EZH2在慢性髓细胞性白血病大鼠中调控机制分析
章宝繁 吴圣豪
[摘要] 目的 分析EZH2在慢性髓細胞性白血病大鼠中调控机制。 方法 选取SPF级Wistar雌性大鼠60只,制备慢性髓细胞性白血病(CML)模型,shEZH2(EZH2敲低)组和shEZH2+IM组大鼠行EZH2敲低实验,移植第2天,IM组、shEZH2+IM组灌胃剂量为100 mg/kg的伊马替尼(IM)药液,shEZH2组、溶剂组灌胃20%磺丁基-β-环糊精(Captisol)。末次给药后解剖观察各组大鼠脾脏肿大和结节情况,检测大鼠髓系细胞与白血病细胞比例、白血病祖细胞比例、白血病干细胞比例情况和骨髓内mTOR、Akt及PI3K蛋白表达量。 结果 shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内髓系细胞与白血病细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内中粒细胞巨噬细胞祖细胞、共同淋巴系祖细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠骨髓内mTOR、Akt及PI3K蛋白表达较溶剂组升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 敲低CML大鼠移植细胞内EZH2,可有效降低骨髓和脾脏内CML细胞不同亚群细胞比例,其作用机制可能和上调PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路内各蛋白表达有关。
[关键词] 慢性髓细胞性白血病;组蛋白赖氨酸甲基转移酶EZH2;造血干细胞;白血病干细胞
[中图分类号] R739.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)31-0034-04
Analysis of the regulation mechanism of EZH2 in chronic myeloid leukemia rats
ZHANG Baofan WU Shenghao
Department of Chemotherapy, Wenzhou Central Hospital in Zhejiang Province, Wenzhou 325000, China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the regulation mechanism of EZH2 in chronic myeloid leukemia rats. Methods 60 SPF-derived Wistar female rats were selected to prepare chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) model. The shEZH2 (EZH2 knockdown) group and the shEZH2+IM group were subjected to EZH2 knockdown test. On the second day of transplantation, IM group and shEZH2+IM group received 100 mg/kg imatinib (IM) solution, shEZH2 group and solvent group received 20% sulfobutyl-β-cyclodextrin (Captisol). After the last administration, the spleen enlargement and nodules of the rats in each group were observed by anatomy. The ratio of myeloid cells to leukemia cells, the proportion of leukemia progenitor cells, the