后路固定融合与非融合治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的对比研究
管波青 杨恺 刘书茂 曲宪芳

【摘要】 目的 對比研究胸腰椎爆裂骨折行单纯后路复位椎弓根螺钉内固定术及后路椎弓根钉内固定结合椎板间和小关节突间融合术治疗后的临床疗效。方法 148例胸腰椎爆裂骨折患者, 根据治疗方法不同分为非融合组(93例)与融合组(55例)。非融合组行单纯后路复位椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗, 融合组行后路椎弓根钉内固定结合椎板间和小关节突间融合术治疗。对比两组手术时间、出血量、术前Cobb角、术后Cobb角、终末随访Cobb角、术前椎体前缘高度、术后椎体前缘高度、终末随访椎体前缘高度及平均随访时间, 记录内固定物取出情况等。结果 非融合组患者手术时间为(90±16)min, 明显短于融合组的(116±23)min, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);非融合组患者出血量(236±14)ml与融合组的(241±26)ml比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。非融合组患者术前Cobb角为(22.9±10.6)°, 术后Cobb角为(9.2±1.4)°, 终末随访Cobb角为(11.2±3.4)°, 术前椎体前缘高度为(12.10±3.60)mm, 术后椎体前缘高度为(23.70±4.00)mm, 终末随访椎体前缘高度为(23.00±4.20)mm;融合组患者术前Cobb角为(22.1±7.6)°, 术后Cobb角为(9.4±1.3)°, 终末Cobb角为(11.4±2.7)°, 术前椎体前缘高度为(12.50±3.20)mm, 术后椎体前缘高度为(23.35±3.90)mm, 终末随访椎体前缘高度为(23.10±4.00)mm;两组患者术前Cobb角、术后Cobb角、终末随访Cobb角、术前椎体前缘高度、术后椎体前缘高度、终末随访椎体前缘高度比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者终末随访时无内固定断裂和椎弓根螺钉拔出。非融合组患者随访18~38个月, 平均随访(26±2)个月, 融合组患者随访19~36个月, 平均随访(25±5)个月, 两组患者平均随访时间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者均取出内固定物, 非融合组局部节段运动恢复良好。结论 对于无需减压的胸腰椎爆裂骨折而言, 采用经后路椎弓根内固定术后无需常规融合, 内定物取出后, 非融合技术可保留局部的运动节段。
【关键词】 胸腰椎爆裂骨折;后路固定融合;后路固定非融合
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2019.11.007
【Abstract】 Objective To compare and study the clinical efficacy of posterior reduction and pedicle screw internal fixation and posterior pedicle screw internal fixation combined with interlaminar and facet fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Methods A total of 148 patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures were divided by different treatment methods into non-fusion group (93 cases) and fusion group (55 cases). Non-fusion group was treated with posterior reduction and pedicle screw internal fixation, and fusion group was treated with posterior pedicle screw internal fixation combined with interlaminar and facet fusion. Comparison were made on operation time, bleeding volume, preoperative Cobb angle, postoperative Cobb angle, final follow-up Cobb angle, preoperative anterior vertebral height, postoperative anterior vertebral height, final follow-up vertebral anterior height and mean follow-up time in two groups, and the removal of internal fixator was recorded. Results Non-fusion group had obviously shorter operation time as (90±16) min than (116±23) min in fusion group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Non-fusion group had no statistically significant difference in bleeding volume as (236±14) ml, comparing with (241±26) ml in fusion group (P>0.05). Non-fusion group had preoperative Cobb angle as (22.9±10.6)°, postoperative angle as (9.2±1.4)°, final follow-up vertebral anterior height as (11.2±3.4)°, preoperative anterior vertebral height as (12.10±3.60) mm, postoperative anterior vertebral height as (23.70±4.00) mm, final follow-up vertebral anterior height as (23.00±4.20) mm. Fusion group had preoperative Cobb angle as (22.1±7.6)°, postoperative angle as (9.4±1.3)°, final follow-up vertebral anterior height as (11.4±2.7)°, preoperative anterior vertebral height as (12.50±3.20) mm, postoperative anterior vertebral height as (23.35±3.90) mm, final follow-up vertebral anterior height as (23.10±4.00) mm. Both groups had no statistically significant difference in preoperative Cobb angle, postoperative Cobb angle, final follow-up Cobb angle, preoperative anterior vertebral height, postoperative anterior vertebral height, final follow-up vertebral anterior height (P>0.05). There were no internal fixation fractures and pedicle screw extraction at the final follow-up of the two groups. Non-fusion group had follow-up time as 18~38 months, with mean follow-up time as (26±2) months, and fusion group had follow-up time as 19~36 months, with mean follow-up time as (25±5) months. Both groups had no statistically significant difference in mean follow-up time (P>0.05). The internal fixator was removed in both groups, and the local segmental motion recovered well in the non-fusion group. Conclusion For thoracolumbar burst fractures without decompression, there is no need for conventional fusion after posterior pedicle fixation. After removal of the internal fixator, the non-fusion technique can preserve the local motion segments.
