Treatment strategies and preventive methods for drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori infection
Ru-Jia Li, Yuan-Yuan Dai, Chun Qin, Xiao-Hua Li, Yan-Chun Qin, Yong Pan, Yong-Yi Huang, Zan-Song Huang,Yan-Qiang Huang
Ru-Jia Li, Yuan-Yuan Dai, Chun Qin, Xiao-Hua Li, Yan-Chun Qin, Yong Pan, Yong-Yi Huang, Zan-Song Huang, Yan-Qiang Huang, Research Center for Prevention and Treatment of Drug Resistant Microbial Infections, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000,Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
Abstract
Key words: Helicobacter pylori; Drug-resistant; Strategies; Methods; Treatment;Prevention
INTRODUCTION
Helicobacter pylori(H.pylori) is an important cause of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers,gastric cancer, and other diseases[1-3].In addition,H.pyloriis associated with a variety of extra-intestinal diseases, such as periodontitis and secondary thrombocytopenic purpura[4].H.pylorinow infects more than half of the world’s population, and the infection rate is higher in developing countries compared to developed countries,with more than 80% of cases diagnosed in underdeveloped areas[5-7].Due to the high infection rate ofH.pyloriand the widespread use of antibiotics for treatment, the drug resistance rate ofH.pyloriis increasing along with a simultaneous decrease in eradication rate, which poses a serious threat to public health.There is an urgent need for better strategies to prevent and treatH.pyloriinfection.In this paper, we review the current advances in methods of prevention and treatment of drug-resistantH.pyloriinfection, aiming to provide reference for eradication of drug-resistantH.pylori.
CAUSES OF DRUG RESISTANCE OF H.PYLORI
The main methods of the internationalH.pylorieradication program include standard triple, non-bismuth quadruple, bismuth quadruple (a proton pump inhibitor +bismuth + two antimicrobial agents) treatments.The non-bismuth quadruple regimens consist of sequential, concomitant, and mixed therapies.Currently, bismuth quadruple treatment is preferentially recommended.The Kyoto consensus emphasizes that eradication is the first-line treatment for patients withH.pyloriinfection with dyspepsia[8].The Toronto consensus provides recommendations onH.pylorieradication methods for adult patients[9].The Maastricht V/Florence Consensus points out that whenH.pyloriis sensitive to clarithromycin (CLA), the eradication rate of the international standard triple protocol is 97.3%[10].In areas with high resistance to CLA or double resistance, the eradication rate of quadruple therapy containing bismuth is up to 86%[11].In the Fifth National Consensus Conference on the Management ofH.pyloriInfection held in China, the eradication rates of the seven regimens are all around 90%[12].
Although the efficacy of first-line treatment containing various antibiotics to whichH.pyloriis sensitive, the eradication rate is less than 100%, and with the failure of the first eradication, the rate of drug resistance increases and so radical treatment becomes more difficult.The causes of eradication failure and drug resistance mainly include history of antimicrobial use, improper use of antibiotics, course of digestive diseases, and certain drug characteristics[13], which are listed in Table 1.Although amoxicillin is not prone to resistance, the rate of resistance to amoxicillin has gradually increased in recent years[13], which highlights the severity of drug resistance ofH.pylori.Consequently, in 2017, the World Health Organization listed CLAresistantH.pylorias one of the 12 pathogens in urgent need of new antibiotics[14].
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR DRUGRESISTANT H.PYLORI INFECTION
At present, strategies targeting drug-resistantH.pyloriinclude prevention of drugresistant bacterial infection, effective diagnosis and standardized treatment, rational application of antibacterial drugs, and prevention of drug-resistant bacteria transmission (Figure 1).Effective prevention is the source of control of drug-resistantH.pyloriinfections.Only with reasonable prevention can the incidence of infections be effectively decreased.When drug-resistant infections occur, effective diagnosis and standardized treatment are essential towards reducing the occurrence of secondary drug resistance and increasing the eradication rate ofH.pylori.Invasive or noninvasive testing is the key to rapid and effective diagnosis.Selection of antibioticsbased on the sensitivity to antibacterial drugs and formulation of rational,standardized, and accurate treatment plans based on patient condition are also critical[12].

