城市历史环境下的景德镇御窑厂遗址申遗研究
项瑾斐/XIANG Jinfei
作者单位:北京国文琰文化遗产保护中心
景德镇是中国首批国家历史文化名城。景德镇因瓷业成镇,具有得天独厚的自然资源并经历上千年的陶瓷生产历史,引领了宋代以后中国瓷业的发展。元代中央集权在景德镇设 “浮梁磁局”,创烧了青花、釉里红、卵白釉等新品种,为明清景德镇的瓷业发展奠定了基础。明朝政府在昌江东岸的珠山建立御窑厂,成为专门烧制御用瓷或办理贡瓷制作和运送的机构,历经600 年一直延续至清末。明清御窑厂将御窑不计成本、精益求精的制瓷技术与御窑厂管理体系有机结合,官窑与民窑分工合作相互促进,整个城市的空间布局和瓷业生产都是围绕御窑厂,由此形成以御窑厂为中心, “沿河建窑,因窑成市”的城市形态(图1、3)。景德镇陶瓷生产也逐渐由宋元以前亦陶亦农的状态,发展为高密集分工合作的手工业复合体,推动景德镇逐步成为全国乃至世界的制瓷中心。
景德镇御窑厂(图2)申报世界文化遗产受到社会各方面的关注。毋容置疑,御窑厂遗址是申遗项目的核心要素,但是关于遗产申报的类型和范围,不同领域的专家有不同的建议:有些认为御窑厂与景德镇城市存在密切的联系,遗产要素应该包含景德镇老城区的历史街区,共同见证中国瓷业发展的鼎盛时期;也有学者提出以御窑厂遗址为核心串联景德镇不同历史时期重要窑址,完整展现瓷业历史发展历程。从乾隆四十八年《浮梁县志》的《景德镇图》、嘉庆《浮梁县志》的《景德镇全图》(图4),可以清晰地辨认出以御窑厂为核心的城市格局;民国三十八年的景德镇地图(图5)显示了南北向主干道与东西巷道形成的鱼骨状城市格局,这些巷道是各个窑厂与码头间运送原料与产品的通道。清末御窑厂解体,景德镇传统手工业开始衰退,建国后景德镇大力发展现代化的陶瓷工业,并经历了以十大瓷厂为代表的辉煌时期(图6)。现在的景德镇城市空间虽然保留了部分历史街道和历史建筑,但是与御窑厂联系密切的渡口码头、官搭民烧的民窑、作坊、瓷行、商铺、会馆等基本消失,街区的历史功能亦完全转变。因此,如果将整个历史城镇认定为遗产要素就会面临真实性与完整性的问题(图7)。
2017 年1 月,景德镇御窑厂遗址列入中国世界遗产申报预备名录,申报文件根据考古研究资料、御窑厂相关历史遗存的保存状况,从时间与空间维度梳理景德镇瓷业发展脉络,研究元代浮梁磁局与明清御窑厂在原料加工、工艺技术、管理体系等产业体系的变化与联系,提出以御窑厂遗址为核心、包含展现景德镇瓷业发展的历代重要窑址,体现御窑厂生产体系的原料开采遗址、渡口码头遗迹、官搭民烧相关的民窑遗址、行帮会馆旧址等共18处遗产要素(图8)。御窑厂遗址体现了景德镇对世界制瓷业发展的重要意义,见证了中国陶瓷对世界审美与生活方式的影响,反映了中国文明对世界文明发展的重要贡献,符合世界遗产突出普遍价值(OUV)的标准ii、iii 和iv。
目前,景德镇申遗的申报角度与价值策略尚待进一步的研究与讨论。景德镇御窑厂遗址列入《世界遗产预备名录》的申报文本(2016 年版)所列入的18 处遗产要素,是分布在景德镇城区及乡村7 个不同区域、不同级别的文物保护单位,其中御窑厂遗址、湖田窑遗址、高岭瓷土矿遗址本身就是国家大遗址项目,各自又包含系统完整、内容丰富的文物遗存,这使申遗工作面临考古研究、保护管理和城市发展的双重压力,存在实际操作性问题(图9)。
近年,景德镇正全面开展产业转型升级、老城改造、名城保护、生态修复等一系列城市复兴的工作,对景德镇申报世界文化遗产既提供契机,也带来挑战。景德镇御窑厂遗址“申遗”工作如何与名城保护、城市更新相协调,建议关注如下方面的问题:
(1)加强申遗对策研究,进一步挖掘御窑厂遗址的核心价值、梳理遗产要素。
申遗研究首先应加强多专业的交流合作,深入开展关于景德镇陶瓷文化在考古学、文化遗产保护、名城保护及手工业传承等领域的专题研究,进一步探讨遗产申报的价值主题,根据不同历史遗存的价值及保存状况,合理调整遗产范围,提高申遗工作的可操作性。根据景德镇明清御窑厂的发展历程、与其他窑场不同时期的关系,高岭瓷土矿遗址、东埠码头、湖田窑遗址、落马桥遗址等这些遗址与景德镇御窑厂的设立,以及制瓷生产体系存在密切的联系,应列入遗产要素。
(2)尽快编制考古研究规划,老城区的更新改造应配合必要的考古勘探工作。
申遗工作应坚持考古先行的原则。考古成果是挖掘景德镇御窑厂遗址核心价值、研究申遗策略的关键性资料,也是遗产地实施各项保护工程的重要支撑。1979-2017 年,御窑厂遗址已经进行了十几次抢救性发掘、两次考古发掘工作。目前已发现

