不同滴灌处理下沙棘林内土壤盐分变化研究
董立国

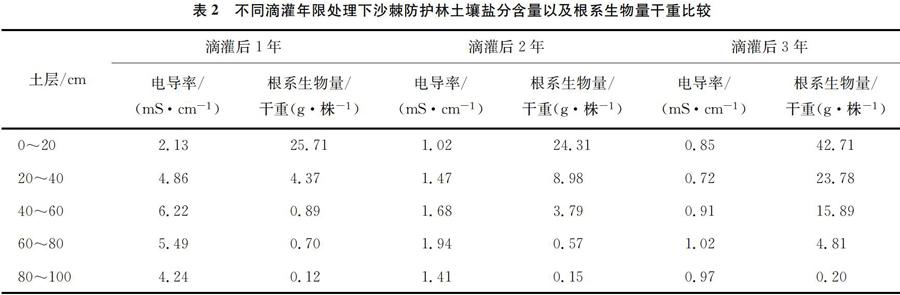
摘 要:为了研究滴灌措施下干旱地区防护林内土壤盐分的变化情况,选择建平地区常见的荒山绿化树种——沙棘作为研究对象,开展了滴灌与不滴灌、不同滴灌年限处理下的土壤盐分含量研究,结果表明,滴灌处理可以明显降低浅层土壤中的盐分含量,不灌溉林地处理下土壤盐分变化情况与流动沙丘的对照处理趋于一致,但是后者盐分空间分布的异质性程度更强;滴灌后1~3年,随着年限的增加,同土层中盐分含量逐渐降低,根系生物量干重逐渐增加,且根系分布情况上移,主要集中在0~60 cm的土层中。由此可知,滴灌对浅层土的洗盐效果较好,但是滴灌时间长了根系有向浅层土层集中的趋势,建议每年大水漫灌1次,以有利于根系的下扎。
关键词:滴灌;沙棘;盐分;根系生物量
中图分类号:S753.5 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1004-3020(2020)02-0023-03
Study on Soil Salinity Changes of Hippophae rhamnoides Forest under Different Drip Irrigation
Dong Liguo
(Baishan Forest Farm of Jianping County Chaoyang 122406)
Abstract:In order to study the changes of soil salinity in protective forests in arid areas under drip irrigation,Hippophae rhamnoides,a common barren hill tree species in Chaoyang area,was selected as the research object. The soil salt content under drip irrigation and non-drip irrigation and different drip irrigation years were studied. The results showed that drip irrigation treatment could significantly reduce the salt content in shallow soil. The change of soil salinity under the treatment of non-irrigated forest land was consistent with the control treatment of mobile sand dune,but the spatial distribution of salt content in the latter was more heterogeneous;After 1~3 years,with the increase of years,the salt content in the same soil layer gradually decreased,the dry weight of root biomass increased gradually,and the root distribution increased,mainly concentrated in the 0~60 cm soil layer. It can be seen that drip irrigation has a good effect on salt washing in shallow soil,but the drip irrigation time has a tendency to concentrate the shallow soil layer. It is recommended to flood the water once a year to facilitate the lowering of the root system.
Key words:drip irrigation;Hippophae rhamnoides;salt;root biomass
沙棘屬于多年生雌雄异株落叶小乔木、灌木,又被称为酸刺、酸柳等,其根系非常发达,耐干旱、寒冷等的能力强,耐土壤瘠薄的生态环境,生长速度快,可快速成林,在生态林建设中的作用明显,可有效减缓土壤的沙漠化,是阜新等干旱地区荒山绿化的先锋树种之一[1]。建平县地处辽宁省的西部地区,境内气候干燥、多风,导致频繁发生干旱,平均2年左右发生1次干旱,严重干旱灾害的发生周期不到3年,对当地的生态环境造成了严重的破坏,土壤的沙化现象明显,土壤盐渍化程度逐年加重。当前水资源是限制干旱地区植被生长的主要因子,推广合理的灌溉方式是实现干旱地区有限水资源的高效利用、降低土壤盐渍化危害的重要途径[2]。滴灌是一种节约水资源的灌溉技术,目前国内滴灌技术在园艺、蔬菜栽植中的应用比较多[3],在林业上的应用目前主要在经济林上,而在沙地防护林的应用相对较少[4]。为了研究建平地区滴灌技术在沙棘防护林中应用后土壤盐分变化情况,特开展了此研究,以期为干旱天气频发的建平地区防护林的可持续发展提供指导。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验地情况
试验安排在建平县某沙棘防护林内进行,原来为半流动式沙丘,植被覆盖度在3%~5%,2016年4月开垦后栽植沙棘防护林。试验地年降水量平均380 mm左右,最低降水量仅为200 mm,风沙大,冬季严寒少雪,夏季炎热,常发生干旱[5]。
1.2 试验材料
供试沙棘品种为扁优,1 a生,来源于县内某苗圃;试验材料包括滴灌设备、电导率仪、取样工具、电子天平等。

