郑州农村汉族男性27个Y-STR遗传多态性及多民族间遗传距离的比较
谢晨 郭仲谦 张广政 王磊 曾昭书 刘开会

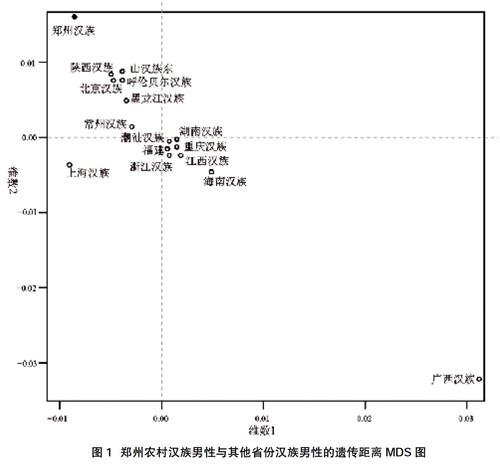
摘要:目的 比较郑州农村汉族男性27个Y-STR遗传多态性及多民族间的遗传距离。方法 采用Yfiler Plus试剂盒对27个Y-STR基因座进行扩增,3500 xL遗传分析仪进行基因分型,统计27个Y-STR基因座的等位基因频率及基因差异度等遗传学参数。以YHRD网站的分子方差分析(AMOVA)程序分析不同省份汉族及不同少数民族男性人群的遗传距离,以该网站的多维尺度分析(MDS)程序绘制MDS图。结果 郑州农村汉族男性中共540个不同的单倍型,27个Y-STR基因座所组成的HD值为0.999974。基因型数据分析显示,27個Y-STR中DYS385b、DYS449、DYS518和DYS627表现出高基因差异度(GD>0.85),而DYS391和DYS438表现出低基因差异度(GD<0.5)。在与其他省份汉族男性的遗传距离比较,郑州农村汉族男性与陕西汉族男性遗传距离最近(Rst=0.0028),与广西汉族遗传距离最远(Rst=0.0891);在与其他省份少数民族男性的遗传距离比较,郑州农村汉族男性与陕西回族男性的遗传距离最近(Rst=0.01526),与四川藏族的遗传距离最远(Rst=0.2873)。结论 Yfiler Plus的27个Y-STR基因座在郑州农村汉族男性中具有良好的多态性,可用于区分郑州农村汉族无关男性个体。由于农村地区一般为多代世居于此,故本结果可视为郑州本地男性代表性数据,可为本地区的法医学应用提供基础数据。
关键词:法医物证学;遗传距离;Y-STR基因座;单体型;遗传多态性;郑州;汉族;男性
中图分类号:D919 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.03.022
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)03-0074-05
Comparison of 27 Y-STR Genetic Polymorphisms and Genetic Distance Among Ethnic Groups
in Rural Han Males in Zhengzhou
XIE Chen1,2,GUO Zhong-qian1,3,ZHANG Guang-zheng1,WANG Lei2,ZENG Zhao-shu1,LIU Kai-hui4
(1.Department of Forensic Medicine,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000,Henan,China;
2.Institute of Criminal Science and Technology,Criminal Investigation Bureau,Zhengzhou Public Security Bureau,
Zhengzhou 450000,Henan,China;
3.Forensic Expertise Center of the Third People's Hospital of Henan Province,Zhengzhou 450000,Henan,China;
4.Material Evidence Identification Center of the Ministry of Public Security,Beijing 100038,China)
Abstract:Objective To compare 27 Y-STR genetic polymorphisms and genetic distances among ethnic groups in rural Han males in Zhengzhou. Methods The Yfiler Plus kit was used to amplify 27 Y-STR loci, the 3500 xL genetic analyzer was used for genotyping, and the genetic parameters such as allele frequency and gene difference were counted for 27 Y-STR loci. The molecular distance analysis (AMOVA) program of the YHRD website was used to analyze the genetic distance of the Han and different minority male populations in different provinces, and the MDS map was drawn using the website's multidimensional scale analysis (MDS) program.Results There were 540 different haplotypes in rural Han males in Zhengzhou, and the HD value composed of 27 Y-STR loci was 0.999974. Analysis of genotype data showed that among 27 Y-STR, DYS385b, DYS449, DYS518, and DYS627 showed high genetic differences (GD>0.85), while DYS391 and DYS438 showed low genetic differences (GD<0.5). In comparison with the genetic distance of Han males in other provinces, the rural Han males in Zhengzhou have the closest genetic distance to the Han males in Shaanxi (Rst=0.0028), and the genetic distance to the Han population in Guangxi is the furthest (Rst=0.0891). For distance comparison, the genetic distance between Han males in rural Zhengzhou and Hui males in Shaanxi is the closest (Rst=0.01526), and the genetic distance between Sichuan males and Sichuan Tibetans is the longest (Rst=0.2873).Conclusion The 27 Y-STR loci of Yfiler Plus have good polymorphism in Han males in rural Zhengzhou, which can be used to distinguish unrelated male individuals in rural Zhengzhou Han. Since the rural areas are usually here for many generations, this result can be regarded as the representative data of local males in Zhengzhou, which can provide basic data for forensic applications in this area.
Key words:Forensic physical evidence;Genetic distance;Y-STR locus;Haplotype;Genetic polymorphism;Zhengzhou;Han;Male
Y染色体为男性所特有,呈父系遗传,不与其他染色体重组,在法医学检验中作用独特[1]。河南位于我国中东部,郑州作为河南的省会,近年来随着经济社会发展加速、人员流动性增加、流入及流出人口均占较大比例,因此在郑州市城区范围内取样进行STR位点的遗传多态性调查时,已经难以保证所取样品均为郑州地区人口。基于此,在男性家族系统建设过程中走村入户的有利形势下,本研究深入到郑州郊县的农村地区,对世代居住在此的老年男性和部分中青年男性进行血样采集,并进行27个Y-STR的遗传多态性研究,以期获得最能代表郑州本地人口的Y-STR分型结果,为法医学应用提供基础数据,同时为汉族人群的起源与迁徙等研究提供27个Y-STR群体数据,现报道如下。
1材料与方法
