认知无线电网络的分布式路由协议的研究
王燕军
摘 要: 分布式路由算法广泛应用于认知无线电网络(CRNs)。为此,分析多跳CRNs的路由问题,利用无中心的Markov决策过程(DEC?POMDP)建立问题模型,并确保次级用户对主级用户的干扰少于预定阈值,进而控制端到端时延。最后引用多智能体学习算法解决此问题模型,进而形成基于多智能体学习的路由(MALR)。实验结果表明,提出的路由能够控制时延,并降低了干扰率。
关键词: 认知无线电网络; MALR; Markov决策过程; 干扰降低; 多智能体学习; 时延控制
中图分类号: TN915.04?34; TP393 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2019)19?0023?05
Abstract: The distributed routing algorithm is widely used in cognitive radio networks (CRNs). The distributed cooperative multi?agent routing problem in multi?hop CRNs is analyzed. The decentralized partially observable Markov decision process (DEC?POMDP) is used to establish the problem model, which can guarantee that the interference from secondary user to primary user is lower than the predefined threshold, and control the end?to?end delay. The multi?agent learning algorithm is introduced to deal with the problem model, so as to form the multi?agent learning?based routing (MALR). The experimental results show that the proposed routing can control the delay and reduce interference probability.
Keywords: cognitive ratio network; MALR; Markov decision process; interference reduction; multi?agent learning; delay control
0 引 言
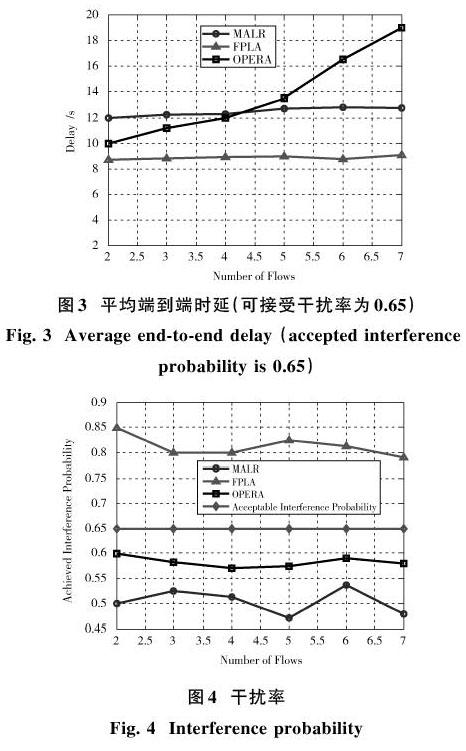
随着无线应用业务的拓展,对无线频谱要求越来越高。当频谱是空闲时,注册用户(也称为主用户,Primary Users,PUs)具有频谱优先接入权。认知无线电网络(Cognitive Radio Networks,CRNs)是解决注册频谱的重新使用問题[1?2]。在CRNs网络内,在不干扰PUs用户传输的条件下,次级用户(Secondary Users,SUs)可以接入已注册频谱。与传统无线网络类似,CRN存在集中网络或分布式(自组网络)形式。在集中网络中,单一基站提供频谱接入和SUs的单跳通信。在分布式网络中,SUs能够与网络内其他用户以多跳方式进行通信。与传统的多跳无线网络不同,CRNs中的路由设计存在挑战,在设计CRNs路由时需要考虑多个因素。首先,路由协议应考虑PUs活动的真实模型。其次,CRNs具有分布式特性。由于SUs不可能使用共同控制信道接收关于网络的分布式信息,仅使用局部信息决策路由,所以路由必须具有分布特性。第三,SUs流量的路由性能严重受到CRNs环境因素的影响,特别是PUs的活动状态和其他SUs的流量。因此,应着重考虑CRNs快速环境变化[3?6]。为此,本文考虑分布式协作多代理的CRNs路由问题。此问题的约束就是因SUs传输导致的PUs的数据包丢失数必须少于预定阈值。为此,利用马尔可夫调制泊松过程(Markov Modulated Poisson Process,MMPP)模拟PUs活动,建立问题模型,再引用多智能体学习求解,从而建立稳定路由。实验数据表明,提出的MALR(Multi?Agent Learning?Based Routing)路由能够有效地降低时延,并控制干扰率。
1 问题描述
1.1 系统模型



5 结 语
本文针对认知无线电网络的路由问题展开分析,并提出基于多智能体学习路由MALR。首先利用Markov决策过程建立问题模型,再利用多智能体学习算法解决路由问题,从而保证数据快速传输,并控制对其他链路的干扰。实验数据表明,与FPLA和OPERA算法相比,提出的MALR路由减少了传输时延,也降低了干扰率。
参考文献
[1] ABDELAZIZ S, ELNAINAY M. Metric?based taxonomy of rou?ting protocols for cognitive radio Ad Hoc networks [J]. Journal of network and computer applications, 2014, 40(3): 151?163.
