波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟*
崔 勇 关长涛 黄 滨 李 娇 公丕海
波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟*
崔 勇 关长涛①黄 滨 李 娇 公丕海
(中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 农业农村部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室 青岛市海水鱼类种子工程与生物技术重点实验室 青岛 266071)
根据有限单元法建立了波浪作用下双层网底网箱的受力运动模型,通过数值计算求解双层网底的位移与倾角。先将上层网底与下层网底的计算值进行比较,然后,将双层网底网箱中下层网底与单层网底网箱开展对比分析。计算结果显示,在波浪周期内,双层网底网箱的2层网底能保持相对平行的状态。2层网底的位移与最大倾角随着波高与周期的增大而增 加,并且2层网底的倾斜方向一致。在相同波浪条件作用下,下层网底的水平位移大于上层网底,二者垂直位移差异较小,下层网底最大倾角值大于上层网底。研究发现,当波高为15 cm、周期为1.4 s时,双层网底网箱的2层网底的倾角相差最大,但并未发生接触碰撞,网底可以保持相对稳定。此外,双层网底网箱的下层网底的最大位移值小于单层网底网箱,最大倾角值大于单层网底网箱。研究表明,当波浪一定时,双层网底网箱的最大锚绳力均大于单层网底网箱。
双层网底;水动力;有限元方法;鲆鲽网箱
鲆鲽类养殖网箱通常底部具有平台结构,主要用于牙鲆()、大菱鲆()等底栖性鱼类的养殖。目前,用于养殖鲆鲽鱼类的网箱多为方形平底结构,其水面框架由金属管材制成,底部配有张紧绳索的框架支撑底部网衣(崔勇等, 2012)。鲆鲽类养殖网箱与HDPE重力式网箱相比,主要区别为网衣深度不同和网箱底部具有平台结构。鲆鲽网箱的网底面积直接决定单体网箱的养殖产量,因此,为增加单体网箱的产量,网箱通常设有双层或多层网底结构,可增加网箱的养殖面积,提高养殖空间利用率。多层结构的网底在波浪作用下会发生倾斜与转动,为确保鲆鲽类养殖网箱多层网底结构的安全性,需对其水动力特性开展研究。
近年来,国内外学者在离岸网箱水动力特性方面进行了一系列的研究,其中包括物理模型实验(Lader, 2005; DeCew, 2010; 黄六一等, 2007),也有利用计算机技术开展数值模拟(Lee, 2008; Tsukrov, 2003; 黄小华等, 2011)等。此外,Fredriksson等(2003、2007)对实际养殖海区水流作用下养殖网箱的锚泊系统受力进行了海上实测。目前,此类研究中针对鲆鲽网箱水动力特性研究的报道还比较少。赵云鹏等(2012)通过集中质量法对波浪作用下一种鲆鲽类方形网箱水动力特性开展了数值模拟研究。Gui等(2014)对一种鲆鲽网箱在波浪作用下的水动力特性进行测试。崔勇等(2016)对一种双层网底结构鲆鲽网箱的耐流特性开展了研究,并与单层网底网箱进行了比较分析。本文以一种双层网底鲆鲽网箱为研究对象,基于有限元软件提供的参数化建模技术,对其在波浪作用下的水动力特性进行数值模拟,研究结果可为多层网底鲆鲽网箱设计优化提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 数值模拟方法