Table 1 Factors influencing drug resistance of Helicobacter pylori
Effective antibacterial drugs are the key toH.pyloriprevention and treatment.The government, health administration departments, drug regulatory departments, and hospital medical staff must proactively perform their respective duties to enhance antibacterial drug management.Other important aspects include forming a management system for rational drug use, formulating medication guidelines,establishing antibacterial drug guidelines and drug resistance monitoring networks,and supporting the development of new types of drugs.Furthermore, preventing transmission is an important step towards stopping the spread of drug-resistantH.pylori.Security control in laboratories and hospitals should be strengthened to prevent the spread of drug-resistant strains.
METHODS FOR PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF DRUGRESISTANT H.PYLORI
Based on the above-mentioned four strategies for the control of drug-resistantH.pyloriand combined with research from our research group, we will conduct a detailed analysis of the prevention methods (Figure 2).
Prevention of infection
Prevention in adolescents:One third of children worldwide have been infected withH.pylori, highlighting the importance of prevention in adolescents[15].Screening for the disease in adolescents can decrease the lifetime risk of gastric cancer.AsH.pyloriis transmitted mainly through fecal-oral and oral-oral routes, parents should pay attention to the diet of adolescents, keep oral hygiene, avoid mouth-to-mouth feeding,promote meal sharing, and avoid mixing water cups, toothbrushes, and mouthwash cups amongst family members.
Prevention in adults < 50 years old with a low gastric cancer risk:For this population, anH.pyloriinfection test and a gastric atrophy test should be combined to effectively prevent transmission to the next generation.In addition, tableware and toilets should be disinfected frequently, and people should develop good eating habits and pay attention to the hygiene of drinking water.Medical workers in hospitals should pay special attention to the transmission ofH.pyloriin hospitals.
Prevention in adults ≥ 50 years old with a high gastric cancer risk:H.pyloriinfection increases with age.One of the main reasons is cross-infection in the home or in the population.In addition to paying attention to health problems in the family, people with a high gastric cancer risk should also undergo screening for the disease.The combined detection of serum pepsinogen andH.pyloriantibodies can increase the level of prevention for people with a high gastric cancer risk[16].
