Significance of 125I radioactive seed implantation on growth differentiation factor and programmed death receptor-1 during treatment of oral cancer
Gang Xue,Yao Feng,Jia-Bin Li
Abstract
Key words: 125I radioactive seeds; Oral cancer; Growth differentiation factor 11;Programmed death receptor-1; Prognosis; Recurrence
INTRODUCTION
Oral cancer (OC) is the most common malignant tumor in the oral cavity,and includes lip cancer,tongue cancer,and gingival cancer[1].OC is mainly found in middle-aged and elderly men,and its morbidity rate is still among the highest of all systemic malignant tumors[2].According to statistics,there are on average,390000 new OC cases per year worldwide[3].Moreover,some studies have shown that from 2000 to 2015,there were more than 350000 new patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma each year,and its morbidity rate is increasing year by year[4].The pathogenesis of OC is a chronic pathological process,and there is even a canceration process lasting for decades before the occurrence of typical canceration features[5].Moreover,due to the absence of significant clinical features in early OC,it is easy for patients to ignore or mistake it for common inflammation resulting in the wrong treatment,which can also cause a negative prognosis for many years[6].According to statistics,the mortality due to OC is as high as 2.4/100000[7].This is also due to the high incidence and mortality of OC,and it is classified as a key research disease in clinical practice[8].
At present,OC is mainly treated clinically by surgery or combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy; but in recent years,more and more studies have shown that the stress trauma caused by surgery and the toxicity and side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy seriously affect the prognosis of patients[9].The drawbacks of OC treatment are gradually being exposed,and the identification of an OC treatment with low side effects and marked efficacy is urgently required.Due to continuous research,the clinical focus has gradually been on125I radioactive seed implantation therapy.125I radioactive seed implantation therapyis a type of brachytherapy,which means that under the guidance of imaging equipment,125I radioactive seeds are directly implanted into the tumor tissue through percutaneous punctures to irradiate the tumor.The main mechanism of this treatment involves destroying DNA in the tumor cell nucleus by a small amount of γ-rays during the proliferation cycle of tumor cells,which results in them losing their ability to reproduce and ultimately leads to apoptosis[10].At present,it has been proved that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy has a significant effect on head and neck neoplasms[11].Moreover,Jieet al[12]and Menget al[13]confirmed that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy had an effect on OC; however,further clinical research is required and the application of this treatment in OC is still not widely used.In order to effectively improve the prognosis of OC patients,the present study analyzed the efficacy of125I radioactive seed implantation therapy in OC patients and the changes in growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) and programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)during treatment for future clinical reference and guidance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General information
A total of 184 OC patients admitted to The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University from May 2015 to May 2017 were selected as research subjects for prospective analysis.Of these patients,89 who received125I radioactive seed implantation therapy were regarded as the research group (RG) and 95 patients who received surgical treatment were regarded as the control group (CG).This experiment was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University,and all the above research subjects signed an informed consent.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria were as follows:Patients conformed to OC clinical manifestations and were determined to have OC following biopsy by the Pathology Department of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University; patients were 20-70 years old;patients with complete case data; local progression of tumor was difficult to control with local control methods or advanced tumor with distant metastasis,causing serious symptoms due to local focus; patients agreed to cooperate with the arrangement of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University medical staff.Exclusion criteria were as follows:patients with multiple tumors; patients with other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases; patients with autoimmune diseases;patients with organ failure; patients with mental diseases; patients with drug allergy;patients who received other antibiotics within 3 mo before treatment; pregnant women or breast-feeding patients; patients with a wide range of lesions; patients with active hemorrhage,necrosis or ulcer at the tumor site; patients who died during the course of treatment or discontinued treatment; patients transferred to another hospital; patients with physical disabilities who were unable to take care of themselves and remained in bed for a long time.
