基于概率的支持向量数据描述方法
杨晨 王婕婷 李飞江 钱宇华


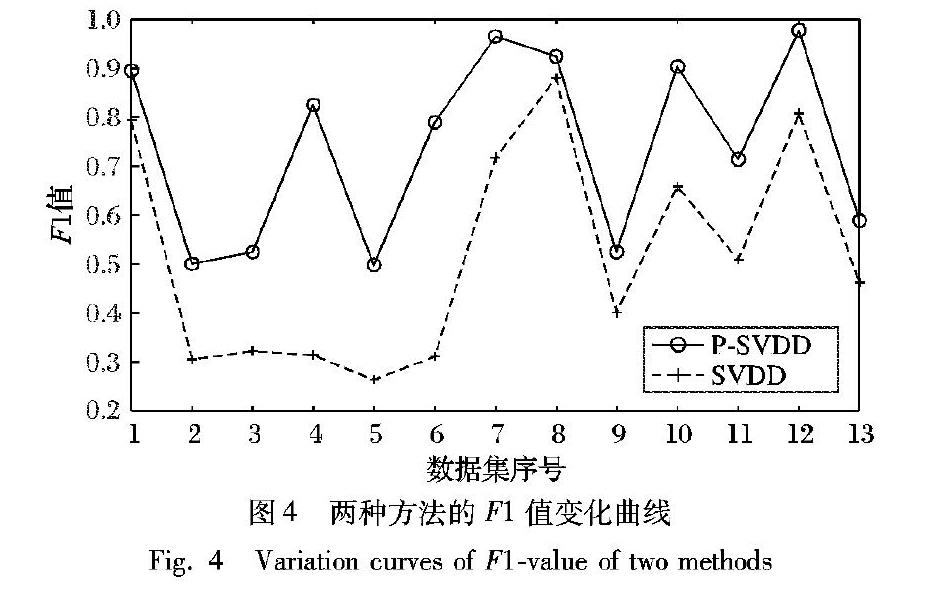
摘 要:针对目前概率机器学习方法在解决概率问题时具有较高的复杂度,而传统的支持向量数据描述(SVDD)作为一种核密度估计方法只能判断测试样本是否属于该类等问题,提出一种基于概率的支持向量数据描述方法。首先,利用传统的SVDD方法分别得到两类数据的数据描述,计算测试样本到超球体的距离;然后,构造一个将距离转换为概率的函数,提出一种基于概率的SVDD方法;同时,使用Bagging算法进行集成,进一步提高数据描述的性能。借鉴分类场景,将所提方法与传统的SVDD方法在Gunnar Raetsch的13种基准数据集上进行实验,实验结果表明,所提方法在准确率和F1值上优于传统的SVDD方法,并且其数据描述的性能有所提升。
关键词:概率机器学习;支持向量数据描述;集成;不确定性;分类
中图分类号:TP181
文献标志码:A
Support vector data description method based on probability
YANG Chen1,2,3, WANG Jieting1,2,3, LI Feijiang1,2,3, QIAN Yuhua1,2,3*
1.Research Institute of Big Data Science and Industry, Shanxi University, Taiyuan Shanxi 030006, China;
2.Key Laboratory of Computational Intelligence and Chinese Information Processing of Ministry of Education(Shanxi University), Taiyuan Shanxi 030006, China;
3.School of Computer and Information Technology, Shanxi University, Taiyuan Shanxi 030006, China
Abstract:
In view of the high complexity of current probabilistic machine learning methods in solving probability problems, and the fact that traditional Support Vector Data Description (SVDD), as a kernel density estimation method, can only estimate whether the test samples belong to this class, a probabilitybased SVDD method was proposed. Firstly, the traditional SVDD method was used to obtain the data descriptions of two types of data, and the distance between the test sample and the hypersphere was calculated. Then, a function was constructed to convert the distance into probability, and an SVDD method based on probability was proposed. At the same time, Bagging algorithm was used for the integration to further improve the performance of data description. By referring to classification scenarios, the proposed method was compared with the traditional SVDD method on 13 kinds of benchmark datasets of Gunnar Raetsch. The experimental results show that the proposed method is better than the traditional SVDD method on accuracy and F1value, and its performance of data description is improved.
