基于Fourier变换离散化的连续小波变换频域算法
易 华
基于Fourier变换离散化的连续小波变换频域算法
易 华
(井冈山大学数理学院,江西,吉安 343009)
对于固定的尺度, 小波变换是待分析信号与小波基函数的线性卷积。当小波基函数的Fourier变换有显式表达式时, 利用其Fourier变换进行线性卷积称为小波变换的频域计算方法。由于线性卷积的长度大于信号的长度, 因此, 选取线性卷积中的哪一部分作为小波变换的系数也是一个亟需回答的问题。本文利用Fourier变换的离散化和离散Fourier变换的关系由小波变换时域算法推导了小波变换频域算法,证明了时域算法与频域算法的等价性; 解释了这两种方法分别应该选取线性卷积中的哪一部分作为小波变换的系数; 分析了频域算法产生边界效应的原因; 给出了频域算法中参数的选取方法, 以便克服边界效应。时间复杂度分析以及数值实验均表明了频域算法至少比时域算法减少了1/3的运行时间。
连续小波变换;Fourier变换;离散时间Fourier变换;离散Fourier变换;线性卷积;周期卷积
0 引言
连续小波变换的算法大致分为两类。第一类快速算法依赖于双尺度方程,得到近似的低通、高通滤波器系数,从而小波变换系数可以迭代求解[1]。这类算法的时间复杂度为Ο(N)[1-2]。但是,此类算法限制了尺度的取值范围,例如限制尺度取二进尺度或者整数值。而且近似的滤波器系数使得其在某些应用中,计算精度不够高。
第二类快速算法直接对连续小波变换的积分表达式离散化,因此要求小波函数的解析表达式是显式给出的。例如Morlet小波、Mexican hat小波等。此类方法的代表有直接数值积分法,基于Mellin变换的快速算法[3-5],基于调频Z变换的方法[6]等。
由于小波变换可以写为信号与小波函数的线性卷积,线性卷积在一定条件下等价于循环卷积,循环卷积又可以转化为频域的乘法。而时频域的转换可以采用FFT、IFFT快速算法。因此,第二类连续小波变换算法的另外一个代表为基于FFT的快速算法,其时间复杂度为Ο(N log(N))。基于FFT的快速算法又可以分为时域算法与频域算法。如果直接对小波函数在时域进行采样,再利用线性卷积函数与信号进行卷积,此方法称为时域算法。如果信号与小波函数进行卷积时,直接利用小波函数的频域表达式进行采样,再与信号的频域表达式进行点点相乘,再进行IFFT,则称此方法为频域算法。
频域算法的精度较高,且这类算法被广泛用于各种开源软件中。例如,Torrence[7]采用连续小波变换方法分析了ENSO数据,并在http://paos. colorado. edu/research/wavelets/给出了计算连续小波变换的源代码。其他的包含连续小波变换算法的开源软件有JLAB(http://www. jmlilly.net)[8],以及Wavelab (http://www-stat.stanford.edu/~wavelab)[9-10]。
但是,频域算法应该注意处理边界效应。虽然文献[7]给出了处理边界效应的一种方法,但是,根据笔者了解的文献来看,边界效应产生的原因未有报道。
Matlab小波工具箱也有实现连续小波变换算法的函数“cwt”,该函数是时域算法的典型代表。但是,其计算精度低。文献[11]摒除了“cwt”函数中冗余且带来误差的差分运算,计算精度有所提高。但是,文献[11]中的连续小波变换方法以及“cwt”函数均涉及到小波基函数的某种近似。文献[12]进一步改进了文献[11]的方法,计算精度较文献[11]有显著提高。
文献[12]中的数值实验结果表明,时域方法和频域方法的计算精度几乎完全一样,揭示了这两种方法的某种等价性,但是相应的等价性理论还不够完备。
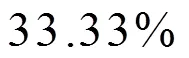
本文在第1节介绍了基本的定义、定理以及之前的工作。在第2节,定理2.1揭示了时域算法、频域算法的等价关系。同时也说明了时域算法、频域算法分别应该选取线性卷积的哪些系数作为小波变换的结果。定理2.2指出了频域算法克服边界效应的方法。定理2.3对比了时域算法、频域算法的时间复杂度。第3节给出的数值实验验证了上述理论结果。第4节为本文的小结。
1 基本的定义、定理以及之前的工作
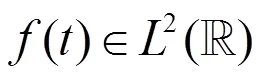
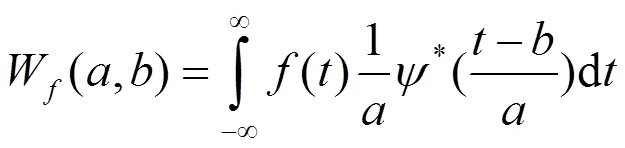
连续小波变换可以写为卷积的形式[9]
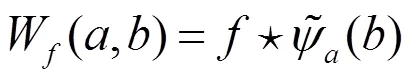
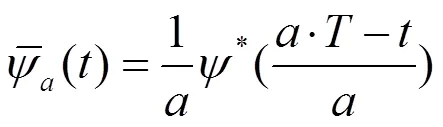
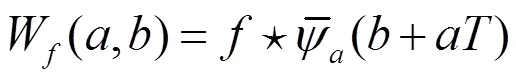
由(4)式离散化,得到了连续小波变换的时域算法。