Methods
According to the lesion sites,we determined their relative position,elevated the implantation site,used color Doppler ultrasound to examine the tumor focus,and avoid important blood vessels to determine the puncture points.These sites were routinely disinfected and draped.After local anesthesia,a puncture needle was implanted into the tumor body under the guidance of ultrasound.At this time,the particle needles were arranged in parallel with a spacing of 1-1.5 cm.If there was no important structure behind the tumor,it was placed outside or at the edge of the tumor.If there was important tissue,a distance of 1 cm was maintained.We connected the implantation gun,performed real-time monitoring under ultrasound,and implanted the particles one by one from deep to shallow according to the needle distribution sequence,with a dose of 0.3-0.8 mCi.We withdrew the needle 1-1.5 cm and implanted particles until the needle tip reached the front edge of the tumor.The distance between the longitudinal and transverse distribution of particles was 1-1.5 cm.After surgery,the puncture site was pressed for 15 min,and local hemorrhage was determined.Ultrasound was performed to assess the distribution and quantity of particles,and replanting was carried out if missed planting was observed.In total,4 mL of fasting venous blood was extracted from patients before treatment (T0),2 wk after treatment (T1),4 wk after treatment (T2) and 6 wk after treatment (T3),and the expression levels of GDF11 and PD-1 were detected by qRT-PCR.The peripheral blood samples were placed at room temperature for 30 min and centrifuged for 10 min (800×g) to obtain the upper serum,which was stored in a refrigerator at -80°C until tested.The collected serum was extracted using the TRIzol kit (kit and required reagents were from Invitrogen Company,United States) for total RNA,and purity,concentration and integrity of the extracted total RNA was detected by ultraviolet spectrophotometry and agarose gel electrophoresis.TransScript®miRNA RT Enzyme Mix and 2× TS miRNA Reaction Mix were used for reverse transcription of total RNA,and the operation steps were carried out in strict accordance with the manufacturer’s kit.The PCR amplification experiment was carried out using the PrimeScript RT Master Mix kit (kit and required reagents were from Takara Bio,Japan).The PCR reaction system was as follows:cDNA 1 μL,upstream and downstream primers 0.4 μL,2× TransTaq®Tip Green qPCR SuperMix 10 μL,Passive Reference Dye (50×) 0.4 μL,and ddH2O added to 20 μL.PCR conditions were as follows:Pre-denaturation at 95°C for 30 s,denaturation at 95°C for 5 s,annealing at 60°C for 30 s,with a total of 40 cycles.Each sample was prepared in triplicate wells,and the experiment was carried out 3 times.GAPDH was used as an internal reference and the 2-ctmethod was used for data analysis.The primer sequence was designed and synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd ( Table 1).
Outcome measures
Main outcome measures:Clinical efficacy:Based on the criteria for judging the efficacy of WTO tumor,we set CR as follows:The tumor focus completely disappeared and lasted for more than 4 wk; PR:The tumor focus was reduced by more than 50% and maintained for more than 4 wk,and no new lesions occurred; NC:The tumor volume was reduced by < 50%,increased by < 20% and maintained for more than 4 wk,and no new lesions were found; PD:The tumor focus increased by more than 20% and a new lesion appeared.Calculated cure rate = (CR + PR)/total number × 100%.Adverse reactions occurring in patients from the beginning of treatment to full recovery and discharge were compared,and their incidence rates were calculated.Recurrence within 6 mo after treatment was recorded and the recurrence rate was calculated.The patients were followed up for 3 years,and the prognosis and survival in both groups were recorded.
Secondary outcome measures:Secondary outcome measures were as follows:The expression levels of GDF11 and PD-1 at T0,T1,T2 and T3 in both groups; the predictive value of GDF11 and PD-1 for treatment efficacy; the predictive value of GDF11 and PD-1 for recurrence after treatment.
Statistical analysis
The results of this experiment were analyzed by SPSS24.0 statistical software(Shanghai Yuchuang Network Technology Co.,Ltd) and all graphical results were drawn by Graphpad8 (Shenzhen Qiruitian Software Technology Co.,Ltd).The counting data were expressed by (rate),and chi-square test was used for comparison between groups.The measurement data were expressed as (mean ± SD),and comparisons between groups were performed using thettest.Repeated measures analysis of variance and Bonferroni back testing were used for comparison among multiple time points.ROC curve was used to analyze the predicted value,the survival rate was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method,and the survival rate was compared by Log-rank test.APvalue less than 0.050 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Comparison of general data
The age,body mass index,disease course,gender,smoking,drinking,preference for betel nut,dietary preference,exercise habits,tissue type,pathological staging,metastasis,degree of differentiation,nationality and living environment of patients in the two groups were compared,and no differences were found (Table 2)
Comparison of efficacy
The cure rate in the RG was 76.40% and was higher than that in the CG which was 61.05% (P= 0.025) (Table 3).
