显微镜下硬膜下穿刺冲洗治疗腰段脊髓损伤的疗效分析
冯文杰 邓海棠 孔志强 邹凯 张震乾 苏晓恩
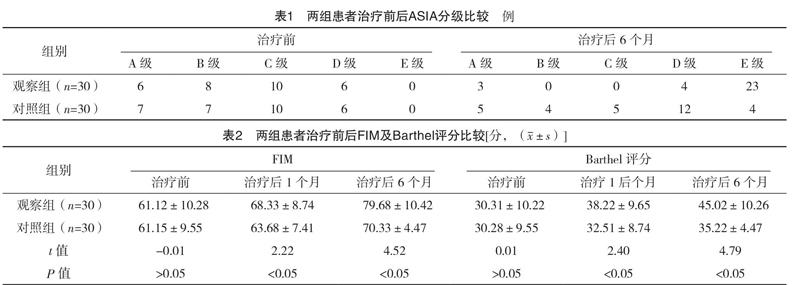
【摘要】 目的:探讨腰段脊髓损伤采取显微镜下硬膜下穿刺冲洗治疗的效果。方法:选取2016年7月-2018年5月本院接收的60例腰段脊髓损伤患者,将患者按照随机数字表法分为对照组(n=30)与观察组(n=30),两组均行椎板减压椎弓根螺钉内固定手术,观察组在此基础上采用显微镜行硬膜下穿刺冲洗损伤部位的脊髓神经,对两组的疗效及相关指标进行观察和比较。结果:治疗后6个月,观察组ASIA分级情况明显优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1、6个月,观察组患者的FIM及Barthel评分均显著高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1、6个月,观察组患者的运动评分明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:对于腰段脊髓损伤患者,采用显微镜下硬膜下穿刺冲洗治疗,能有效改善患者的脊柱神经功能,改善患者的生活自理能力和运动功能,安全性较高,值得推广。
【关键词】 腰段脊髓损伤; 硬膜下穿刺冲洗; 显微镜
【Abstract】 Objective:To discuss the efficacy of microscopic subdural puncture and flushing in lumbar spinal cord injury.Method:60 lumbar spinal cord injury patients treated from July 2016 to May 2018 in our hospital were selected,patients were divided into control group(n=30)and observation group(n=30)according to the random number table method.Both groups were treated with laminar decompression and pedicle screw internal fixation,and the observation group was treated with subdural puncture to flush the injured spinal nerves,the curative effect and relative indexes of the two groups were observed and compared.Result:6 months after treatment,the ASIA grading in the observation group was significantly better than that in the control group,with statistically significant difference(P<0.05).1 and 6 months after treatment,the FIM and Barthel scores of patients in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group,with statistically significant differences(P<0.05).1 and 6 months after treatment,the exercise scores of patients in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:The microscopic subdural puncture and flushing can efficiently improve the spinal nerve function,self-help ability,motor function and clinical safety,it is worthy of promotion.
【Key words】 Lumbar spinal cord injury; Subdural puncture and flushing; Microscope
First-authors address:Zhaoqing First Peoples Hospital,Zhaoqing 526000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.08.007
【摘要】 目的:探討腰段脊髓损伤采取显微镜下硬膜下穿刺冲洗治疗的效果。方法:选取2016年7月-2018年5月本院接收的60例腰段脊髓损伤患者,将患者按照随机数字表法分为对照组(n=30)与观察组(n=30),两组均行椎板减压椎弓根螺钉内固定手术,观察组在此基础上采用显微镜行硬膜下穿刺冲洗损伤部位的脊髓神经,对两组的疗效及相关指标进行观察和比较。结果:治疗后6个月,观察组ASIA分级情况明显优于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1、6个月,观察组患者的FIM及Barthel评分均显著高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗后1、6个月,观察组患者的运动评分明显高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:对于腰段脊髓损伤患者,采用显微镜下硬膜下穿刺冲洗治疗,能有效改善患者的脊柱神经功能,改善患者的生活自理能力和运动功能,安全性较高,值得推广。

