Haihui 818 is a new restorer line by cross breeding with Hua 23S and Huahui 8131. Good plant type, high tillering ability, fine grain quality, strong restoring ability and high yield were shown in hybrid production. After artificial inoculation and field stress and molecular market-assisted selection, the results showed that rice-blast resistance genes Pi1, BB resistance genes Xa7, and brown planthopper resistance genes Bph3, Bph14 and Bph15 were pyramided together. Among its hybrids, Bo II You 818 (Bo II A/Haihui 818) was approved for commercial production by Hainan Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee in 2015.
Key words Restorer line; Haihui 818; Gene pyramiding; Molecular market-assisted selection; Breeding
Received: June 8, 2020 Accepted: August 11, 2020
Supported by Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-01-89); Crop Genetics and Breeding-Tropical Characteristic Rice Genetic Breeding (JBKYYNF-2020-03); Identification and Development of Tropical Rice Germplasm Resources in Southeast Asia (KJCX-2020-11).
Xiaowei YAN (1974-), female, P. R. China, researcher, master, devoted to research about rice resources and genetic breeding.
*Corresponding author. E-mail: xfn6653@163.com.
Rice planthopper is one of the most serious pests in rice production. In 2012, the total occurrence of rice planthoppers in China was 17.33 million hm2, with a year-on-year increase of nearly 50%[1]. According to preliminary statistics from the agricultural department of Hainan Province, the area of rice planthopper damage in Hainan from 2010 to 2011 was close to 267 000 hm2, and the loss of rice output was about 240 000 t. Plus the costs of prevention and control drugs and machines and labor, the direct economic loss reached more than 500 million yuan. Bacterial blight and rice blast are the most important major diseases in rice production, and they often occur in rice planting areas. Bacterial blight can cause about 50% of economic losses in severe years[2-3]. Therefore, through multi-gene aggregation, breeding hybrid rice restorer lines with good resistance to rice planthopper, rice blast and bacterial blight and then breeding new hybrid rice varieties with strong resistance is an effective way for breeding resistant rice[4-5].
Breeding Process
In 2005, the late crop was the combination of Hua 23S harboring Xa-7 and Xa-21 bacterial blight genes and Huahui 8131 harboring Bph14 and Bph15 rice planthopper genes. In 2006, the hybrid F1 generation was planted in the early cropping season and the seeds were harvested. In the same year, the seeds were plated in the late cropping season, and individual plants were screened and isolated from the F2 generation population by the pedigree method. In the early cropping season of 2007, selected single plants of the F3 generation were planted in duplicate in Yongfa Town, Chengmai County, Hainan, where the rice blast occurred severely. Resistant single plants were selected in the conventional cultivation field where the disease occurred naturally, and the bacterial liquid obtained by soaking leaves of local rice with blast disease in Hainan was inoculated to the progeny individual plants in an identification network room. After 20 d, the degree of leaf lesions was identified, and individual plants with strong resistance were selected. In the late cropping season of the same year, selected single plants of the F4 generation were planted in duplicate in Luoniu Mountain, Haikou City, Hainan, where the bacterial blast occurred severely. Resistant single plants were selected in the conventional cultivation field where the disease occurred naturally, and the bacterial liquid obtained by soaking leaves of local rice with blast disease in Hainan was inoculated to the progeny individual plants in an identification network room. After 20 d, the degree of leaf lesions was identified, and 26 individual plants with strong resistance were selected. In 2008, the early F5 generation was screened for resistance to rice brown planthoppers in facilities during the seedling stage in Haikou, Hainan. When the seedlings grew to 3 leaves, they were inoculated with 2-3 instar brown planthopper nymphs, with an average of 5 nymphs per seedling. The single plants that survived the pests entered the tillering stage and were subjected to low-nitrogen drought stress. Nine resistant plant lines were selected from the 26 plant lines, and the late F6 generation was planted in the late cropping season of the same year and subjected to test cross with sterile lines Longtefu A, II-32A and Y58S. In 2009, the lines were planted in the early cropping season and subjected to test cross with the sterile lines Bo IIA, Longtefu A, II-32A, Y58S, etc. The hybrid F1 was observed. It was found that the hybrid F1 obtained from 5 lines had obvious advantages, and the corresponding lines were harvested. The F8 generation was planted later in the same year, and the hybrid generation was observed. Three lines with stable agronomic traits and strong resistance were selected and screened. In the following year, the selected lines were tested with the sterile line Bo IIA in large quantities, and the hybrid generation was planted and observed in the late cropping season. The combination of the plant line numbered 818 and Bo IIA had outstanding advantages with good comprehensive traits, and was designated Haihui 818.