proportion of leukemia stem cells and the expression of mTOR, Akt and PI3K protein in bone marrow were detected. Results The ratio of spleen and bone marrow mesangial cells to leukemia cells in shEZH2 group and shEZH2+IM group was significantly lower than that in the solvent group(P<0.05). The proportion of neutrophil macrophage progenitor cells and common lymphoid progenitor cells in spleen and bone marrow of shEZH2 group and shEZH2+IM group was significantly lower than that in the solvent group (P<0.05). The protein expression of mTOR, Akt and PI3K proteins in rat bone marrow of shEZH2 group and shEZH2+IM group was higher than that in the solvent group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion The knockdown of EZH2 in the transplanted cells of CML rats can effectively reduce the proportion of different subpopulations of CML cells in bone marrow and spleen. The mechanism may be related to the up-regulation of the expression of various proteins in PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS19.0统计软件进行数据分析,计量资料用(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,多组间计量资料比较采用方差分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 敲低EZH2对大鼠脾脏和骨髓内髓系细胞与白血病细胞比例影响情况比较
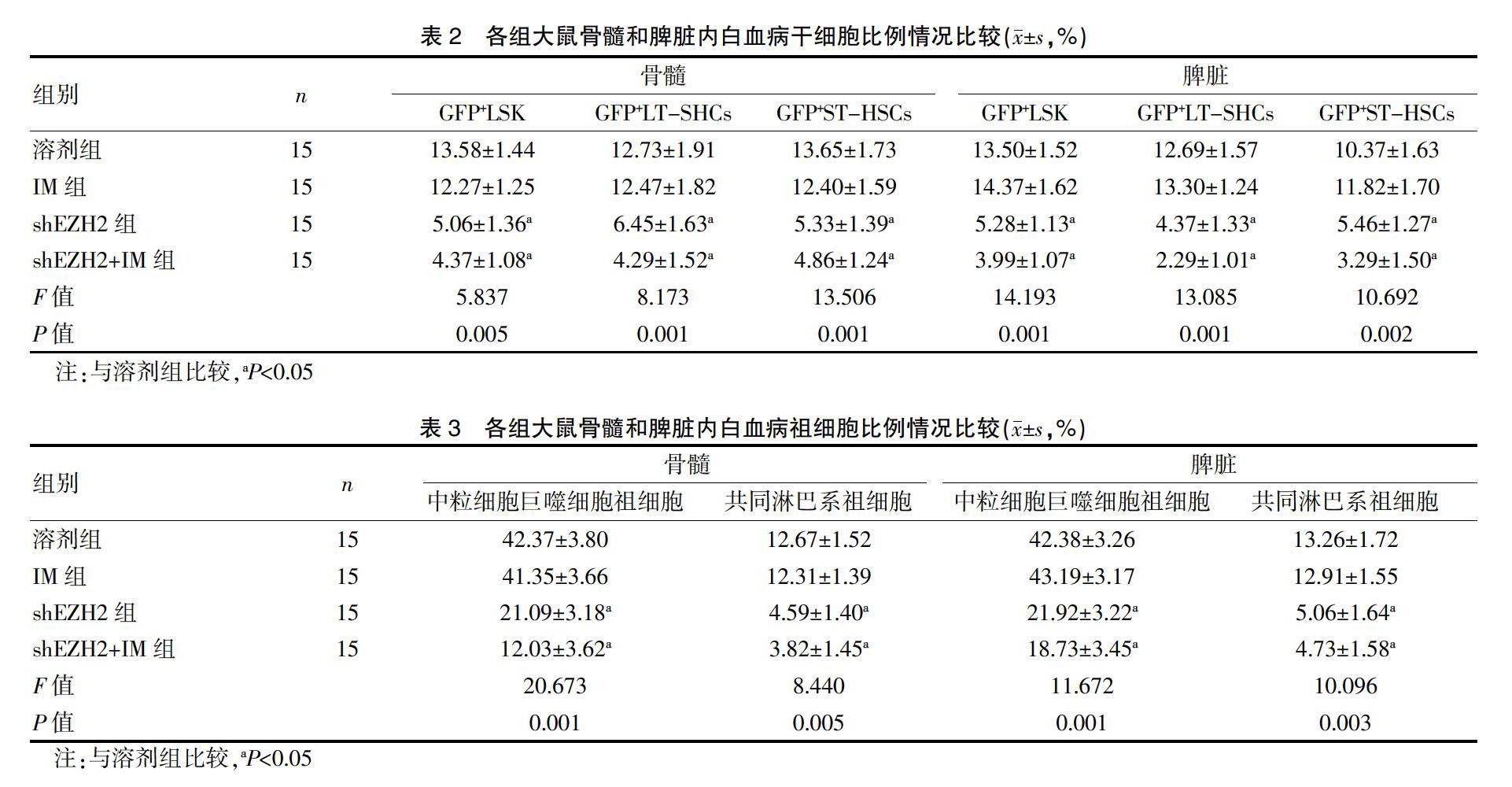
shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内髓系细胞与白血病细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表1。
2.2 敲低EZH2对大鼠骨髓和脾脏内白血病干细胞比例影响情况比较
shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内GFP+LSK、GFP+LT-SHCs及GFP+ST-HSCs细胞含量较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
2.3 敲低EZH2对大鼠骨髓和脾脏内白血病祖细胞比例影响情况比较
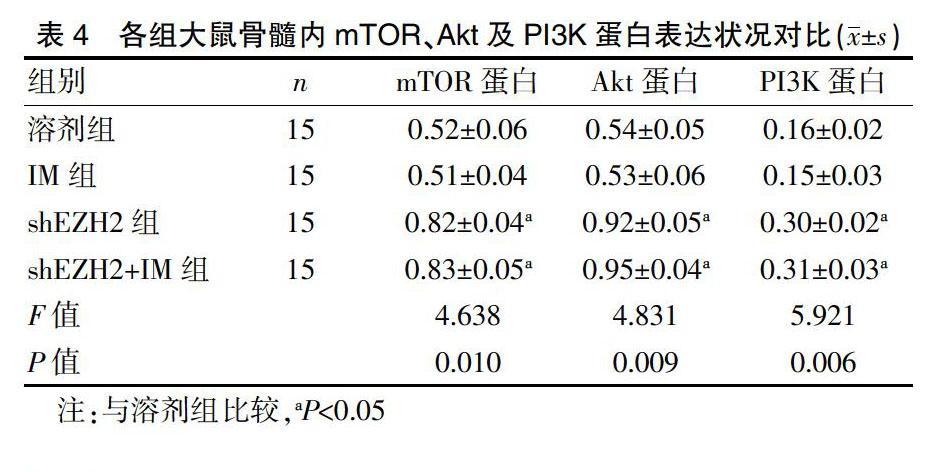
shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内中粒细胞巨噬细胞祖细胞、共同淋巴系祖细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
