Dietary Supplementation with Black Garlic Powder Exerts Immunostimulatory Activity in Cyclophosphamide Induced BALB/c Mice
YANG Ming, QIN Ye, HAO Junyu, WU Tao, LIU Rui, SUI Wenjie, ZHANG Min*
(Engineering Research Center of Food Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, Institute for New Rural Development,College of Food Engineering and Biotechnology, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin 300457, China)
Abstract: The present study aimed to investigate the immunostimulatory activity of black garlic powder on immunosuppressed BALB/c mice. Cyclophosphamide was injected to establish an immunosuppressed model. Then, the effect of black garlic powder at doses of 100, 300 and 900 mg/kg on splenic and thymus index, the transformation of splenic lymphocytes, delayed type hypersensitivity, quantity of antibody-producing cells, half hemolysis value (HC50), carbon clearance rate, interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-12 gene expression levels in splenic cells of mice were investigated. The results indicated that all three doses of black garlic powder significantly improved thymus index, antibody production, splenic lymphocyte proliferation and the expression of IL-8 and IL-12 in splenic cells when compared with the model control(MC) group (P < 0.05). In addition, compared with the MC group, black garlic powder at the middle and high doses could significantly enhance splenic index and delayed-type hypersensitivity response (P < 0.05). Moreover, compared with the MC group, black garlic powder at the high dose effectively improved serum hemolysin level and mononuclear macrophage phagocytosis activity (P < 0.05). Thus, black garlic powder appears to be an excellent candidate to improve immune function in BALB/c mice.
Keywords: black garlic powder; BALB/c mouse model; immunostimulatory
Black garlic is obtained from fresh garlic(Allium sativumL.)that has been fermented for a period of time at a high temperature (60-90 ℃) and relative humidity (80%-90%).Compared with fresh garlic, black garlic exhibits more nutritional and physiological effects because of the changes of physicochemical properties[1-2]. In the development of black garlic, oligosaccharides converted into fructose[3], which not only increased the sweetness of black garlic but also reduced the content of volatile sulfide.
Several studies reported that black garlic extract activates helper T cell (Th)1 and Th2 cells by stimulating T lymphocyte of mice splenic and promotes immune regulation by activating cellular and humoral immunity. Feng Yonghui et al[4]found black garlic extracts exhibited better activity for natural killer cells and better secretion ability of the non-specific immune molecule-nitric oxide. In addition, the extract of black garlic inhibited the promotion of Th1 type cytokines, interleukin (IL)-2, interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α. Besides, several studies have reported that black garlic contains kinds of immunological substances such as serine, lysine, VC and trace element zinc etc.[5].
Black garlic powder (BGP) is a powder product of black garlic. As a new garlic product, BGP not only can prolong the storage period, but also reduce transportation, packaging and other costs, and expand its application range. In addition,BGP is nutritional and easy to eat. It can be widely used as ingredients for processed foods. Thus, the objective of this work is to determine whether BGP can improve the immune function of mice and to further provide basic information in the immune regulation ability of BGP.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Materials, animals and reagents
Black garlic were purchased from Dawn Food Co. Ltd..As shown in Fig. 1, BGP (B) processed from black garlic (A)is dark brown powder. In this study, mice were given BGP to verify its immune efficacy.
BALB/c mice were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (Production license number: 2012-0004) and kept in Animal Laboratory of Central Barrier system (Use license number: 2006-0005).
BGP was prepared by differential pressure expansion in laboratory (Tianjin University of Science & Technology);3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), concanavalin A (Con A) and Red Blood Cell Lysis Buffer America Sigma Co. Ltd.; TRIzol reagent America Invitrogen Co. Ltd.; RNA Extraction Kit Beijing Kangwei century Co. Ltd.; SuperRT cDNA first-chain synthesis kit and SYBR Green PCR mixture Beijing Transgen Co. Ltd.. All the other chemicals used in the experiment were of analytical-purity grade.