本研究基于有限元方法对波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱的水动力特性进行数值模拟。网箱结构主要由框架、网衣和锚绳单元构成,本研究采用的有限元模型将网箱结构分成不同特性的单元来计算载荷。如果单元位于水中,其水动力载荷自动施加;如果单元位于水面以上,则只有重力载荷。因此,数值模型可针对结构单元的位置对其水动力进行自动调节。该数值模型通过物理水槽实验验证(Cui, 2013),可用于网衣与框架结构的模拟。
根据有限元动力分析方法,网箱整体结构在波流场中的运动可由公式(1)表示(李茜等, 2003; ANSYS Incorporated, 2009):


1.2 算例
计算用例采用与崔勇等(2016)的双层网底鲆鲽网箱一致。其中,原型网箱主尺寸为5 m×5 m×4 m,网底面积为16 m2,上层网底距离水面为2 m,底面积为9 m2,即双层网底网箱的总养殖面积为25 m2。上层网底四角通过聚乙烯绳索连接网箱上框架与底框架四角,在静水条件下,上层网底可保持水平状态(图1)。为了与崔勇(2012)的单层网底鲆鲽网箱进行比较,本研究计算用例采用重力相似准侧,大尺度比为1∶20,模型网箱参数见表1。波浪工况见表2,设计水深为0.6 m。

图1 双层网底鲆鲽网箱
2 结果与讨论
2.1 网箱运动模拟结果
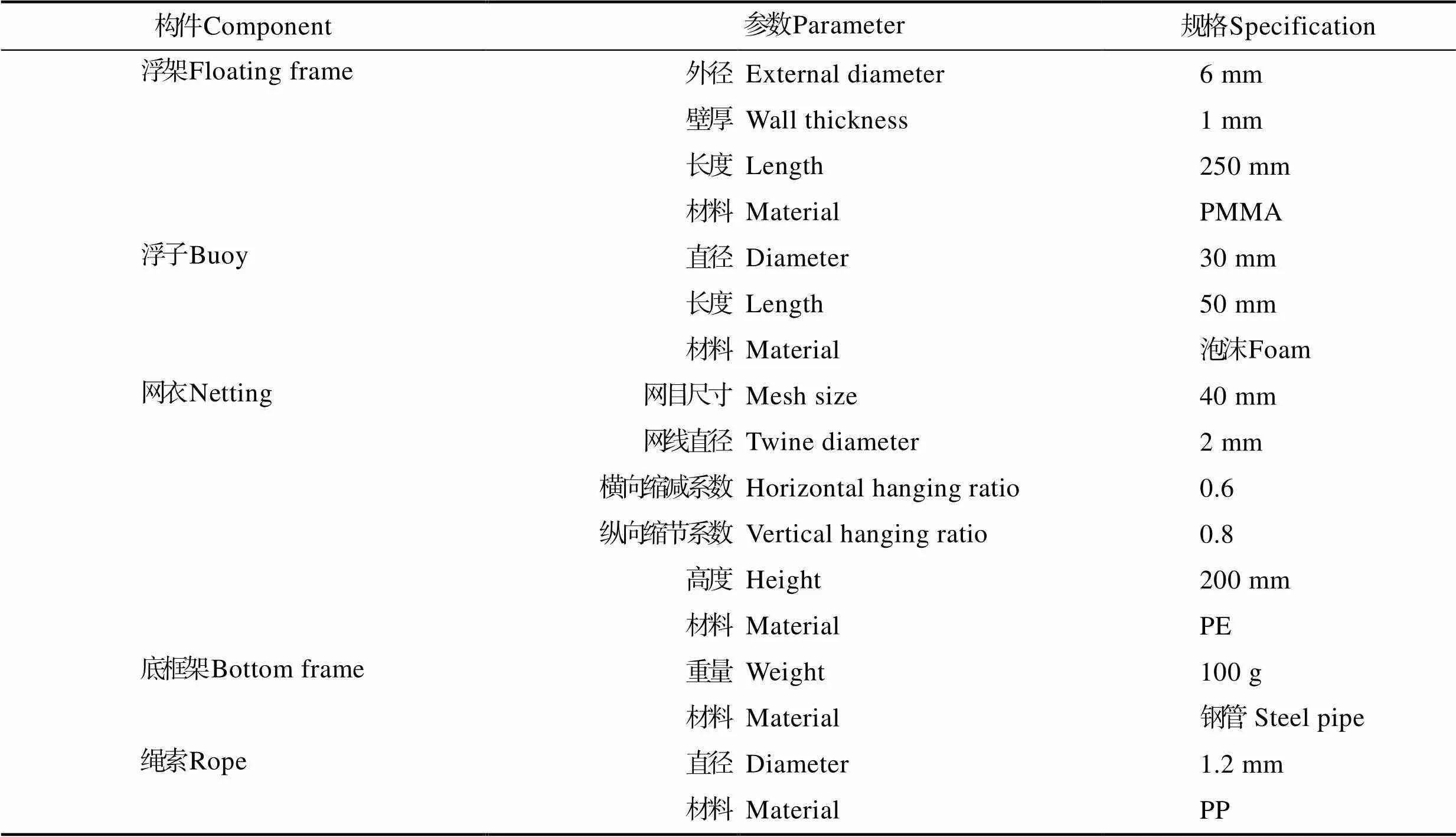
在波浪作用下,双层网底鲆鲽网箱在1个周期内运动变形情况的数值模拟结果见图2。图2中波浪工况条件波高为9 cm,波周期为1.2 s。每张图片的时间间隔为1/8波浪周期,图2中颜色深浅表示网箱离散单元位移大小。从图2可以看出,双层网底鲆鲽网箱整体结构随着波浪传播方向呈现周期性的运动趋势。本研究的计算用例中,浮框和底框架单元本身具有一定的刚度,其单元的形状变化较小,而网衣单元随着时间的推移,在波浪力的作用下产生了明显的变形。从图2还可以看出,在波浪作用下,网箱的上层网底与下层网底框架基本保持平行状态,即2层网底的倾斜方向相同,倾斜角度也基本一致。此结果与单纯水流作用下网箱2层网底的运动变形情况差别较大。当水流作用时,网箱上层网底与下层网底的倾斜方向恰好相反,导致在高流速时出现双层网底发生相互碰撞的情况(崔勇等, 2016)。而当网箱在单纯波浪作用下,网箱的双层网底始终保持一定的间距,并未发生相互接触的情况。此外,从其他波浪工况作用下的计算机仿真结果显示,当波高和波周期取更大值时,网箱的2层网底仍然可以保持相对平行的状态。究其原因,可能与上层网底通过8根绳索分别与上框架与底框架连接有关,2层网底框架与网箱整体结构可以保持相对同步的运动状态。
表1 模型网箱参数
Tab.1 Properties of the flounder fish cage used for tests
表2 波浪工况

Tab.2 Wave conditions
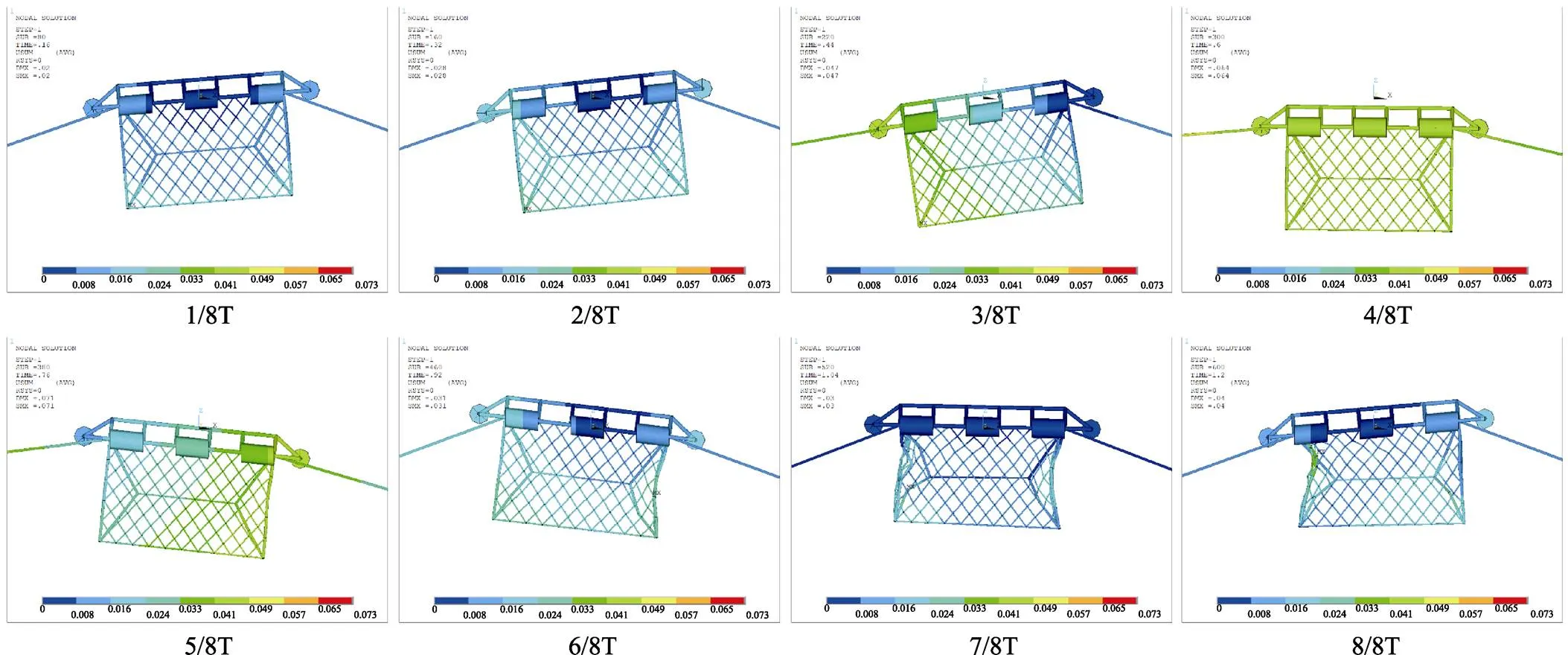
图2 波浪作用下网箱变形模拟结果
2.2 网底位移与最大倾角
