Assessment of load-sharing thoracolumbar injury: A modified scoring system
Qi-Hang Su, Yong-Chao Li, Yan Zhang, Jun Tan, Biao Cheng
Qi-Hang Su, Biao Cheng, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200072, China
Qi-Hang Su, Yong-Chao Li, Yan Zhang, Jun Tan, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200120, China
Abstract BACKGROUND Many classification systems of thoracolumbar spinal fractures have been proposed to enhance treatment protocols, but none have achieved universal adoption.AIM To develop a new patient scoring system for cases with thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score (TLICS) = 4, namely the load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score (LSTLIS).METHODS Based on thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score, this study proposes the use of the established load-sharing classification (LSC) to develop an improved classification system (LSTLIS). To prove the reliability and reproducibility of LSTLIS, a retrospective analysis for patients with thoracolumbar vertebral fractures has been conducted.RESULTS A total of 102 cases were enrolled in the study. The scoring trend of LSTLIS is roughly similar as the LSC scoring, however, the average deviation based on the former method is relatively smaller than that of the latter. Thus, the robustness of the LSTLIS scoring method is better than that of LSC. LSTLIS can further classify patients with TLICS = 4, so as to assess more accurately this particular circumstance, and the majority of LSTLIS recommendations are consistent with actual clinical decisions.CONCLUSION LSTLIS is a scoring system that combines LSC and TLICS to compensate for the lack of appropriate inclusion of anterior and middle column compression fractures with TLICS. Following preliminary clinical verification, LSTLIS has greater feasibility and reliability value, is more practical in comprehensively assessing certain clinical circumstances, and has better accuracy with clinically significant guidelines.
Key Words: Retrospective analysis; Thoracolumbar fractures; Load-sharing classification;Thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score; Scoring system; Clinical protocols
INTRODUCTION
Many classification systems of thoracolumbar spinal fractures have been proposed to facilitate communication among clinicians and to enhance treatment protocols, but none have achieved universal adoption[1]. Therefore, it is urgent to establish a unified,reliable, and reproducible classification system to guide clinical practice in thoracolumbar fractures.
The following four thoracolumbar injury classification systems have been widely used: Denis classification[2], AO classification[3], load-sharing classification (LSC)[4], and thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score (TLICS)[5]. However, the Denis classification system and AO classification systems are complicated and do not include important factors affecting fracture prognosis, such as neurological status and posterior soft tissue repair, which limits their clinical application for a wider range.The TLICS proposed by Vaccaroet al[5]in 2005 incorporates morphology (fracture pattern), the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex (PLC), and neurologic status, and its reliability and practicability have been fully validated[6]. The proposed TLICS provides an important guide for the clinical treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Although previous literature[7-9]demonstrate that the spine is still relatively stable after the anterior and middle column fractures, the TLICS classification and assignment of the anterior and middle column compression fracture scores is limited for the following four reasons: (1) TLICS does not include the degree of vertebral compression and comminution and occupation of the spinal canal by the fractures into the assessment; (2) Many patients with severe vertebral bursts (but TLICS ≤ 4)experience conservative treatment failure[10], and patients with LSC ≥ 7 may have more severe outcomes in terms of kyphosis, pain, and malfunction, which have a crucial impact on their prognosis; (3) Vertebral body rupture may involve tremendous risk for more severe fractures to the posterior vertebra, with the possibility of further inducement and/or aggravation of nerve damage; and (4) Patients with TLICS = 4 can choose conservative treatment or surgery, since no objective criteria are available, and subjective selectivity is ambiguous.