线性卷积的计算可以根据线性卷积的定义进行计算,也可以采用基于FFT的快速算法。
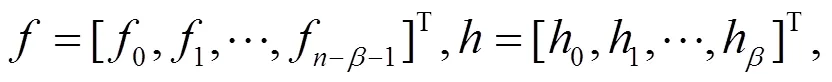

则
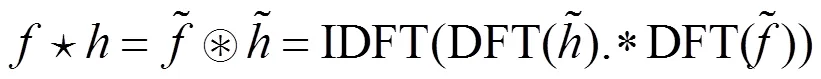

利用Fourier Parseval公式,由(1)定义的连续小波变换可以写为频域积分的形式:

这里
(8)


附注1.4 该算法中有一个参数需要预先给定,算法的推导未给出选取的方法。文献[10]将选为信号的长度,该方法的好处在于信号的频谱可以直接由信号的离散Fourier变换得到,同时离散Fourier反变换后得到的结果长度也为。只是,当数据本身不具有周期性质时,该方法得到的连续小波变换具有边界效应。
在本文的下一小节,将由连续小波变换时域算法推导频域算法。
2 本文的工作
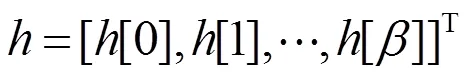
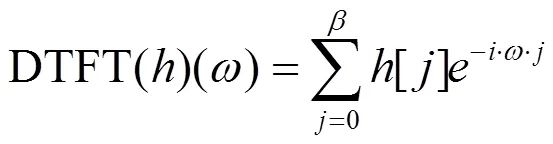
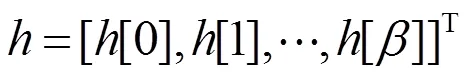
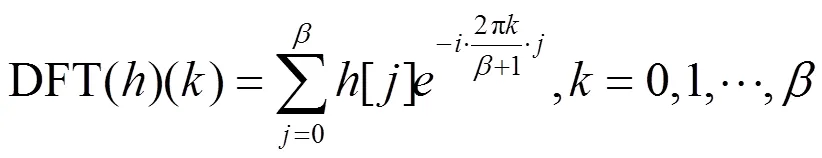
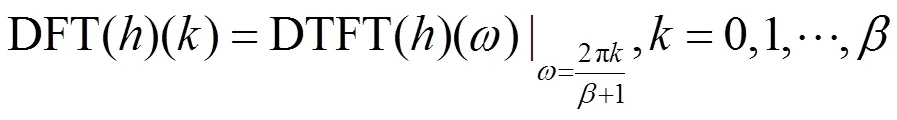
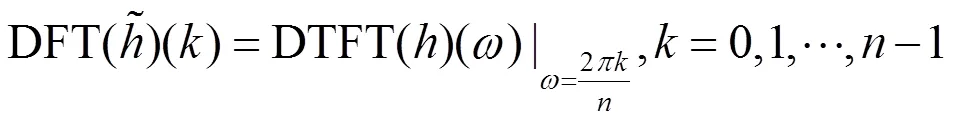

