Patterns of Eye-Infiltrating Cells between Chronic and Acute Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
Zi-Lin Chen, Hong-Yan Zhou, Wai-Po Chong, Jun Chen
State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510060, China
Keywords:Experimental autoimmune uveitis Autoimmune uveitis Eye-infiltrating cell
ABSTRACT Objective: To characterize the cellular infiltrate of eyes in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) induced in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII strains. Methods: EAU was induced by interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein with complete Freund's adjuvant in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice. Clinical scores were evaluated by funduscopy and electroretinography. Cells were isolated from inflamed eyes and analyzed by flow cytometry. Results: Different forms of EAU disease were showed with earlier disease onset, peak and higher clinical scores in acute EAU mice than chronic EAU mice [1]. In addition to increase of CD4+ T lymphocytes, percentage of CD11b+ cells were higher in the eyes of acute EAU mice than those in chronic EAU mice, while no differences were showed in CD8+ T cells, natural killer cells or natural killer T cells. Among those infiltrated CD11b+ cells, percentages of macrophages and myeloidderived suppressor cells were higher in acute EAU mice than those in chronic EAU mice. Conclusions: The different disease pattern in EAU between acute form and chronic form is associated with the increase of infiltrated CD4+ T lymphocytes, macrophages and myeloidderived suppressor cells.
1. Introduction
Autoimmune uveitis (AU) is a group of chronic and recurring autoimmune disorders which involves iritis, choroiditis, cyclitis, retinal vasculitis and uveoretinitis. The disease is harmful to visual function and common in young adults. Serious consequences such as blindness can be leaded if treatment is not timely. At present, AU has become the major disease that causes blindness in China [2,3]. The etiology and pathogenesis of AU is not yet fully understood, because eye specimens are difficult to obtain in the clinic due to ethics problems, leading to the obstacles in research of disease involved mechanisms. Therefore, experimental animal that highly mimics human AU will help solve this problem, allowing us better understand the pathogenesis of AU, so as to promote AU strategies development.
Experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU), established by Dr. Rachel Caspi [4], is a T cell-mediated animal model for AU. EAU can be induced by immunization with interphotoreceptor retinoidbinding protein (IRBP). Disease manifestation like retinitis, choroiditis, damage in photoreceptor and retinal function will be developed in EAU, which are similar to clinical manifestation of AU [5]. Therefore, EAU is considered as a classic animal model for human AU.
EAU can be established in mice with various background. C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice are the most commonly used ones [6,7]. Our group [1] and others showed that EAU induced in C57BL/6 exhibited a chronic pattern while EAU induced in B10.RIII mice showed an acute pattern, implying the distinct disease patterns of EAU models may represent different spectrum of human AU [8,9]. In this study, we compared and evaluated the disease progression and the eye-infiltrating cells in two models of EAU induced in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice to better characterize the animal models for preclinical studies.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
Thirteen C57BL/6 were purchased from Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center and six B10.RIII mice (6-8 weeks) were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory. Animals were housed in animal facility (SPF) of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center. The protocol for the animal use was reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center.
2.2 Induction of EAU
EAU was induced in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice as previously described [5], by subcutaneously injection to tail base and legs with complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA, Sigma-Aldrich) and 150 μg IRBP1-20 or 30 μg IRBP161-180 emulsion. Pertussis toxin (PTx, Sigma-Aldrich) was injected i.p. to mice on day 0, 1 post immunization (p.i.).
2.3 Funduscopy
Micron IV retinal imaging system was used for EAU scoring. Mice were treated with Proparacaine Hydrochloride eye drop for cornea anesthesia, Tropicamide Phenylephrine eye drop for mydriasis, Hypromellose eye drop for cornea moisturizing and Tobramycin eye drop for injection prevention. EAU clinical scores were evaluated in 6-13 mice (12-26 eyes) as previously described [5,10]. Small focal lesions and minimal vasculitis scored 0.5; few linear lesion, cell infiltration and mild vasculitis scored 0.1; multiple lesions, cell infiltration and severe vasculitis scored 2; pattern of linear lesion, severe cell infiltration and retinal hemorrhages scored 3; retinal detachment and retinal atrophy scored 4.