不同波浪工况作用下,2层网底在水平与垂直方向最大位移的比较值见图3和图4。其中,位移计算结果采用网底中心点位置。从图3可以看出,当波浪工况相同时,上层网底的水平位移均小于下层网底。2层网底的水平位移随着波高与波周期的增加而增大,其中,当波高一定时,最大水平位移随周期增加而增大的幅度较小;当周期一定时,最大位移随波高增加而增大的幅度较大。从图4可以看出,当波浪工况一定时,2层网底的最大垂直位移值比较接近,上层网底略小于下层网底,仅在波高与周期取较大值时,上层网底的垂直位移明显小于下层网底。由于 2层网底在垂向的位移基本一致,因此,上层网底与下层网底框架可以保持稳定的间距。此外,2层网底的垂直位移随波高与波周期的变化趋势与图3所示的水平位移变化趋势基本相同。
上层网底与下层网底最大倾角随波浪变化模拟值的比较见图5。从图5可以看出,在同一波浪工况作用下,上层网底的最大倾角均小于下层网底,并且2层网底取最大倾角时的倾斜方向一致,均为逆时针方向。2层网底的最大倾角均随波高与周期的增加而增大,波高的改变对网底倾斜角度的影响更加显著。从数值上看,上层网底的最大倾角范围为7°~14°,而下层网底的最大倾角约为14°~36°。从模拟结果看,同时参考图2所示的计算机仿真虚拟呈现,2层网底最大倾角的差值并不是很大,二者的倾斜方向相同,并且在垂直方向位移也基本相同,因此,2层网底并不会发生接触碰撞而影响鲆鲽鱼类的安全生长。这与双层网底网箱在单纯水流作用下,2层网底由于倾斜方向相反而发生碰撞的情况差别明显。

图3 上层网底与下层网底水平位移
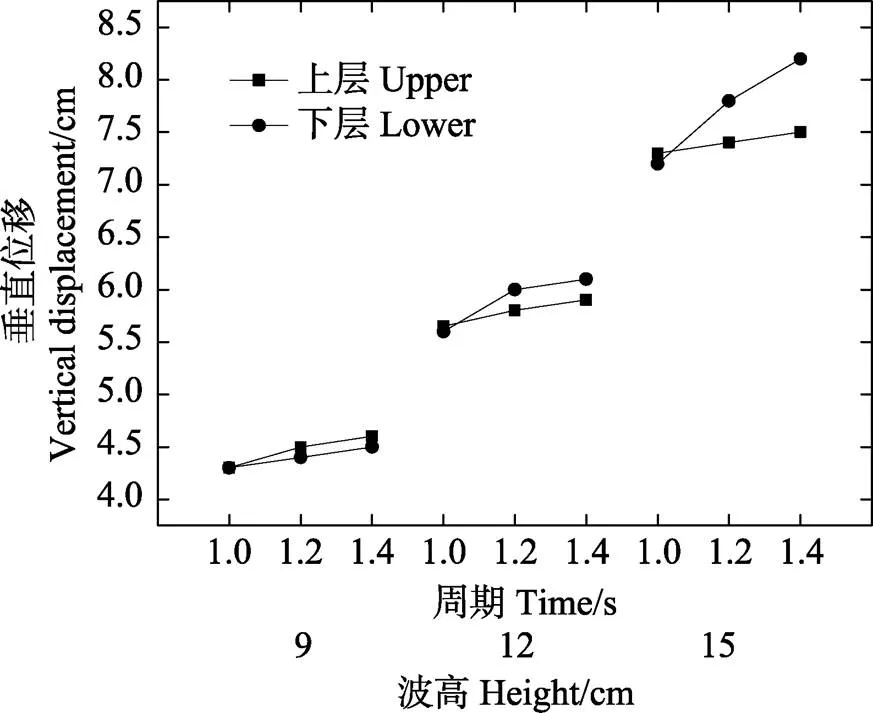
图4 上层网底与下层网底垂直位移

图5 上层网底与下层网底最大倾角
本计算用例中,双层网底网箱与崔勇(2012)所述单层网底网箱的网底最大位移值的比较见图6和图7。其中,双层网底网箱的水平与垂直位移均为下层网底。由图6和图7可以看出,在相同波浪条件下,双层网底网箱在水平与垂直方向的最大位移均小于单层网底网箱,这可能与双层网底网箱的上层网底结构有关。由于上层网底的四角通过绳索分别与下层网底四角相连接,2层网底在波浪作用下的同步运动从而形成一个整体,致使双层网底网箱在2个方向的最大位移均小于单层网底网箱。
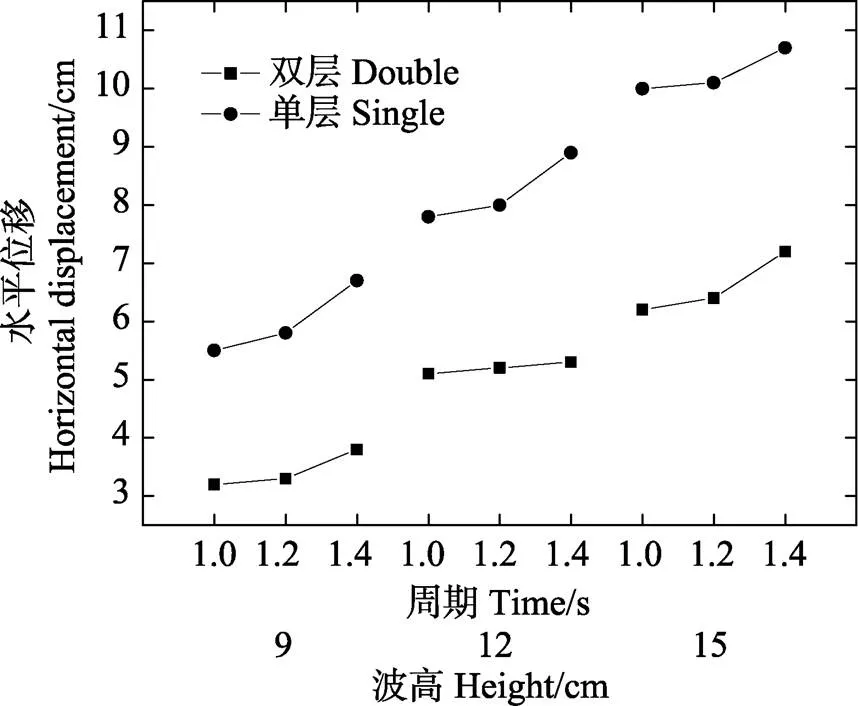
图6 双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱水平位移

图7 双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱垂直位移
双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱在波浪作用下最大倾角变化的比较见图8。从图8可以看出,当波浪工况相同时,双层网底网箱下层网底的最大倾角均大于单层网底网箱,这可能与双层网底网箱中上层网底的同步效应有关。从前面计算机模拟结果可以看出,双层网底网箱的上层网底与下层网底在波浪作用下,可以保持相对平行的状态,2层网底通过绳索相连接,作为整体结构惯性较大,因而加剧了网底的倾斜。此结果与单纯水流作用下,双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱比较恰恰相反。当水流作用时,双层网底网箱的 2层网底倾斜方向相反,由于互相抵消作用而导致双层网底网箱的倾角小于单层网底网箱。

图8 双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱最大倾角
2.3 锚绳力