另外一方面,
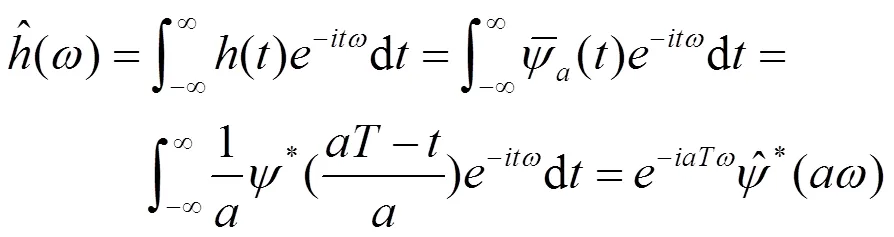
所以,(14)得到了证明。
引理2.3表明小波变换时域算法可以由(15)式进行计算。

则

从而

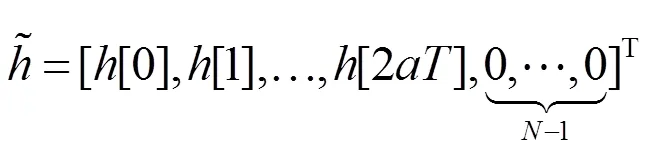
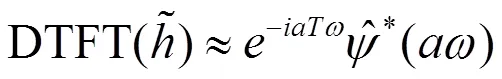
进一步,
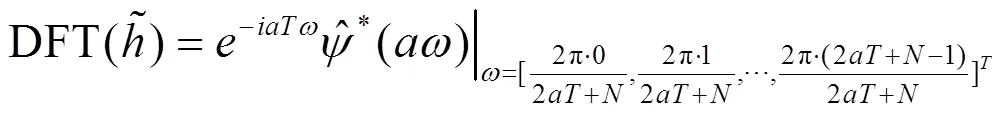
由定理1.2,可知
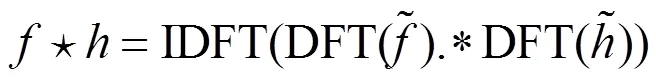
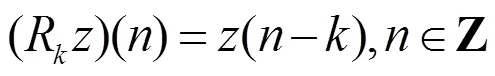
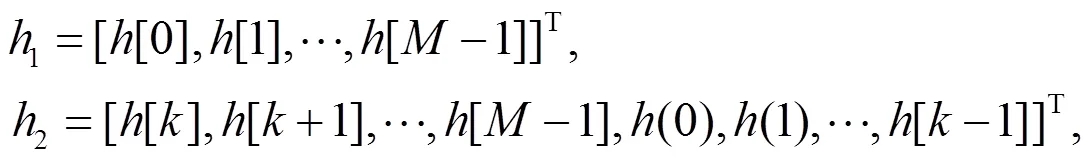
则
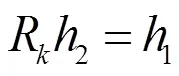