Therefore, this study proposes the use of the LSC established by McCormacket al[4]to develop an improved classification system. Based on TLICS, the fracture morphology score is increased,and the degree of vertebral compression,the degree of vertebral fracture separation, and the kyphosis angle are added to improve the comprehensiveness of the assessment and address the limitation of TLICS, which is not enough attention given to the front and middle columns of the spine. Based on prior literature, clinical experience, expert consultations, and retrospective analysis,the present study has developed a new patient scoring system for cases with TLICS =4, namely the load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score (LSTLIS) (Table 1 and Figure 1).Through clinical retrospective analysis and verification for the feasibility, reliability,and reproducibility of LSTLIS, we have hypothesized that the scoring system provides a more comprehensive assessment for thoracolumbar fractures and recommendations for most difficult cases with TLICS = 4, thereby offering more accurate and comprehensive guidelines for clinical decision making and improving patients’outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
LSTLIS interpretation
The compression score of the TLICS Morphology (Fracture Pattern) has been added to the three sub-items (Comminution/Involvement, Apposition of Fragments, and Deformity Correction), and the remaining items remain unchanged (Figure 1). For the Comminution/Involvement project score from sagittal reconstruction images through computed tomography (CT), when the damaged area is less than or equal to one-third of the vertebral body, it is rated as 0.5 point; when the area is greater than one-third or less than or equal to two-thirds, it is rated as 1 point; and when it is greater than twothirds of the vertebral body, it is rated as 1.5. For the apposition/displacement of fracture fragments detected from CT coronal section, we first draw two vertical lines along the medial line of the pedicle, and then two flat lines that divide the vertebral body into three equal parts are added to the vertebral body, which has been divided into nine regions[11]. When the fracture displacement is < 2 mm and the fracture involvement is less than or equal to six regions, the score is 0.5. When the fracture is displaced by at least 2 mm, the cumulative fracture is less than or equal to four regions; the displacement is < 2 mm and the affected region occupies more than six areas, the score is 1 point; when the fracture is displaced by at least 2 mm and the fracture involvement area ranges between five and nine regions, this is rated as 1.5.Regarding correction of kyphotic deformity, 0.5 point is assigned for 3° or less correction, 1 point is assigned for 4°-9° of correction, and 1.5 is assigned for 10° or more correction. Finally, for cases with LSTLIS ≤ 4, non-surgical and conservative treatment should be taken; while for cases with LSTLIS > 4, surgical treatment is advisable.
Subjects