双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱迎波面最大锚绳力的比较见图9。从图9可以看出,2种结构网箱迎波面锚绳的最大张力随着波高与波周期的增加而增大。其中,在波浪条件相同时,双层网底网箱最大锚绳力均大于单层网底网箱。当波高为9 cm时,双层网底网箱锚绳力略大于单层网底网箱;当波高增加时,双层网底网箱锚绳力明显大于单层网底网箱。这可能与波高较大时,双层网底网箱作同步运动时惯性较大所致。此结果与2种网箱在单纯水流作用时的比较结果也有所不同。崔勇等(2016)研究表明,单层网底网箱与双层网底网箱在水流作用下,无论迎流面还是背流面最大锚绳力均差异不大,究其原因可能与水流作用下双层网底网箱的2层网底的倾斜方向相反有关。
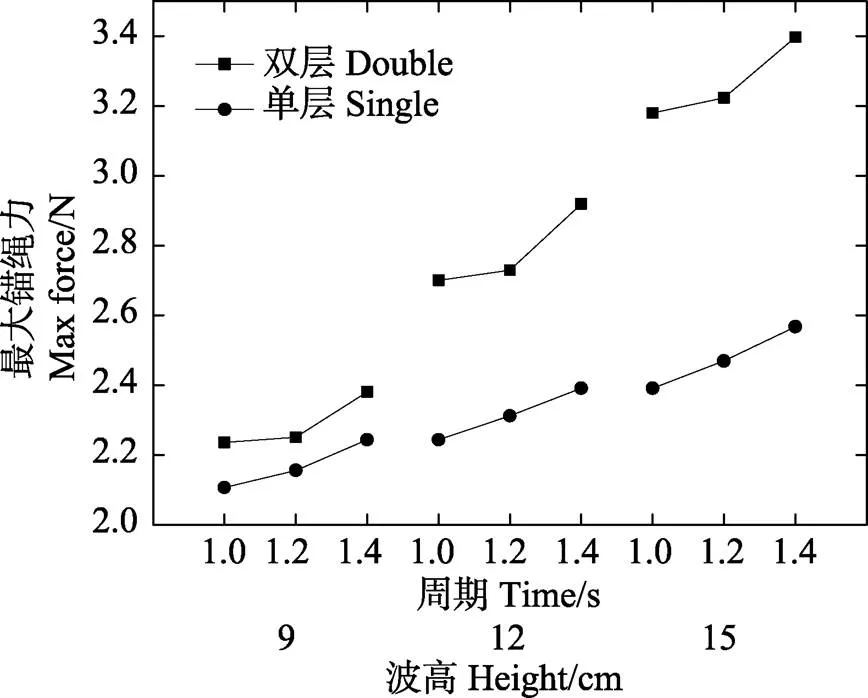
图9 双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱最大锚绳力比较
3 结论
本文利用有限元方法对一种双层网底鲆鲽网箱在波浪作用下的水动力特性进行了数值模拟研究,对上层网底与下层网底的位移与最大倾角进行比较分析,同时,将双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱进行横向对比。从上述比较中可以看出,在几种不同波浪工况作用下,双层网底网箱的上、下2层网底最大倾角差距不大,并且二者的倾斜方向始终一致。2层网底在垂直方向的位移也比较接近,在波浪作用下可以保持相对平行的状态,从而保证网底结构的稳定。在与单层网底网箱比较时可以看出,双层网底网箱中的下层网底最大倾角要大于单层网底网箱,约为单层网底网箱最大倾角的2倍。双层网底网箱与单层网底网箱位移比较时,双层网底网箱中下层网底的位移要小于单层网底网箱,这可能与双层网底网箱中上层网底的连接方式有关。此外,对于波流联合作用下双层网底网箱水动力特性的研究,有待于今后进一步开展。
Incorporated. ANSYS user’s manual. Canonsburg. USA: ANSYS, Incorporated, 2009, 270–275
Cui Y. Guan CT, Wan R,. Numerical simulation of a flatfish cage system in waves and currents. Aquacultural Engineering, 2013, 56: 26–33
Cui Y, Guan CT, Huang B,. Dynamic analysis of the long-line culture facility under waves. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2014, 35(4): 125–131 [崔勇, 关长涛, 黄滨, 等. 波浪作用下筏式养殖结构的动力分析. 渔业科学进展, 2014, 35(4): 125–131]
Cui Y, Guan CT, Li J,. Numerical simulation of the anti-current characteristics of double-bottom cages for flounder fish. Fishery Modernization, 2016, 43(6): 39–44 [崔勇, 关长涛, 李娇, 等. 双层网底鲆鲽网箱耐流特性的数值模拟. 渔业现代化, 2016, 43(6): 39–44]
