右美托咪定加单次小剂量肌松全身麻醉在鼻内窥镜手术ERAS中应用
董龙禹 刘冰 孙玉明

[摘要] 目的 探討右美托咪定加单次小剂量肌松全身麻醉在鼻内窥镜手术ERAS中的应用效果。 方法 选择2018年5月~2019年4月本院收治的拟择期行鼻内窥镜手术患者30例,男16例,女14例,随机分为两组,每组各15例。观察组麻醉诱导采用右美托咪定0.5 μg/kg缓慢静注、丙泊酚2 mg/kg,罗库溴铵0.8 mg/kg、芬太尼1 μg/kg,全麻插管控制呼吸。麻醉维持:丙泊酚50~60 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼0.3 μg/(kg·min)行麻醉维持,不再使用右美托咪定及肌松剂。对照组采用常规麻醉方法,手术结束麻醉停药后,待患者意识清醒,TOF≥0.9时,拔除气管导管,10 min内MAS≥9分,送入外科病房,达不到出室条件患者送入PACU。术中监护HR、MAP,术毕停药后,记录患者命令反应时间、拔管时间、MAS≥9时间、有无EA。 结果 两组HR、MAP改变比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),观察组术后各项苏醒指标分别为命令反应时间为(2.5±1.1)min、拔管时间为(2.8±1.0)min、MAS≥9时间为(4.5±2.1)min,与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。无EA发生,全部患者术后5 min内达到出室条件。对照组患者10 min内全部没有达到MAS≥9,送入PACU,7例(46.7%)发生EA。两组无其他麻醉相关并发症。 结论 右美托咪定加单次小剂量肌松全麻在鼻内窥镜手术ERAS中应用与常规全麻比较,效果明显,无须进入PACU,无EA发生,有临床推广价值。
[关键词] 右美托咪定;内窥镜手术;ERAS;全麻;气管插管
[中图分类号] R614.2 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)31-0118-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application efficacy of dexmedetomidine combined with single and low dose of muscle relaxant for general anesthesia in ERAS of nasal endoscopic surgery. Methods A total of 30 patients(16 males and 14 females were included) who were scheduled to undergo nasal endoscopic surgery and admitted to our hospital from May 2018 to April 2019 were randomLy divided into the observation group(n=15) and the control group(n=15). In the observation group, 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine, 2 mg/kg propofol, 0.8 mg/kg rocuronium and 1 ug/kg fentanyl were used for anesthesia induction, and general anesthesia intubation was used to control breathing. In the anesthesia maintenance, 50-60 μg/(kg·min) propofol and 0.3 μg/(kg·min) remifentanil were used, while dexmedetomidine and muscle relaxant were no longer used. On the other hand, the conventional anesthesia was used in the control group. After the anesthesia was stopped after the operation, when the patient was conscious and TOF≥0.9, the endotracheal tube was removed. Within 10 minutes, when MAS≥9 points, the patient was sent to the surgical ward, and if he could not meet the condition of discharge, he would be sent to PACU. HR and MAP were monitored during operation. After stopping the drug after operation, the patient′s reaction time on command, extubating time, MAS ≥9 time and with or without EA were recorded. Results There were no significant differences in HR and MAP changes between the two groups. The wake-up indexes in the observation group were(2.5±1.1)min after operation,(2.8±1.0)min after extubating, and(4.5±2.1)min after MAS ≥9. Compared with the control group, there was statistically significant difference(P<0.01).No EA occurred, and all patients reached the discharge condition within 5 min after operation. None of the patients in the control group reached MAS≥9 within 10 minutes. And after they were sent to PACU, EA occurred in 7 patients(46.7%). There was no other anesthesia related complications in the two groups. Conclusion Compared with conventional general anesthesia, dexmedetomidine combined with a single and low dose of muscle relaxant for general anesthesia has obvious efficacy. There is no need to enter PACU, no EA occurs. Therefore, it is worthy of clinical promotion.