Utilizing the pictures archived from communication system database, a retrospective analysis for the spine radiographs of patients with thoracolumbar vertebral fractures(T11-L2) from January 2007 to August 2019 has been conducted based on CT, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and medical history data. Inclusion criteria were as follows:(1) Single-segment thoracolumbar vertebral fracture (T11-L2) and TLICS = 4; (2) Age ranging between 18-60 years; and (3) Non-osteoporotic, non-pathological vertebral fractures. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) A history of spinal surgery; (2)Congenital spinal deformity, spinal tuberculosis, spinal tumor, and ankylosing spondylitis; and (3) Incomplete data collection for X-ray plain, CT, and MRI. The first author of the article, an experienced spine surgeon, a senior spine surgeon, and a spine specialist were involved in assessments of these enrolled cases through LSC, TLICS,and LSTLIS. After consultations with several spinal specialists, the LSTLIS scoring system has been analyzed, adjusted, and refined.
Statistical analysis
Chi-square test was employed to analyze the correlation between actual surgical or non-surgical treatment groups and LSTLIS-recommended surgical or non-surgical treatment groups (matching group, MG: LSTLIS recommended surgery and actual surgery; non-matching group, NMG: LSTLIS recommended surgery which have not undergone surgery, LSTLIS recommended non-surgical but surgery has been conducted), and the prognosis was the same (testing level α = 0.05). A good prognosiswas defined as an improvement in Oswestry Disability Index scoring[12], no thoracolumbar kyphosis, no secondary vertebral fractures or further aggravation of the fracture, no further neurological or spinal cord injury, and no other secondary clinical complications.
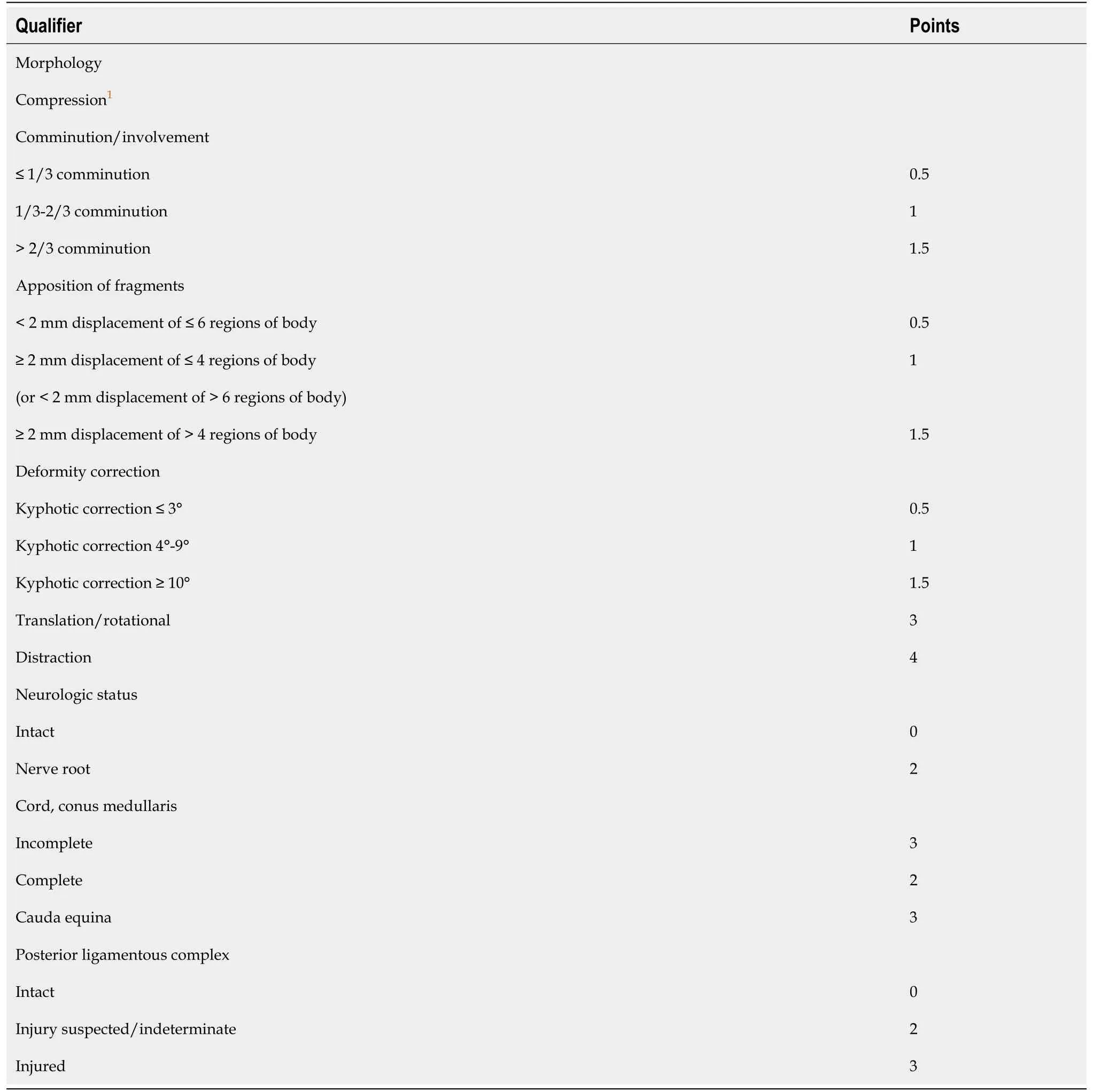
Table 1 Loading-sharing thoracolumbar injury score
RESULTS
A total of 102 cases were enrolled in the study, containing middle-aged men exclusively, with an average age of 42 years. The fracture segments that met the inclusion criteria were mostly at the level L1 and L2 segment (88/102) (Table 2). In addition, the majority of LSTLIS recommendations were consistent with the ultimate clinical treatment plan [MG = (S-S) + (NS-NS), 75/102] (Table 2). Figure 2 shows the scores of the three patients through LSC, TLICS, and LSTLIS. It should be noted that the scoring trend of LSTLIS was roughly similar to the LSC scoring, however, the average deviation based on the former method was relatively smaller than that of thelatter. Thus, the robustness of LSTLIS scoring method was better than the LSC. LSTLIS can further classify patients with the TLICS = 4, so as to assess more accurately this particular circumstance, and the majority of LSTLIS recommendations were consistent with actual clinical decisions, as shown in b and d quadrants in Figure 2. Nevertheless,no cases with TLICS = 4 and LSC > 7 were found in this study. Table 3 shows that the difference in clinical prognosis between the LSTLIS recommendation and complying/non-complying group was statistically significant (P= 0.000185). In addition, the clinical prognosis of the cases, which were in accordance with LSTLIS recommendation, were relatively better.