2.4 各组大鼠骨髓内mTOR、Akt及PI3K蛋白表达状况比较
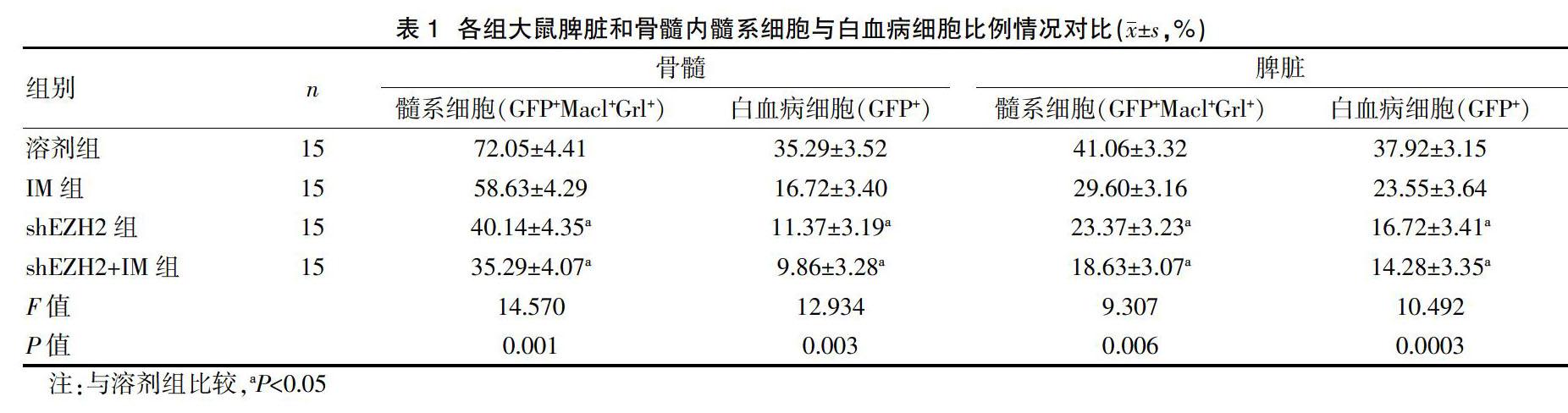
shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠骨髓内mTOR、Akt及PI3K蛋白表达较溶剂组升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
3 讨论
白血病干细胞(LSCs)为CML患者出现TKIs耐药根源,其一般被定义成BCR-ABL+CD34+CD38-原始祖细胞[8-9]。目前,越来越多研究显示,即便在获得完全分子生物学缓解CML患者机体内依然能够检测到BCR-ABL+LSCs,并最终会造成CML复发,所以将LSCs靶向清除可能为治愈CML有效策略之一[10-12]。尽管LSCs存活对BCR-ABL激酶活性无依赖性,但会受到多条信号路径的调节,包含TGF-β、Notch及Wnt/β-catenin等。许多肿瘤细胞内EZH2表现为功能性获得性突变或者高表达,同时上述变化和患者的不良预后联系紧密。EZH2为保持很多CSCs功能必需的(包含急性髓细胞性白血病、乳腺癌、神经胶质瘤及胰腺癌等)。EZH2还能够调控很多条对CSCs有关键作用的信号路径,包含STAT3、Notch及Wnt/β-catenin等。近期有研究显示,EZH2敲除能够对LSCs自我更新和存活抑制,增大了LSCs对IM敏感性[13-15]。
CML大鼠体内祖细胞和GFP-HSCs含量能够反映正常造血细胞含量,本文研究显示,shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内髓系细胞与白血病细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓內GFP+LSK、GFP+LT-SHCs及GFP+ST-HSCs细胞含量较溶剂组显著降低,shEZH2组及shEZH2+IM组大鼠脾脏和骨髓内中粒细胞巨噬细胞祖细胞、共同淋巴系祖细胞比例较溶剂组显著降低,差异有统计学意义,说明敲低EZH2可显著抑制白血病HSCs含量。CML细胞内,BCR-ABL可连续激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号路径,并在CML细胞增殖和存活中有重要影响。虽然IM敏感CML细胞内PI3K/AKT/mTOR能够被IM抑制,但IM长期处理所形成IM耐药内PI3K/AKT/mTOR路径则被明显激活[16]。同时,激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号路径还会受到其他一些信号路径的控制,BCR-ABL非依赖性PI3K/AKT/mTOR路径激活可能为CML细胞对于IM天然耐药主要因素。相关研究显示,CML细胞内对PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号路径抑制则可使耐药细胞对IM敏感性增大。本文研究显示,将EZH2敲低可抑制PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号路径,说明敲低EZH2降低CML大鼠骨髓及脾脏内各项细胞比例可能和PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号路径被抑制有联系。由于时间和人力等条件限制,本研究中部分数据难免存在偏颇,今后还需进一步学习相关理论知识,进行更深入分析。
综上所述,敲低CML大鼠移植细胞内EZH2,可有效降低骨髓和脾脏内CML细胞不同亚群细胞比例,其作用机制可能和上调PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路内各蛋白表达有关。
[参考文献]
[1] 黎韵瑶,陈纯.急性髓细胞白血病甲基化改变及临床治疗的研究进展[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2018,41(1):30-36.