Comparison of adverse reactions
The incidence of adverse reactions in the RG was 23.60% compared with 24.21% in the CG.The difference was not statistically significant (Table 4).
Prognosis
Recurrence rate in the RG within 6 mo after treatment was 13.48% (12/89),lower than that in the CG at 6 mo after treatment (27.37%) (26/95) (P< 0.05).176 patients were successfully followed up,with a follow-up success rate of 95.65%.Three cases were lost to follow up in the RG and 5 cases were lost to follow up in the CG.There was no difference in the 3-year survival between the two groups (Table 5 and Figure 1).
Changes in GDF11 and PD-1 during treatment
There were no differences in GDF11 and PD-1 between the two groups at T0 and T1,while GDF11 and PD-1 in the RG were lower than those in the CG at T2 and T3 (P<0.05).GDF11 and PD-1 in both groups decreased from T1 to T3 (P< 0.05) (Figure 2).
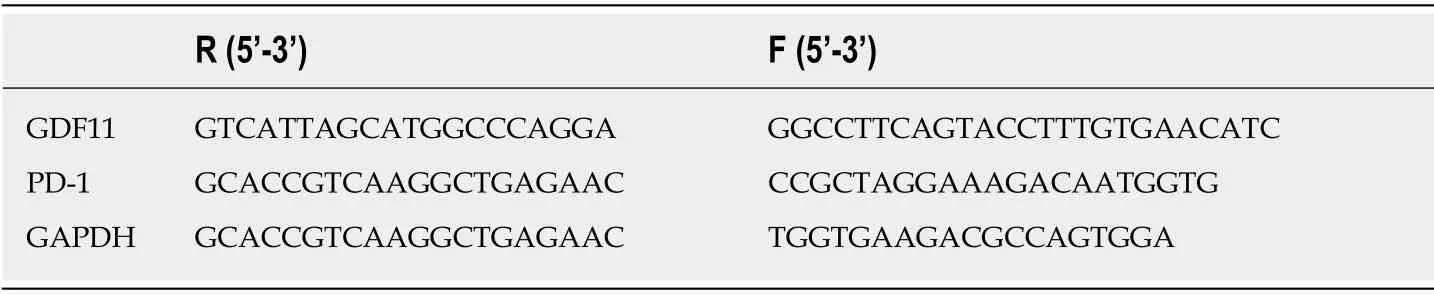
Table 1 Primer sequence
Predictive value of GDF11 and PD-1 for efficacy
Patients with CR and PR were included in group A and patients with NC and PD were included in group B.GDF11 and PD-1 detection at T2 were selected as predictive indices of efficacy for ROC curve analysis,and this showed that GDF11 and PD-1 in group A were lower than those in group B (P< 0.05).When the cut-off value was 2.605,GDF11 had a predictive sensitivity of 63.79% and specificity of 69.92%.When the cut-off value was 1.565,PD-1 had a predictive sensitivity of 53.45% and specificity of 83.74%.Using GDF11 and PD-1 as two independent variables to carry out binary Logistic regression analysis,a joint prediction model log (P) = -4.425 + 0.921 × GDF11+ 0.910 × PD-1 was obtained.When the cut-off value was 0.314,the sensitivity and specificity of the model for predicting efficacy were 96.55% and 67.48%,respectively(Figure 3 and Table 6).
Predictive value of GDF11 and PD-1 for recurrence
Patients without recurrence after treatment were included in group C and those with recurrence were included in group D.GDF11 and PD-1 at T3 were selected as predictive indices of recurrence after treatment for ROC curve analysis,which showed that GDF11 and PD-1 in group C were significantly lower than those in group D (P< 0.05).When the cut-off value was 1.655,GDF11 had a predictive sensitivity of 92.46% and specificity of 46.48%.When the cut-off value was 1.125,PD-1 had a predictive sensitivity of 61.54% and specificity of 77.46%.Using GDF11 and PD-1 as two independent variables for binary Logistic regression analysis,a joint prediction model log (P) = -4.462 + 3.034 × GDF11 + -3.380 × PD-1 was obtained.When the cutoff value was 0.310,the predictive sensitivity of the model for recurrence was 82.05%and its specificity was 88.73% (Figure 4 and Table 7).
