Investigations on the Performance of the Blending Natural and Artificial Graphite for Lithium ion Battery
倪强 韦林玲 黄煜 熊永莲
【Abstract】In this work, it was found that the improved battery performance such as thermal stability and cycle performance with the blending of nature and artificial graphite.
【Key words】Natural graphite; Artificial graphite; Blending
中圖分类号: TM912.9文献标识码: A文章编号: 2095-2457(2019)11-0121-002
DOI:10.19694/j.cnki.issn2095-2457.2019.11.055
0 Introduction
Graphite is widely used as a negative material for lithium ion batteries with high reversible capacity and good electrochemical performance. Natural graphite has its shortcomings with lower 1st efficient and poor cycle performance. Artificial graphite has lower capacity and high cost. The blending graphite will show the better performance[1].The major analytic tools for the results including ARC, impedance spectroscopy,XPS, CV, SEM, Raman spectroscopy,Mercury Porosimetry and XRD in conjuction with standard electrochemical technical.
1 Experimental
Natural graphite A(>99%, spherical-like, BET: 1.6m2/g, D50:18.3), artificial graphite B(>99%, flake-like, BET:4.2m2/g, D50:21.8 ), blending negative C (50%A+50%B) and all materials in this work are purchased from commercial materials company. Electrochemical performance was performed with CR2430 type coin cell with Li anode and 18650 type cell with LiCoO2 as cathode. The negative electrode was prepared by 97.5% graphite, 1% carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and 1.5% styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) coated on the copper foil and pressing density of 1.6. 96%LiCoO2, 2% Conductive agent and 2%PVDF were mixed to prepare for positive electrode. The electrolyte was 1.0Mol/L LiPF6 in EC+EMC+DMC+FB with 3:3:3:1 volume ratio. The sample preparation to be tested is seen everywhere. The cycles were performed at 1C in the voltage range of 3.0-4.2V at room temperature.
2 Results and Discussion
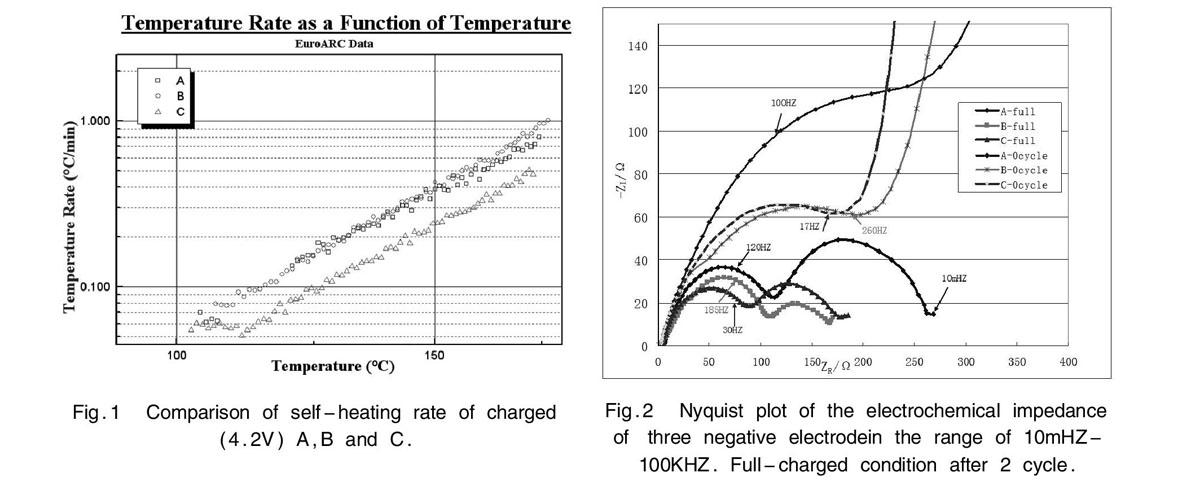
Fig.1 showed the thermal stability of three negative electrode by fully charging for 18650 type cells by ARC ( THT,UK).The data were accordance with the hotbox (150℃) results. It was found that blending negative C(50%A+50%B) showed a comparatively lower exothermic behaviour. It meant that the blending negative indicated more thermal stability. In addition,the blending negative showed better cycling performance than the other two. It is well known that cycling performance is affected by many factors such as SEI on the negative electrode surface, arrangement of active particles on the current collector, ionic conductivity of the electrolyte, etc. Here we focused on the arrangement of graphite particles on the copper foil. It was known that morphology (particles shape) was an important factor. Although the arrangement of spherical-like active particles on the foil is adopted closet-packing, the gap between particles exsisted and less conductivity occured. The flake-like particles were easily to cracked and lower porosity which affected the SEI under the high pressing density. In this way, soakage of electrolyte decreased and the tendency of Li deposit increased. Here, the blending of spherical-like and flake-like graphite compensated for the shortcomings of single materail. Flake-like graphite can fill into the gap to improve the particles contact and spherical-like graphite buffers the pressure on the flake-like graphite surface[2]. Porosity results indicated extensive pore structure of the blending negative. From EIS (Fig.2) and XPS data, SEI film was formed more effectively on blending negative surface[3-4].

