Network pharmacology studies on the effect of Chai-Ling decoction in coronavirus disease 2019
Lu Yang,Yu-Ting Li,Jing Miao,Li Wang,Hui Fu,Qin Li,Wei-Bo Wen,Zhai-Yi Zhang,Rui-Wen Song,Xiang-Guo Liu,Hong-Wu Wang*,Huan-Tian Cui*
1Graduate School, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; 2College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; 3Department of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Tianjin Second People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300192, China; 4Department of Pharmacy,Tianjin Second People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300192, China; 5College of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; 6Department of Endocrinology in Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650021, China; 7School of Management, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China; 8Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Animal Cell and Developmental Biology,School of Life Sciences,Shandong University,Qingdao 250100,China.
Abstract
Keywords: Chai-Ling decoction, Coronavirus disease 2019, Network pharmacology, Molecular docking, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
Background
Since December 2019, a number of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases have been detected in various provinces and cities in China, and the disease quickly spread many foreign countries and regions [1].Following severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)and Middle East respiratory syndrome, the worldwide epidemic of COVID-19 has become one of the significant threats to human health and public safety.
Fever, dry cough, and fatigue are major clinical symptoms of COVID-19.Besides, some patients also exhibit myocardial,digestive,and neurological damage.Currently, no effective antiviral drug on COVID-19 has been developed.It remains unclear whether the drugs discovered, such as protease inhibitor indinavir,saquinavir, and kyprolis, have a definite effect on COVID-19.Although remdesivir has been shown to inhibit the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), further evidence is still needed.Besides, other possible drugs for COVID-19, including arbidol and darunavir, have shown low bioactivity.Zhou.et al found that SARS-CoV-2 mainly infected target cells by binding the spike protein (S protein) on the envelope to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2(ACE2)[2], which is the receptor on the surface of target cells, similar to SARS-CoV [3].ACE2 is a type I transmembrane protein composed of 805 amino acids, mainly distributes in the lung, kidney,testicle, heart,and other tissues.Disrupting the binding of S protein and ACE2 could be a therapeutic target of COVID-19[4].
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has accumulated abundant experience in the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases and shown beneficial effects on COVID-19.Studies indicate that TCM can decrease the transformation of mild to severe cases [5].Qing Fei Pai Du decoction, which is a modification of Xiao-Chai-Hu (XCH) decoction,Wu-Ling-San(WLS),Ma Xing Shi Gan decoction,and She Gan Ma Huang decoction in Shang Han Za Bing Lun (Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders,200-210 C.E.),has shown 90%effective rate on COVID-19[6].Previous studies have demonstrated that XCH (Chaihu(Bupleuri Radix), Banxia (Pinelliae Rhizoma),Renshen (Panax GinsengC.A.Mey), Gancao(Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma), Huangqin(Scutellariae Radix), Shengjiang (Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens), and Dazao (Jujubae Fructus)) can alleviate fever [7], cough [8], and fatigue [9], the primary clinical outcomes of COVID-19.According to theDiagnosis and treatment program of TCM on COVID-19 in Hunan (China), XCH can be used to treat patients with COVID-19 with bitter taste, hiccup,and fever [10].Additionally, WLS decoction (Guizhi(Cinnamomi Ramulus), Fuling (Poria), Zhuling(Polyporus), Zexie (Alismatis Rhizoma), and Baizhu(Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma)) has shown apparent effects on attenuating gastrointestinal symptoms[11].
Chai-Ling decoction (CLD) (Chaihu 24 g (Bupleuri Radix), Huangqin 9 g (Scutellariae Radix), Guizhi 6-9 g (Cinnamomi Ramulus), Baizhu 9 g (Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma), Fuling 10 g (Poria),Zhuling 10 g (Polyporus), Zexie 9 g (Alismatis Rhizoma), Gancao 6 g (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma),Shishangbai 30 g(Selaginella Doederleinii),and Lianqiao 30 g (Forsythiae Fructus)) was derived from a modification of XCH and WLS decoctions,which originated from Shang Han Za Bing Lun(Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders,200-210 C.E.)written by Zhang Zhongjing.Moreover,CLD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant,antioxidant, hypoglycemic, immunomodulatory, and diuretic effects and used in the treatment of liver,kidney, and joint diseases [12].According to thePrevention and Treatment Guidelines of Damp-Heat Syndrome of “Taiyin” Lung(respiratory system in the theory of traditional Chinese medicine)Epidemic Disease(coronavirus pneumonia), CLD could be used to treat the early stage of COVID-19[13].
Due to the multiple targets and components of TCM,network pharmacology has been used as an essential tool to identify the key targets and mechanisms of TCM[14].The molecular docking method can be used to analyze the interactions between drug components and targets protein to investigate the binding affinity and predict the possible binding sites of drugs [15].In this study, the active components of CLD were screened through network pharmacology, and the potential targets and mechanisms of CLD in COVID-19 were predicted.The molecular docking method was used to identify the key compounds in CLD with high binding affinity on the SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2, which is the key target of SARS-CoV-2 in entering target cells.
Materials and methods
Identification of the main active compounds
The main compounds in CLD were screened based on the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform(TCMSP) (http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php) and literatures, and Chaihu (Bupleuri Radix), Huangqin(Scutellariae Radix), Guizhi (Cinnamomi Ramulus),Baizhu (Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma), Fuling(Poria), Zhuling (Polyporus), Zexie (Alismatis Rhizoma), Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma),Shishangbai (Selaginella Doederleinii), and Lianqiao(Forsythiae Fructus) were used as keywords to query the candidate components of CLD.Compounds with an oral bioavailability (OB) ≥30% are considered to be absorbed and utilized by the human body [16].Drug-like (DL) is a necessary condition for the preparation of compound medicine.The DL value represents the similarity between the composition and known chemical medicine.It is generally considered that the composition with DL value ≥0.18 has an important reference value for the activity of the body[17].The OB and DL values of each compound can be directly obtained in the TCMSP, and the effective components of CLD were obtained by screening for OB ≥30%and DL value ≥0.18.
Prediction of potential targets and annotation of gene names
Reverse pharmacophore search was used to identify the targets with a high binding affinity with drug components.Initially, the molecular structures of compounds identified from CLD were matched reversely to the pharmacophore database.The chemical composition obtained in 1.1 was imported into the PubChem database(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) by name, and the three-dimensional structure of each component were obtained and stored in sdf format and uploaded to the PharmMapper (http://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmappe r/) to obtain human-related protein targets for active ingredients [18].The UniProt database(https://www.uniprot.org/) was used to obtain the relative gene name of each target.