【Key words】 Thoracolumbar burst fracture; Posterior fixed Fusion; Posterior fixed non-fusion
胸腰椎骨折為最常见的脊柱骨折, 随着椎弓根内固定技术的发展, 经后路复位固定已成为主要治疗方式, 但融合与否还存在争议。作者回顾分析了胸腰椎爆裂骨折行单纯后路复位椎弓根螺钉内固定术及后路椎弓根钉内固定结合椎板间和小关节突间融合术治疗后的临床疗效, 对比两种术式的临床效果, 报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1. 1 一般资料 选取北京市大兴区人民医院骨科2012年
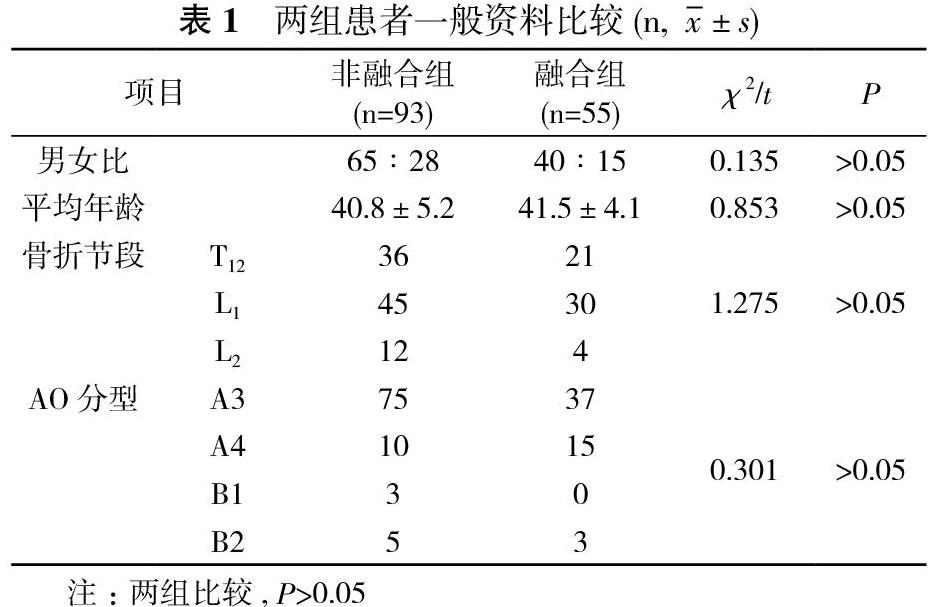
3月~2015年6月治疗的148例胸腰椎爆裂骨折患者, 根据治疗方法不同分为非融合组(93例)与融合组(55例)。纳入标准:单节段胸腰段椎体骨折;AO分型中A3、A4型及B型中椎体压缩>50%、椎管侵占>30%;胸腰椎损伤分型及评分系统(TLICS)评分≥4分;手术方法为伤椎置钉短节段固定;不合并神经损伤, 无需减压;无显著骨质疏松。两组患者一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 具有可比性。见表1。
1. 2 手术方法 两组患者行后路复位椎弓根螺钉内固定术, 所有患者均采用气管插管全身麻醉(全麻), 患者俯卧于手术床上, 采用胸腰部后正中入路, 向两侧剥离椎旁肌, 显露小关节突, 胸椎采用Roy-Camille法置入椎弓根螺钉, 腰椎采用人字嵴法置入。临近椎体均为单轴螺钉(螺钉厂家:ZIMMER, 直径6.5 mm), 伤椎为万向螺钉, 螺钉直径同临近椎体无差异, 伤椎螺钉的长度均较临近椎体短5.0 mm(长度范围30.0~40.0 mm), 螺钉置入完成后, 将连接钛棒给予适度的预弯, 根据骨折类型进行伤椎上下椎体间后方撑开或加压。C型臂透视确认椎体复位良好, 局部后凸纠正后最终锁紧。融合组在上述基础上实施椎板间和小关节突间融合术, 将上方临椎和伤椎关节突关节及椎板间用高速磨钻去关节突间软骨及椎板去皮质化处理, 植入同种异体骨进行融合。计算出血量。放置负压引流管一根并缝合伤口。
1. 3 术后处理 术后使用头孢呋辛、头孢替安或阿洛西林钠预防性抗感染治疗48 h, 引流量<50 ml后拔除引流管, 复查X线片后佩戴胸腰支具下达活动。胸腰支具佩戴3个月。术后1、2、3、6个月及取内固定术时、终末随访时复查X线片。所有患者均在术后1.5~2.0年取出内固定物。
1. 4 观察指标 对比两组手术时间、出血量、术前Cobb角、术后Cobb角、终末随访Cobb角、术前椎体前缘高度、术后椎体前缘高度、终末随访椎体前缘高度及平均随访时间, 记录内固定物取出情况等。
1. 5 统计学方法 采用SPSS18.0统计学软件进行数据分析。计量资料以均数±标准差( x-±s)表示, 采用t检验;计数资料以率(%)表示, 采用χ2检验。P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
非融合组患者手术时间明显短于融合组, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者术前Cobb角、术后Cobb角、终末随访Cobb角、术前椎体前缘高度、术后椎体前缘高度、终末随访椎体前缘高度、出血量比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表2。两组患者终末随访时无内固定断裂和椎弓根螺钉拔出。非融合组患者随访18~38个月, 平均随访(26±2)个月;融合组患者随访19~36个月, 平均随访(25±5)个月;两组患者平均随访时间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者均取出内固定物, 非融合组局部节段运动恢复良好。
3 讨论
胸腰椎骨折是临床上十分常见的一种脊柱创伤。对于椎体压缩程度>90%、TLICS评分>4分的骨折目前均主张行手术治疗, 随着椎弓根螺钉技术的发展, 目前大部分胸腰椎骨折的病例均可采用经后路复位椎弓根螺钉技术[1-3]。但是否融合仍有争议。
为了保持脊柱的稳定性, 传统认为脊柱手术应进行融合。而且有学者认为不行融合术是断钉、螺钉松动等并发症的重要原因, 李想等 [4]回顾性分析了采用后路短节段椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰段爆裂骨折, 并对比术中行后外侧植骨融合与不行植骨融合临床疗效, 其进行研究后认为非融合手术可以减少手术时间及术中出血量;但在维持后凸矫正度数方面差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);而融合手术在减少内固定松动、防止内固定断裂方面具有显著的优势。考虑目前的医疗环境, 建议在使用后路短节段椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰段爆裂骨折时常规采取植骨融合技术。