DISCUSSION
At present,OC is a very common systemic malignant tumor,and its morbidity is increasing worldwide[14].Due to the increasingly serious clinical challenges brought by OC,researchers urgently require an effective method that can not only effectively treat OC,but also has low side effects and does not affect the prognosis of patients[15].Although the space in the oral and maxillofacial region is narrow,it involves many important functional organs.When a tumor occurs in this region,it poses a great threat to humans[16].Implantation of radioactive seeds into tissues is a type of brachytherapy.A microparticle source is implanted into tumors and continuously emits low-energy radiation into the affected tissues; thus,destroying and damaging tumors[17].At present,the application of radioactive seeds is very common in the treatment of head and neck tumors[18,19],but there is little research on their application in OC.However,by determining the effect of125I radioactive seed implantation on OC,this article is of great significance for clinical practice.
The results of this study showed that clinical efficacy in patients in the RG implanted with125I radioactive seeds was better than that in the CG who underwent traditional surgery.These findings suggest that the efficacy of125I radioactive seed implantation on OC was better than that of traditional surgery,which is consistent with the studies of Yueet al[20]on the efficacy of125I radioactive seed implantation in OC rats.The advantage of125I radioactive seed implantation therapy is that it is an interstitial radiotherapy,with a high local dose and long duration of action in the tumor focus,has less impact on surrounding normal tissues,and can greatly improve the local tumor control rate[21].A comparison of adverse reactions between the two groups showed that there were no significant differences between the groups.However,the adverse reactions in patients in the RG were mainly skin reactions toradiotherapy,and the effects in other systems were relatively small.These results also confirmed the practicability of125I radioactive seed implantation therapy,and were consistent with previous studies[22].The principle of125I radioactive seed implantation therapy is that the low-energy γ rays released by125I radioactive seeds can break the DNA double chains in the nucleus,destroy the original structure of tumor cells,and reduce the activity of tumor cells.Therefore,it is especially suitable for some metastatic and aggressive tumors[23].In addition,125I radioactive seeds can alsoaccelerate the damage to tumor cells by inducing the ionization of water molecules to cause DNA damage[24].Moreover,due to the limited penetration ability of125I radioactive seeds,the damage to normal tissues around the tumor is small,especially in some tumors with complicated tissue structures[25].With traditional radical resection,tumors may recur due to incomplete resection of lesions in complex areas[26].OC has a high recurrence rate.Therefore,we compared the recurrence rate in the two groups within 6 mo after treatment,and found that the recurrence rate in the RG was significantly lower than that in the CG.This also suggested that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy could effectively reduce the recurrence rate of OC,which was in line with our above analysis.However,when comparing the prognosis of patients in the two groups,we discovered that there was no difference between the groups,which indicated that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy did not significantly improve the prognosis of OC patients.It should be noted that the current application of125I radioactive seed implantation therapy for OC is not comprehensive,and improvements in dose,time,or manual operation selection are required.In addition,it is possible that the follow-up time in this study was too short.It is hoped that researchers worldwide will carry out more in-depth analyses of these factors.

Table 2 Comparison of general data in the two groups,n (%)

Table 3 Comparison of efficacy between the two groups,n (%)
In order to further determine the effect of125I radioactive seed implantation on OC,we evaluated GDF11 and PD-1 during the treatment process in both groups.The results showed that there were no differences between the two groups at T0 and T1,while GDF11 and PD-1 in the RG were lower than those in the CG at T2 and T3.GDF11 is also called bone morphogenetic protein 11 (BMP11),which belongs to the BMP/GDF subtype and can induce apoptosis of erythrocyte precursors[27].Previous studies have confirmed the abnormal expression of GDF11 in OC[28],which showed a decreasing trend with treatment time.Ungaroet al[29]pointed out that GDF11 plays the role of an oncogene in colorectal cancer,and we speculated that its role in OC is the same.However,the expression of GDF11 was significantly reduced by125I radioactive seed implantation,which also indicated the efficacy of125I radioactive seed implantation on OC.PD-1,as a new member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily,is a type I transmembrane protein,which is highly expressed in many tumors,and accelerates the development of tumors[30,31].In OC,the influence of PD-1 has been confirmed.PD-1 inhibitors can effectively prevent OC[32],and the results in this study are consistent with the principle of PD-1 inhibitors in treating OC.However,as the mechanisms of GDF11 and PD-1 in OC have not yet been determined byin vitroexperiments,this will also be a research focus in the future.By detecting the expression levels of GDF11 and PD-1,we found that they had good predictive value for clinical efficacy and recurrence rate in patients after treatment.This also suggested that the recovery and recurrence of OC patients can be predicted by detecting the levels of GDF11 and PD-1 in future clinical practice,which is significant for improving efficacy and prognosis.The abnormal expression and changing trend of GDF11 and PD-1 in OC not only indicated the efficacy of125I radioactive seed implantation,but also suggested that GDF11 and PD-1 might be therapeutic targets for OC in the future.At present,the effect of PD-1 inhibitors on OC has been confirmed,and we will conduct an in-depth analysis of GDF11 inhibitors.