Potential targets for prediction of the disease
Novel coronavirus pneumonia was used as the keyword and imported to the GeneCards database(https://www.genecards.org) to identify the key targets of COVID-19 [19].The targets of CLD components and COVID-19 were intersected using Venny (version 2.1, http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/) to obtain the key targets of CLD on COVID-19.
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis and identification of key targets
STRING (https://string-db.org) can be used to study the PPI [20].The potential targets of CLD in COVID-19 were imported into the STRING database to obtain the PPI among each target.According to the PPI network, proteins with high connectivity showed larger numbers and width of connections.Key targets with the top five connectivity were identified as the key targets.
Pathway enrichment using Gene Oncology (GO)analysis
GO analysis of targets of CLD on COVID-19 was conducted using DAVID database(http://www.david.niaid.nih.gov).DAVID database can provide detailed annotations of pathways, including cell components (CCs), molecular functions (MFs),and biological processes (BPs) [21].Pathways withP≤0.05 and q ≤0.05 were obtained.
Pathway enrichment using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes(KEGG)
Targets of CLD on COVID-19 were imported into the KOBAS 3.0 database (http://kobas.cbi.pku.edu.cn) to obtain the KEGG terms.Pathways that may be involved in COVID-19 withP≤0.05 and q ≤0.05 were identified, and the top ten KEGG pathways with lowP-value were selected as the potential pathways of CLD on COVID-19.
Establishment of compound-target-pathway network
Cytoscape 3.7.2 was used to generate the compound-target-pathway network of CLD on COVID-19 [22].According to the compound-target-pathway network, different active compounds, targets, and pathways were visualized with the nodes in different colors.
Molecular docking of major components in CLD with SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2
The three-dimensional structures of S protein of SARS-CoV-2 (PDB ID, 6LU7) and ACE2 (PDB ID,IR42) were downloaded in the RCSB database(https://www.rcsb.org/) and saved as pdb format.The three-dimensional structures of S protein in SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 were added with hydrogen,electron,and ROOT using AutoDock software.The top 20 candidate compounds in CLD were selected for molecular docking, and the results of molecular docking were visualized using PyMOL software.