1 景德镇窑址分布情况(左起:五代-宋、元、明、清)
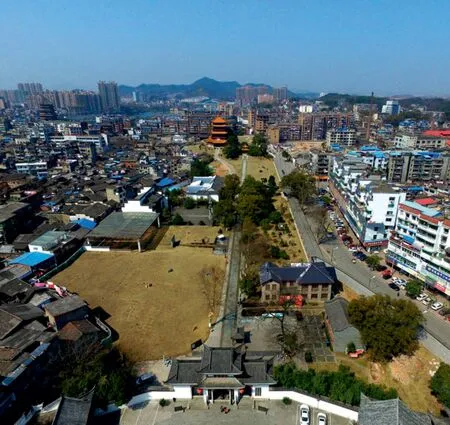

2 景德镇实景

3 景德镇城市空间演变

4a 乾隆四十八年《浮梁县志》的《景德镇图》

4b 嘉庆版《浮梁县志》景德镇全图

4c 嘉庆二十年御厂图(《景德镇陶录》附)

5 民国地图

6 首都博物馆藏青花御窑厂图瓷板
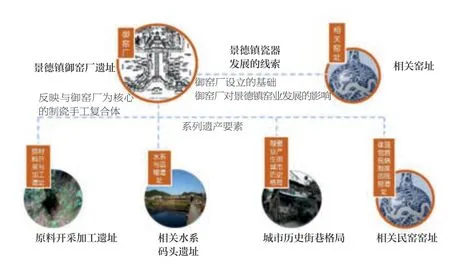
7 景德镇御窑厂遗址的遗产构成框架
项目信息/Credits and Data
项目团队/Project Team: 清华大学建筑设计研究院,北京国文琰文化遗产保护中心/THAD, CHCC of Beijing Guowenyan项目规模/Project Scale: 遗产区/Heritage Area: 303.42hm2,缓冲区/Buffer Zone: 405.1hm2
工作周期/Working Period:
世界遗产预备名录申报文本/Application Text for World Heritage Tentative List: 2015.09-2016.03;
申遗专题研究及文本修编工作/Special Studies and Revision for the Inscription: 2019.09至今/to-day
8 御窑厂周边及历史环境要素
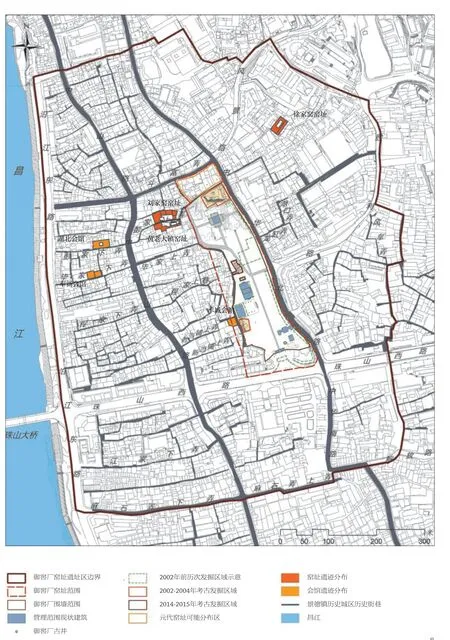
摄影/Photos: 贾玥/JIA Yue(fig.2),庄宇晨/ZHUANG Yuchen(fig.10-13)两组明代窑炉遗址与大量作坊遗址、生活遗迹及瓷业堆积,并探明明代御窑厂东北角和西侧南段的围墙(图10、11)。但是仍有亟待查明与研究的问题:明代御窑厂的格局与范围、明清两朝御窑厂格局及边界的变化;根据《江西大志·陶书》及清代舆图,明清御窑厂应包含管理办公区与作坊区,这两个区域的边界及中路建筑的形制与布局如何?这些是见证明清御窑厂管理与生产特点的重要资料。因此,建议考古工作整合历次的考古成果,并结合御窑厂遗址各项工程实施进度,制定考古工作计划。