Fig. 1 Photographs of black garlic (A) and BGP (B)
1.2 Instruments and equipment
DH-101 Oven Tianjin Zhonghuan Experimental Electric Furnace Co. Ltd.; SX2-25-10 Fluorination furnace Tianjin Sanshui Scientific Instrument Co. Ltd.;WK21027 Electromagnetic furnace Guangdong Midea Life Appliance Manufacturing Co. Ltd.; SOX-406 Soxhlet extractor, K9840 Kjeldahl nitrogen determinator Jinan Haineng Instrument Manufacturing Co. Ltd.; TY-150 Flour mill Wuyi Haina Electric Appliance Co. Ltd.;TU-1810PC Ultraviolet spectrophotometer Beijing Puxi General Instrument Co. Ltd.; JX-1000 Differential pressure extruder Shandong Delico Industrial Equipment Co. Ltd..
1.3 Methods
1.3.1 Determination of basic nutritional components of BGP
The water content of BGP was determined according to the method of GB 5009.3–2016. The protein content of BGP was determined according to the method of GB 5009.5–2016.The fat content of BGP was determined according to the method of GB 5009.6–2016. The ash content of BGP was determined according to the method of GB 5009.4–2016. The crude fiber content of BGP was determined according to the method of GB/T 5515–2008.
1.3.2 Grouping of mice and immune model
The establishment of immune model was determined according to the method of Liu Jiancheng et al[6]. After one-week adaptation, the mice were randomly divided into 5 groups consisting of 12 mice each. One group of healthy mice was used as a normal control (NC) group and was treated once per day with physiological saline for 30 days. For Days 1–3,the other 4 groups of mice were given cyclophosphamide at 80 mg/(kg·d) via intraperitoneal injection. For Days 4–30,the mice were administered as follows: model control (MC)group, physiological saline was administered via gavage;three BGP (BGP-L, BGP-M and BGP-H) groups, at 100, 300,and 900 mg/kg BGP were administered via gavage.
1.3.3 Calculation of splenic and thymus indices
After 30 days of gavage, the mice were weighed and killed immediately. The immune organs, splenic and thymus of each animal of all experimental groups were collected after sacrificing. Splenic and thymus of each animal were weighed upon collection. Splenic and thymus indices were calculated based on splenic or thymus mass and animal body mass[7].The calculating formula as formula (1) and (2).

1.3.4 Con A induced splenic lymphocyte transformation
The splenic was removed aseptically and placed in a plate with a proper amount (3-5 mL) of aseptic Hanks solution. Grinding the splenic and making a single cell suspension. Erythrocytes in the splenic lymphocytes were lysed with double distilled water (DDW), splenic lymphocytes were washed twice in sterile Hanks solution and centrifuged at 1 000 r/min for 10 min, and finally suspended in 2 mL complete culture solution.
In 24-well plates, 3 × 106splenocytes from each mice were seeded into two wells, one with 75 μL Con A and the other without Con A. After incubation for 72 h, 0.7 mL supernatant was gently removed from each well, then 0.7 mL of RPMI-1640 (no bovine foetal serum) containing 50 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) was added into each well. The cells were continuously cultured for further 4 h. Finally, 1 mL of acid isopropyl alcohol was added into each well to fully solubilise the formazan precipitate. Then it was packed into 96-well culture plate. The optical density (OD) value was measured at 570 nm[8].
1.3.5 Analysis of delayed type hypersensitivity
Abdominal skin of each mice was depilated with barium sulfide in a range of 3 cm × 3 cm and sensitized with 50 μL dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) solutions for 5 days. 10 μL DNFB solution was evenly applied to the right ear of the mouse (two sides) to attack for 24 h. After the attack, the mice were killed by cervical dislocation and the left and right ear shells were cut off, punched holes to remove ear slices 8 mm in diameter and weighed them. The results were expressed as the mass difference between left and right ears[9].
All the animals were immunized with 2% washed sheep red blood cells (SRBCs) 0.2 mL for 5 days. On Day 6 mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. Single cell suspension of splenocytes was made. Splenic cells were counted under the microscope and its count was adjusted up to 1 × 107cells/mL.50 µL of 10% SRBCs and 200 µL of splenocytes were taken in a test tube containing 0.5 mL top layer. Rapidly mixed,pour into the 6-well plate and smooth the top mixture. These culture plates were incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h. Then 500 μL of complement (1:10) was added to each pore and incubated for 2 h. The plaques were observed under an automatic image analyzer. The average number of plaques in parallel wells was taken as the hemolytic plaque value of the sample, which was expressed as plaque number/106splenic cells[10].
1.3.7 Serum hemolysin analyses
Five days before the end of the administration, mice were injected intraperitoneally with 0.2 mL/d 10% SRBCs and blood from mice orbit was collected. Briefly, both the serum and the guinea-pig serum were diluted with 0.85%saline before used. One millilitre of diluted serum was mixed with 0.5 mL 5% SRBCs in a tube. Then 1 mL diluted guinea pig serum was added into the reaction.
After incubation at 37 ℃ for 30 min, the reaction was terminated in ice. Samples were centrifuged at 3 000 r/min at 4 ℃ for 5 min to remove intact erythrocytes. One millilitre supernatant was collected and mixed uniformly with 3 mL of Kathmandu’s reagent for 10 min. The OD value of the reaction was measured at 540 nm[11]. Then another 0.25 mL 10% SRBC suspension was mixed with 3.75 mL of Kathmandu’s reagent. The OD value was determined as half of the hemolysis value (HC50). The calculation of HC50value is shown in the equation (3).