Results
Results of chemical compounds in CLD
A total of 1,068 compounds were obtained from the TCMSP, including 288 from Chaihu (Bupleuri Radix),58 from Huangqin (Scutellariae Radix), 280 from Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma), 106 from Guizhi (Cinnamomi Ramulus), 55 from Baizhu(Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma), 34 from Fuling (Poria), 31 from Zhuling (Polyporus), 46 from Zexie (Alismatis Rhizoma), 20 from Shishangbai(Selaginella Doederleinii), and 150 from Lianqiao(Forsythiae Fructus).After removing the duplicated compounds,106 active compounds in CLD with OB ≥30% and DL ≥ 0.18 were selected.Based on the literature, compounds that could not be detected by mass spectrum were removed and 106 compounds were identified as the main compounds of CLD,including 12 from Lianqiao (Forsythiae Fructus) [23],6 from Zexie (Alismatis Rhizoma) [24], 1 from Shishangbai (Selaginella Doederleinii) [25], 5 from Zhuling (Polyporus) [26], 9 from Fuling (Poria) [27],4 from Baizhu (Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma)[28], 3 from Guizhi (Cinnamomi Ramulus) [29], 14 from Huangqin (Scutellariae Radix) [30], 6 from Chaihu (Bupleuri Radix) [31], and 46 from Gancao(Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma)[32-34].The detailed information of selected active compounds is presented in Table 1.
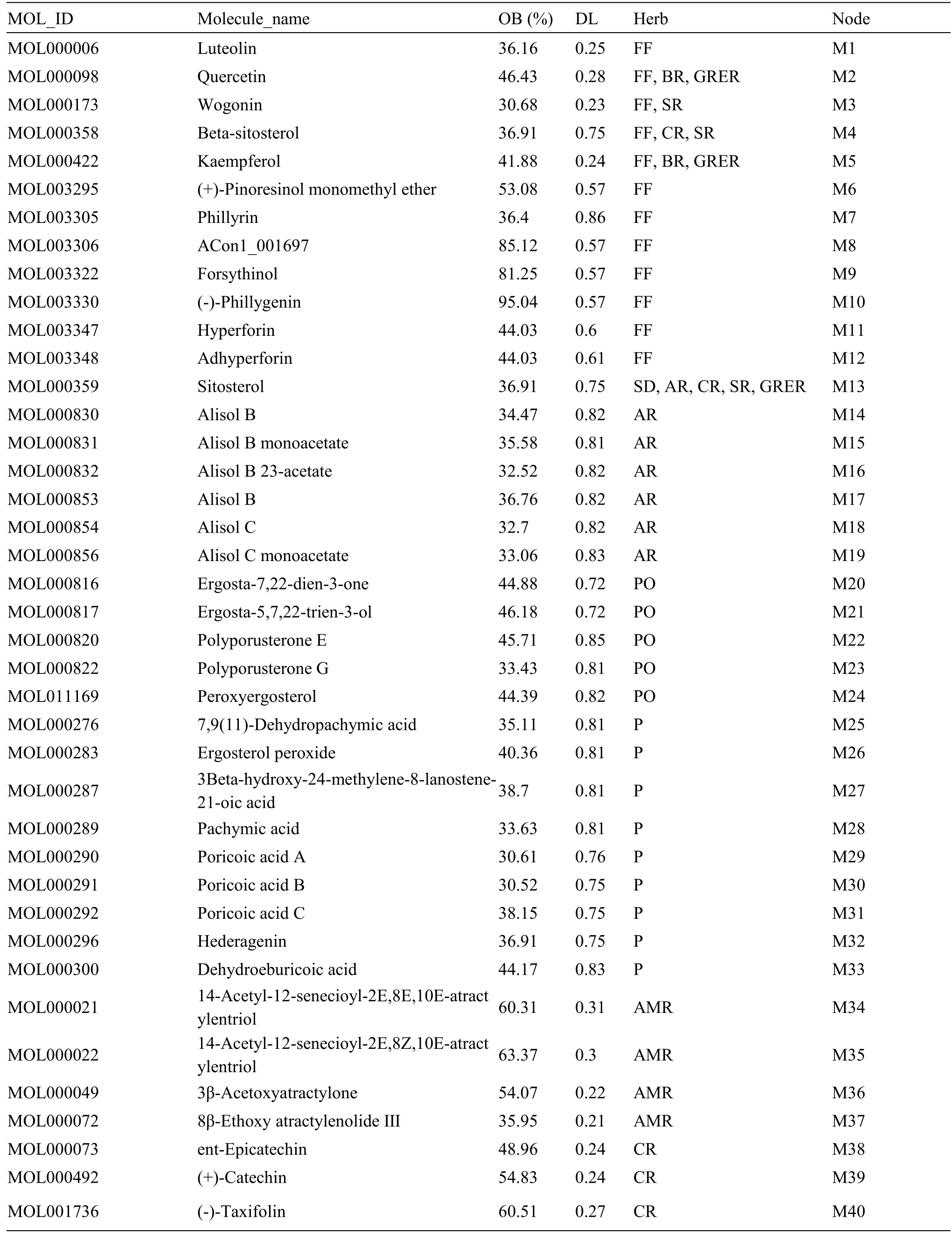
Table 1 Information of active compounds in CLD
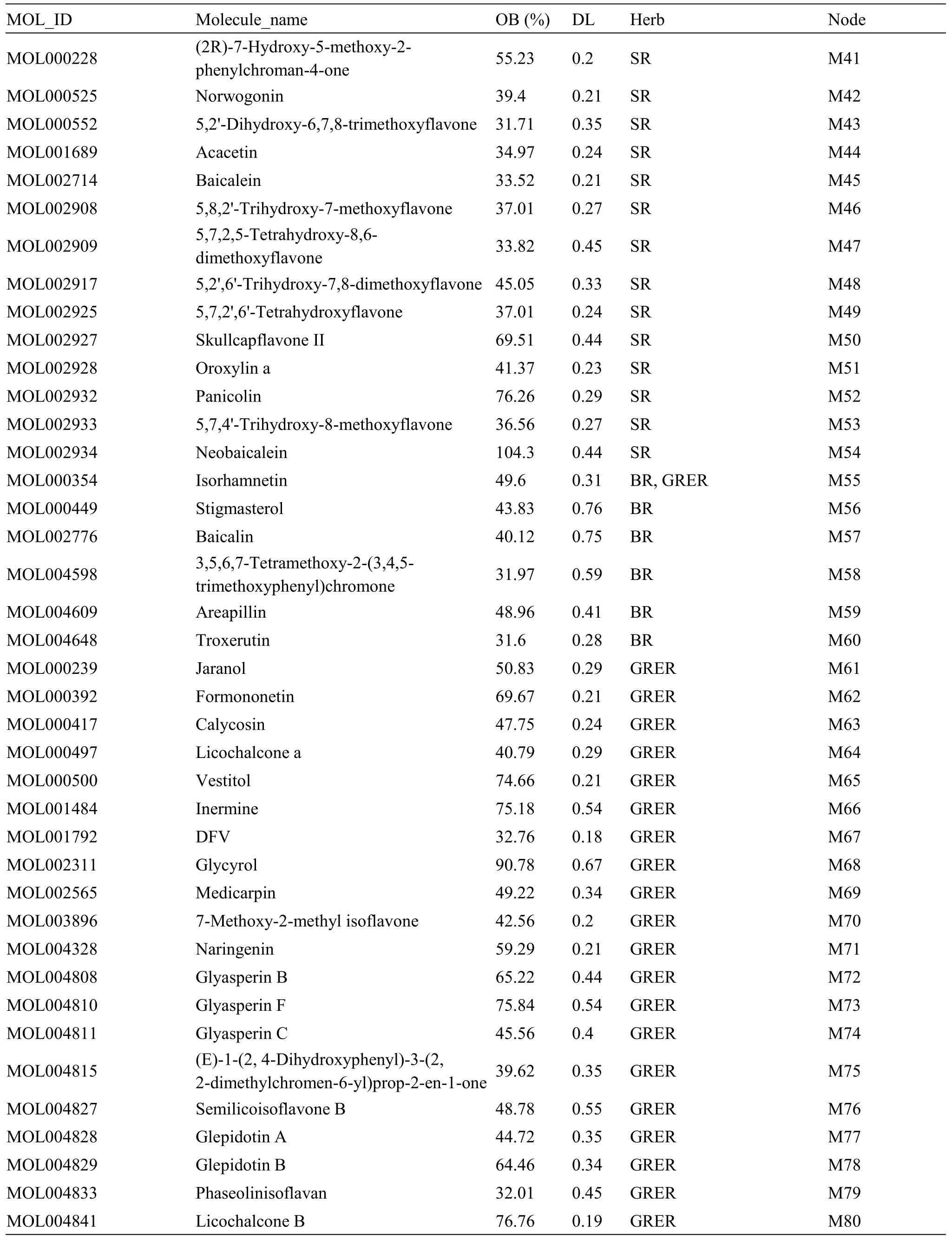
Table 1 Information of active compounds in CLD(Continued)
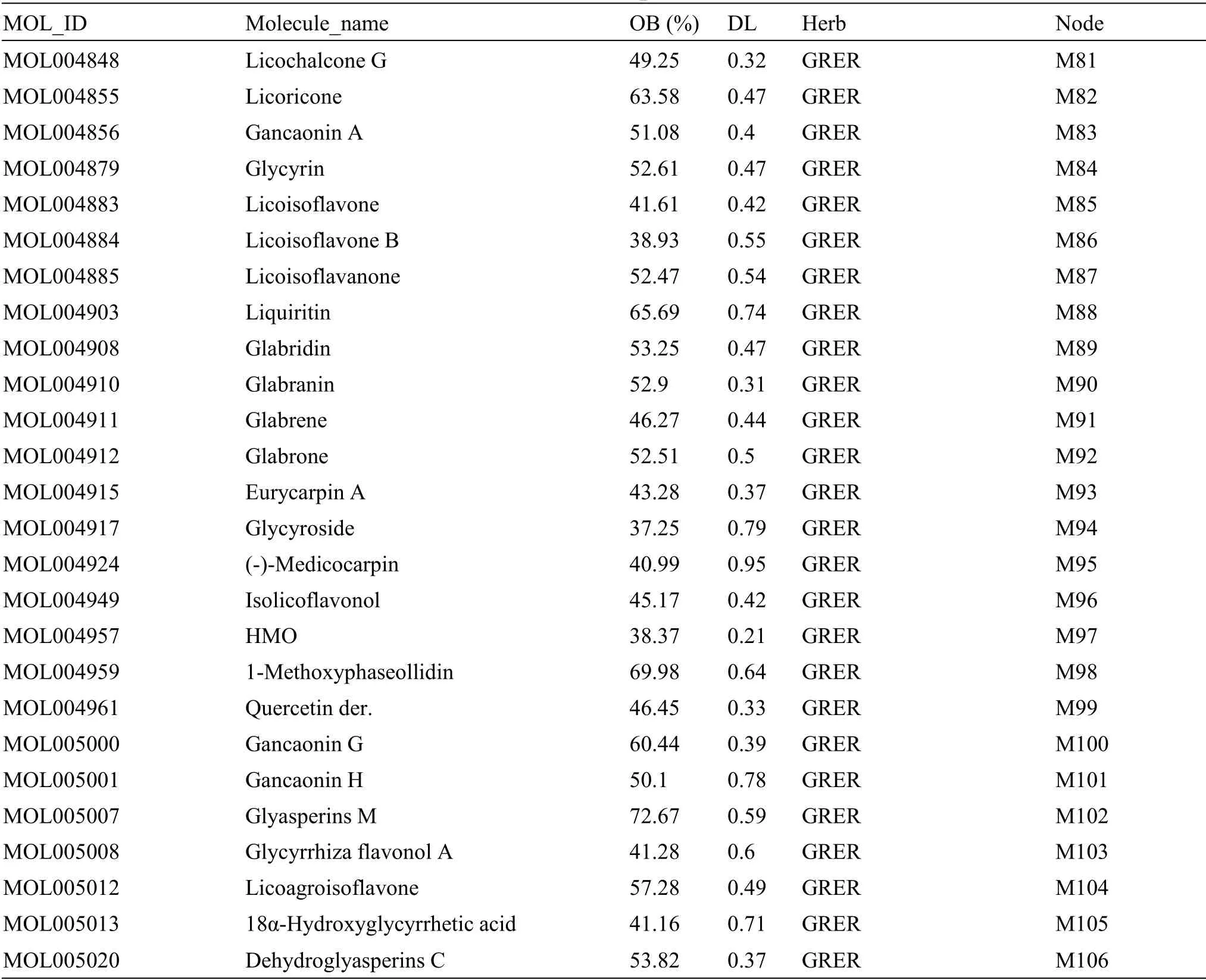
Table 1 Information of active compounds in CLD(Continued)
Identification of the targets of CLD on COVID-19
Initially, 160 active ingredient targets were generated using PubChem and PharmMapper databases.The relative gene names of targets were obtained using UniProt database.Then, 251 targets of COVID-19 were identified according to the GeneCards database.After intersecting the targets of CLD in COVID-19,24 potential targets of CLD in COVID-19 were obtained(Figure 1).
Establishment and analysis of PPI network