Effective diagnosis
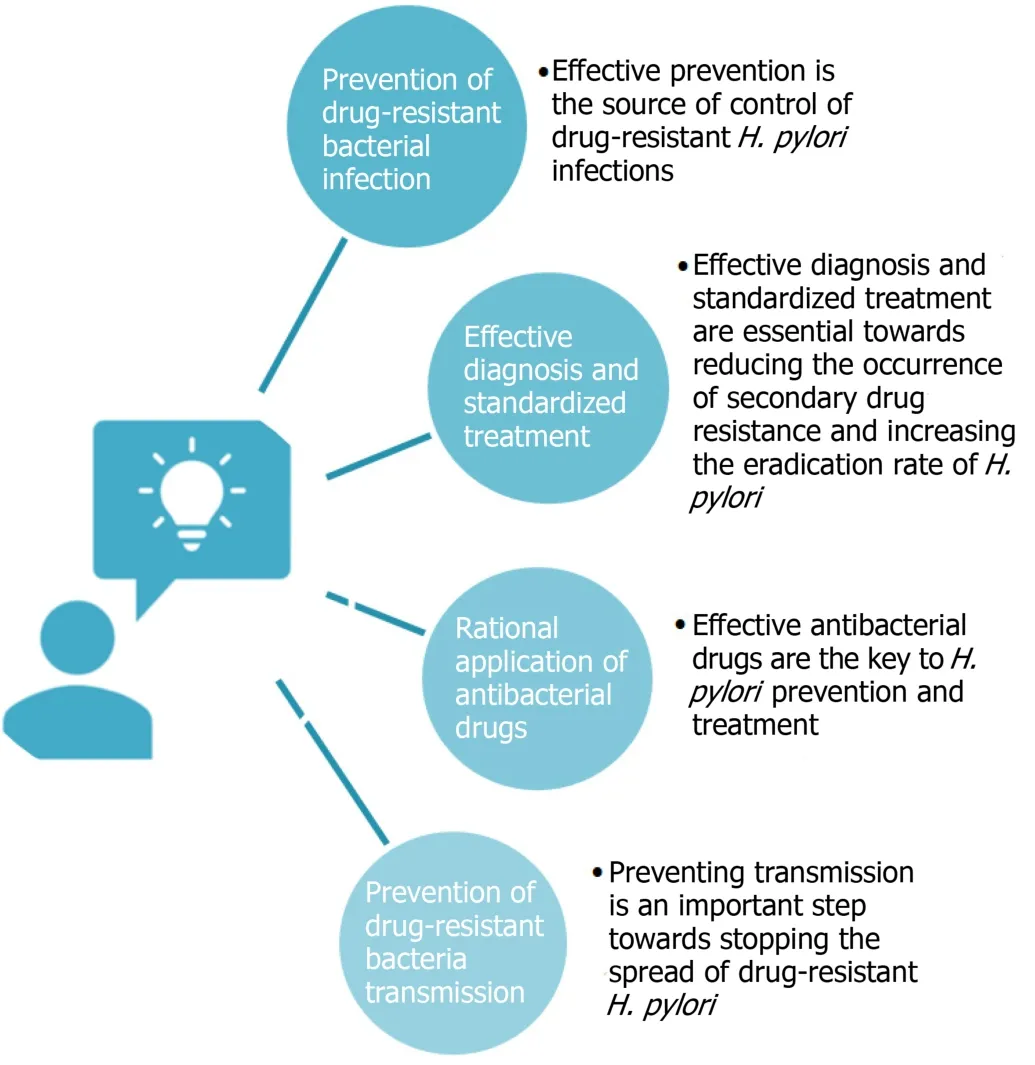
Figure 1 Strategies for prevention and treatment drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori infection.
Diagnosis ofH.pyloriinfection is extremely important.Invasive or non-invasive detection methods are usually used in the individual diagnosis ofH.pyloriinfection.Invasive detection methods include endoscopy[17], rapid urease test[18], histological method, and bacterial culture[19].Non-invasive detection methods include13C urea breath test[20], serum antibody test[21], stool antigen test[22], and other molecular biology techniques.Each test method has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be selected from person to person.Considering the accuracy and safety of diagnosis, non-invasive detection methods are generally recommended.There are also some other approaches used to assist diagnosis such as serum pepsinogen measurement[23]and gastric X-ray[24].
Standardized treatment
Adjusting standardized medication:Drug-resistantH.pyloriis a strain that is not easily eradicated after the first standardized treatment.To treat this refractory disease caused by drug resistance, antibiotics should be adjusted in time for remedial treatment based on the results of drug sensitivity testing or medication history.Seven common antibiotic combinations[25], as shown in Figure 3, are used in the remedy in the treatment of antimicrobial drugs with low drug resistance.In the protocol,antibacterial drugs such as tetracycline, metronidazole, and amoxicillin have a high eradication rate[26].H.pylorihas high resistance to CLA, with a primary resistance rate of 20% to 50%.In areas with high rates of CLA, or high rates of metronidazole-CLA dual resistance, quadruple therapy is recommended in preference to CLA and metronidazole as first-line therapy[27].Non-bismuth quadruple concomitant and sequential therapies can also be used as an eradication protocol.Patients were less well tolerated and had poor compliance to these two treatment regimens[28].The 7-d concomitant therapy has been shown to be better than 7-d or 10-d triple therapy[29].With the same treatment course, concomitant therapy is superior to sequential therapy[30].Moreover, antimicrobial treatment should be controlled[31].The actual trend is towards the use of quadruple instead of triple therapy and prolongation of the duration of each eradication regimen (10-14 d).