1.3.8 Determination of mononuclear-macrophage phagocytosis activity
After 30 days of gavage, India ink (0.01 mL/g) was injected into the caudalis vein of the mice. Twenty microlitres of blood sample were collected after 2 min (t1) and 10 min(t2), and was mixed with 2 mL 0.1% Na2CO3solution. The OD of the blood was measured at a wavelength of 600 nm[12].The mononuclear-macrophages phagocytic activity (α) was calculated as formula (4) and (5).
He was very careful not to leave enough space for the dragon to jump out, but unluckily there was just room for his great mouth, and with one snap the king vanished down his wide red jaws16

1.3.9 Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reactions analysis
RNA extraction from splenocytes: The splenic of 0.1 g mice was weighed and ground into powder in liquid nitrogen without enzyme. Moved the powder to the centrifugal tube,adding 1 mL trazole to each tube. After repeated absorption,it was kept for 5 min and dissolved sufficiently. According to general RNA Extraction Kit manual to extract and ensured the ratio of OD260nm/OD280nmof all RNA samples was 1.6–1.8[13].
Establishment of reverse transcription (RT) system: A Kit for First Chain Synthesis of Trans Gen Super RT cDNA.The sample adding system: 5 μL template + 1 μL enzyme +1 μL buffer + 3 μL DDW. The mixture was incubated in polymerase chain reactions (PCR) instrument at 37 ℃ for 30 min. Then the mixture was denatured subsequently at 85 ℃ for 5 min. The synthesized cDNA is stored in the refrigerator of -80 ℃.
Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR): 12.5 μL mixed SYBR,1 μL cDNA, upstream and downstream primers (Table 1)1 μL each, 9.5 μL DDW. Internal reference isGAPDH. The template is cDNA.

Table 1 Primer sequences used for qPCR
The operating procedure is based on the instructions of qPCR mixture kit. The reaction system of 25 μL qPCR was used in this experiment.
1.4 Statistical analysis
Results are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test for multiple comparisons among groups. Statistical analysis and image processing were conducted using Origin 8.0 software.P< 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Basic nutritional components of BGP
The water content in black garlic was greatly reduced by pressure differential expansion technology, and the basic nutritional components of BGP were obtained as shown in the Table 2.

Table 2 Compositions of the BGP
2.2 Effects of BGP on the splenic and thymus indices in BALB/c mice