[Key words] Dexmedetomidine; Endoscopic surgery; ERAS; General anesthesia; Tracheal intubation
1997年,丹麦外科教授Kehlet等[1]提出的术后快速康复(Enhanced recovery after surgery,ERAS)理念,可有效提高病床使用率,减少住院时间[2],患者术后的功能状态更快恢复。2006年,黎介寿院士首次将ERAS理念引入中国,在我国ERAS积极推广,特别是普外科及腹腔手术应用ERAS[2-6],其他外科手术也相继推广了ERAS,骨科、妇科、创伤外科也有临床报道[7-10],麻醉科对ERAS报道较少[11],作为麻醉科,麻醉医师应当在麻醉及手术期间精确使用麻醉剂,维持生命体征稳定,使患者手术后快速苏醒,降低麻醉及手术后并发症,并且减少麻醉后监护病房(Post anesthesia care unit,PACU)滞留时间。本研究探讨右美托咪定加小剂量肌松全身麻醉在鼻内窥镜手术在ERAS中应用效果,现报道如下。
1 資料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2018年5月~2019年4月本院耳鼻喉科收治的拟择期行鼻内窥镜手术患者30例,男16例,女14例,年龄20~55岁,随机数字法分为两组,每组各15例。对照组中,男8例,女7例,年龄20~54岁,平均(32.81±7.15)岁,体重(60.51±4.5)kg;观察组中,男8例,女7例,年龄20~55岁,平均(33.58±6.91)岁,体重(61.03±3.97)kg。两组患者男女比例、年龄分布、体重比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。所有患者均签署知情同意书,本研究经医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。
纳入标准[5]:美国麻醉学会麻醉分级(ASA)Ⅰ~Ⅱ级;体重50~70 kg;无心脑血管疾病;无高血压及心律失常;无肝肾功能损害;无呼吸道及肺疾病。排除标准[6]:神经精神病史;吸毒史;酒精依赖;药物依赖;认知功能障碍;体质量过高或过低者。
1.2 方法
两组患者均不使用术前药物,观察组麻醉诱导采用右美托咪定(四川国瑞药业有限责任公司,国药准字H20110097,2 mL∶0.2 mg)0.5 μg/kg缓慢静注,丙泊酚(广东嘉博制药有限公司,国药准字H20051843, 10 mL∶100 mg)2 mg/kg,芬太尼(宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,国药准字H42022076,2 mL∶0.1 mg)1 μg/kg、罗库溴铵(浙江仙琚制药有限公司,国药准字 H2009 3186,5 mL∶50 mg)0.8 mg/kg静脉注射,麻醉诱导后气管插入加强气管导管,机械通气。麻醉维持:丙泊酚50~60 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼(宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,国药准字H20030197,粉针剂:1 mg)0.3 μg/(kg·min)连续静脉注射麻醉维持,不再使用右美托咪定及肌松剂。对照组使用普通诱导方法,静脉注射丙泊酚2 mg/kg、罗库溴铵1 mg/kg、芬太尼1 μg/kg,麻醉诱导后插入加强气管导管,机器控制通气。丙泊酚60~70 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼0.3 μg/(kg·min)行麻醉维持,术中根据肌松监测结果,四个成串刺激(TOF)≥0.5时,罗库溴铵0.5 mg/kg静注维持肌松,两组控制通气频率8~12次/min,机械控制通气潮气量8~12 mL/kg,维持呼气末CO2浓度4.5~5.5 Kpa。手术结束麻醉停药后,待患者意识清醒,达到拔管条件TOF≥0.9时,拔除气管导管,10 min内修正的Aldrete 评分(Modfied aldrete score,MAS)[3]达到≥9分,送入外科病房,10 min内达不到MAS≥9分患者送入PACU。
1.3 观察指标
两组患者入室后连接迈瑞T5监护仪,记录麻醉前(T0)、麻醉后5 min(T1)、手术结束(T2)时的心率(HR)和平均动脉压(MAP)。术毕从停止麻醉用药开始,观察患者命令反应时间、拔管时间、MAS≥9时间、有无术后躁动(Emergence agitation,EA)。
1.4 统计学方法
应用SPSS21.0统计学软件行数据处理,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,采用t检验,三组以上正态计量资料比较采用方差分析,计数资料采用χ2检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组不同时间MAP、HR比较
手术时间为40~60 min,观察组平均为(47.5±5.8)min,对照组平均为(45.5±6.8)min,两组比较,差异无统计学意义(t=0.451,P>0.05)。两组不同时间MAP、HR比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
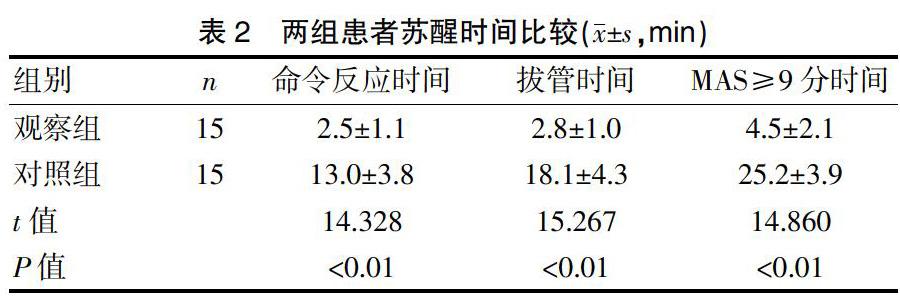
2.2 两组患者苏醒时间比较
观察组术后各项苏醒指标与对照组比较,显著加快(P<0.01)。见表2。观察组无术后EA,全部患者术后5 min内达到出室条件,送入病房。对照组10 min内皆没有达到MAS≥9分,需要进入PACU,7例(46.7%)发生EA。两组无其他麻醉相关并发症。
3 讨论
ERAS的核心要求呈微创手术、目标导向围术期处理、术后快速恢复等,ERAS理念用于胃癌手术[2-5]、结肠癌手术[6]、髋膝关节手术[7-8]、产科手术[9]、创伤外科手术[10]等,效果良好。麻醉科是所有外科手术患者最重要关键的环节,ERAS强调多学科团队合作的重要性,麻醉学科贯穿ERAS始终[13],没有麻醉学科参与ERAS难以实现,麻醉科与外科一同联手,规范化、系统化地进行ERAS,才能顺利开展。加快术后康复是患者和医师的共同愿望,ERAS应当在麻醉后使患者的功能状态更快恢复,麻醉管理应当维持麻醉期间HR、MAP平稳,降低麻醉相关并发症,减少PACU滞留时间。