[2] AI?RAWI H A A, YAN K L A, MOHAMD H, et al. A reinforcement learning?based routing scheme for cognitive radio Ad Hoc networks [C]// Proceedings of 2014 IFIP Wireless and Mobile Networking Conference. Vilamoura: IEEE, 2014: 1?8.
[3] BARVE S, KULKARNI P. Multi?agent reinforcement learning based opportunistic routing and channel assignment for mobile cognitive radio Ad Hoc network [J]. Mobile networks and applications, 2014, 19(6): 720?730.
[4] 沈艳霞,薛小松.无线传感网络移动信标节点路径优化策略[J].传感器与微系统,2012,31(12):42?46.
SHEN Yanxia, XUE Xiaosong. Path optimization strategy of WSNs mobile beacon nodes [J]. Transducer and microsystem technologies, 2012, 31(12): 42?46
[5] 陈友荣,王章权,程菊花,等.基于最短路径树的优化生存时间路由算法[J].传感技术学报,2012,25(3):406?413.
CHEN Yourong, WANG Zhangquan, CHENG Juhua, et al. Lifetime optimized routing algorithm based on shortest path tree [J]. Chinese journal of sensors and actuators, 2012, 25(3): 406?413.
[6] CALEFFI M, AKYILDIZ I F. OPERA: optimal routing metric for cognitive radio Ad Hoc networks [J]. IEEE transactions on wireless communication, 2012, 11(5): 2884?2894.
[7] CHU S C A, ALFA A S. A model for bursty PU channel and its impact on the study of cognitive radio networks [C]// Proceedings of 2013 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference. Sardinia: IEEE, 2013: 461?466.
[8] DING L, MELODIA T, BATALAMA N. Distributed resource allocation in cognitive and cooperative Ad Hoc networks through joint routing, relay selection and spectrum allocation [J]. Computer networks, 2015, 83(3): 315?331.
[9] EL?SHERIF A A, MOHAMED A. Joint routing and resource allocation for delay minimization in cognitive radio based mesh networks [J]. IEEE transactions on wireless communication, 2014, 13(5): 186?197.
[10] GRONDMAN I, BUSONIU L. A survey of actor?critic reinforcement learning: standard and natural policy gradients [J]. IEEE transactions on systems, man and cybernetics, 2012, 42(6): 1291?1307.
[11] KAE W C, HOSSAIN E. Estimation of primary user parameters in cognitive radio systems via hidden Markov model [J]. IEEE transactions on signal processing, 2013, 61(7): 782?795.
[12] LIANG Q, WANG X, TIAN X. Two?dimensional route swit?ching in cognitive radio networks: a game?theoretical framework [J]. IEEE/ACM transactions on networking, 2015, 2(23): 1053?1066.
[13] PING S, AIJAZ A. SACRP: a spectrum aggregation?based cooperative routing protocol for cognitive radio Ad?Hoc networks [J]. IEEE transactions on communications, 2015, 63(8): 2015?2030.
[14] ZHU Quanyan, YUAN Zhou, SONG Jubin, et al. Interfe?rence aware routing game for cognitive radio multi?hop networks [J]. IEEE journal on selected areas in communications, 2012, 30(10): 2006?2015.