2.4 Electroretinography (ERG)
Retinal function was evaluated by dark-adapted ERG via RETIPort/Scan 21 System (Roland Consult, Germany) as described previously [11]. Before ERG examination, mice were dark adapted overnight. Experiment was conducted in red light. For the ERG assessment, eye electrodes were put on the cornea. Ground and reference electrodes were injected to the tail base and neck-back region subcutaneously. The amplitudes of a-wave and b-wave reflect the retinal function. The a-wave amplitude was assessed from the baseline to the bottom of the a-wave. The b-wave amplitude was assessed from the bottom of the a-wave to the top of the b-wave.
2.5 Flow cytometry
Eye infiltrating cells were extracted as previously described [12]. Single cell suspended in 100 μl PBS containing 10 % FBS. Single cell suspensions were then stained with BV421-conjugated anti-CD4, BV650-conjugated anti-CD8 (BD Biosciences), BV785-conjugated anti-CD3, PE-conjugated anti-NK1.1, FITC-conjugated anti-CD11c, PerCP-conjugated anti-CD11b and APC-Cy7-conjugated anti-Gr-1 (Biolegend) for 30 minutes in the dark. Cells were then analyzed by BD LSRFortessa analyzer (BD Biosciences).
2.6 Statistical analysis
All data are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by GraphPad 6.0. Statistical analysis is performed with two-tailed unpaired Mann-Whitney test. P<0.05 is considered as statistically significant.
3. Result
3.1 Characteristics of EAU in chronic and acute form
To evaluate the difference of EAU progression between chronic and acute EAU, we immunized mice in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII strains respectively with CFA/IRBP. Onset and peak of disease were showed in table 1. EAU onset day was 10.46±0.33 post immunization (p.i.) in B10.RIII mice while C57BL/6 mice onset on day 15.67±1.09, indicating EAU onset significantly earlier in B10.RIII mice than C57BL/6 mice. Similar with the onset day, we also found that B10.RIII mice reached the peak of EAU (day 14.92±0.62 p.i.) significantly earlier than C57BL/6 mice (day 24.50±2.25 p.i.).

Table 1 Characteristics of EAU in chronic and acute form
3.2 Evaluation of EAU in chronic and acute form
