回收式自体输血对剖宫产术中产后出血的应用价值
何小波 周俊俊 李洁


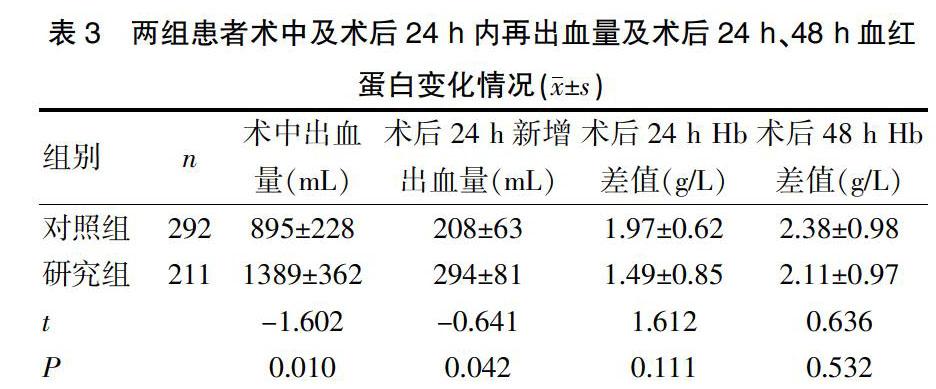
[摘要] 目的 研究回收式自体输血对剖宫产术中产后出血的临床疗效评价。 方法 选取2014年1月~2016年12月在我院行剖宫产术,以回收式自体输血211例作为研究组,未输血或异体输血292例为对照组,比较两组患者术中、术后24 h出血量,术后发热,术后24h及48h血常規、血红蛋白、血浆白蛋白等指标变化,及切口愈合情况、住院天数比较。 结果 研究组的年龄(31.74±5.00)岁大于对照组(30.58±4.91)岁(P<0.05),研究组术中出血量(1389±362)mL、术后24 h再出血量(294±81)mL明显多于对照组(P<0.05),且术后发热、术后24 h白细胞数及中性粒细胞的差值均少于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。在血液输注过程中,研究组出现过敏现象10例与对照组6例比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 自体血回输技术保留术中失血、减少异体输血的输注,其操作简单,处理迅速,可安全有效地应用于剖宫产术中血液保护。
[关键词] 回收式自体输血;异体输血;产后出血;剖宫产
[中图分类号] R457.1;R719.8 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)09-0067-04
[Abstract] Objective To study the clinical effect of autotransfusion salvage on bleeding after cesarean section. Methods Patients undergoing cesarean section in our hospital from January 2014 to December 2016 were taken as the study subjects. 211 cases who applied autotransfusion salvage were enrolled into the study group, while 292 cases who applied allogeneic transfusion or had no transfusion as the control group. The changes of bleeding volume during and after operation, postoperative fever, blood routine after 24 and 48 h of operation, hemoglobin, plasma albumin and other indexes, wound healing and hospitalization stay were compared between the two groups. Results The age of the study group was(31.74±5.00) years old, which was higher than that of the control group(30.58±4.91) years old(P<0.05). The bleeding volume during operation and 24 h after operation in the study group was(1389±362) mL and (294±81) mL respectively, which was significantly higher than that in the control group(P<0.05). Postoperative fever, the amount of white blood cells and neutrophil differential value in the study group were lower than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). In the course of blood transfusion, 10 cases developed allergy in the study group, which was more than that in the control group, and the difference was not statistically significant(P>0.05). Conclusion Autotransfusion savage is a simple, rapid and safe technique for preserving intraoperative blood loss and reducing transfusion of allogeneic transfusion.