Cui Y. Study on hydrodynamic characteristics of square flatfish cage. Doctoral Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2012 [崔勇. 方形金属框架鲆鲽类网箱水动力学特性研究. 中国海洋大学博士研究生学位论文, 2012]
DeCew J, Tsukrov I, Risso A,. Modeling of dynamic behavior of a single-point moored submersible fish cage under currents. Aquacultural Engineering, 2010, 43(2): 38–45
Fredriksson DW, DeCew JC, Tsukrov I,. Development of large fish farm numerical modeling techniques with in-situ mooring tension comparisons. Aquacultural Engineering, 2007, 36(2): 137–148
Fredriksson DW, Swift MR, Irish JD,. Fish cage and mooring system dynamics using physical and numerical models with field measurements. Aquacultural Engineering, 2003, 27(2): 117–146
Gui FK, Zhao YP, Xu TJ,. Numerical simulation of dynamic response of a net cage for flatfish in waves. China Ocean Engineering, 2014, 28(1): 43–56
Huang LY, Liang ZL, Song WH,. Experimental study on effect of reducing current velocity by square net cage structure. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2007, 14(5): 860–863 [黄六一, 梁振林, 宋伟华, 等. 方形箱网结构减流效果试验. 中国水产科学, 2007, 14(5): 860–863]
Huang XH, Guo GX, Hu Y,. Numerical simulation of forces and motion deformation of deep-water net cages in waves and currents. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(2): 443−450 [黄小华, 郭根喜, 胡昱, 等. 波流作用下深水网箱受力及运动变形的数值模拟. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(2): 443−450]