New quadruple therapy has a modification to the traditional triple and quadruple therapy that should be used as the first treatment option.Recent studies indicated that minocycline, cephalosporins[32], and rabeprazole can be used as alternatives to antibacterial agents in quadruple therapy[33].However, new quadruple therapy is in its early stage, and the dosage and course of treatment should be further optimized.
Combination of Chinese and Western medicines:Antibiotics are broad-spectrum agents and prone to drug resistance, while traditional Chinese medicines are less prone to drug resistance, less toxic, and have complex mechanisms.Combining the two can effectively treatH.pyloriinfection.In a previous study, 162 patients withH.pyloriinfection were randomly divided into two groups.The treatment group received traditional Chinese medicine combined with Western medicine for anti-H.pyloritherapy.After three courses, the effective rate was as high as 100%, which was significantly higher than that of the control group treated with Western medicine alone[34].This result showed that the combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicines is significantly better than Western medicine alone, which may improve the prognosis of patients.
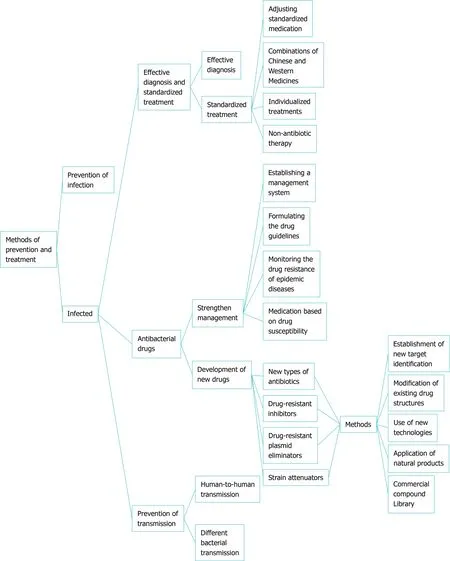
Figure 2 Methods for prevention and treatment of drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori infection.
Individualized treatments in special pathological conditions:As amoxicillin is not prone to drug resistance and has few adverse reactions, it is often the first choice forH.pylorieradication therapy.However, when patients are allergic to penicillin, other antibiotics with low resistance should be selected instead of amoxicillin, such as tetracycline[35].When choosing a regimen containing antibiotics to whichH.pyloriis highly-resistant, treatment time can be appropriately extended[28].Patients withH.pyloriinfection should have their blood glucose well-controlled during treatment[36].In the treatment of such patients withH.pyloriinfection accompanied by special pathological conditions, individualized treatment plans should be formulated based on the patient’s condition.
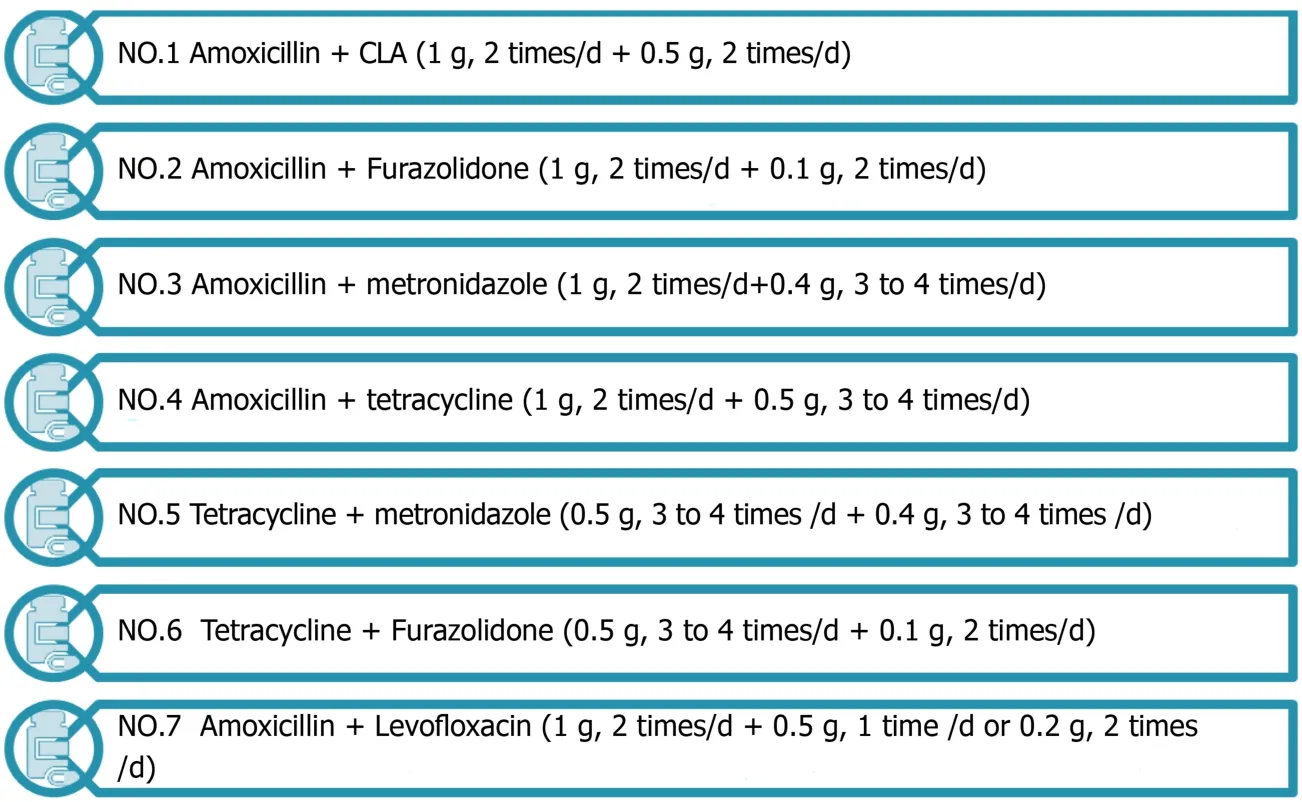