Characteristics
Agronomic traits
Haihui 818 has a tight plant type, strong tillering ability, and a plant height of about 102 cm. The flag leaves are straight, and the leaves have medium leaf width and are green in color. The main stem has a total of about 17 leaves, the sheath of which is green. The panicle is about 24.5 in length, and carries a total of 142.5 seeds. The seed setting rate is 90.6%, and the 1 000-grain weight is 23.8 g. The grains are yellow, slender, but full, and the glume tip and the palea tip are colorless. The stalk is medium thick, and has good toughness, fertilizer resistance and lodging resistance. Haihui 818 has good late color turning performance.
Growth period
The whole growth period of Haihui 818 is 145-146 d for early cropping sown in December in Hainan, 130-138 d when sown in February, and 128-130 d for late cropping sown in July.
Flowering habit
According to the two-year multi-site systematic observation, Haihui 818 has the characteristics of neat heading. The heading duration is 7-8 d, in which the single-head flowering period is 4-5 d, and the flowering time is concentrated. Its flowering begins at around 09:10 on a sunny day, and the blooming period is from 10:00 to 11:30. The anthers are full, contain sufficient amount of pollen, and have a high pollinating rate.
Resistance
In 2011, we commissioned the Institute of Agricultural Environment and Plant Protection, Hainan Academy of Agricultural Sciences to identify the resistance of Haihui 818 to rice blast and bacterial blight by artificial inoculation. The seedling blast and leaf blast were of grade 3, and the neck blast and leaf blight were of grade 4. No rice blast occurred in field planting, and bacterial blight occurred slightly. It was identified to have high resistance to rice planthoppers under the stress conditions of natural and artificial pest sources.
Rice quality
Haihui 818 has long and slender rice grains, which are crystal clear and shiny. In 2012, 500 g of rice was sampled in Yongfa Experimental Field of Hainan Academy of Agricultural Sciences for rice quality inspection. The main indicators were as follows: brown rice rate 77.0%, milled rice rate 64.5%, head rice rate 43.5 %, chalky grain rate 24%, chalkiness degree 5.0%, amylose content 20.8%, gel consistency 40.0 mm, grain length 6.3 mm, length-width ratio 3.3, transparency level 1, alkali spreading value 3, and moisture 9.6%. The combination Bo II You 818 was tested by National Food Quality Supervision and Inspection Center of the Ministry of Agriculture (Wuhan) in the regional test of Hainan Province, and the rice quality reached level 3 of the national standard High Quality Rice (GB/T17891-1999).
Restoring ability
In the late cropping season of 2008, sterile lines such as Bo A, Bo IIA, Longtefu A and II-32A were used for cross test. In 2009, the early crops were observed and identified for heterosis. The average seed setting rate of the combinations reached 86.8%, showing strong restorability. And cross test was continued in the late cropping season of the same year, and observation and identification of heterosis were all performed. In the following year, the early crops were tested with the sterile line Bo IIA in large quantities for the combining ability. The combination of the individual plant numbered 818 and Bo IIA showed a total number of 168.5 grains and 152.6 filled grains; and the average seed setting rate reached 90.6%, and the yield reached 7 902 kg/hm2, showing strong restorability.
Molecular Marker Detection
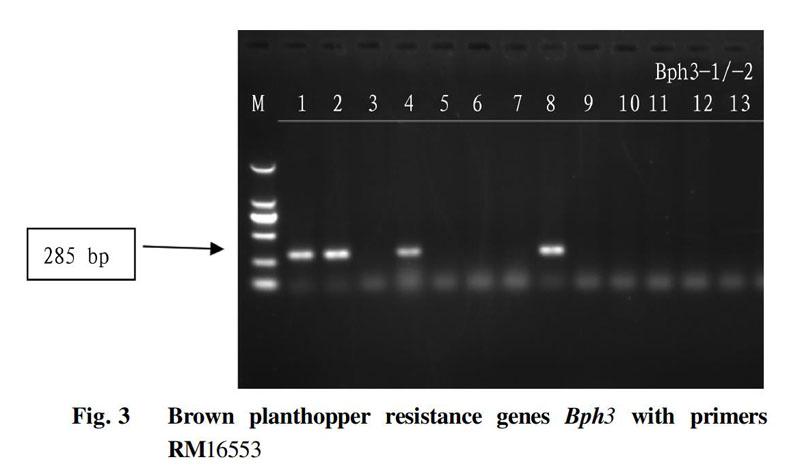