Generally, 24 target protein nodes and 181 interaction edges were obtained using PPI network analysis.The average degree of target protein was 15.1.According to the connectivity of target proteins, IL6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), C-C motif ligand (CCL) 2,mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) 1, and MAPK3 were identified as the key targets of CLD in COVID-19(Figure 2).
GO analysis of common targets
Generally, 283 GO terms withP≤0.05 andq≤0.05 were generated to be related to the targets of CLD in COVID-19, including 229 BPs terms, 22 CCs terms,and 32 MFs terms.Lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway and positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process were the top two GO terms in BPs with lowP-value.Caveola and extracellular space were the top two GO terms in CCs with lowP-value.Enzyme binding and MAP kinase activity were the top two GO terms in MF with lowP-value(Figure 3).
KEGG analysis of targets of CLD in COVID-19
A total of 181 KEGG terms were enriched as the potential pathways of CLD in COVID-19.The top ten pathways with high significance were selected and presented in Table 2.interleukin (IL)-17 signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) signaling pathway, and the differentiation of T helper cell 17 (Th17) were related to the potential therapeutic pathway of CLD in COVID-19.
Compound-target-pathway network construction
The compounds, targets, and pathways of CLD in COVID-19 were imported into Cytoscape 3.7.2 to generate the compound-target-pathway network.According to the compound-target-pathway network,red nodes represent the genes, orange nodes represent pathways, light green nodes represent the active ingredients of Chaihu (Bupleuri Radix), purple nodes represent active ingredient of Huangqin (Scutellariae Radix), light yellow nodes represent active ingredients of Lianqiao (Forsythiae Fructus), light blue nodes represent active ingredients of Gancao (Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma),and pink nodes represent the active ingredients of Guizhi (Cinnamomi Ramulus),Baizhu(Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma),Fuling(Poria),Zhuling (Polyporus),Zexie (Alismatis Rhizoma),Shishangbai(Selaginella Doederleinii)(Figure 4).
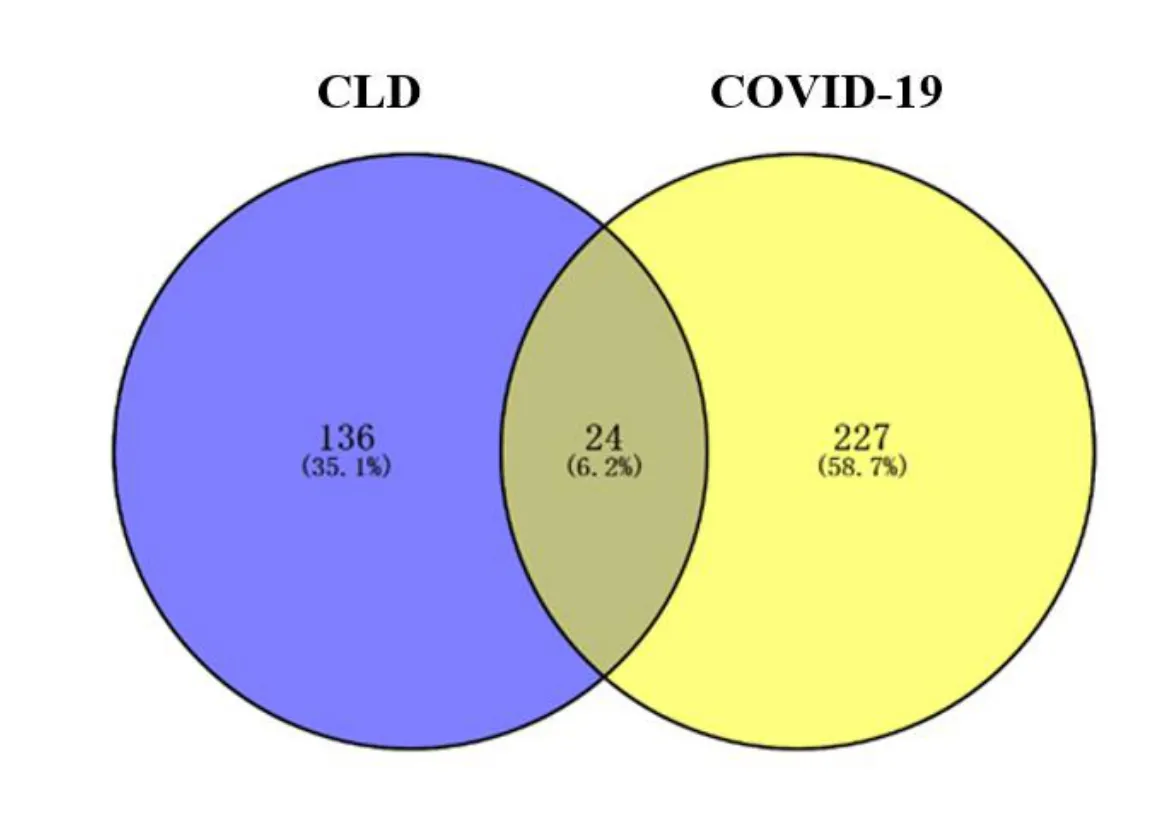
Figure 1 Common targets of CLD in COVID-19.