Figure 3 Combination of common antibacterial drugs.
Non-antibiotic therapy:Currently, triple or quadruple therapies are widely accepted as first-lineH.pylorieradication treatment regimens; however, these regimens often lead to some adverse outcomes, such as intestinal flora imbalance and drug resistance.Probiotics are an important factor in the human body to maintain the micro-ecological balance.Combining probiotics with other therapies to treatH.pyloriinfection is safe,feasible, and beneficial.For example, Lactobacillus can influence the colonization ofH.pylori[37], and the triple treatment combined with Blaird's yeast had a significantly higher eradication rate than the traditional triple treatment[38].However, the adjuvant role of probiotics in the eradication ofH.pyloriremains controversial and more research is warranted[39].
Traditional Chinese medicine treatments are methods with Chinese characteristics.Some monomer components containing Chinese medicine mucosal-protective agents exhibit the characteristics of high eradication rate, low drug resistance, few adverse reactions, and low toxicity.These medicines even kill drug-resistantH.pyloriand may therefore provide new tools for the eradication ofH.pylori[40].For example, some quinolone alkaloids inFructus Evodiainhibit the growth ofH.pyloriand achieve eradication without affecting the intestinal flora[41].According to epidemiological statistics, the total effective rate of traditional Chinese medicine treatment can reach 95.45%[42].
The bacteriostatic effect of berberine is strongest amongst the monomer components of Chinese medicine, followed by rhubarb, and scutellaria.Cortex, Radix Ginseng, Forsythia, and Hedyotis diffusa also exert a certain antibacterial effect[43].The mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicines may be related to the inhibition of functional protein synthesis[44], biofilm synthesis[45], inflammatory factor release[46],and virulence factor release[44]and the reduction of adhesion[47].The mechanism of action for these medicines is complex.Also, the extraction and analysis of active ingredients have not fully completed, and the course of treatment is difficult to control.