[2] 程艳红,徐修才.慢性髓细胞性白血病耐药机制的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2018,34(11):521-524.
[3] Zhou J,Nie D,Li J,et al. PTEN is fundamental for elimination of leukemia stem cells mediated by GSK126 targeting EZH2 in chronic myelogenous leukemia[J]. Clinical Cancer Research,2018,24(1):17-22.
[4] 刘杨,余康捷,王哲,等.组蛋白甲基转移酶EZH2和MLL2在弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤中的最新研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2018,26(10):1634-1638.
[5] G?llner S,Oellerich T,Agrawalsingh S,et al.Loss of the histone methyltransferase EZH2 induces resistance to multiple drugs in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Nature Medi-cine,2017,23(1):69-78.
[6] 吴家林,陈香宇,田钦.急性病毒感染条件下组蛋白甲基化转移酶EZH2对CD4+T细胞mTOR信号通路的影响[J].免疫学杂志,2019,7(4):304-308.
[7] Min C,Moore N,Shearstone JR,et al. Selective inhibitors of histone deacetylases 1 and 2 synergize with azacitidine in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Plos One,2017,12(1):128-132.
[8] 徐金升,高少輝,白亚玲,等.干扰组蛋白赖氨酸甲基转移酶SET8对肾透明细胞癌786-O细胞增殖的影响[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2017,24(8):524-528.
[9] Zhang G,Zhang L,Yang X,et al. High ETS2 expression predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J].Annals of Hematology,2018,11(8):1-7.
[10] Fujita S,Honma D,Adachi N,et al.Dual inhibition of EZH1/2 breaks the quiescence of leukemia stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia[J].Leukemia,2018,32(4):855-859.
[11] 王珍珍,邱少伟,王建祥.治疗急性髓细胞白血病新药的研究进展[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2017,40(2):169-173.
[12] Bapat A,Keita N,Martelly W,et al. Myeloid disease mutations of splicing factor SRSF2 cause G2-M arrest and skewed differentiation of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells[J]. Stem Cells,2018,36(11):204-208.
[13] 李正发,刘伟,杜云云,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗慢性髓细胞性白血病监测染色体核型及融合基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(29):4691-4696.
[14] Kandarpa M,Wu YM,Dan R,et al. Clinical characteristics and whole exome/transcriptome sequencing of coexisting chronic myeloid leukemia and myelofibrosis[J]. American Journal of Hematology,2017,92(6):555-559.
[15] 宋磊,徐鑫,赵瑶,等.组蛋白去甲基化酶KDM3B在急性髓系白血病中的靶基因鉴定[J].现代肿瘤医学,2018, 26(8):307-311.
[16] 张玉峰,刘红玉.药物基因组学在慢性髓细胞白血病靶向治疗中的研究进展[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2017, 40(40):425-428.
[17] Najafabadi MM,Shamsasenjan K,Akbarzadehalaleh P. Angiogenesis status in patients with acute myeloid leukemia:From diagnosis to post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. International Journal of Organ Tran-splantation Medicine,2017,8(2):57-67.
[18] Yu T,Wang Y,Hu Q,et al. The EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 suppresses cancer stem-like phenotypes and reverses mesenchymal transition in glioma cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(58):98348-98359.
[19] Razmkhah F,Soleimani M,Mehrabani D,et al. Leukemia microvesicles affect healthy hematopoietic stem cells[J]. Tumour Biol,2017,39(2):2234-2238.
[20] Xu DD,Ying W,Zhou P J,et al. The IGF2/IGF1R/Nanog signaling pathway regulates the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2018,9(5):687-690.
(收稿日期:2019-05-27)