御窑厂遗址周边的传统街巷,基本保留了明清时期的主要巷道与名称,街巷内的建筑大量使用附着窑汗的窑砖,体现瓷都传统建筑的风貌特征,这些街巷地下仍埋藏较丰富的地下遗存与瓷业堆积,所以历史街区的保护应是对地上地下历史遗存的整体保护。御窑厂周边的建设工程实施前,已经开展了一些考古勘探工作,建议要特别探明明代御窑厂西界的走向、明清时期御窑厂与街巷之间的联系、明清官搭民烧的民窑遗址分布、民国江西瓷业公司与清代晚期御窑厂的关系等(图12、13),以此进一步明确遗产核心区的边界及御窑厂遗址的管理范围,识别传统街巷内的历史遗迹,为保护遗产的真实性、完整性提供依据;同时也可丰富传统街巷的展示内容,整合遗产阐释的展示主题,使之更符合遗产价值阐释的要求。
(3)景德镇申遗工作应与老城改造、旧厂区更新利用等项目相统筹,实现多规合一、协调管理。
当前景德镇老城改造的核心区域是以御窑厂遗址为中心的传统街巷改造及十大瓷厂之一建国瓷厂的更新利用项目(图12),此区域属于全国重点文物保护单位保护区划范围,也是景德镇御窑厂遗址申遗的遗产区,为推进申遗工作的顺利开展,御窑厂遗址也在进行保护规划修编及遗址保护展示、环境整治工程等专项工程。由于此范围是遗产要素的核心区域,任何项目实施效果都将对遗产真实性、完整性的评估产生影响,这也反映出遗产地的综合管理能力,这些都是遗产申报与评定的关键性问题。因此,景德镇御窑厂及周边的建设项目,在规划设计阶段应加强部门之间的协调、设计团队的沟通,确保各项规划的目标与策略相衔接,并符合御窑厂遗址的核心价值;各类建设工程与保护工程在范围和技术方面能够对接,避免对遗产保护的真实性和完整性产生威胁,以便提高申遗与旧城更新的效率。
总之,御窑厂遗址的申遗与景德镇老城的保护密不可分,对景德镇御窑厂遗址价值的研究,也是对景德镇城市空间及陶瓷文化发展脉络的梳理,而历史城区的保护、陶瓷文化的保护与传承、城市业态的更新与发展也会助力申遗工作的推动。申遗过程,是不断发掘、研究、保护与展示景德镇文化遗产体系的内涵,不断探求城市文化遗产保护可持续的发展途径,实现景德镇所代表的陶瓷文化内涵的延伸活化,推动城市全面发展、提升城市管理水平的过程。□