EAU severity were then evaluated. We found that clinical score of EAU at peak was significantly higher in B10.RIII mice (chronic EAU) than in C57BL/6 mice (acute EAU) with more cell infiltration and vasculitis (Figure 1A, C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 1.94±0.17, 3.19±0.16, P<0.0001). Retinal function of these mice was evaluated by electroretinography (ERG) via photostimulation and electric signal production. Graphs of ERG showed the normal a-wave and b-wave for naïve mice. Milder wave was showed in C57BL/6 EAU mice than the naïve ones, and the lowest amplitude was showed in B10.RIII EAU mice than C57BL/6 mice, indicating that acute EAU suffer a severer loss in retinal function than chronic during EAU development (Figure 1B).
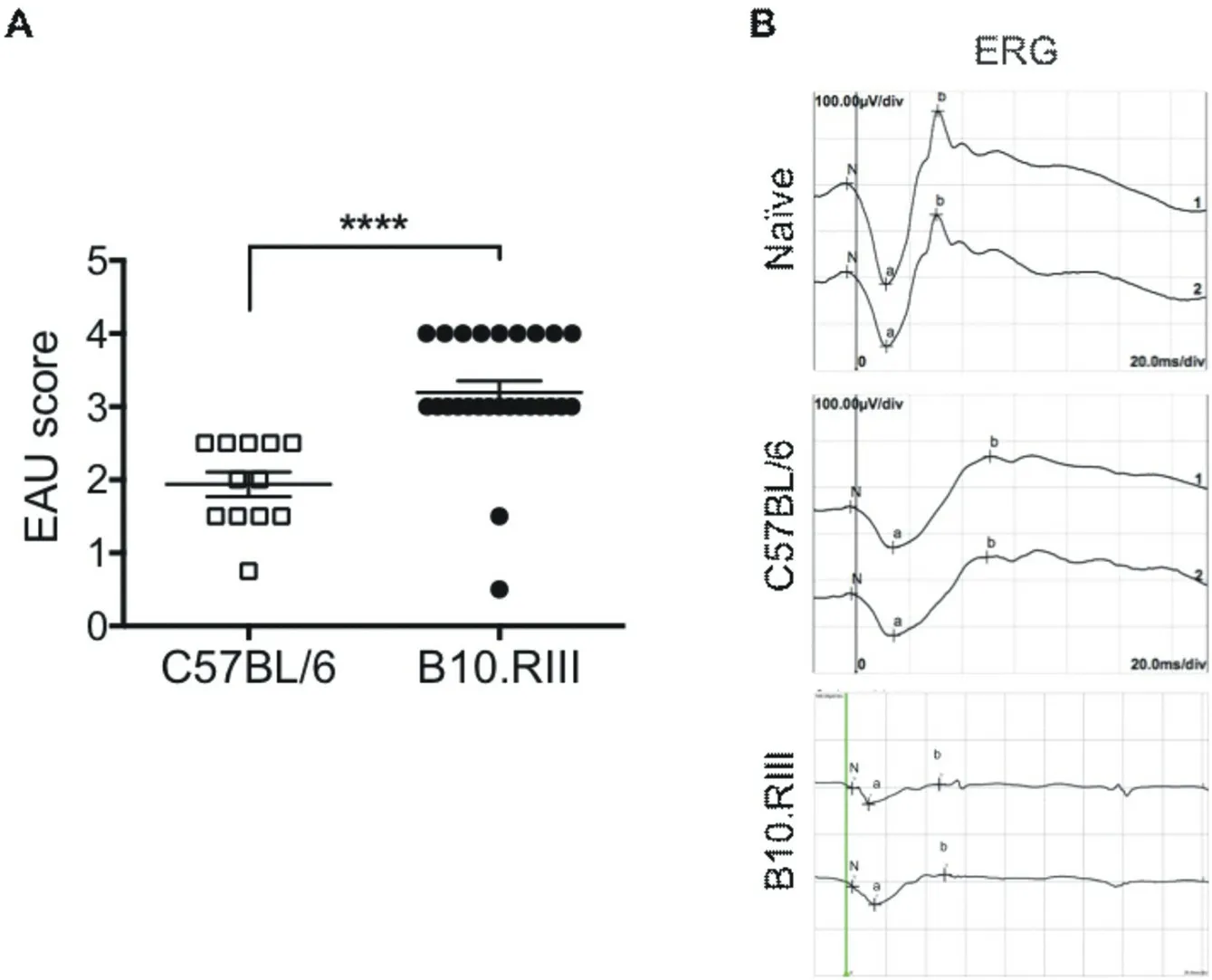
Figure 1. Evaluation of EAU in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice
3.3 Eye-infiltrating cells of EAU in chronic and acute form
To better understand the eye-infiltrating cell profile between chronic and acute EAU mice, we analyzed the cell types and their composition in the inflammatory eyes from C57BL/6 and B10.RIII mice via flow cytometry (FCM). We found that CD4+T lymphocytes and CD11b+cells are the most dominant cell types among the eyeinfiltrating cells in both pattern of EAU with distinct differences, while CD8+T lymphocytes showed similar proportion. Natural killer cells (NK) and natural killer T cells (NKT) contributed small proportion in the infiltrating cells (Figure 2A). FCM data showed eye-infiltrating CD4+T lymphocytes (C57BL/,B10.RII: 10.90±2.44, 20.43±1.70, P=0.0476) and CD11b+cells (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 21.12±3.58, 33.44±2.84, P=0.0476) were significantly higher in B10.RIII than in C57BL/6 mice (Figure 2B), indicating the differences of chronic and acute EAU pattern may related to CD4+T lymphocytes and CD11b+cells but not CD8+T lymphocytes (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 10.53±1.65, 11.33±0.66, P=0.7143), CD3-NK1.1+ NK cells (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 1.64±0.39, 1.95±0.29, P=0.7143) and CD3+NK1.1+ NKT cells (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 0.32±0.18, 0.35±0.22, P=0.9048) since no significant differences within the two strains was observed (Figure 2B).