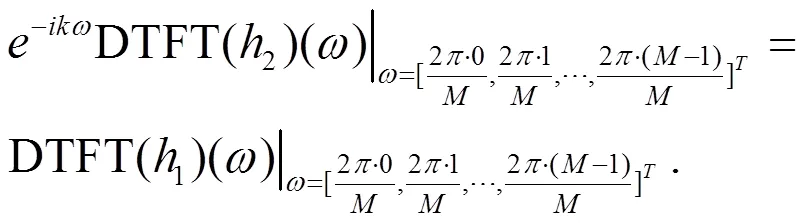

从而

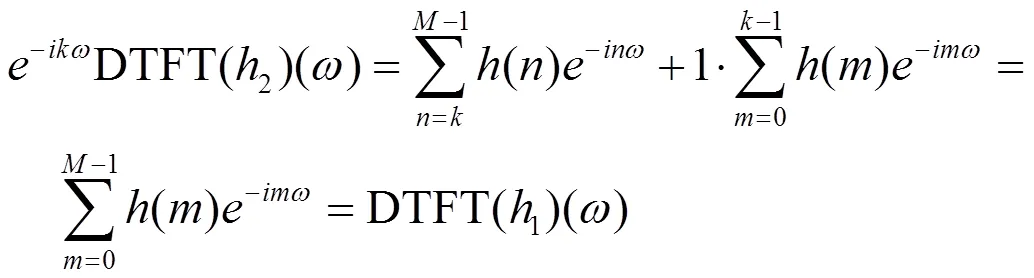
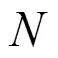
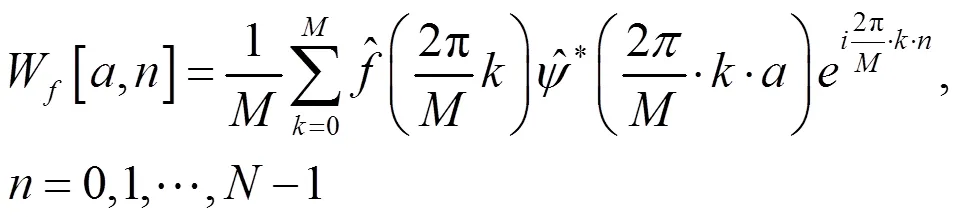
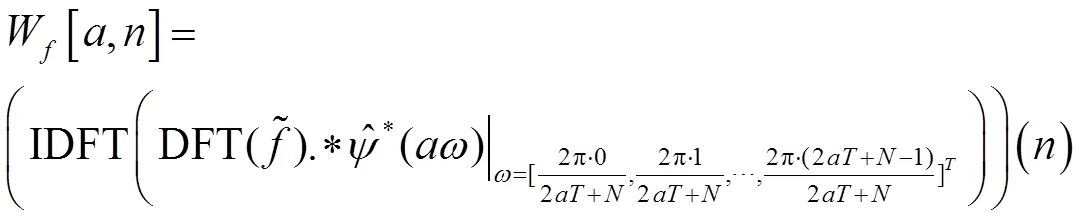

对比时域算法(15)式与频域算法(29)式,可以知道时域算法与频域算法的滤波器的离散Fourier变换分别为

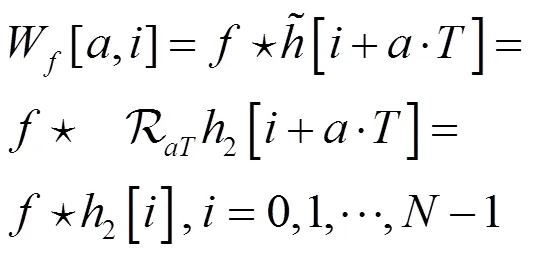
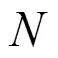
下文的数值实验也表明该选取方法可以避免边界效应的产生。
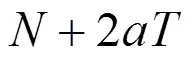
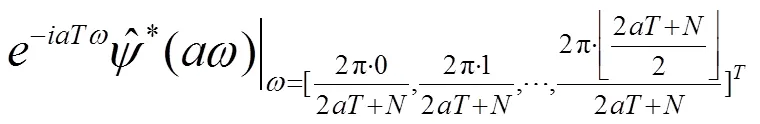
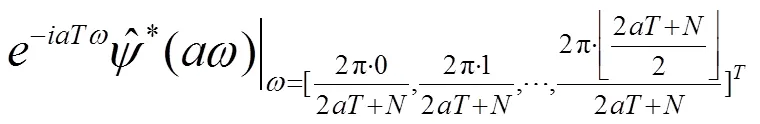
3 数值实验