9 景德镇以御窑厂遗址为核心的主要遗址分布状况

10 御窑厂遗址附近的龙缸弄

11 御窑厂遗址周边的刘家窑
As one of the most renowned nation-level famous historical and cultural cities in China, Jingdezhen has developed into a town driven by its porcelain industry. With unique natural resources and hundreds of years of history on porcelain production, Jingdezhen led the growth of Chinese porcelain industry after the Song dynasty. Prompted by the Imperial Kiln in the Ming and Qing dynasties, Jingdezhen has gradually become a major porcelain production centre, both at home and abroad.
The application of the Jingdezhen imperial kiln as a world cultural heritage has drawn immense attention of the society. Undoubtedly, the imperial kiln site is the core element of the application project, experts in various fields, however, hold different suggestions on the application type and scope.
In 2017, the Jingdezhen imperial kiln site was inscribed on the World Tentative Heritage List. It is proposed in the application documents that the imperial kiln site should be considered as the focus, coupled with important kiln sites that revealed the development of Jingdezhen's porcelain industry across different dynasties, to highlight the key heritage elements such as the raw material mining site for the production of the imperial kiln, the ferry terminal site, the relevant sites on folk kilns officially built for porcelain production by civilians, and the former hall sites on trade associations. The strategy for Jingdezhen's world heritage application needs to be further studied and discussed.
At present, a series of urban revitalisation work, such as industrial transformation and upgrading, old town renovation, famous city preservation and ecological restoration, is comprehensively being conducted in Jingdezhen, which brings both opportunities and challenges to the coming application project. The following issues as suggested should be paid more attention for coordination of world heritage application with the famous city preservation and urban renewal in Jingdezhen:
(1) Improvement of the countermeasures for the world heritage application, further explorations of the core value of the imperial kiln site, and sorting out the key elements of the heritage.
(2) Preparations of archaeological research plan as soon as possible to make sure the renewal and renovation of the old town will not cause any inconvenience to the necessary archaeological exploration.
(3) The efforts on world heritage application should be coordinated with projects such as renovation of the old city as well as the renovation and utilisation of old factories to achieve multiple planning and coordinated management.
In short, the world heritage application of the imperial kiln site is closely related to the preservation of the old town of Jingdezhen. Research on the significance of the Jingdezhen imperial kiln site is also a review of the urban space in the context of development of porcelain culture in this city, protection of the historical town, and protection and inheritance of porcelain culture, as well as the renewal and development of city business categories would impel the world heritage application. The application process lies on continuous exploring, studying, protecting and displaying the connotations of Jingdezhen's cultural heritage system while improvising the sustainable development approaches on protection of urban cultural heritages. Moreover, realising the extension and activation of the porcelain culture connotations represented by Jingdezhen, promoting all-round city development and enhance the city administration level are also utmost critical in such application project.□

12 从御窑厂遗址望向博物馆、建国瓷厂

13 御窑厂遗址南麓的馒头窑炉遗址
参考文献/References
[1] 江建新. 景德镇陶瓷考古研究[M]. 科学出版社, 2013.
[2] 刘朝晖. 明清以来景德镇瓷业与社会[M]. 上海世纪出版集团, 2010.
[3] 北京大学考古文博学院, 江西省文物考古研究所, 景德镇市陶瓷考古研究所. 江西景德镇明清御窑遗址发掘简报[J]. 文物, 2007(05).
[4] 江建新. 元青花与浮梁瓷局及其窑场[J]. 中国国家博物馆馆刊, 2013(06).
[5] 刘昌兵. 景德镇瓷业城市的形成和历史遗存[J]. 文物世界, 2008(03):72-76.
[6] 权奎山. 景德镇明清御窑遗址的考古发现和研究[J]. 故宫博物院院刊, 2013(03).
[7] 赵宏.“官搭民烧”考[J]. 故宫博物院院刊, 1996(01).