Lader PF, Enerhaug B.Experimental investigation of forces and geometry of a net cage in uniform flow. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2005, 30(1): 79–84
Lee CW, Kim YB, Lee GH,. Dynamic simulation of a fish cage system subjected to currents and wave. Ocean Engineering, 2008, 35(14–15): 1521–1532
Li Q, Yang SG. The finite element dynamic analysis for self-elevating platform by ANSYS/multi-physics program. China Offshore Platform, 2003, 18(4): 41–46 [李茜, 杨树耕. 采用ANSYS程序的自升式平台结构有限元动力分析. 中国海洋平台, 2003, 18(4): 41–46]
Tsukrov I, Eroshkin O, Fredriksson DW,. Finite element modeling of net panels using a consistent net element. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30(2): 251–270
Zhao YP, Chen XF, Xu TJ,. Numerical investigation of hydrodynamic properties of gravity cage for flat-fish culture during exposure to wave action. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2012, 19(5): 889–899 [赵云鹏, 陈小芳, 许条建, 等. 波浪作用下一种鲆鲽类方形网箱水动力特性数值模拟研究. 中国水产科学, 2012, 19(5): 889–899]
Numerical Simulation of the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Double-Bottom Cage for Flounder Fish Under Waves
CUI Yong, GUAN Changtao①, HUANG Bin, LI Jiao, GONG Pihai
(Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Qingdao Key Laboratory for Marine Fish Breeding and Biotechnology, Qingdao 266071)