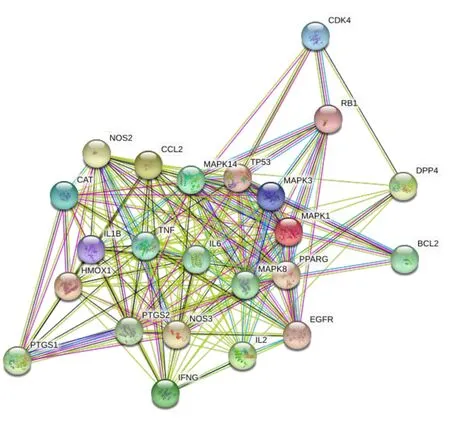
Figure 2 PPI network of target proteins.
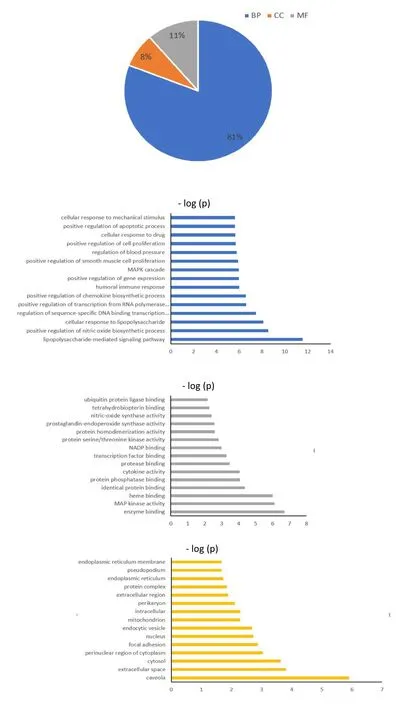
Figure 3 GO enrichment analysis of the common targets.
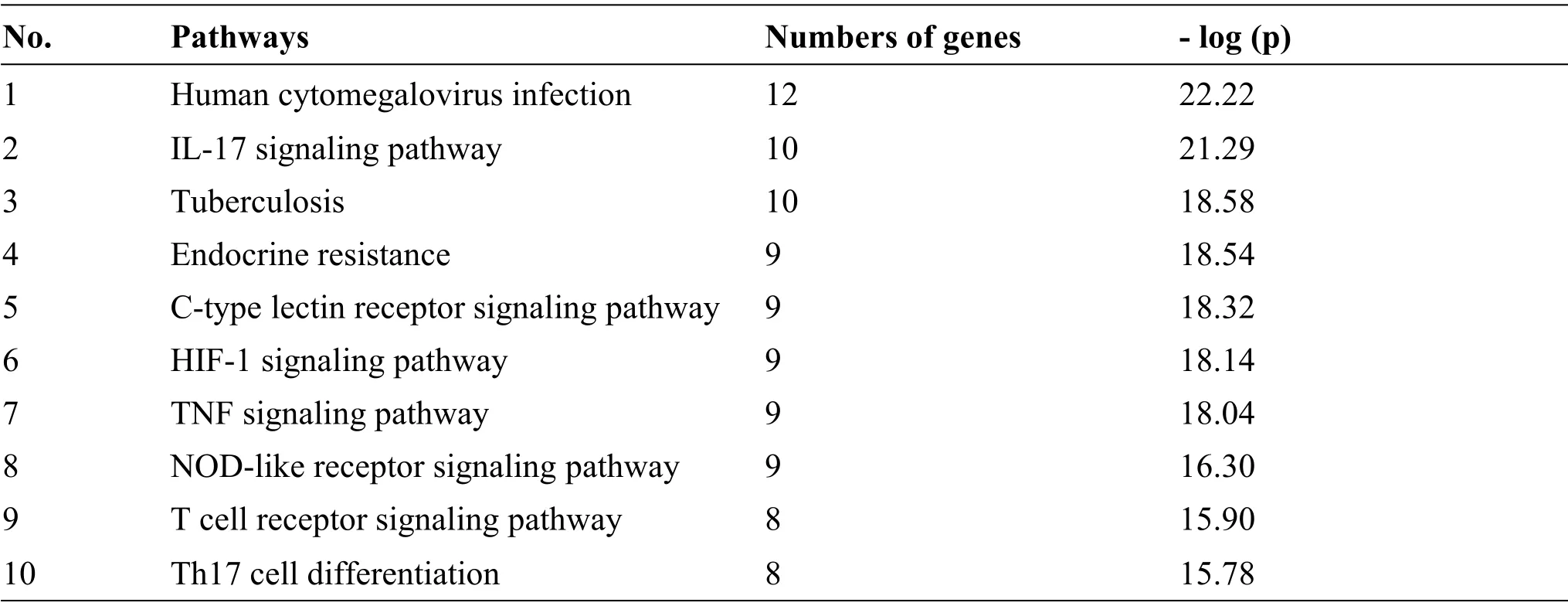
Table 2 KEGG enrichment analysis of the common targets
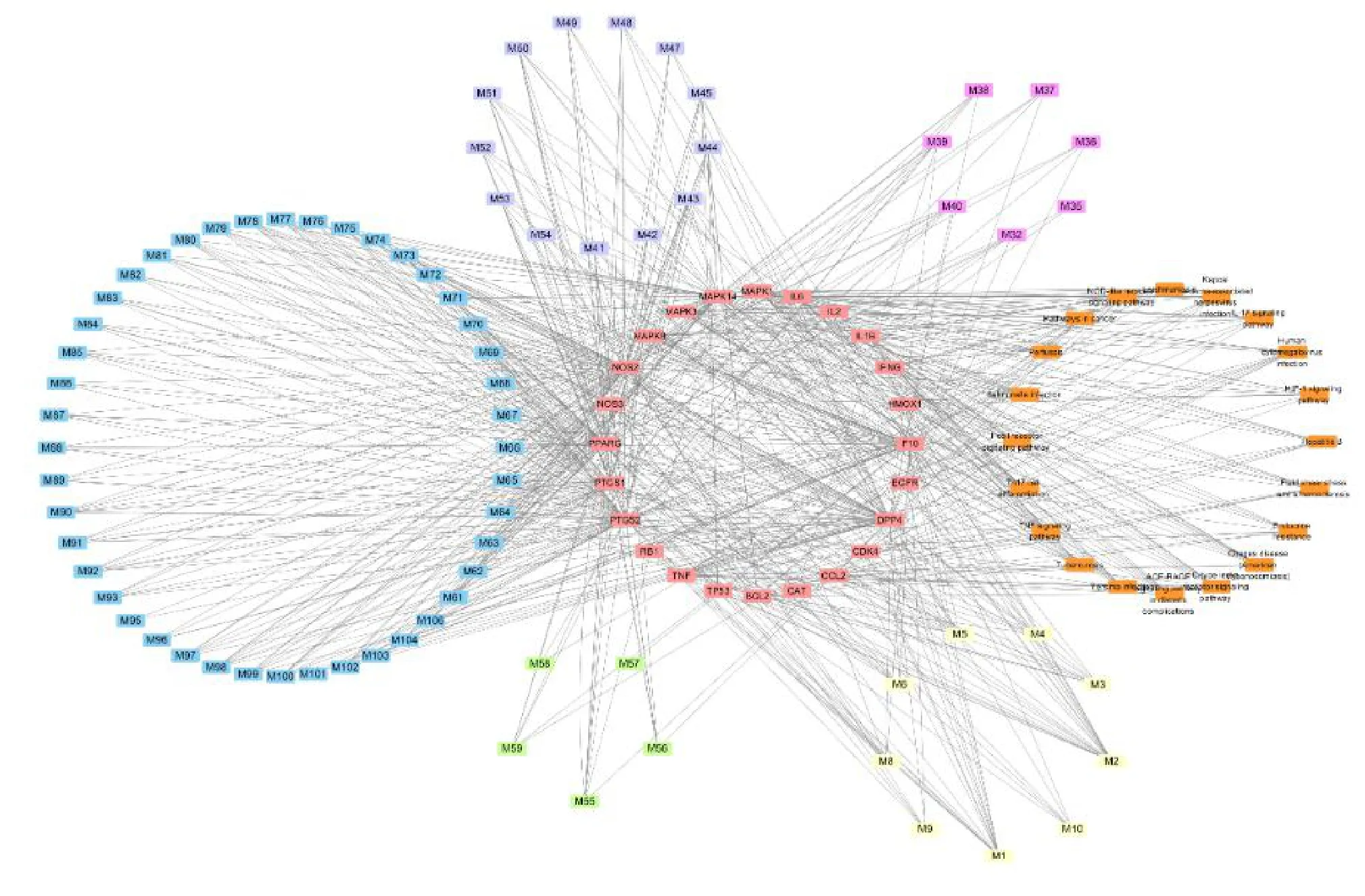
Figure 4 Compound-target-pathway network of CLD in COVID-19.
CLD,Chai-Ling decoction;COVID-19,coronavirus disease 2019.
Molecular docking analysis of active components in CLD with SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2
Compounds with high connectivity are associated with more targets.According to the number of related