Rational application of antibacterial drugs
Strengthening the management of antibiotics:According to the regulations covering the use of antibiotics in the "Administrative Measures for the Classification of Prescription Drugs and Over-the-Counter Drugs"[48], the management system for antibiotics should be strictly enforced.Measures include enhancing the management of antibiotics in hospitals, formulating a reasonable medication management system,and preventing antibiotic abuse.In particular, medical workers should ensure that patients use antibiotics safely, reasonably, and effectively, to ensure their health and well-being.
Following the principles of antibiotic use:The principles of antibiotic use should be strictly followed:(1) Clear medication indications and corresponding antibiotics need to be used forH.pyloriinfection; (2) For targeted use, triple therapy is preferred; (3)The rational dosage of drugs and the sufficient course of treatment can not only ensure efficacy but also prevent the development of drug resistance; (4) The patients should be asked about the history of drug allergy in detail before the medication; (5)The appropriate method of administration needs to be selected so that the generalH.pylorimedication is orally administered; (6) The drug should be carefully changed along with the treatment plan after confirming failure of the triple or quadruple therapy; and (7) Patients with impaired liver and kidney function should be cautious in medicine taking.
Biological standards for rational drug use:Rational drug use refers to the selection of the best drug and the formulation of a dosing plan to effectively, safely, and economically prevent and cure diseases.The World Health Organization has established biological standards for rational drug use as follows:(1) Proper use of drugs needs to be ensured; (2) The drug information is appropriate; (3) The efficacy,safety, use, and price are appropriate for patients; (4) Dosage, usage, and course of treatment should be appropriate; (5) The subject is appropriate, without contraindications or significant adverse reactions; (6) The drug resource allocation is correct; and (7) Patients have good drug compliance.
Indications for antibiotic application:Antibiotics can be classified into first, second,and third-line drugs according to the antibiotics management classification.H.pyloriinfections are usually treated with first- and second-line drugs.First-line drugs refer to antibiotic drugs that are non-restricted, narrow-spectrum, and positive in effect,have slight adverse reactions and low prices, and are available in sufficient supply.Second-line drugs are the drugs that are restricted in use, have a broad antibacterial spectrum and good curative effects, but have obvious adverse reactions or are more expensive, or are drug varieties that may develop rapid resistance and have controlled use.Third-line drugs are generally used in a unique way as they exert curative effects but are relatively toxic and expensive.They are a class of drugs that will have serious consequences once drug resistance occurs.In the treatment of drugresistantH.pyloriinfection, the most suitable antibiotic should be selected and used according to the best course of treatment.Narrow-spectrum, "low-grade" antibiotics should be used as much as possible.
Drug susceptibility testing for accurate treatment:Differences in the rates of drug resistance are closely associated with region[49], medical standards, economic development level, and quality of life[50].The resistance rate ofH.pylorito antibacterial drugs can determine the eradication rate of treatment options.The epidemic of drug resistance differ among different regions.Based on local drug resistance monitoring data, specific drug resistance conditions should be combined with drug sensitivity tests to make a reasonable plan to achieve the purpose of a precise treatment.
Development of new drugs and more drug candidates
H.pylorihas serious drug resistance, particularly multiple drug resistance, for which there are not many drug candidates available.Therefore, new types of antibiotics,drug-resistance inhibitors, drug-resistance plasmid eliminators, and strain attenuators urgently need to be researched and developed based on the following methods:
Establishment of new target identification and screening systems:Screening new targets provides new avenues for the development of new antibacterial drugs.Some enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, such asH.PYLORI0773 (FabX), a decapeptide from the decanoyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) in a parallel reaction with the first enzyme of acyl-CoA dehydrogenase of the fatty acid βoxidation cycle.Also it isomerizes trans-2-decenol-ACP to form a key UFA synthesis intermediate, cis-3-decenoyl-ACP, which reverses the normal fatty acid synthesis cycle ofH.pyloriin the c10 phase[51].However, there remains a certain distance from the screening of targets to drugs entering clinical trials.
