JCI标准下院内急救体系运行及对急救时效性的影响
颜莉

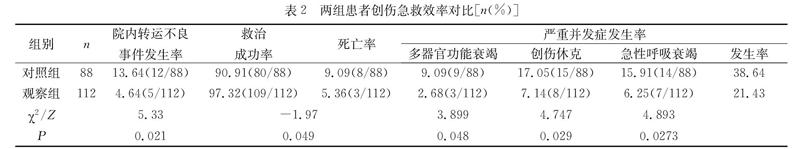
【摘要】 目的:探讨JCI标准下院内一体化快速急救体系新模式对严重创伤患者急救时效性的影响。方法:将JCI标准下院内一体化快速急救体系新模式启动前后的相同时间段内(12个月)严重创伤急救患者分为对照组(88例)和观察组(112例)。对照组实施院内传统急诊救治、转运和交接,观察组实施院前呼叫预警,院内多学科多部门系统协同急救小组紧急干预、抢救和转运的一体化快速急救模式。回顾性分析对比两组患者院内急救时效性。结果:观察组患者院内急救过程中各阶段的平均救治时间均明显较对照组缩短(P<0.05);观察组救治成功率明显高于对照组,观察组院内转运交接不良事件发生率、并发症发生率和死亡率明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:JCI标准下院内一体化快速急救体系新模式可显著提高严重创伤患者急救工作时效性,提高抢救成功率,降低创伤并发症发生率和死亡率,保证了患者医疗安全。
【关键词】 JCI标准;院内急救;一体化;多学科;严重创伤;成功率
[Abstract] Objective:To explore the effect of the new model of integrated rapid first aid system in the lower court of JCI standard on the timeliness of emergency treatment for patients with severe trauma.Methods:The patients with severe trauma in the same time period (12 months) before and after the start of the new model of the integrated rapid emergency system in the JCI standard were divided into the control group (88 cases) and the observation group (112 cases). The control group implemented traditional emergency treatment, transshipment and handover in the hospital, the observation group implemented pre-hospital call warning, and the integrated rapid emergency mode of emergency intervention, rescue and transshipment of the multidisciplinary multi-sector system synergy emergency team in the hospital. Retrospective analysis compared the timeliness of in-hospital first aid in both groups.Results:The average treatment time of the patients in the observation group was significantly shorter than that of the control group (P<0.05). The success rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group. The incidence of adverse events and the incidence of complications in the observation group. The mortality rate was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion:The new model of integrated rapid emergency system in the lower court of JCI standard can significantly improve the timeliness of emergency work for severely injured patients, improve the success rate of rescue, reduce the incidence of trauma complications and mortality, and ensure the medical safety of patients.
[Key words]JCI standard; Hospital first aid; Integration; Multidisciplinary; Severe trauma; Success rate
嚴重创伤患者急救效果和生命安全的救治意义取决于急诊救治的时效性。我国传统的急诊救治受限于院前呼叫预警信息系统配置不完善,院内急救人力资源配备不足,调配机制不合理等情况,严重影响严重创伤患者急救时效性[1]。自2011 年1月1日起,国际联合委员会(JCI)要求通过国际医院标准的医院实施国际患者安全目标(IPSG)。国际患者安全目标的目的是促进病人安全的具体改进。这些目标关注医疗照护中容易出问题的领域,并提出以循证或专家共识为基础的解决方案,充分认识到设计完善的系统是保障提供安全、高质量医疗照护的关键[2-3]。2018年1月,本院参照JCI标准,改造院内急救流程,启动院内一体化快速急救体系,包括成立院前院内紧急呼叫HIS系统平台、院内多

