社区老年糖尿病患者管理达标现况研究
吴娟丽 石济顺 陈远虹 刘轶 管佳希 郑羽翔 刘辉 施榕


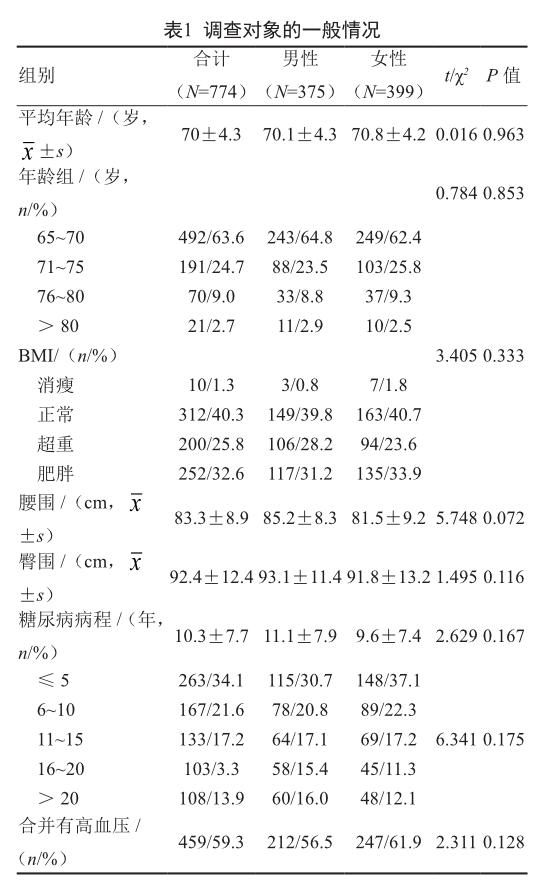
摘 要 目的:调查社区65岁以上老年糖尿病患者管理达标现况,分析管理中的不足之处。方法:采用分层随机抽样法,从65岁及以上老年糖尿病患者中选出符合纳入标准的研究对象774名,年龄65~90岁,平均年龄(70±4.3)岁,糖尿病平均病程(10.3±7.7)年;其中男性375人(48.4%),女性399人(51.6%)。分析身高、体重、腰围、臀围、血脂、血糖、糖化血红蛋白的测量结果。结果:糖尿病各项管理指标的达标率由低到高依次为血压(16.8%)、总胆固醇(38.0%)、体质指数(41.6%)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(46.4%)、空腹血糖(56.3%)、三酰甘油(56.8%)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(65.8%)、糖化血红蛋白(66.3%)。结论:社区65岁以上糖尿病患者管理现况仍未达到理想水平,需继续做好血糖管理,强化血脂、血压管理。
关键词 糖尿病;老年人;管理达标率
中图分类号:R587.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2019)16-0043-04
Study of the status quo of meeting the management standards of elderly diabetic patients in the community
WU Juanli1, SHI Jishun1, CHEN Yuanhong1, LIU Yi1, GUAN Jiaxi1, ZHENG Yuxiang1, LIU Hui1, SHI Rong2
( 1 . Daqiao Community Health Service Center affiliated to School of Medicine of Tongji University (preparation), Comprehensive Prevention and Health Care Department of Daqiao Community Health Service Center of Yangpu District, Shanghai 200090, China; 2. Public Health School of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the current status of meeting the management standards of elderly diabetes patients over 65 years old in the community and to analyze the deficiencies in the management. Methods: A stratified random sampling method was used to select 774 subjects aged 65 years and older with diabetes who met the inclusion criteria, the age ranged from 65 to 90 years, the average age was (70±4.3) years, and the average duration of diabetes was (10.3±7.7) years; there were 375 males(48.4%) and 399 females(51.6%). The measurement results of height, weight, waist circumference, hip circumference, blood lipid, blood sugar and glycosylated hemoglobin were analyzed. Results: The compliance rates of diabetes management indicators from low to high were blood pressure(16.8%), total cholesterol(38.0%), body mass index(41.6%), low density lipoprotein cholesterol(46.4%), fasting blood sugar(56.3%), triglyceride(56.8%), high density lipoprotein cholesterol(65.8%) and glycosylated hemoglobin(66.3%). Conclusion: The management status of diabetes patients over 65 years old in the community has not yet reached the ideal level, and it is necessary to continue to do a good job of blood sugar management, strengthen blood lipid and blood pressure management.
KEY WORDS diabetes mellitus; elderly people; management compliance rate
糖尿病是一種以血糖升高为特征的代谢性疾病。受多种因素影响,老年人群中糖尿病患病率居高不下,加之病程持久、认识不足,容易引发各种急慢性并发症,造成生活质量下降,甚至危及患者的生命[1]。世界卫生组织估计,到2025年全球糖尿病患者预计增长到3亿人,75%发生在发展中国家,我国将成为糖尿病患者人数最多的国家之一[2]。2013年,中国的糖尿病知晓率为36.5%,治疗率为32.2%,控制率仅为49.2%[3]。老年糖尿病人群因病情复杂、体质下降,更容易发生并发症。本研究旨在调查65岁及以上老年糖尿病患者管理达标现况,寻找疾病管理薄弱环节,为提升社区糖尿病患者的治疗率和控制率提供依据。