The purpose of this experiment was to determine the effect of125I radioactive seed implantation on OC and its influence on GDF11 and PD-1.Due to the limited experimental conditions,there are still some limitations.For example,in this study,patients in the CG were treated by conventional tumor surgery,and it is still impossible to determine the difference between125I radioactive seed implantation and conventional radiotherapy on OC.Moreover,the mechanism of GDF11 and PD-1affecting OC is not completely clear,and requires further investigation.However,due to the short experimental period,we were unable to determine the long-term prognosis of patients in the two groups.In addition,in the follow-up survey of prognosis,we did not compare the quality of life of patients in the two groups.We intend to carry out a more complete and comprehensive analysis of the above limitations as soon as possible to obtain the best experimental results.
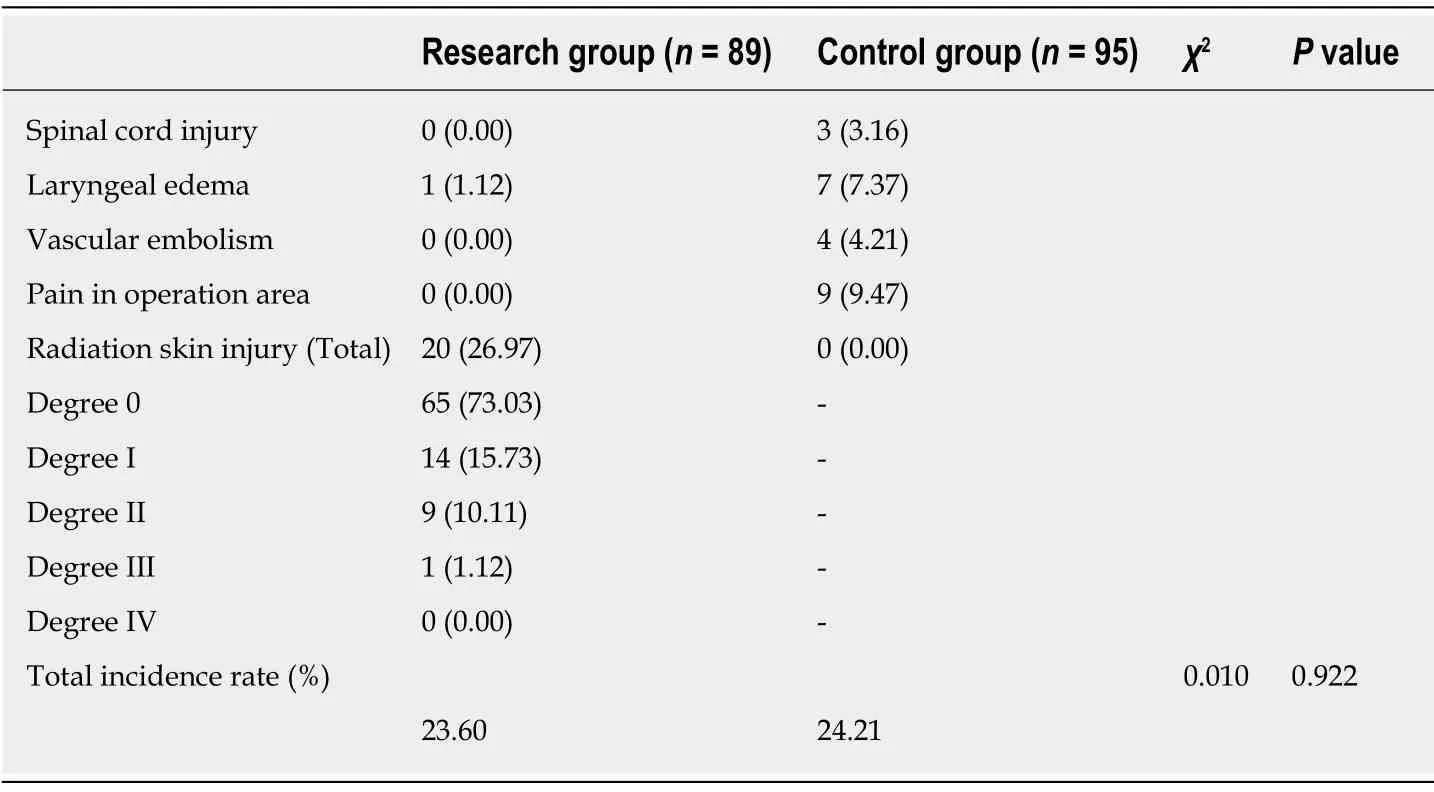
Table 4 Comparison of adverse reactions between the two groups,n (%)
In summary,125I radioactive seed implantation therapy showed clinical efficacy in OC patients,reduced the recurrence rate,and has significant potential in clinical application.The detection of GDF11 and PD-1 during the treatment of OC patients has good predictive value for efficacy and recurrence,and GDF11 and PD-1 may be potential targets for OC treatment in the future.