Key words:
probabilistic machine learning; Support Vector Data Description (SVDD); ensemble; uncertainty; classification
0 引言
機器学习主要是计算机通过已知数据训练模型,运用模型对未知数据进行预测。机器学习面临的未来的数据和将来的行为引发的结果是不确定的, 而概率机器学习[1]针对这种不确定性提供了一个概率框架,对模型和预测的不确定性进行表示和控制,因此在很多领域发挥着重要的作用,比如语音识别[2]、图像分类[3-4]、文本预测[5]等。Ghahramani[1]在2015年指出概率机器学习框架的主要思想是,学习可以被认为是通过推断合理的模型来解释预测数据,然后机器使用模型来预测未来的数据,并且根据这些预测作出合理的决策,不确定性在这一切中起着至关重要的作用,对于给定的数据而言,哪个模型是合适的尚不确定;同样,对未来数据和未来行动结果的预测也是不确定的,因此使用概率论描述这种不确定性,概率论为不确定性建模提供了一个框架[1]。相对于二值输出而言,以概率作为输出的结果能够提供更多的信息,预测结果更加准确。
目前已有的概率机器学习方法主要有贝叶斯学习、高斯过程和深度学习等,其中:神经网络是具有许多参数的可调非线性函数,深度学习的概念源于人工神经网络的研究,但是也有一些重要的改变,比如新的架构和算法创新、有更大的数据集、大规模的计算资源等。神经网络和深度学习系统在许多基本测试任务上都有很高的性能,但是也有一些局限性,比如需要大量的数据、需要大量的计算资源进行训练等,因此这些方法在解决概率问题时具有较高的复杂度。
近年来,数据描述问题得到了大量的研究。在域描述领域中,数据描述的任务不是以“区分不同的类”为目标的分类问题,也不是以“对每一个样本产生一个期望输出”为目标的回归问题,而是给出一个关于训练样本集的描述,同时检测那些与训练样本集相似的新样本。该描述应该覆盖训练样本集的所有样本,同时,在理想情况下,该描述应该能够将样本空间中其他所有可能的异常样本排除在外。
20世纪末,Tax等[6]在支持向量机(Support Vector Machine, SVM)的基础上提出了一种数据描述方法,即支持向量数据描述(Support Vector Data Description, SVDD)。SVDD方法是一种基于边界数据(即支持向量)的描述方法,其思想是寻找一个几乎包含所有目标样本并且体积最小的超球体。SVDD方法相对于贝叶斯学习、高斯过程和深度学习等具有算法复杂性低、扩展性强、对数据规模需求低等优点。Lee等[7]提出了一种改进的局部密度支持向量数据描述方法(Densityinduced Support Vector Data Description, DSVDD),结果表明,DSVDD的性能优于SVDD和k近邻数据描述方法。Kim等[8]针对SVDD在处理大数据集时存在一定的局限性提出了一种基于k均值聚类的快速SVDD算法,该方法与原始SVDD方法有相同的结果,并且降低了计算成本。Luo等[9]针对矩阵操作的空间复杂性,提出了一种基于分解和组合策略的快速SVDD算法,该算法在实现样本描述方面优于原SVDD算法,尤其是在大规模样本数据集上。然而在现实生活中,目标数据集往往包含一类以上的对象,每一类对象都需要同时进行描述和区分,在这种情况下,传统的SVDD只能给出一个描述目标数据集,不区分不同的目标类数据集,或者给目标数据集中每个类的对象一个描述,Huang等[10]提出了一种改进的支持向量数据描述方法——两类支持向量数据描述(TwoClass Support Vector Data Description, TCSVDD)。
传统的SVDD方法作为一种核密度估计方法,对未知数据进行预测主要是先对已知样本进行数据描述,然后判断测试样本是否属于该类,是二值输出;相对于二值输出而言,以概率作为输出的结果能够提供更多的信息,获得更准确的数据描述。而传统的SVDD方法判断测试样本是否属于该类,主要是计算测试数据到超球体中心的距离,但是该距离无法得知测试数据所属类别的概率。因此,本文提出了一个将距离转换为概率的函数,在本文第2章详细解释。
集成学习算法[11]是通过集成多个学习器共同决策的机器学习技术,通过不同的样本集训练有差异的个体学习器,然后使用某种规则把个体学习器的结果进行集成,得到的集成分类器可以有效提高单个分类器的学习效果。根据个体学习器的生成方式,目前的集成学习方法大致分为两大类,即个体学习器间存在强依赖关系、必须串行生成的序列化方法,以及个体学习器间不存在强依赖关系、可同时生成的并行化方法。前者的代表是Boosting[12],后者的代表是Bagging[13]和随机森林(Random Forest)[14-15]。借鉴分类场景,本文主要使用Bagging集成算法来提高传统SVDD方法的数据描述能力。
为了解决目前深度学习等概率机器学习在解决概率问题时具有较高的复杂度,而且传统的SVDD方法只能判断测试样本是否属于该类等问题,本文首先介绍了SVDD方法和Bagging集成算法的相关知识;然后构造了一个将距离转换为概率的函数,提出了一种基于概率的支持向量数据描述方法(SVDD method based on Probability, PSVDD);最后,实验验证了PSVDD方法的有效性。
1 相关工作
本文算法是基于概率的支持向量数据描述方法,因此在本章简要回顾了SVDD方法和Bagging集成算法的相关知识。
1.1 SVDD相关理论
支持向量数据描述(SVDD)是一种对目标数据集进行球形描述并用于离群点检测或分类的数据描述方法。它的基本思想是通过利用核函数将样本从低维空间映射到高维特征空间,并寻求一个超球体,尽可能在使超球体的半径小的情况下把所有训练样本包围起来,并以最小超球体的边界对数据进行描述和分类。在测试阶段,判断测试样本与所构造的超球体的球心之间的距离是否小于半径:如果小于超球体半径则认为是目标点;若大于超球體的半径则被认为是异常点。SVDD示意图如图1所示。
设X={xi,i=1,2,…,n}为Rd空间中的训练数据集,a和R分别表示球面的中心和半径。该目标被表述为一个二次规划问题:
minR,a,ξi(R,a,ξi)=R2+C∑iξi(1)
s.t.‖xi-a‖2≤R2+ξi, ξi≥0, i=1,2,…,n
其中ξi是一个松弛变量,允许训练数据集中出现异常值的可能性; C为误差惩罚系数,用来平衡错分误差和球体体积。为了该二次规划问题进行求解,引入拉格朗日乘子αi,γi构造拉格朗日函数:
L(R,a,ξi,αi,γi)=R2+C∑iξi-
∑iαi[R2+ξi-(xi-a)2]-∑iγiξi(2)
其中拉格朗日乘子αi≥0,γi≥0。将R,a,ξi偏导数设为零得到约束条件:
[2]HINTON G, DENG L, YU D, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: the shared views of four research groups[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97.