但有研究表明, 胸腰椎骨折融合后临近节段退变明显增加[5, 6], 而且限制脊柱活动。因此, 许多学者在不断总结和分析非融合后的临床结果, Chou等[7]进随机对照研究, 平均随访134个月发现, 融合和非融合技术在局部后凸角度的维持和丢失方面无显著差异, 在断钉和断棒发生率方面无差异, 但非融合患者在取出内固定物后可恢复局部的节段运动。Lan等[8]对Pubmed进行检索纳入445例病例进行的Meta分析结果表明, 对爆裂的胸腰段椎体骨折, 单独进行后方椎弓根螺钉内固定而不进行融合足以提供满意的临床和放射学结果, 而且非融合组还有着更少的出血量、更短的手术时机、更好的节段运动。
植骨融合之后会增加临近节段的应力, 加速退变。另外, 为恢复节段运动, 应取出内固定物, 本研究的两组患者均取出了内固定物, 发现非融合组局部节段运动恢复良好。本组融合患者采用的是椎板间和小关节突间植骨融合, 同传统的横突间植骨融合相比, 无需扩大暴露, 因此有采用相似融合方法的研究结果显示, 融合组患者并不会过度增加出血量[9-11]。
综上所述, 对于无需减压的胸腰椎爆裂骨折而言, 采用经后路椎弓根内固定术后, 无需常规融合。内定物取出后, 可保留局部的运动节段。
参考文献
[1] Wei FX, Liu SY, Liang CX, et al. Transpedicular fixation in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures:monosegmental fixation versus short-segment instrumentation. Spine, 2010, 35(15):E714.
[2] Toyone T, Tanaka T, Kato D, et al. The treatment of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite grafting following indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation:A prospective study. Spine, 2006, 31(3):208-214.
[3] Yaldiz Can, Asil Kiyasettin, Ozkal Birol, et al. Thoracolumbar burst fractures requiring instrumented fusion:Should reducted bone fragments be removed? A retrospective study. Neurologia I Neurochirurgia Polska, 2015, 49(6):358-366.
[4] 李想, 王以朋, 邱貴兴, 等. 后路融合与不融合结合短节段椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰段脊柱爆裂骨折的系统评价. 中国骨伤, 2011, 24(1):5-9.
[5] Aiki H, Ohwada O, Kobayashi H, et al. Adjacent segment stenosis after lumbar fusion requiring second operation. J Orthop Sei, 2005, 10(5):490-495.
[6] Sehulte TL, Leistra F, Bullmann V, et al. Disc height reduction in adjacent segments and clinical outcome 10 years after lumbar 360 degrees fusion. Eur Spine J, 2007, 16(12):2152-2158.
[7] Chou PH, Ma HL, Wang ST, et al. Fusion may not be a necessary procedure for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spines:a follow-up of at least ten years. Spine, 2006, 3l(23):1724-1731.
[8] Lan T, Chen Y, Hu SY, et al. Is fusion superior to non-fusion for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci, 2017, 22(5):828-833.
[9] 高峰, 张智达, 任应清, 等. 胸腰椎爆裂骨折后路内固定手术中融合与非融合手术疗效的比较研究. 中国现代医生, 2017, 55(2):56-59.
[10] 雷飞, 叶飞, 周庆忠, 等. 后路短节段固定融合与非融合治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的比较研究. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016(9):1111-1117.
[11] 张晓林, 马信龙, 陈长宝, 等. 后路短节段固定非融合方式治疗严重胸腰椎爆裂骨折. 中华创伤杂志, 2013, 29(6):493-497.
[收稿日期:2018-09-25]