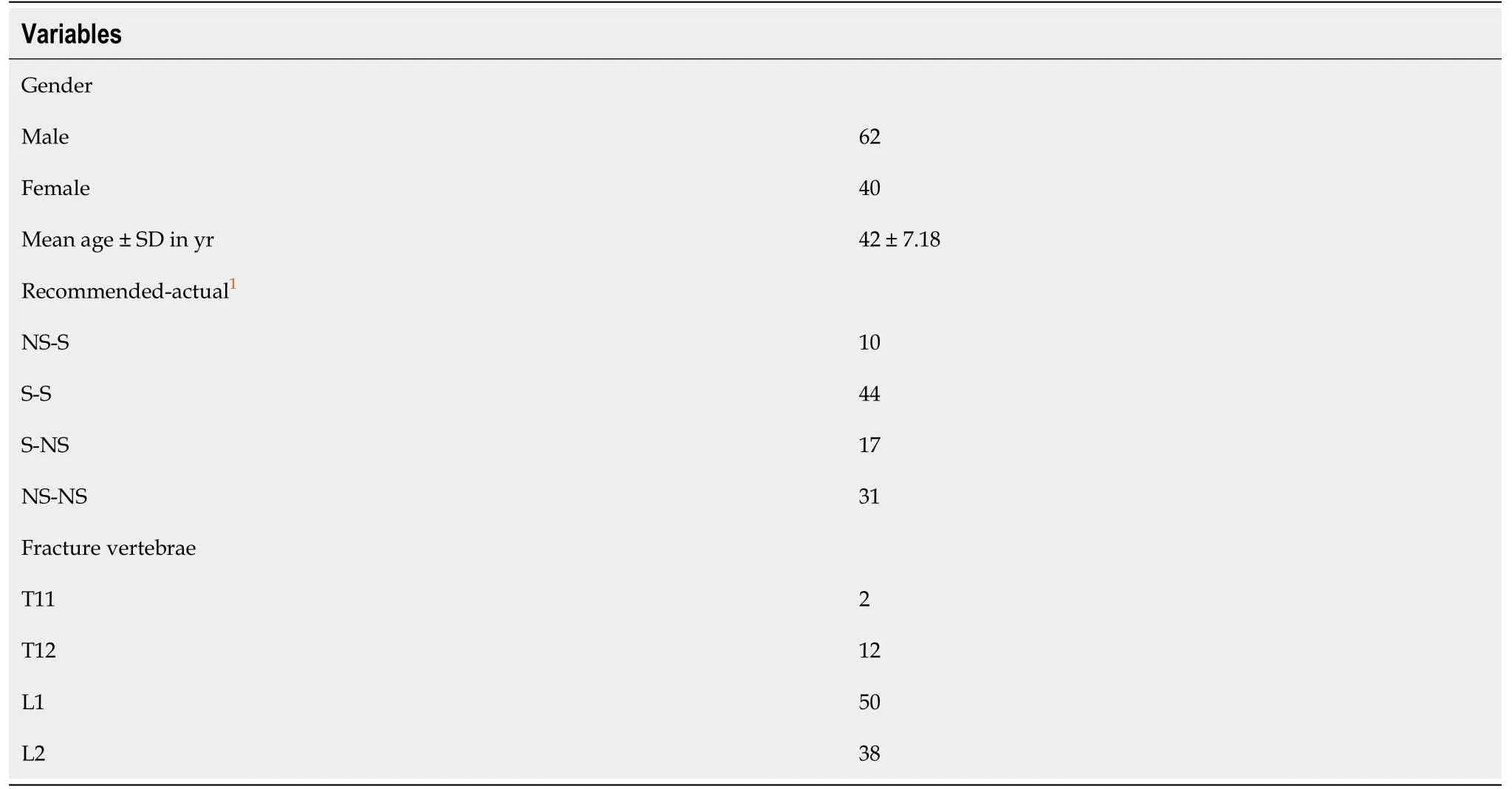
Table 2 Patient demographics, n = 102
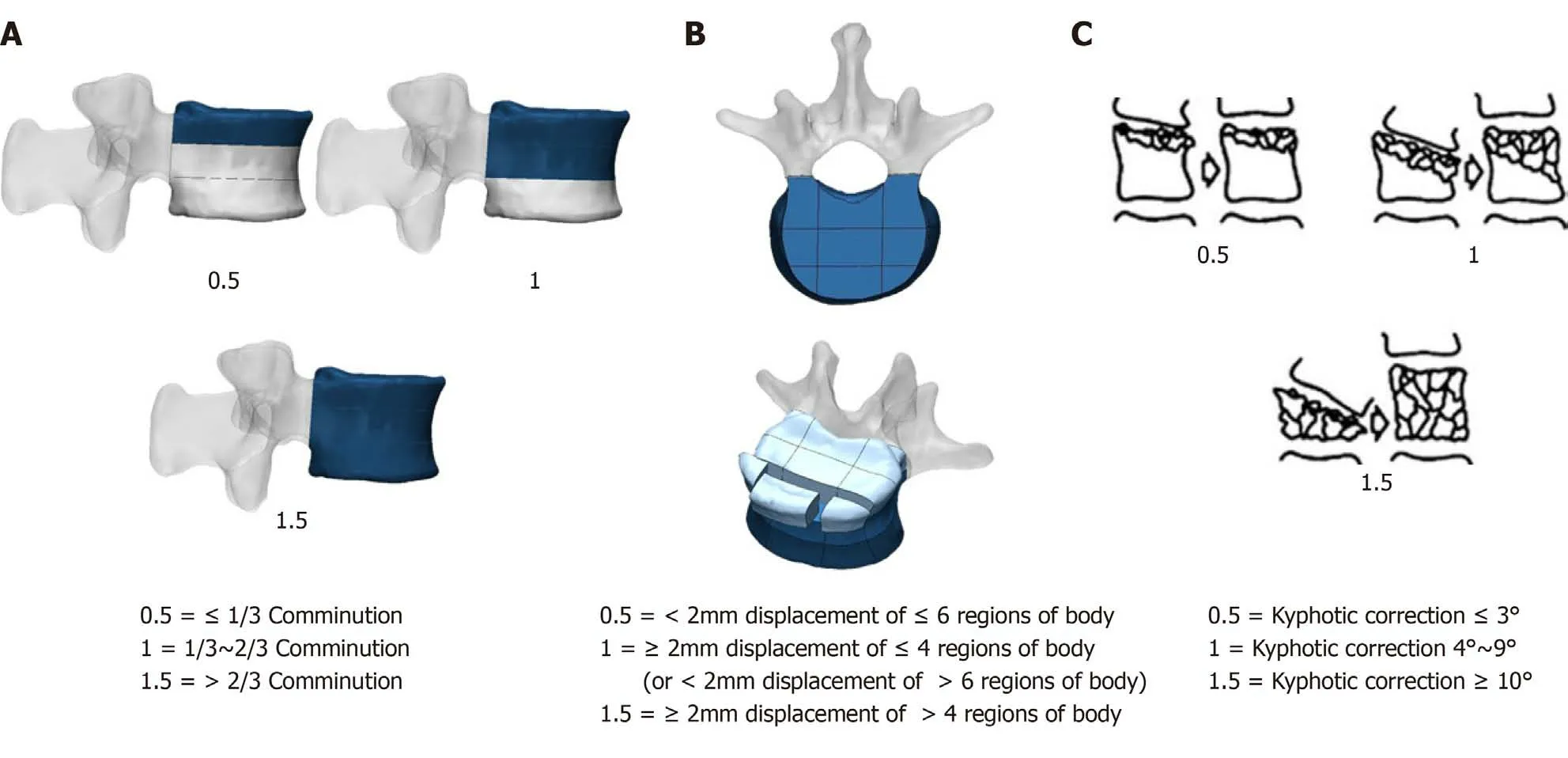
Figure 1 Scoring sub-items of the compression in load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score. A: Comminution/involvement; B: Apposition of fragments; and C: Deformity correction (from McCormack et al[4]).
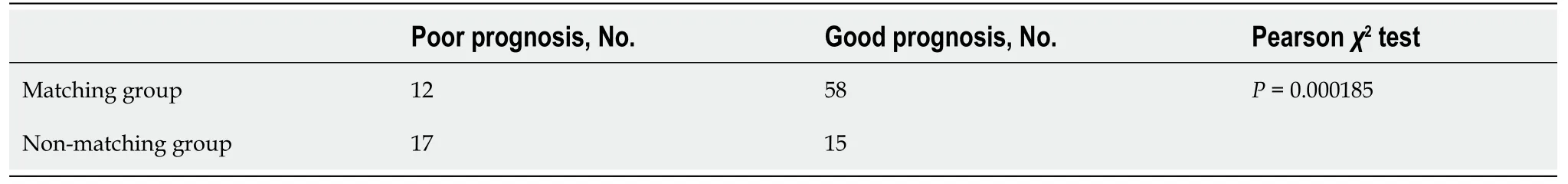
Table 3 Chi-square test for prognosis
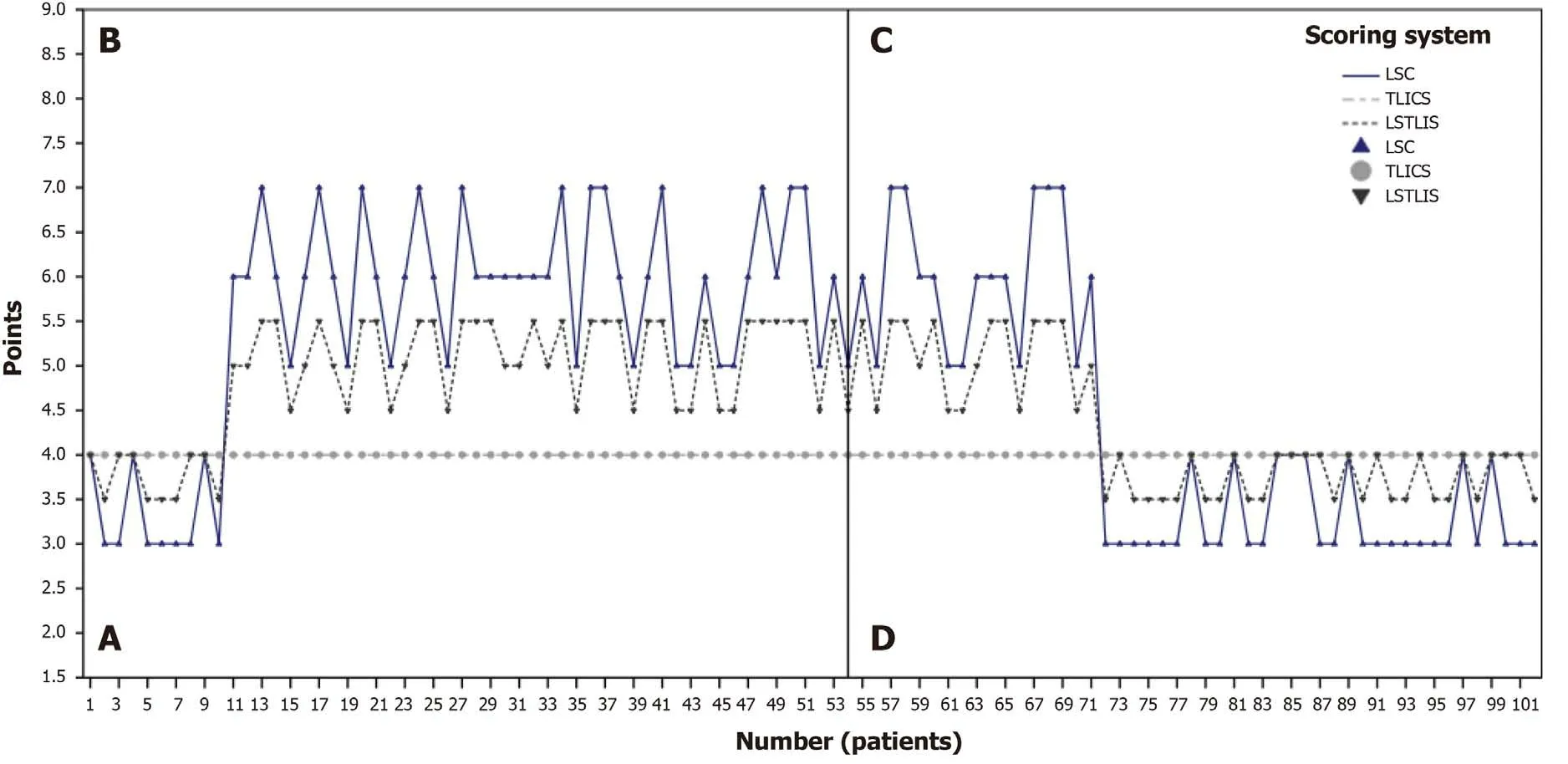
Figure 2 Score distribution analysis of 102 patients. A: This quadrant represents load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score (LSTLIS) recommended nonsurgical treatment but where surgery is performed; B: This quadrant represents LSTLIS-recommended surgery, but surgery is not performed; C: This quadrant represents LSTLIS-recommended surgery, and actual surgery is performed; D: This quadrant represents LSTLIS-recommended non-surgical treatment, and hence surgery was not performed. LSC: Load-sharing classification; TLICS: Thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score.
DISCUSSION
All the relevant scoring systems, such as TLICS and LSC, have differing advantages and disadvantages. It is a common goal for scholars to establish a more comprehensive and reliable scoring system. Therefore, many studies[13-15]have been focused on