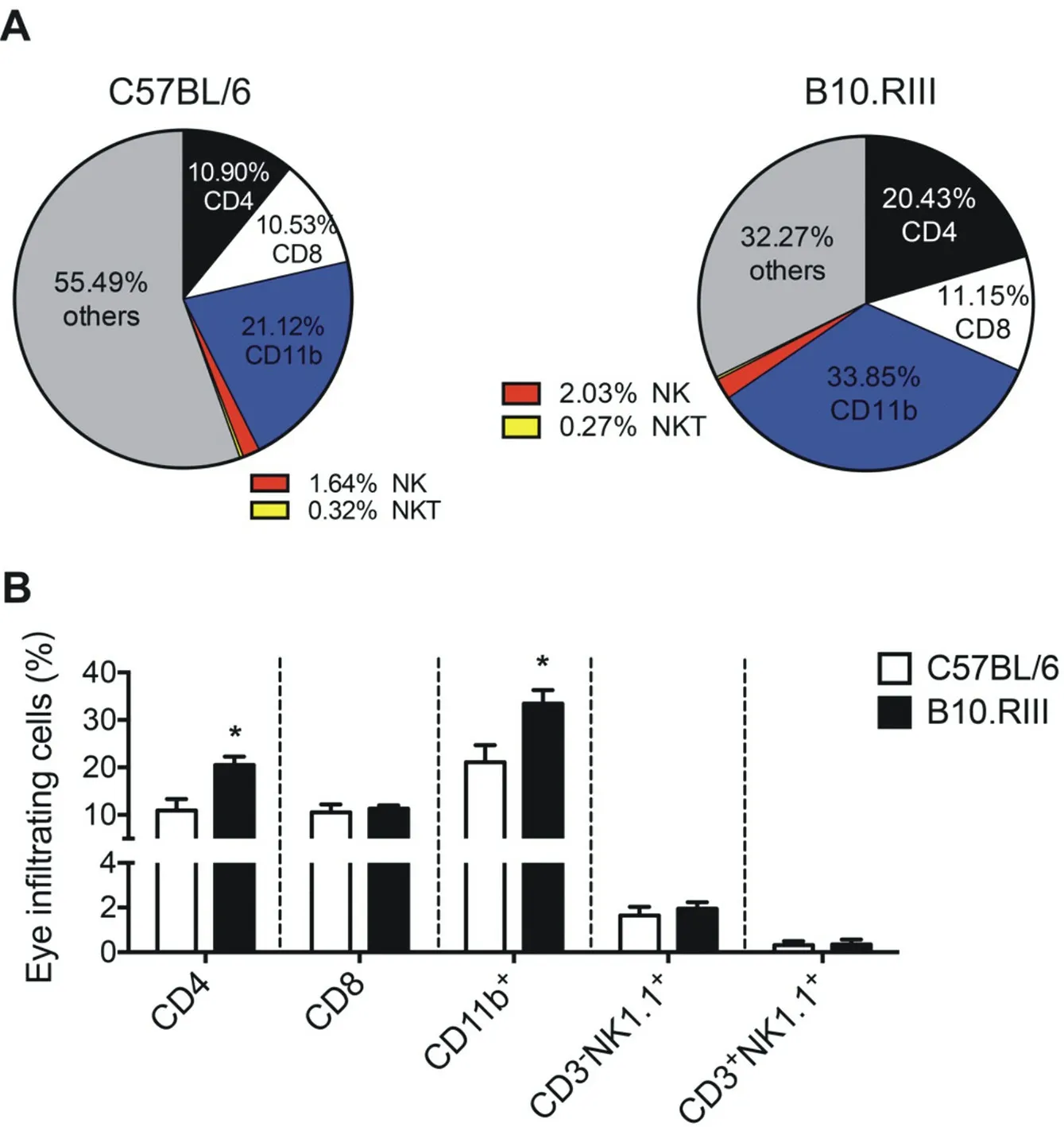
Figure 2. Eye-infiltrating cells in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII EAU mice
3.4 Eye-infiltrating CD11b+ cell subsets of EAU in chronic and acute forms
As increased percentage of CD11b+cells were found in acute EAU mice than the chronic one, we then asked which specific subset of CD11b+cells is contributed. No significant differences were showed in CD11b+CD11c+dendritic cells (DC) between the two strains (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 2.70±0.96, 2.14±0.61, P=0.9643), whereas increased proportion were showed in CD11b+CD11c-macrophage (C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 18.42±3.12, 31.30±2.23, P=0.0238) and CD11b+Gr-1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC, C57BL/6, B10.RIII: 11.78±2.67, 24.53±3.50, P=0.0476) in B10.RIII than C57BL/6 strain mice (Figure 3 and 4). The results indicated that macrophages and MDSC, but not DC, may account for the higher CD11b+cells in acute EAU than chronic EAU.