[Key words] Autotransfusion salvage; Allogeneic transfusion; Postpartum hemorrhage; Cesarean section
由于我国剖宫产率居高不下,加之“二孩生育政策”的实行,合并凶险型前置胎盘、多胎、高龄产妇等高危因素的孕妇明显增加,现产后出血明显增多,围术期输血,特别是术中、术后输血的需求量明显增加,据统计妇产科临产用血量名列第3名,约占全部输血量的5%~6%,但临床上输注同种异体血可能引起输血感染、过敏、免疫抑制和肺损伤等[1];鉴于输血可能带来的风险及血源日益紧张,尤其在产科方面,血液保护技术越来越引起重视。目前常用的血液保护措施包括:术前自体血贮存、急性等容量血液稀释、术中血液回收(Intra-operative cell salvage,IOCS)技术[2]。上述血液保护措施中以血液回收技术在普外科、移植外科和心血管外科等科室发展迅速[3-10]。鉴于产科特殊性,虽然术中血液回收技术一直未在产科领域得到较好的发展,然而我院已于2010年开展术中回收式自体输血技术。现对我院自2014年1月因产后出血,行术中血液回收技术的病例进行分析研究,现报道如下。
回收式自体血回输未在产科得到良好的进展原因之一,多考虑为自体输血后引起的羊水栓塞的风险。有研究发现在行择期剖宫产的健康产妇的血液循环中全都证实有羊水的存在,因此羊水可能常规进入母体血液循环中,但大部分不会造成危害[15-17]。自体血回输,即使有少量羊水污染,对于有羊水暴露的孕妇来说没有额外的危险。Haley Goucher等[18]发表的文章中统计出,对接受自体血回输的299个产妇经过详细的调查,并没有发现严重的并发症,故自体血回输的风险和异体血回输的风险相平行,与我院503例的研究对象相符,其中对照组有6例在输血过程中出现过敏反应,研究组有10例,均表现为皮疹,予对症治疗后好转。我院术中自体血液回收多开始于胎盘娩出、宫腔清理干净后,且并未发现羊水栓塞的病例。术前充分的评估,使用双管吸引系统,一根吸引管吸引母体血液,另一根吸引羊水,待羊水吸尽、胎盘娩出后吸引母体血液,即可最大程度减少羊水吸入血液回输中。并且只要没有羊水污染,也应充分血液回收[20-21]。故剖宫产时应用IOCS应注意下列事项:确定母婴血型;尽量避免吸引脐带血;在胎盘分离后开始收集失血;充分的生理盐水洗涤;除去回收血中血沉棕黄层(胎儿细胞存在部位)。此外。在产科应用IOCS推荐将血液回收机与白细胞过滤器联合使用以增加安全性。最后,使用双套吸引装置可能对妊娠妇女有益[22-23]。
另外结合国外的文献和我院实际使用中的情况,血液回收机容易安装,大部分麻醉医师可在5 min内安装并使用,其操作完全自动化,使用简单,特别适合产科大出血;故每个手术间应常规备有一次性吸收罐、吸引管和肝素化生理盐水以备急需时能及时收集创口出血[24-26]。
术中自体血回输技术保留术中失血、减少异体输血的一种安全方法。在异体血液供应有限、输血需求量大的情况下,其操作简单,处理迅速,可安全有效的用于剖宫产术中血液保护。
[参考文献]
[1] 王立中,鲍红光. 产科手术中血液保护技术的应用前景[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2008,35(5):367-370.
[2] 严海雅,吴云,叶松,等.剖宫产术中回收式自体输血的回顾性分析[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2016,36(11):1297-1301.
[3] 侯红瑛,高倩. 剖宫产产后出血自体血回收的处理[J].中华产科急救电子杂志,2017,6(4):219-222.
[4] Sukhjit K Dhariwal,Khalid S Khan,Shubha Allard,et al. Does current evidence support the use of intraoperative cell salvage in reducing the need for blood transfusion in caesarean section?[J].Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol,2014,26(6):425-430.
[5] 马晓丽,李莲英. 回收式与稀释式自体血回输在凶险性前置胎盘剖宫产中的应用[J].中国妇幼保健,2017,32(24):6094-6097.