Table 5 Comparison of recurrence between the two groups,n (%)
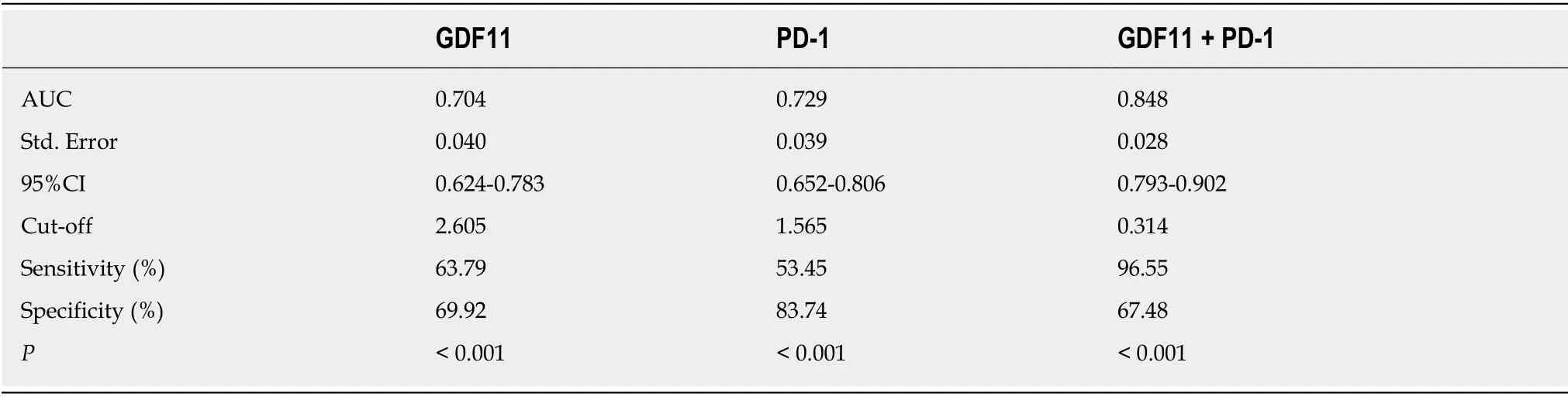
Table 6 Predictive value of growth differentiation factor 11 and programmed death receptor-1 for efficacy

Table 7 Predictive value of growth differentiation factor 11 and programmed death receptor-1 for recurrence after treatment
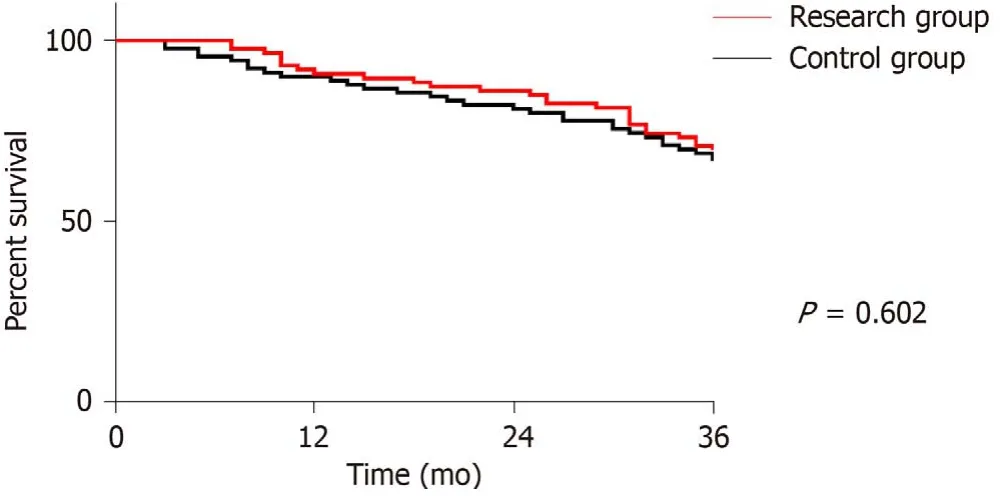
Figure 1 Three year survival curve of the two groups.