SSR molecular markers were used to detect the correlation between the restorer line material Haihui 818 (F11) and resistance genes such as rice blast, bacterial blight and rice planthopper. The PCR reaction system was 25 μl in volume, including template DNA 2.5 μl, Taq enzyme, Buffer and other mixed solutions 12.5 μl, primers 1 μl each, and water 8 μl. The amplified products were electrophoresed on a 3% agarose gel for about 35 min. The test results showed that Haihui 818 aggregated the rice blast resistance gene Pi-1 (Fig. 1 molecular marker RM244, sequence F: ATCGATCGATCTTCACGAGG, R: TGCTATAAAAGGCATTCGGG), Xa-7 bacterial blight resistance gene (Fig. 2, molecular marker M5, Sequence F: CGATCTTACTGGCTCTGCAACTCTGT, R: GCATGTCTGTGTCGATTCGTCCGTACGA), and Bph3+Bph14+Bph15 rice planthopper resistance gene (Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5). The SSR marker closely linked to Bph3 was RM16553, with the sequences F: TTTGCTTAGTCGGCAGATGTCC, R: CATAAGAACGTACCTCCACTGATrCC; the SSR marker closely linked to Bph14 was MRG2329, with the sequences F: GCACATACAGAAATGGTGAA, R: GGCAAGGGACATGTAGTAAC5; and the SSR marker closely linked to Bph15 was MS5, with the sequences F: TTGTGGGTCCTCATCTCCTC, R: TGACAACTTTGTGCAAGATCAAA.
Combination performance
The hybrid rice combination Bo II You 818 from Haihui 818 participated in the regional test of Hainan Province for the first time in late 2012. It showed an average yield of 6 849.15 kg/hm2, which increased by 1.00% compared with Bo II You 15 (CK), which did not reach a significant level; the daily yield was 56.55 kg; and the proportion of sites with an increased yield was 66.7%. It was retested in the late cropping of 2013, and the average yield was 5 880.6 kg/hm2, which was 0.63% less than Bo II You 15 (CK), which did not reach a significant level; the daily yield was 48.45 kg; and the proportion of sites with an increased yield was 25.0%. In the late cropping test in 2014, the average yield was 5 864.55 kg/hm2, which was 5.18% higher than Bo II You 15 (CK). The whole growth period is 115-132 d, which is 2-3 d longer than Bo II You 15 (CK) on average. The comprehensive resistance performance in two years was seedling blast 3, leaf blast 4, neck blast 4, bacterial blight 5, and sheath blight 5, and it was highly resistant to rice planthoppers in field planting. The rice quality index performance was brown rice rate 81.3%, milled rice rate 71.7%, head rice rate 43.5%, grain length 6.8 mm, grain length/width ratio 3.1, chalky grain rate 24%, chalkiness degree 3.1%, amylose content 19.3%, gel consistency 55mm, alkali spreading value 3.0, transparency level 1, and moisture 11.9%, reaching the third level of the national standard. In 2015, it was approved by the Hainan Provincial Crop Variety Approval Committee (QSD 2015003).
References
[1] Ministry of Agriculture. A total of 260 million mu of rice planthoppers occurred nationwide this year. http://news.sina.com.cn/o/2012-08-28/165825053365.shtml. (in Chinese)
[2] XIONG ZM, CAI HF, MIN SK. Chinese rice[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1992. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHAI WX, ZHU LH. Research on rice bacterial blight resistance genes and molecular breeding[J]. Progress in Biotechnology, 1999, 19(6): 9-15. (in Chinese)
[4] NI DH, XI CX, LI L, et al. Developing rice lines resistant to bacterial blight and blast with molecular marker-assisted selection[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2008, 34(1): 100-105. (in Chinese)
[5] LI JB, XIA MY, QI HX, et al. Marker-assisted selection for brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens St(a)l) resistance genes Bph14 and Bph15 in rice[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2006, 39(10): 2132-2137. (in Chinese)
Editor: Yingzhi GUANG Proofreader: Xinxiu ZHU
- 农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Effects of LPS on the Gene Expression of NMB and Its Receptor in the Hypothalamic-pituitary-testicul
- Comparative Nutritional Analysis on Fish Meal and Meat and Bone Meal of Harmless Treatment of Dead Pig Carcass
- A Monophyletic Status of Axis Genus in Subfamily Cervinae Supported by the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Chinese Hog Deer (Axis porcinus)
- Prevention and Control Measures of the Occurrence of Ceracris kiangsu Tsai in Sugarcane Areas of Yunnan Province
- Study on the Accuracy of Different CASA Systems in the Quality Detection of Fresh Boar Semen
- Evaluation and Selection of Appropriate Tobacco Varieties for Badong Hubei Province