Modification of existing drug structures:Modification, semi-synthesis, and synthesis of existing drugs are currently the recommended methods.Amoxicillin-UCS-2/tripolyphosphate (TPP) nanoparticles constructed with urea-modified chitosan derivatives UCS-2 and sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP) have more effective and specific effects in eliminatingH.pylori in vitro.Amoxicillin UCCS-2/TPP nanoparticles reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreased inflammatory damage caused byH.pyloriinfection[52].Modification of drugs can ensure their activity and shorten the time of preparation and mechanistic exploration; however,the toxicity of newly modified drugs should also be tested.
Use of new technologies:MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs widely found in intergenic or intron regions.They play a role in suppressing cancer mainly by regulating the expression of tumor suppressor genes[53].MiRNA210 is a candidate molecule that is often highly expressed in gastric cancer and mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition.It is considered a viable molecular target in the treatment of gastric cancer and can inhibit the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer[54].
Application of natural products:Natural products include plants, microbial secondary metabolites, and marine life.Both live cells and the supernatant ofLactobacillus plantarumZDY201 can inhibit the growth and urease activity ofH.pylori.Owing to its good lactic acid production and anti-inflammatory effects againstH.pyloriSS1 infection, it is expected to become a candidate strain of probiotics[55].Traditional Chinese medicine has anH.pylorikilling effect, low drug resistance, and low toxicity, and can be used as non-antibiotic drugs to treatH.pyloriinfection[56].Some natural products and agents have been shown to affect the TLR4 and MAPK signaling pathway activation byH.pylori[57].Screening active ingredients from plants is a fast and effective method for treating drug-resistantH.pyloriinfection.
Commercial compound library:Some old drugs that are used in clinical trials can be used.For example, furazolidone has been used as a replacement for CLA or metronidazole[58].However, due to the limited types of old medicines, it is difficult to purchase such medicines, which limits their usage.
Prevention of transmission
Although drug-resistantH.pyloriis weakly infectious, in terms of preventing transmission, in addition to preventing human-to-human transmission, the most important thing is to prevent transmission of drug-resistant plasmids.The spread of drug-resistant plasmids can occur between different bacteria, as well as between different individuals, strains, and animals, making humans susceptible to drug freeH.pyloriinfection[59].Livestock management[60], drug resistance testing[61], and management of antibiotics for other infectious diseases should also be implemented.
OUTLOOK
Through the unremitting efforts of scientific researchers and people from all works of life, some results in the prevention and treatment of drug-resistantH.pylorihave been acquired.For example, zinc linolenate can specifically act onH.pyloriand does not easily result in drug resistance[62].However, there is still a long way to deal with the key problem of lowH.pylorieradication rate.Drug resistance monitoring, application of drug susceptibility testing, and research and development of new drugs warrant further exploration.H.pyloriassociated gastritis is an infectious disease.Vaccines are the most effective method forH.pyloriinfection prevention, however, no vaccine is currently available.A vaccine that is expected to preventH.pyloriinfection will be introduced to the market in the near future.
CONCLUSION
Currently, there is no effective way to prevent and treat drug resistance inH.pyloriinfection.To cope with this situation, we suggest comprehensive prevention and treatment measures.First, the factors of causing drug resistance are suggested to be eliminated to ensure the success of the first triple or quadruple treatment for patients with drug resistance, whose accurate treatment is based on individual drug history and drug-sensitivity testing results.Traditional Chinese medicine plays a unique role in the treatment of drug-resistant bacteria with relatively few side effects, which is worthy of further exploration.
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年2期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2020年2期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- Effectiveness and safety of sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopy:An opinion review
- Chinese research into ulcerative colitis from 1978 to 2017:A bibliometric analysis
- Single-balloon and spiral enteroscopy may have similar diagnostic and therapeutic yields to double-balloon enteroscopy:Results from a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and prospective studies
- Systematic review with meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence relating smoking to type 2 diabetes
- Utility of gastrointestinal ultrasound in functional gastrointestinal disorders:A narrative review
- Helicobacter pylori and gastric cardia cancer:What do we know about their relationship?