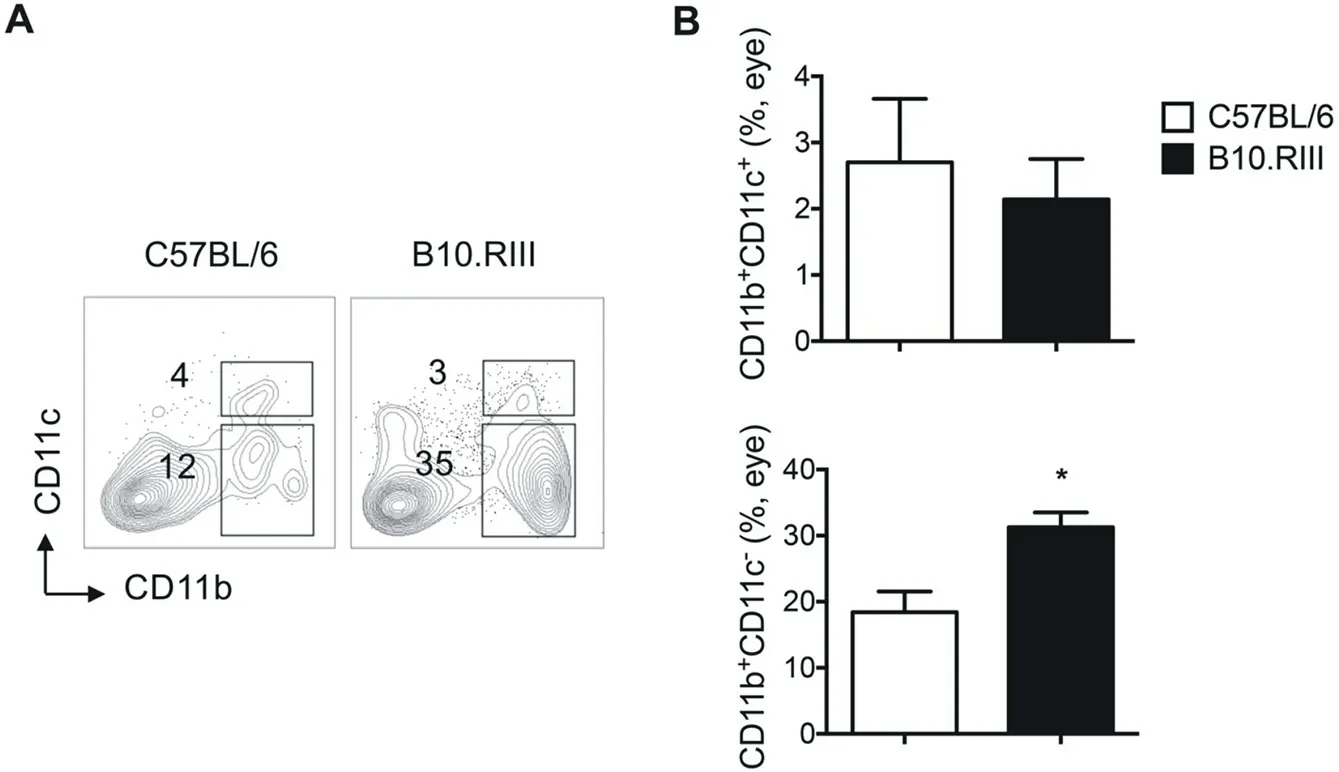
Figure 3 Percentage of CD11b+CD11c+ and CD11b+CD11c- cells in eye infiltrating cells in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII EAU mice.