1.1样本来源 收集2018年5月~12月现居住在郑州市农村且超过三代以上,民族皆为汉族的542名健康男性,年龄15~55岁,均充分了解采血的实验目的、自愿接受采血,并同意将基因信息作于研究使用,排除存在认知障碍者。血样经EDTA抗凝后保存于实验室-80℃冰箱内备用。
1.2 DNA提取 采用QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit(德国QIAGEN公司)试剂盒进行DNA提取,按照说明书进行。NanoDrop 2000c(美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)进行DNA定量。
1.3 PCR扩增及扩增产物分型 参照Yfiler Plus试剂盒(Thermo Fisher Scientific)说明书,应用ABI 9700热循环仪(美国AB公司)进行复合扩增,扩增产物用ABI 3500 xL遗传分析仪(美国AB公司)进行检测,以GeneMapper ID-X软件对数据结果进行STR分型。
1.4统计学分析 通过直接计数计算等位基因和单倍型频率,将两个多拷贝基因座DYS385a/b和DYF387S1a/b视为等位基因组合。根据Nei M等[2]的公式计算基因差异度(GD)和单倍型差异度(HD),GD(或HD)=n1-■P■■/(n-1),其中n是观察到的等位基因或单倍型的总数,Pi表示第i个等位基因(或单倍型)的频率。通过YHRD网站[3]的分子方差分析(AMOVA)软件估计Rst的成对遗传距离和不同群体之间的数值,并使用YHRD网站的多维尺度分析(MDS)工具绘制MDS图。
2结果
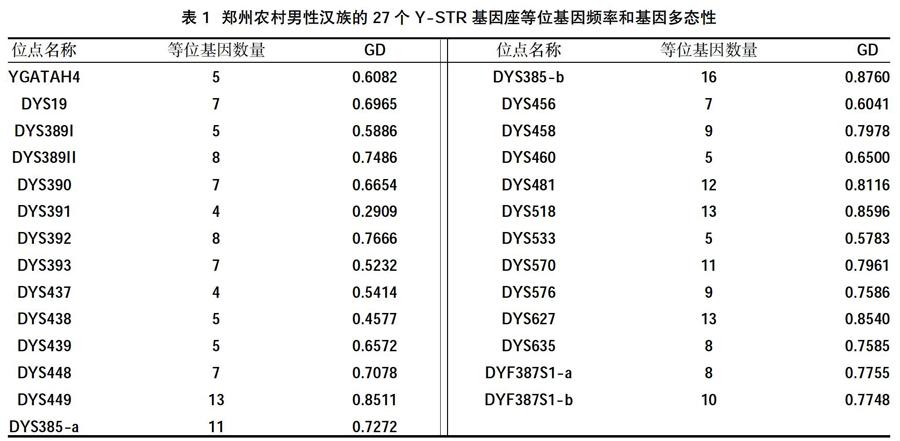
2.1郑州农村男性汉族的27个Y-STR基因座等位基因频率和基因多态性 在郑州农村汉族男性中共观察到540个不同的单倍型,27个Y-STR基因座所组成的HD值为0.999974。单个基因座的等位基因数为DYS437的4个~DYS385b的16个。在DYS385a/b中检测到59个等位基因组合,其中DYS385a有11个不同的等位基因,DYS385b有16个不同的等位基因。在DYF387S1a/b中检测到39个不同等位基因组合,其中DYF387S1a有8个不同的等位基因,DYF387S1b有10个不同的等位基因。此外,在河南汉族中检测到多个中间等位基因:DYS385a/b(12.1)、DYS485(14.1)、DYS19(14.3)、DYS627(17.2,18.2)、DYS458(14.1)、DYS448(19.2)、DYS449(29.2)、DYS518(33.2,37.2)、DYF387S1a/b(37.2)。基因型数据分析显示,27个Y-STR中DYS385b、DYS449、DYS518和DYS627表现出高基因差异度(GD>0.85),而DYS391和DYS438表现出低基因差异度(GD<0.5),见表1。
2.2郑州农村汉族男性与其他省份汉族男性的遗传距离比较 利用YHRD在线软件,手动添加其他省份汉族男性数据(包括陕西汉族[4]、山东汉族[4,5]、北京汉族[4]、呼伦贝尔汉族、黑龙江汉族、常州汉族[5,6]、潮汕汉族[7,8]、福建汉族、浙江汉族[5]、上海汉族[5,9,10]、湖南汉族[11]、重庆汉族、江西漢族、海南汉族,以及广西汉族),结果显示在所有参考群体中,郑州农村汉族男性与陕西汉族男性的遗传距离最近(Rst=0.0028),而郑州农村汉族男性与广西汉族男性的遗传距离最远(Rst=0.0891),见图1。
2.3郑州农村汉族群体与其他省份少数民族男性的遗传距离比较 利用YHRD在线软件,手动添加其他省份少数民族数据(包括甘肃回族,河南回族,青海回族,陕西回族,山东回族,四川回族,新疆回族,云南回族,宁夏回族[12-15],延边朝鲜族[16],海南临高族[17],海南黎族[18],贵州苗族[19],甘肃藏族,青海藏族,四川藏族[20],湖北土家族,新疆维吾尔族[16,21],新疆哈萨克族[22],贵州彝族,四川彝族,云南彝族[23],广西壮族[24,25]),结果显示在与少数民族男性的遗传距离方面,郑州农村汉族男性与陕西回族男性的遗传距离最近(Rst=0.01526),郑州农村汉族男性与与四川藏族男性间的遗传距离最远(Rst=0.2873),见图2。
Y-STR loci for the Han ethnic in Hunan province,China[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2017,131(1):115-117.