combining two or more scoring systems to guide clinical practices. The LSTLIS proposed in the present study is based on the LSC scoring concept to compensate for the failure of TLICS to address adequately the anterior and middle column compression fractures. Retrospective analysis indicates that LSTLIS is more feasible and reliable for difficult cases with a TLICS of 4 and more accurately assesses the actual clinical condition and offers accurate guidelines for clinical decision-making.
TLICS is a relatively more comprehensive scoring system proposed by Vaccaroet al[5]based on TLISS[16]. However, the scoring system is more focused on the evaluation of the total score, with less attention directed to the evaluation of each categorized item. This is incompatible with the classification, but the overall score has a greater correlation[17]. Some studies[18]observed that the anterior and middle columns of the spine are more essential in maintaining the axial mechanical stability of the spine. They account for roughly 70% to 80% of the axial compressive stress of the spine and become the major architectural factor in restoring spinal mechanics. The fracture morphology is the primary indicator before and during the evaluation. Comparatively,scoring assignments and PLC damage do not contribute to determining significant distinctions. It does not reflect the main role of the anterior and posterior column in the stability of the spine. Therefore, even if the overall score of TLICS is consistent, the surgical treatment plan for a 4-point patient, for example, could still be quite different[19]. However, the importance and the evaluation of a scoring assignment for both PLC integrity and neurologic status have been supported by many studies,including the present study[20-22].
Given the issues mentioned above, Parket al[23]increased the degree of vertebral compression and spinal canal occupancy in the fracture morphology score of TLICS in order to improve the comprehensiveness of the score. Even so, the score is still too general, and its feasibility still requires clinical studies with larger sample sizes for further validation. At the same time, Radcliffet al[24]revealed that high load-sharing scores are not necessarily related to PLC damage or neurological status.Therefore,the LSTLIS proposed in this study takes into account the LSC's systematic assessment of anterior and middle column compression fractures as well as the importance of TLICS for PLC integrity and neurologic status, which is more systematic and comprehensive than the modified TLICS proposed by Parket al[23]and has also been confirmed by related retrospective analyses.