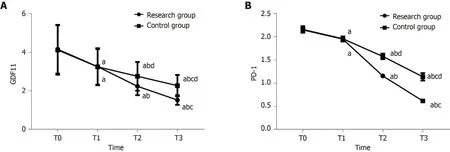
Figure 2 Changes in growth differentiation factor 11 and programmed death receptor-1 during treatment.
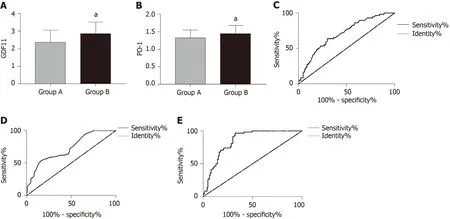
Figure 3 Predictive value of growth differentiation factor 11 and programmed death receptor-1 for efficacy.
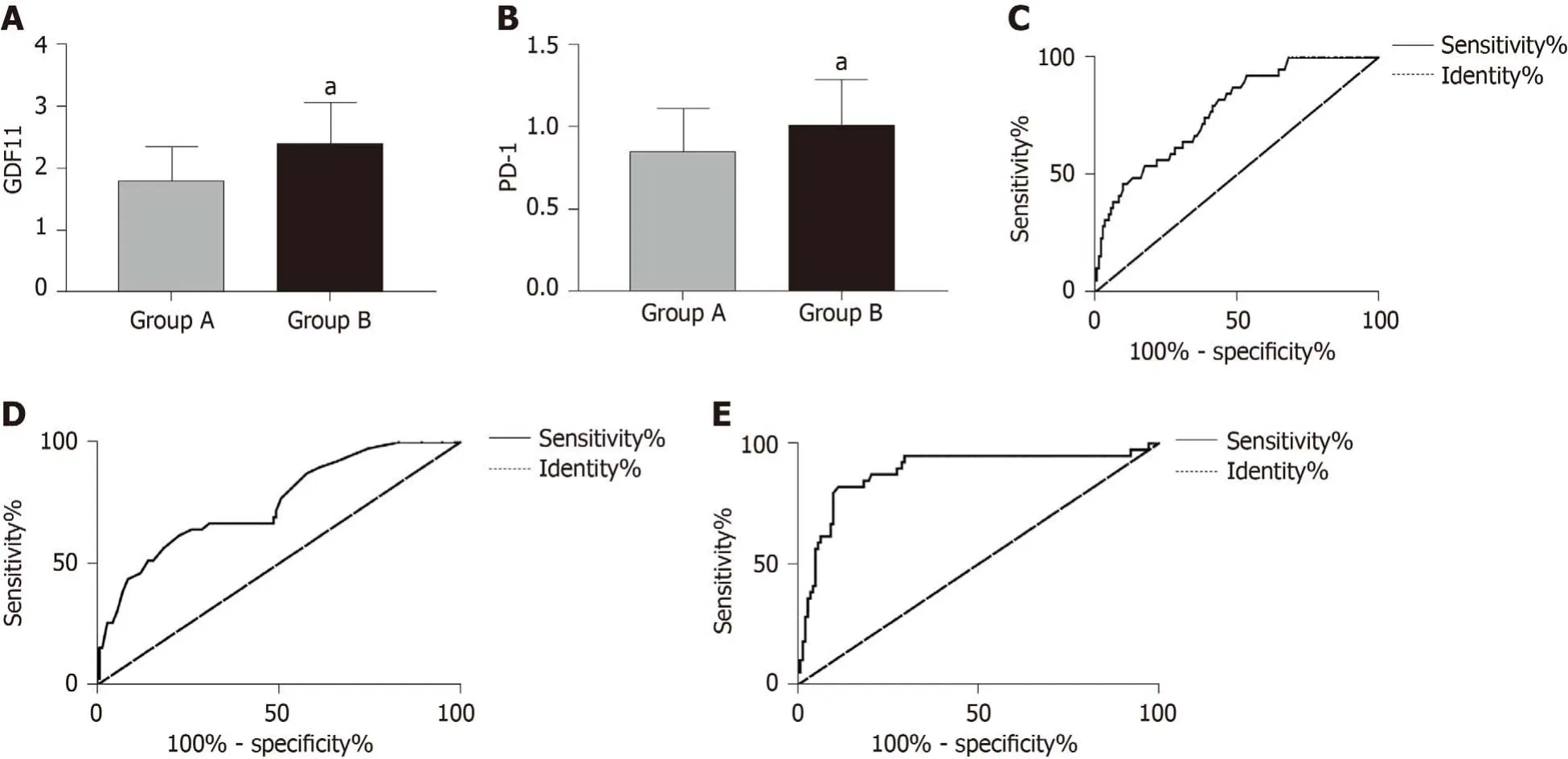
Figure 4 Predictive value of growth differentiation factor 11 and programmed death receptor-1 for recurrence.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Oral cancer (OC) is the most common malignant tumor in the oral cavity,and is mainly seen in middle-aged and elderly men.Its morbidity is still among the highest of all systemic malignant tumors.In recent years,morbidity due to OC has increased year by year.At present,OC is mainly treated clinically by surgery or combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy; but recently,more and more studies have shown that the stress trauma caused by surgery and the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy seriously affect the prognosis of patients.The disadvantages of OC treatment have gradually been exposed,and it is essential to identify an OC treatment with low side effects and marked efficacy.
Research motivation
125I radioactive seed implantation therapy is a type of brachytherapy,which means that under the guidance of imaging equipment,125I radioactive seeds are directly implanted into tumor tissue through percutaneous punctures to irradiate the tumor.
Research objectives
It has been proved that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy has a significant effect on head and neck neoplasms,and relevant research has proved that it has some effects on OC.However,there is currently limited clinical research on125I radioactive seed implantation therapy and it is not widely used in OC.We speculate that125I radioactive seed implantation therapy is expected to be an effective treatment for OC in the future.
Research methods