[12]Yao HB,Wang CC,Tao X,et al.Genetic evidence for an East Asian origin of Chinese Muslim populations Dongxiang and Hui[J].Scientific Reports,2016(6):38656.
[13]Zhao Q,Bian Y,Zhang S,et al.Population genetics study using 26 Y-chromosomal STR loci in the Hui ethnic group in China[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2017(28):e26-e27.
[14]Xie M,Song F,Li J,et al.Genetic substructure and forensic characteristics of Chinese Hui populations using 157 Y-SNPs and 27 Y-STRs[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2019(41):11-18.
[15]Zhu B,Deng Y,Zhang F,et al.Genetic analysis for Y chromosome short tandem repeat haplotypes of Chinese Han population residing in the Ningxia province of China[J].Journal of Forensic Sciences,2006,51(6):1417-1420.
[16]Ou X,Wang Y,Liu C,et al.Haplotype analysis of the polymorphic 40 Y-STR markers in Chinese populations[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2015(19):255-262.
[17]Bai R,Liu Y,Lv X,et al.Genetic polymorphisms of 17 Y chromosomal STRs in She and Manchu ethnic populations from China[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2016(22):e12-e14.
[18]He J,Guo F.Population genetics of 17 Y-STR loci in Chinese Manchu population from Liaoning province,Northeast China[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2013,7(3):e84-e85.
[19]Chen P,He G,Zou X,et al.Genetic diversities and phylogenetic analyses of three Chinese main ethnic groups in southwest China:A Y-Chromosomal STR study[J].Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):15339.
[20]Song F,Xie M,Xie B,et al.Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analysis of 29 Y-STR loci in the Tibetan population from Sichuan Province,Southwest China[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2019:1-4.
[21]Bian Y,Zhang S,Zhou W,et al.Analysis of genetic admixture in Uyghur using the 26 Y-STR loci system[J].Scientific Reports,2016(6):19998.
[22]Shan W,Ablimit A,Zhou W,et al.Genetic polymorphism of 17 Y chromosomal STRs in Kazakh and Uighur populations from Xinjiang,China[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2014,128(5):743-744.
[23]He GL,Chen PY,Zou X,et al.Genetic polymorphism investigation of the Chinese Yi minority using PowerPlex? Y23 STR amplification system[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2017,131(3):663-666.
[24]Luo H,Song F,Zhang L,et al.Genetic polymorphism of 23 Y-STR loci in the Zhuang minority population in Guangxi of China[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2015,129(4):737-738.
[25]Guo F,Li J,Chen K,et al.Population genetic data for 27 Y-STR loci in the Zhuang ethnic minority from Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in the south of China[J].Forensic Science International:Genetics,2017(27):182-183.
[26]Fu X,Fu Y,Liu Y,et al.Genetic polymorphisms of 26 Y-STR loci in the Mongolian minority from Horqin district,China[J].International Journal of Legal Medicine,2016,130(4):941-946.
[27]Xu H,Wang CC,Shrestha R,et al.Inferring population structure and demographic history using Y-STR data from worldwide populations[J].Molecular Genetics and Genomics,2015,290(1):141-150.
[28]劉亚举,张俊涛,史绍杏,等.河南汉族人群27个Y-STR基因座遗传多态性[J].刑事技术,2014,39(4):18-20.
[29]杜若甫,肖春杰,Cavalli-Sforza LL.用38个基因座的基因频率计算中国人群间遗传距离[J].中国科学C辑,1998,25(1):83-89.
[30]王文菲,吕自力,张勇,等.新疆哈萨克族15个常染色体STR位点检测及40个中国人群遗传关系[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2017,15(3):8-9.
[31]宋土生,黄辰,司履生,等.应用网络STR生物信息对中国14个人群遗传距离的研究[J].西安交通大学学报,2003,24(1):1-4.
[32]Chu JY,Huang W,Kuang SQ,et al.Genetic relationship of populations in China[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,1998,95(20):11763-11768.
收稿日期:2019-12-12;修回日期:2019-12-29
编辑/杜帆