Compared with TLICS, LSTLIS increases the weighted proportion of compression fractures, including burst fractures, and re-defines the threshold of surgery or nonsurgery category. Patients with LSTLIS ≤ 4 can achieve better clinical outcomes without non-surgical treatment. Nevertheless, patients with LSTLIS > 4 require surgery to prevent clinical complications. In the retrospective analysis, shown in Figure 2, actual clinical situations can be reflected more comprehensively in LSTLIS.By further accurately evaluating and classifying patients with previous TLICS = 4,more precise guidance can be provided for clinicians. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show two typical cases where TLICS = 4, but ultimately different clinical treatments were used.The case shown in Figure 3 has a LSTLIS of 5.5. After evaluation by three senior spine surgeons, the patient's spine stability is poor, and neurological function is impaired. If conservative treatment is employed, the patient's prognosis cannot be improved,improving neither economic nor psychological outcomes. Therefore, this patient was eventually treated with surgery, and a good long term outcome was observed. For the case displayed in Figure 4 (LSTLIS = 3.5), conservative treatment also resulted in a good clinical outcome. Therefore, LSTLIS is clinically effective and useful.
However, the current study has the following limitations: (1) The study does not include cases with TLICS = 4 and LSC > 7, since such extreme cases must be greater than 4 with LSTLIS. Given the fact that LSTLIS recommends surgical treatment, this perspective cannot be verified due to the absence of certain cases; (2) Regarding the retrospective analysis of LSTLIS, only cases with TLICS = 4 have been evaluated,because the authors conclude that the treatment plan is less unclear for cases with TLICS greater or less than 4. The results evaluated by LSTLIS are similar to TLICS, but further verification is still required; and (3) This study is a retrospective study, and hence a prospective large-scale multi-center study is required in the future as well as related investigations, potentially involving additional investigators and study sites.
CONCLUSION
LSTLIS is a scoring system that combines load-sharing classification and thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score to compensate for the lack of appropriate inclusion of anterior and middle column compression fractures with thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score. Following preliminary clinical verification, load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score has greater feasibility and reliability value, is more practical in comprehensively assessing certain clinical circumstances, and has better accuracy with clinically significant guidelines. In the future, a prospective multi-center study with a larger population will be conducted for further analysis and refinement.
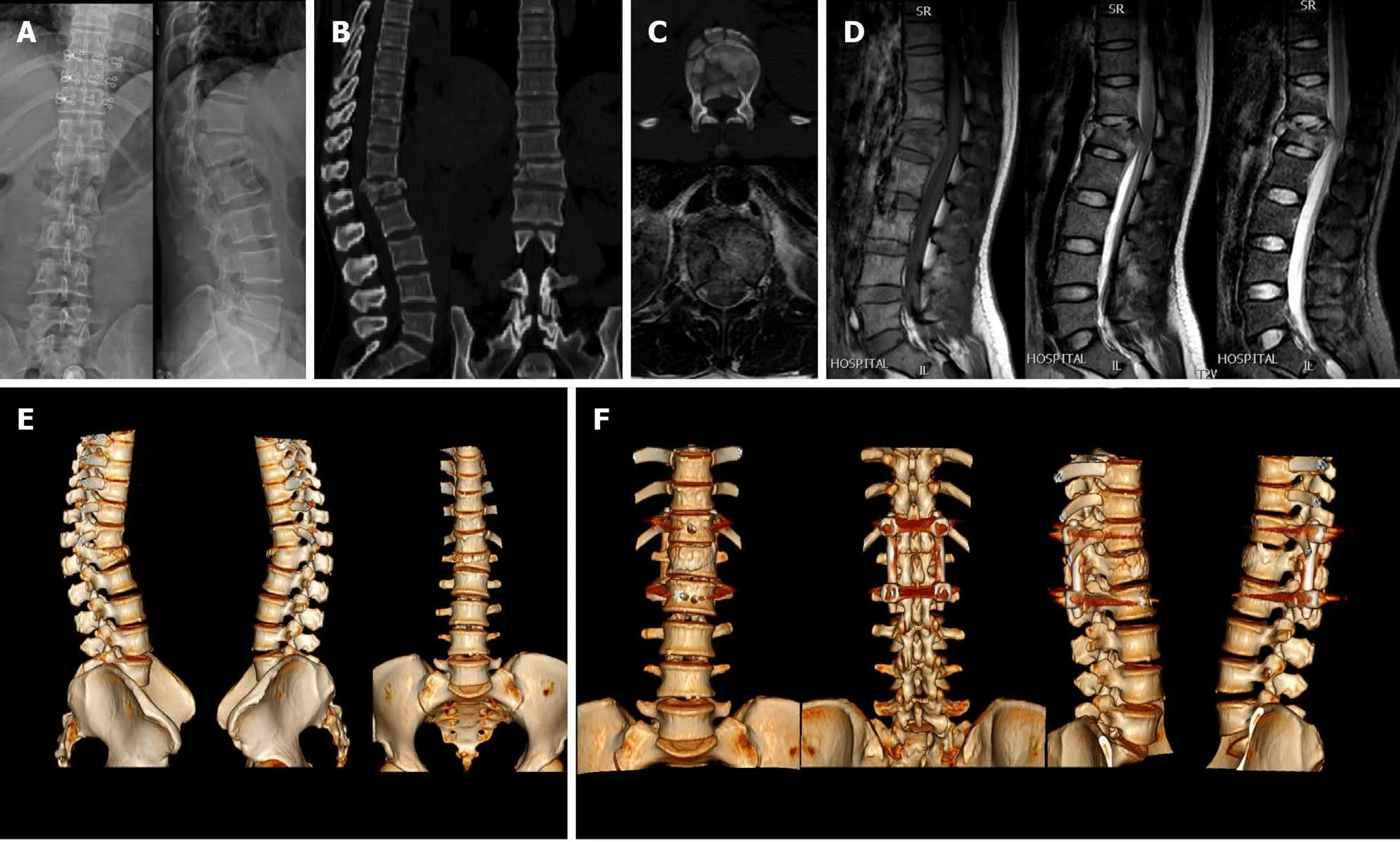
Figure 3 Two typical cases where thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score = 4, but ultimately different clinical treatments were used. A: Typical young female patient, thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score = 4, load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score = 5.5 (Compression:C/A/D = 1/1.5/1; Nerve root injury = 2), X-ray; B: Computed tomography; C: Transverse planes of computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging; D:Magnetic resonance imaging: T1WI, T2WI, STIR; E: Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lumbar spine before surgery; F: Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lumbar spine after surgery.