Fig. 2 Effect of BGP on splenic index (A) and thymus index (B) of BALB/c mice
As shown in Fig. 2, BGP increased the splenic and thymus indices as compared to MC group at the end of the experiment. Compared with the MC group, splenic index in the middle and high dosage of BGP were remarkably increased (P< 0.05). Meanwhile, insignificant variation was found between the splenic index in the low dosage of BGP and the MC group (P> 0.05). On the other hand, all the dosage of BGP displayed a significant enhancement in the thymus index (P< 0.05). Besides, the thymus index also showed a significantly increase with the increasing dosage of the BGP (P< 0.05).
2.3 Effects of BGP on Con A-induced splenic lymphocyte transformation and DNFB-induced delayed type hypersensitivity in BALB/c mice
To investigate the effects of different dosage of BGP to cellular immune function in mice, Con A-induced splenic lymphocyte transformation and DNFB-induced delayed type hypersensitivity were determined. As shown in Fig. 3, all the dosage of BGP displayed a significant enhancement in splenic lymphocyte transformation when compared with MC group(P< 0.05) and a significant difference among each dosage of BGP was observed (P< 0.05). On the other hand, the middle and high dosage of BGP significantly reduced the mass difference between left and right ears in a DNFB-induced delayed type hypersensitivity model (P< 0.05). However, no significant difference was observed among the low and MC groups (P> 0.05).
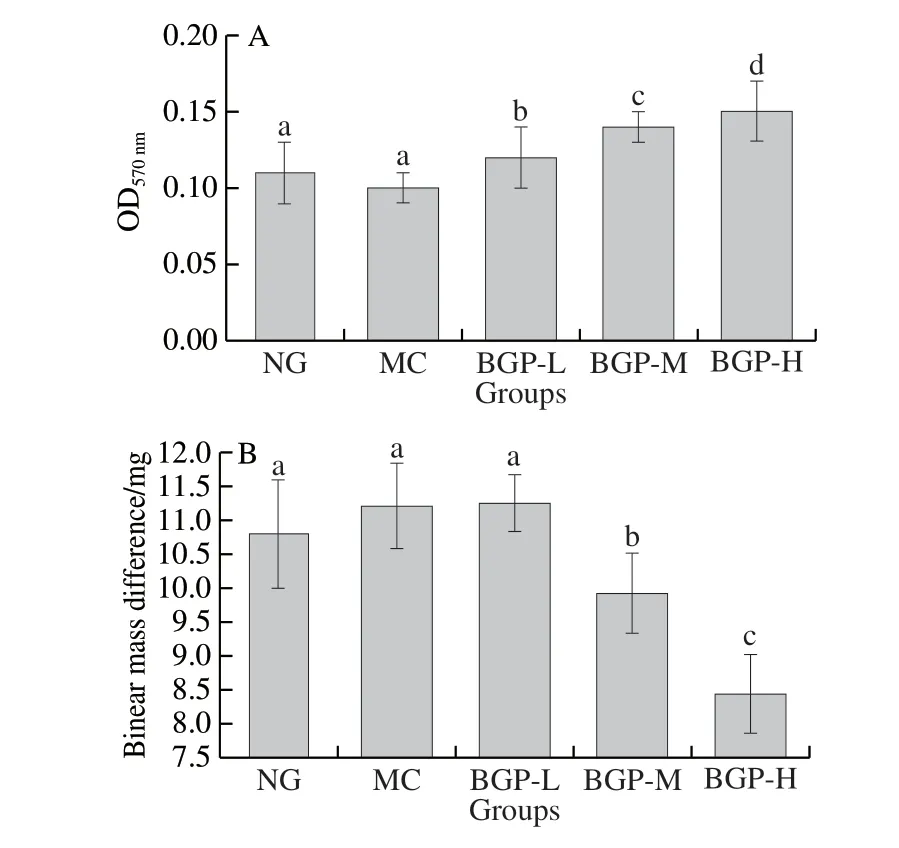
Fig. 3 Effects of BGP on splenic lymphocyte transformation activity (A)and delayed-type hypersensitivity response (B) in BALB/c mice
2.4 Effects of BGP on hemolytic plaque value and serum haemolysin level in BALB/c mice

Fig. 4 Effect of BGP on hemolytic plaque value (A) and HC50 (B) of BALB/c mice
The ability of antibody-producing in mice splenic are presented in Fig. 4A, all the dosage of BGP displayed a significant enhancement in the number of the antibody-producing cells compared with the MC group (P< 0.05).Among the BGP groups, the number of the antibody-producing cells dramatically increased with the dosage increasing(P< 0.05). As shown in Fig. 4B, the maximum value of HC50was achieved in the high dosage of BGP, which significantly higher than other groups (P< 0.05). However, the low and middle dosage of BGP presented an insignificant difference in the production of serum haemolysin when compared with the MC group (P> 0.05).
2.5 Effects of BGP on mononuclear-macrophages phagocytic index in BALB/c mice

Fig. 5 Effect of BGP on mononuclear macrophage phagocytic index of BALB/c mice
As shown in Fig. 5, the phagocytic index of the high dosage of BGP was significantly higher than that of other groups(P< 0.05). However, the low and middle dosage of BGP did not present an increased tendency of mononuclear-macrophages phagocytic index when compared with the MC group and no significant difference was observed among them.
2.6 Effects of BGP on the mRNA levels of cytokines of splenocyte in BALB/c mice