[3]KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E, et al. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90.
[4]黄凯奇, 任伟强, 谭铁牛. 图像物体分类与检测算法综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2014, 36(6):1-18.(HUANG K Q, REN W Q, TAN T N. A review on image object classification and detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2014, 36(6): 1-18.)
[5]KANDOLA E J, HOFMANN T, POGGIO T, et al. A neural probabilistic language model[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2006, 194: 137-186.
[6]TAX D M J, DUIN R P W. Support vector data description[J]. Machine Learning, 2004, 54(1): 45-66.
[7]LEE K Y, KIM D W, LEE D, et al. Improving support vector data description using local density degree[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2005, 38(10):1768-1771.
[8]KIM P J, CHANG H J, SONG D S, et al. Fast support vector data description usingkmeans clustering[C]// Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Neural Networks. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 506-514.
[9]LUO J, LI B, WU C, et al. A fast SVDD algorithm based on decomposition and combination for fault detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Control and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE, 2010: 1924-1928.
[10]HUANG G, CHEN H, ZHOU Z, et al. Twoclass support vector data description[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(2): 320-329.
[11]李勇, 刘战东, 张海军. 不平衡数据的集成分类算法综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2014, 31(5): 1287-1291.(LI Y, LIU Z D, ZHANG H J. Summary of integrated classification algorithm for unbalanced data[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2014, 31(5): 1287-1291.)
[12]FREUND Y, SCHAPIRE R E. A decisiontheoretic generalization of online learning and an application to boosting[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1997, 55(1): 119-139.
[13]BREIMAN L. Bagging predictors[J]. Machine Learning, 1996, 24(2): 123-140.
[14]BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5-32.
[15]周志華. 机器学习[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社, 2016: 171-189.(ZHOU Z H. Mechine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 171-189.)
[16]QIAN Y, LI F, LIANG J, et al. Space structure and clustering of categorical data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2016, 27(10):2047-2059.
[17]ZHOU Z. Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms[M]. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis Group, 2012: 1-22.
[18]QIAN Y, LI F, LIANG J, et al. Fusing monotonic decision trees[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(10): 2717-2728.
[19]EFRON B. Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife[J]. Breakthroughs in Statistics, 1979, 7(1): 569-593.
[20]CAWLEY G, TALBOT N. Gunnar Raetschs benchmark datasets [DB/OL].[2018-11-20]. http://theoval.cmp.uea.ac.uk/~gcc/matlab/default.html#benchmarks.
[21]NAGANJANEYULU S, KUPPA M R. A novel framework for class imbalance learning using intelligent undersampling[J]. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 2(1): 73-84.
[22]ZHANG X, SONG Q, WANG G, et al. A dissimilaritybased imbalance data classification algorithm[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2015, 42(3): 544-565.
[23]JIANG K, LU J, XIA K. A novel algorithm for imbalance data classification based on genetic algorithm improved SMOTE[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2016, 41(8): 3255-3266.
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61672332), the Program for the Outstanding Innovative Teams of Higher Learning Institutions of Shanxi, the Program for the San Jin Young Scholars of Shanxi, the Overseas Returnee Research Program of Shanxi Province (2017023).
YANG Chen, born in 1996, M. S. candidate. Her research interests include statistical machine learning theory.
WANG Jieting, born in 1991, Ph. D. candidate. Her research interests include statistical machine learning theory, reinforcement learning.
LI Feijiang, born in 1990, Ph. D. candidate. His research interests include group learning, unsupervised learning.
QIAN Yuhua, born in 1976, Ph. D., professor. His research interests include machine learning, complex network, rough set theory, granular computing.