targets,the top 20 active compounds in CLD with high connectivity in compound-target-pathway network were selected for molecular docking.Besides, ten Western medicine compounds (arbidol, atazanavir,darunavir, indinavir, kyprolis, lopinavir, remdesivir,ritonavir, saquinavir, and tipranavir), which have been reported to be possibly used in COVID-19 treatment in Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, were used as positive control for molecular docking based on the news report (http://www.simm.cas.cn/xwzx/kydt/2020 01/t20200125_5494417.html).Based on the docking score, a lower docking score indicates a stronger binding affinity to target protein.Beta-sitosterol,kaempferol, and stigmasterol had the strongest affinity with SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2.Moreover, their affinity with SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 was better than some of these Western medicine compounds (Table 4 and Figures 5-6).
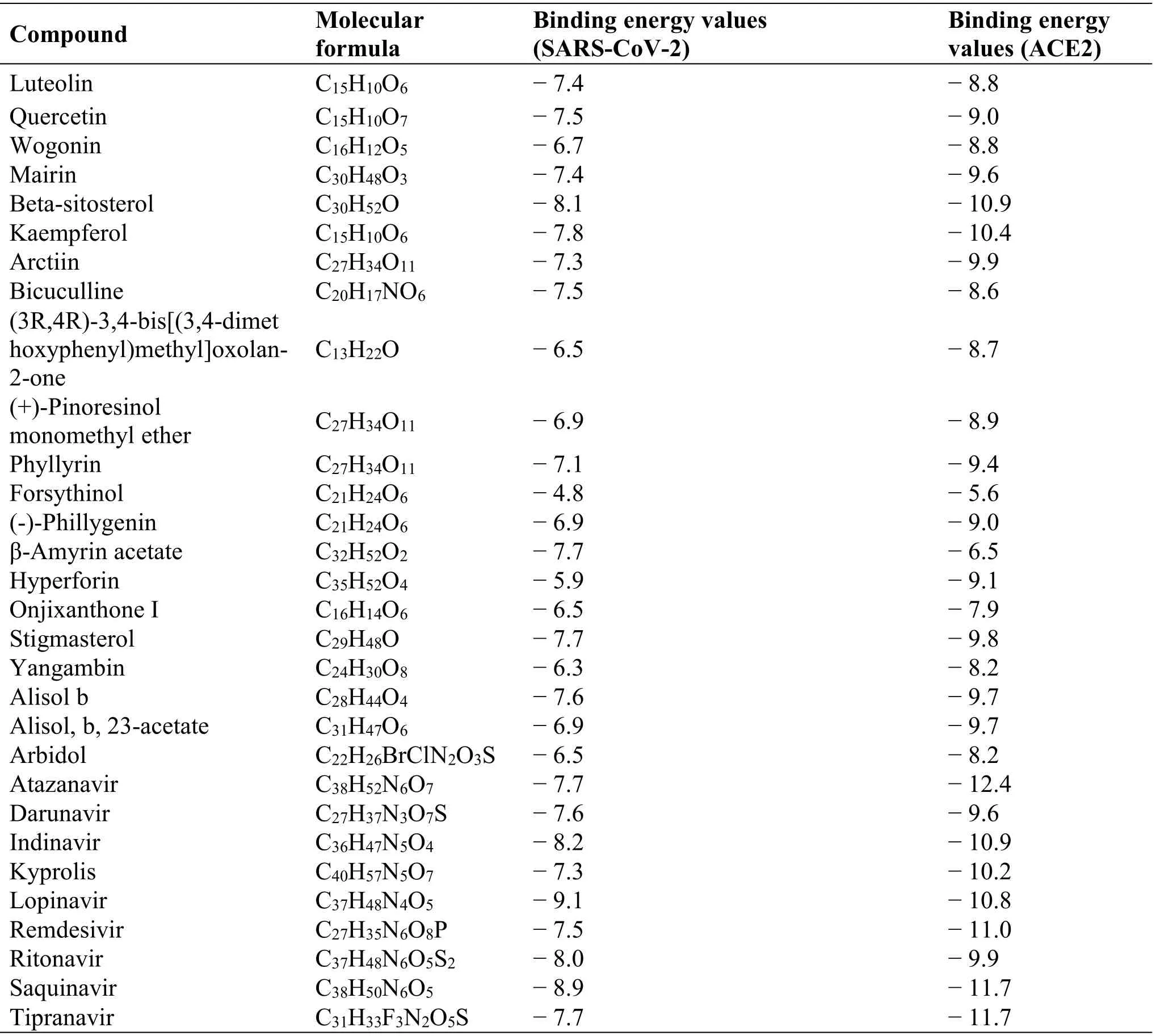
Table 4 Molecular docking table of ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 with 20 active components in CLD and 10 Western medicine compounds
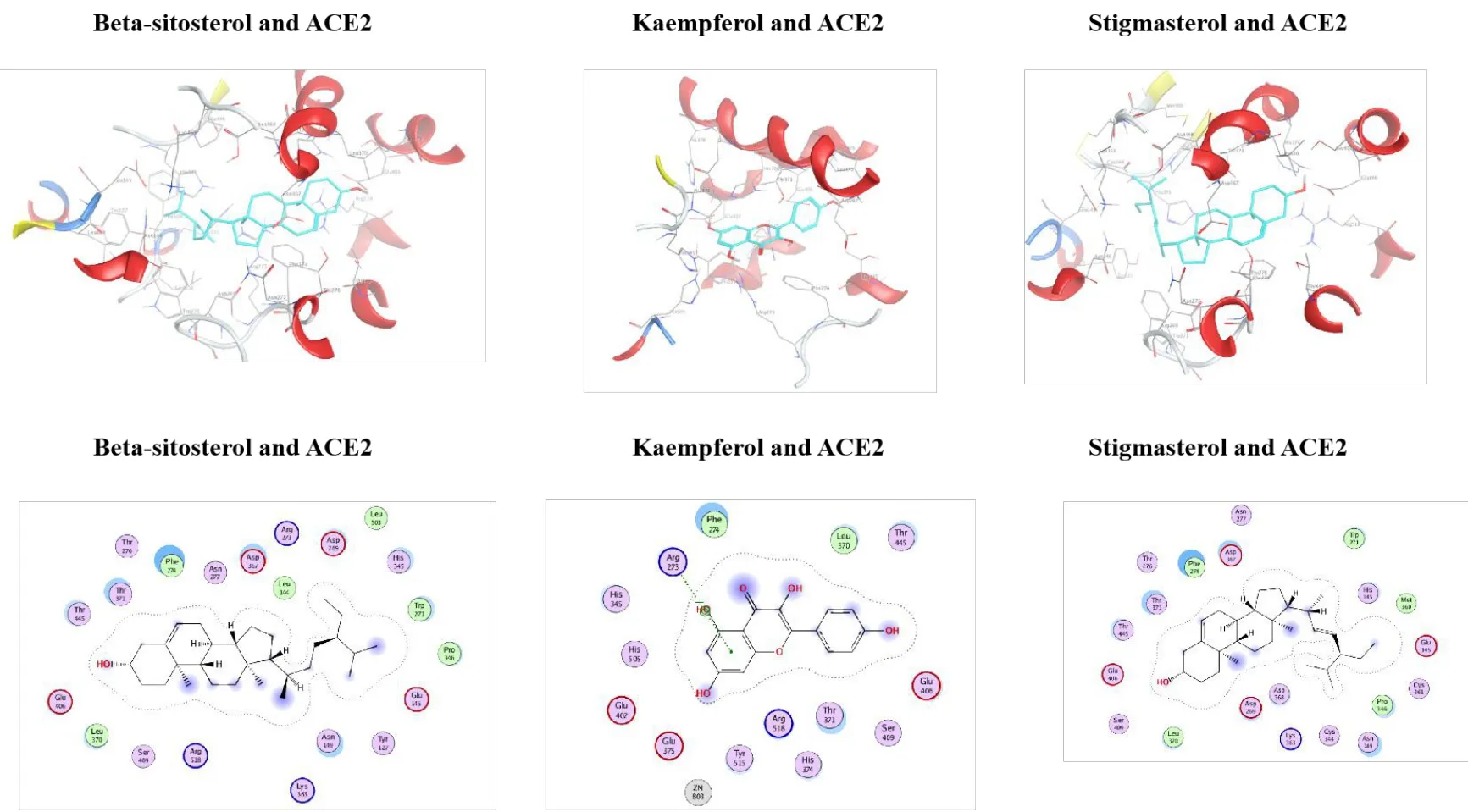
Figure 5 Molecular docking diagram of ACE2 with β-sitosterol, kaempferol, and stigmasterol.