Thedouble-bottom cages for flounder fish tend to move and deform under waves. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out hydrodynamic analysis for the stabilization of flounder fish cages. Herein, a numerical model of deformation of double-bottom cages under waves was established based on the finite element method, and then maximum displacement and the pitch of the double-bottom were calculated. First, results of the upper bottom were compared with that of the lower bottom. Afterwards, the results of the lower bottom of double-bottom cage were compared with that of the single-bottom cage. The simulation results showed that the two bottoms of double-bottom cages were able to stay relatively parallel during wave periods. The maximum displacement and pitch of the two bottoms increased along with not only wave height but also wave period. In addition, the inclined direction of the two bottoms was the same. Under the same wave conditions, the horizontal of displacement and the maximum pitch of lower bottom were larger than those of the upper bottom, but their vertical displacements were not much different. It was found that the difference in pitch between upper and lower bottoms was the largest when the wave height was 15 cm and the wave period was 1.4 s. However, the upper and lower bottoms of the cage did not collide with each other, and the two bottoms of the cage could remain relatively stable. Moreover, under the same wave conditions, the displacement of the lower bottom of the double-bottom cage was less than that of the single-bottom cage, but the pitch of the lower bottom of the double-bottom cage was larger than that of the single-bottom cage. Additionally, the maximum mooring-line force of double-bottom cages for flounder fish was larger than that of single-bottom cages. Furthermore, the study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of double-bottom cages for flounder fish under the combined action of wave and flow should be carried out in the future.
Double-bottom; Hydrodynamic characteristics; Finite element method; Cages for flounder fish
S953.4
A
2095-9869(2019)06-0018-07
10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20180820001
http://www.yykxjz.cn/
崔勇, 关长涛, 黄滨, 李娇, 公丕海. 波浪作用下双层网底鲆鲽网箱水动力特性的数值模拟. 渔业科学进展, 2019, 40(6): 18–24
Cui Y, Guan CT, Huang B, Li J, Gong PH. Numerical simulation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of double-bottom cage for flounder fish under waves. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2019, 40(6): 18–24
* 现代农业产业技术体系建设专项(CARS-47-22)、“一带一路”国家水产养殖科技创新合作项目2018–2020和深远海智能化网箱整装装备产业链协同创新示范项目共同资助 [This work was supported by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-47-22), “The Belt and Road” National Aquaculture Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project 2018–2020, and Deep Sea Intelligent Fish Cage Equipment Industry Chain Collaborative Innovation Demonstration Project]. 崔 勇,E-mail: cuiyong@ysfri.ac.cn
关长涛,研究员,E-mail: guanct@ysfri.ac.cn
2018-08-20,
2018-11-09
GUAN Changtao, E-mail: guanct@ysfri.ac.cn
(编辑 陈 严)