[6] 何明海,蔡回钧,芶大明. 剖宫产应用自体血回收联合白细胞过滤器对患者血常规及生化指标影响的观察[J].遵义医学院学报,2017,40(6):660-664.
[7] 韩晓丽,张卫. 剖宫产术中自体血回输相关急性低血压的研究进展[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2017,38(7):634-650.
[8] 吴云,严海雅. 剖宫产手术自体血回收-回输的危险因素[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2018,38(3):355-358.
[9] Justine V Sullivan,Maria E Crouch,Gary Stocken,et al.Blood cell salvage during cesarean delivery[J].Int J Gynaecol Obste,2011,115(2):161-173.
[10] 曾葵,黄蔚. 剖宫产术中回收式自体输血在中央型前置胎盘患者的应用[J].四川医学,2017,9(38):1049-1051.
[11] Hussain S,Clyburn P. Cell salvage-induced hypotension and London buses[J]. Anaesthesia,2010,65(7):661-663.
[12] 林毅,张仕铜,赵羽玲. 凶险性前置胎盘行剖宫产时两种自体血回输应用的比较[J].实用产科杂志,2016,32(1):38-41.
[13] Geoghegan J,Daniels JP,Moore PAS,et al. Cell salvage at caesarean section:The need for an evidence-based approach[J]. BJOG,2010,117(1):122-133.
[14] 卫新,彭云水,张卫,等. 剖宫产术中自体血回收可靠性的临产评价[J].中華麻醉学杂志,2015,35(5):598-600.
[15] Sullivan I,Faulds J,Ralph C. Contamination of salvaged maternal blood by amniotic fluid and fetal red cells during elective Caesarean section[J]. Br J Anaesth,2008, 101(2):225-229.
[16] Harkness M,Clark V. The use of cell salvage during obstetric procedures:An audit of Scotland's maternity units[J].Scott Med J,2008,53(3):24-27.
[17] Carol McLoughlin,Tracy E Roberts,Khalid S Khan,et al. Cell salvage and donor blood transfusion during cesarean section:A pragmatic,multicentre randomised controlled trial(SALVO)[J].PLoS Med,2017,14(12):124-135.
[18] Haley Goucher,Cynthia A Wong,Samir K Patel,et al. Cell salvage in obstetrics[J].Anesth Analg,2015,121(2):465-468.
[19] Megan E Milne,Mark H Yazer,Jonathan H Waters. Red blood cell salvage during obstetric hemorrhage[J]. Obstet Gynecol,2015,125(4):919-923.
[20] Catherine M Albright,Dwight J Rouse,Erika F Werner. Cost savings of red cell salvage during cesarean delivery[J].Obstet Gynecol,2014,124(4):690-696.
[21] Radmila Spari■,Biljana Lazovi■,Nenad Sulovi■,et al. Our experience with intraoperative cell salvage during cesarean delivery in women with uterine myomas-four case reports[J].Med Pregl,2014,67(3):111-117.
[22] Choi ES,Ahn WS,Lee JM,et al. A laboratory study of the effects of processing blood through a cell salvage device and leucocyte depletion filter on levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and bradykinin[J].Anaesthesia,2013, 68(12):1259-1265.
[23] William Kirke Rogers,Sarah A Wernimont,Girish C Kumar,et al. Acute hypotension associated with intraoperative cell salvage using a leukocyte depletion filter during management of obstetric hemorrhage due to amniotic fluid embolism[J]. Anesth Analg,2013,117(2):449-520.
[24] Kessack LK,Hawkins N. Severe hypotension related to cell salvaged blood transfusion in obstetrics[J]. Anaesthesia,2010,65(7):745-748.
[25] Vicki Clark. Facilities for blood salvage(cell saver technique)must be available in every obstetric theatre[J]. Int J Obstet Anesth,2005,14(1):50-52.
[26] Potter PS,Waters JH,Burger GA,et al. Application of cell-salvage during cesarean section[J].Anesthesiology,1999,90(2):619-621.
(收稿日期:2019-09-30)