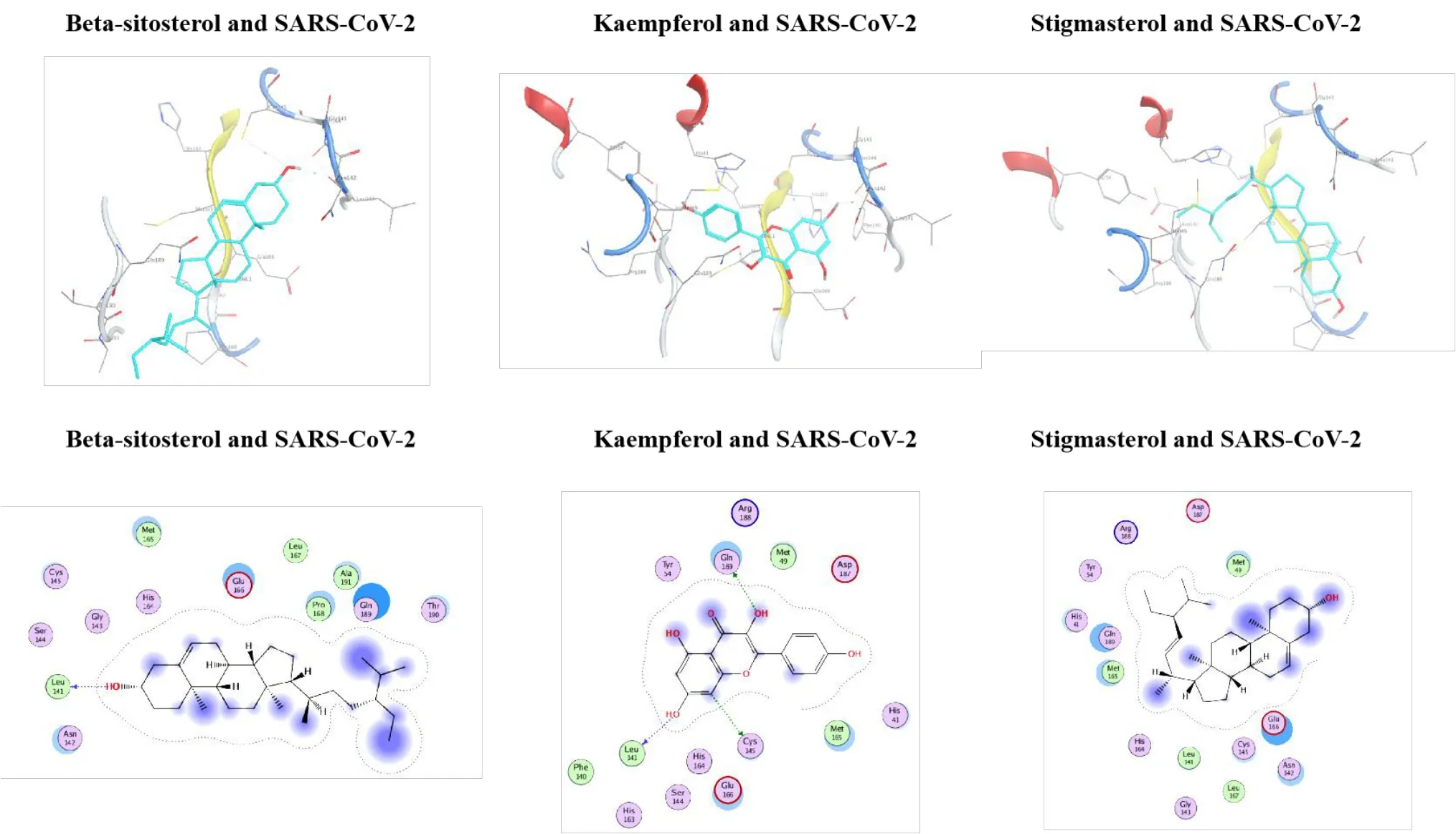
Figure 6 Molecular docking diagram of SARS-CoV-2 with β-sitosterol, kaempferol, and stigmasterol.
Discussion
Network pharmacology is commonly used to analyze the potential targets of TCM in COVID-19.A previous study corroborated that the components of Huoxiang Zhengqi Oral Liquid could be combined with ACE2 binding to prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2,heat shock protein 90 AB1, and calmodulin-regulated spectrin-associated protein 2 to modulate multiple signaling pathways, thereby exerting a preventive or therapeutic effect on COVID-19 [35].Wang et al.indicated that the active compounds of Huanglian Jiedu decoction could bind novel coronavirus 3CL hydrolase on a target [36], such as prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2, heat shock protein 90 AA1,and estrogen receptor 1, which probably had an antiviral effect on COVID-19.Likewise, the main active components of Qing-Fei-Pai-Du decoction in the treatment of COVID-19 could regulate targets(e.g.,MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK8, MAPK14, and IL6) and pathways (e.g., TNF and nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathways), thereby inhibiting inflammatory reaction, regulating immune function, reducing lung injury,and protecting nerve function[37].
Currently, according to the clinical investigation,patients with COVID-19 develop an excessive inflammatory response, known as cytokine storm [38,39].High levels of cytokines and inflammatory chemokines can overactivate the immune response against viral infections and cause extensive immunopathological damage in vital organs, such as the heart, lung, and kidney [40].Our results showed that MAPK1,IL-6,TNF,CCL2,and MAPK3 might be the potential targets of CLD in COVID-19.MAPKs are essential transmitters of signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, which regulate many physiological activities, such as inflammation,apoptosis, oncogenesis, invasion, and metastasis of tumor cells [41].MAPK signaling pathway also plays an essential role in the inflammatory response, which can be activated by some pro-inflammatory factors,such as TNF-α and IL family (e.g., IL-1 and IL-6),thereby aggravating the inflammatory response [42].GO and KEGG analyses revealed that COVID-19 treatment by CLD involved a variety of BPs, CCs, and MFs.Meanwhile, the potential targets of CLD in COVID-19 were significantly enriched in multiple pathways, including IL-17 signaling pathway, Th17 cell differentiation, TNF signaling pathway, and HIF-1 signaling pathway, indicating that CLD may exhibit significant immunoregulatory effects in COVID-19 treatment.HIF-1, as a hypoxic signaling transcription factor, regulates the occurrence and development of immune inflammation in dendritic cells, macrophages,and T cells by regulating the expression of metabolization-related genes, thereby regulating the expression of immune-related genes and proteins and maturation and differentiation of related cells [43].CCL can specifically promote chemotaxis and activation of eosinophils, leading to an inflammatory response [44].Th17 secretes various effectors, such as IL-17, IL-6, and TNF-α, and IL-17 mediates the inflammatory response by inducing chemokines and various pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-α[45].
Following molecular docking, the active components in CLD, including beta-sitosterol,kaempferol, and stigmasterol, showed high binding affinity with both S protein of SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2, indicating that these compounds may directly inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection.Interestingly,beta-sitosterol, kaempferol, and stigmasterol showed higher binding affinity to S protein than arbidol,kyprolis, and remdesivir and showed higher binding affinity to ACE2 than arbidol and darunavir.
Conclusion
This study indicates that modulating the inflammatory response can be the potential mechanisms of CLD in COVID-19.Besides, beta-sitosterol, kaempferol, and stigmasterol can be the key compounds that exert antiviral effects against SARS-CoV-2.Our prediction also provides the research fields to further study the mechanisms of CLD in SARS-CoV-2 infection in the future.
 Traditional Medicine Research2020年3期
Traditional Medicine Research2020年3期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Medical workers in traditional medicine who sacrificed their lives in the battle against COVID-19 deserve to be remembered forever
- Overview of the plague in the late Ming Dynasty and its prevention and control measures
- The potential application of the traditional Chinese herb Exocarpium Citri grandis in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19
- The role of natural products in regulating pyroptosis
- Complementary and alternative medicine in European countries—legislative framework