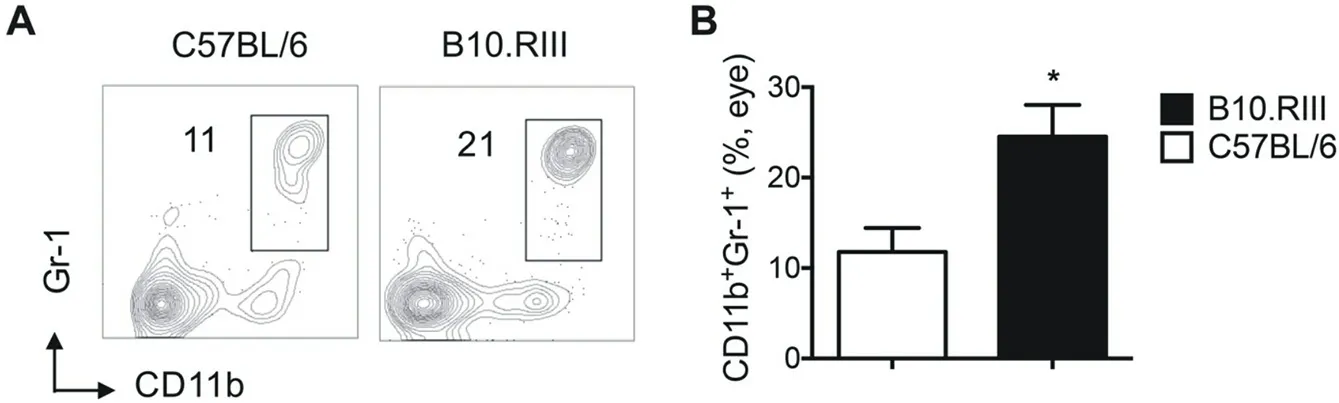
Figure 4 Percentage of CD11b+Gr-1+ cells in eye infiltrating cells in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII EAU mice.
4. Discussion
EAU, served as a classic animal model for human AU, has been used for preclinical studies in discovering the disease mechanisms and novel therapy strategies. However, EAU exhibits different disease pattern in mouse with different genetic backgrounds and these differences are not fully understood. Thus, it is important to characterize EAU in different backgrounds for the selection of optimal AU mouse model.
Mice in C57BL/6 and B10.RIII background are frequently for EAU. Recent study has reported EAU induced in C57BL/6 mice serves as a chronic EAU model while acute EAU model can be induced in B10.RIII mice [1]. Here, we demonstrated the acute EAU with higher clinical score showed earlier disease onset and peak than chronic EAU. The results indicate that EAU pathogenesis in chronic and acute pattern may be different.
Along with EAU progression, large numbers of inflammatory cells infiltrate in the eyes [5]. In this study, we found eye infiltrating cells subsets were different between chronic and acute EAU. We observed that CD4+T lymphocytes and CD11b+cells accounted for the major cell types to infiltrate into the inflamed eyes, with higher proportion in acute EAU, when compared to chronic EAU. These observations imply these two cell subsets may promote EAU progression. Published paper reported that NK cells and NKT cells have protective function to EAU [13]. However, percentage of NK cells and NKT cells in eye infiltrating cells was relatively low and showed no differences between chronic and acute EAU, indicating these cells might not play a dominant role in retinal inflammation and only regulate EAU progression peripherally.
EAU is a CD4+T cell-mediated autoimmune disease model. Align with this, our study found that acute EAU, with higher clinical score than chronic EAU, showed more CD4+T lymphocytes infiltration. On the other side, it is well known that innate immune cells, like macrophages, DCs, are able to regulate adaptive immune response. Published studies have indicated that CD11b+cells are involved in the homeostasis and immune surveillance of retinal inflammation [14,15]. Similarly, our results found that there was higher proportion of macrophages in acute EAU than in chronic EAU, implying macrophages is related to EAU severity. Unexpectedly, more eye infiltrated CD11b+Gr-1+ MDSC were observed in acute EAU. Though MDSC are highly immunosuppressive and believed to have therapeutic potential in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis [16], an animal model for multiple sclerosis that shares similar pathogenesis with EAU, these suppressive cells might be recruited in the inflamed sites to play the regulatory roles as reported [17].
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated the acute EAU in B10.RIII background, with more susceptible and severer EAU pattern than the chronic EAU in C57BL/6 background, showed higher frequency of eye infiltrating CD4+T lymphocytes, macrophages and MDSC, indicating these cells may play important roles in the EAU pathogenesis. These findings provide new clues for selecting the suitable EAU model for pre-clinical study for AU.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年1期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年1期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effect of Liraglutide Combined with Nephritis Rehabilitation Tablets for Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy
- Screening and bioinformatics analysis of diabetic peripheral neuropathyrelated genes in women
- Study on TCM Syndrome Types and Syndromes of Knee Osteoarthritis Based on Modern Literature
- Study on the medication rule of Wang Xun in the treatment of dysentery based on Data Mining
- A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis for Duhuo Jisheng Decoction Combined with Manipulation in Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Correlation analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with blood lipid and coagulation indexes