A total of 184 OC patients admitted to The Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University from May 2015 to May 2017 were selected as research subjects for prospective analysis.Of these patients,89 who received125I radioactive seed implantation therapy were regarded as the research group (RG) and 95 patients who received surgical treatment were regarded as the control group (CG).The clinical efficacy,incidence of adverse reactions and changes in growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) and programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) during treatment in both groups were compared.
Research results
The efficacy and recurrence rate in the RG were better than those of the CG,but there were no differences between the two groups in terms of the incidence of adverse reactions,prognosis and survival.During treatment,GDF11 and PD-1 in the RG were lower than those in the CG.By ROC curve analysis,both GDF11 and PD-1 had predictive value for efficacy and recurrence.
Research conclusions
125I radioactive seed implantation therapy has clinical efficacy in OC patients,reduces the recurrence rate,and has significant potential in clinical application.The detection of GDF11 and PD-1 during the treatment of OC patients has good predictive value for efficacy and recurrence,and GDF11 and PD-1 may be potential targets for OC treatment in the future.
Research perspective
125I radioactive seed implantation therapy has efficacy and high safety in the treatment of OC,and it may be the first treatment choice in the future.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年6期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年6期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Late-onset multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency with cardiac syncope:A case report
- Misdiagnosis of primary intimal sarcoma of the pulmonary artery as chronic pulmonary embolism:A case report
- Anomalous retinal artery associated with branch retinal artery occlusion and neovascular glaucoma:A case report
- Two bone blocks sandwich technique for horizontal reconstruction of severely atrophic alveolar ridge in anterior maxilla:A case report
- Muscular involvement of extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as polymyositis:A case report and review of literature
- Total endovascular repair of an intraoperative stent-graft deployed in the false lumen of Stanford type A aortic dissection:A case report