Figure 4 Conservative treatment also resulted in a good clinical outcome. A: Typical middle-aged female patient, thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score = 4, load-sharing thoracolumbar injury score = 3.5 (Compression: C/A/D = 0.5/0.5/0.5; posterior ligamentous complex injury suspected = 2), X-ray;B: Magnetic resonance imaging: T1WI, T2WI, T2WI-FS, Transverse plane; C: Computed tomography; D: Three-dimensional reconstruction of lumbar vertebrae.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Many classification systems of thoracolumbar spinal fractures have been proposed to facilitate communication among clinicians and to enhance treatment protocols.
Research motivation
No classification system has achieved universal adoption. Therefore, it is urgent to establish a unified, reliable, and reproducible classification system to guide clinical practice in thoracolumbar fractures.
Research objectives
The present study aimed to develop a modified patient scoring system for cases with thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score (TLICS) = 4, namely the loadsharing thoracolumbar injury score (LSTLIS).
Research methods
Based on thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score, this study proposes the use of the established load-sharing classification (LSC) to develop an improved classification system (LSTLIS). To prove the reliability and reproducibility of LSTLIS, a retrospective analysis for patients with thoracolumbar vertebral fractures (T11-L2) has been conducted.
Research results
A total of 102 cases were enrolled in the study. The scoring trend of LSTLIS is roughly similar to the LSC scoring, however, the average deviation based on the former method is relatively smaller than that of the latter. Thus, the robustness of LSTLIS scoring method is better than the LSC. LSTLIS can further classify patients with the TLICS = 4, so as to assess more accurately this particular circumstance, and the majority of LSTLIS recommendations are consistent with actual clinical decisions.
Research conclusions
LSTLIS is a reliable scoring system that combines LSC and TLICS to compensate for the lack of appropriate inclusion of anterior and middle column compression fractures with TLICS.
Research perspectives
This study is a retrospective study, and hence a prospective large-scale multi-center study is required in the future as well as related investigations, potentially involving additional investigators and study sites.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年21期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年21期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Strategies and challenges in the treatment of chronic venous leg ulcers
- Peripheral nerve tumors of the hand: Clinical features, diagnosis,and treatment
- Treatment strategies for gastric cancer during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Oncological impact of different distal ureter managements during radical nephroureterectomy for primary upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma
- Clinical characteristics and survival of patients with normal-sized ovarian carcinoma syndrome: Retrospective analysis of a single institution 10-year experiment
- Accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided needle aspiration specimens for molecular diagnosis of non-small-cell lung carcinoma