Fig. 6 Effect of BGP on the expression of IL-8 (A) and IL-12 (B)mRNA in BALB/c mice
As shown in Fig. 6, the expression levels of cytokines(IL-8,IL-12) mRNA in the MC group decreased significantly when compared to the NC group (P< 0.05), and the administration of BGP group remarkably up-regulated the mRNA expression levels ofIL-8andIL-12compared to the MC group (P< 0.05).
3 Discussion
At present, research in nutritional immunology has focused on the role of natural food and its ability in improving the immunological response[14]. Nutritional research is targeted towards the development of health food formula to reduce the risk of infection. Among plant derived food, BGP is found to be a rich source of unique bioactive molecules such as flavonoids, organosulfur compounds, dietary fiber,phenolic compounds and others[15]. Recent animal studies have shown that supplementation of BGP extract to mice activates Th1 and Th2 cells by stimulating T lymphocytes in mouse splenic cells and leads to immunomodulation by activating cellular and humoral immune responses of the immune system[16].
Splenic and thymus are the main immune organs of the body so that changes of organ indices are the key indicators of immunity in body[17-18]. Thymus plays an important role in the establishment of immune function and the recovery of immune regulatory function after the loss of immunity. A large number of thymocytes produced by thymus can be used as backup for T lymphocyte when T cells are insufficient.Mature thymocytes can also reach the peripheral organs of the body with blood to assist B lymphocyte forits cellular immune function[19]. The splenic is a large immune organ of the body. The specific immunity of the body mostly occurs in the splenic. It has a certain filtering effect on all kinds of tumor cells and harmful microorganisms[20]. In the present study, the levels of both thymus and splenic indices revealed markedly increased in mice treated with BGP which was able to increase lymph contents in both splenic and thymus so that the mass of thymus and splenic significantly increased in mice.
Splenic lymphocyte transformation activity and delayed type hypersensitivity are two important parameters of cellular immunity. Con A is a non-specific mitotic source. It can promote lymphocyte proliferation and transformation when it acts on lymphocyte alone. When Con A acts on some specific antigens, it has synergistic effect on lymphocyte proliferation and transformation[21]. Mice models of delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) reactions were generated by DNFB-induced subcutaneous sensitization to the ears of mice. By feeding with BGP, the swelling degree of mice’s ears were observed to determine whether BGP could alleviate local inflammation induced by DTH[22]. The present study revealed that there is a significantly increase of splenic lymphocyte transformation activity by feeding with BGP and BGP has a positive effect on attenuating DTH reactions when compared with MC groups.
The ability of secreting antibodies is an important aspect for evaluation of the host humoral immune response. The hemolytic plaque formation assay and serum haemolysin analysis are well-documented models to measure antibody production in response to an antigenic stimulation[23-24]. On one hand, the number of hemolytic plaques reflects the total number of antibody-producing cells in the splenic. The number of haemolytic plaques in antibody level increased significantly, suggesting that the host ability to defend against foreign body invasion was enhanced[25]. On the other hand,the content of hemolysin in the serum of mice was estimated by the content of Hb released by erythrocyte. HC50can reflect the level of antibody produced by immunizing mice, and the content of hemolysin in animal serum can be reflected by measuring the content of hemoglobin[26]. In the present study the number of splenic antibody-producing cells increased significantly in all doses of BGP groups, but only in high doses of BGP group, HC50increased significantly.
As important immune cells in the body, macrophage phagocytosis targeting on xenobiotic acts as a crucial role for early host defence against foreign invasion. Removal of carbon particles from the blood circulation is correlated with an enhanced phagocytic activity[27-28]. Results from this project suggest that the high dose of BGP can effectively improve the phagocytosis ability of mononuclear-phagocyte in mice.
Cytokine is a kind of polypeptide molecule, which can act on the immune system and play an important role in regulating cell interaction, cell proliferation and differentiation. IL-8 is a chemokine derived from a variety of cells[29]. It has chemotaxis to T lymphocyte and basophil[30].After activation, the expression ofIL-8gene was significantly enhanced, and a large number ofIL-8genes were clustered together. The gene clustering can induce resistance of host defense system to bacterial invasion and play an important role in regulating inflammation and immune function[31-33].IL-12is a multifunctional immunoregulatory factor that can stimulate the proliferation of activated T cells[34-36]. In order to evaluate whether BGP activated splenocyte produced cytokines, the mRNA levels ofIL-8,IL-12in splenic were analyzed using qPCR. In this study. The results presented here suggested that the expression ofIL-8andIL-12mRNA suppressed by cyclophosphamide in mice gradually returned to normal level upon treatment with BGP.
4 Conclusion
In summary, BGP, as a new fruit-vegetable powder, showed potential immunostimulatory properties and could reverse immunosuppression by enhancing immune organ’s development,lymphocyte proliferation and monocyte-macrophages phagocytosis. BGP could also induce the expression ofIL-8andIL-12mRNA. Therefore, we suggested that BGP could be used as a novel immunological fruit-vegetable powder for numerous fields of food processing.