图1 Matlab产生的长度为1024的信号以及时频图(三个时频图分别采用了时域算法、Wavelab中的算法[10]以及频域算法)
图1中的(b,c,d)是对(a)中信号进行连续小波变换后的时频图。所采用的基本小波为Morlet小波

图2为频域算法与时域算法得到的小波系数模值的误差图。这里最大的误差为3.2872e-15。
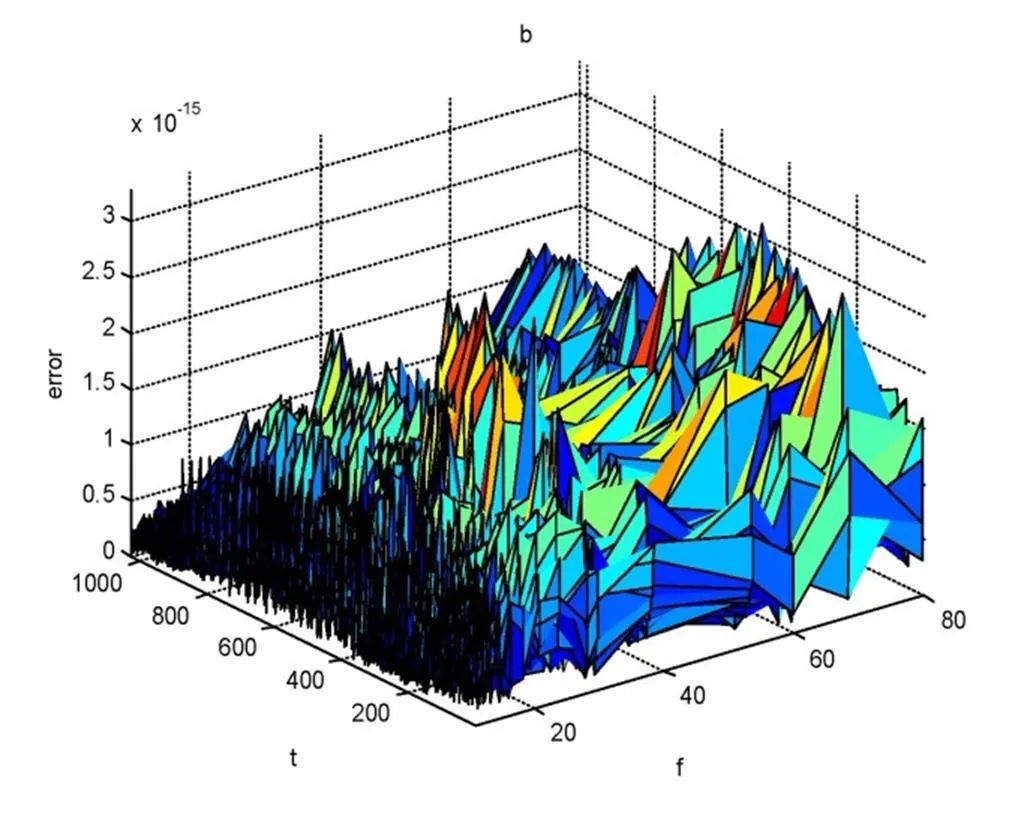
图2 图1中(d)与(b)的误差,即频域算法与时域算法小波系数的误差。这里最大的误差为3.2872e-15。
为了比较时域算法与频域算法的运行时间,需要将这两种算法在相同的运行环境下独立运行多次。再取每次运行的平均时间进行比较。
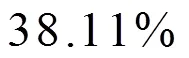
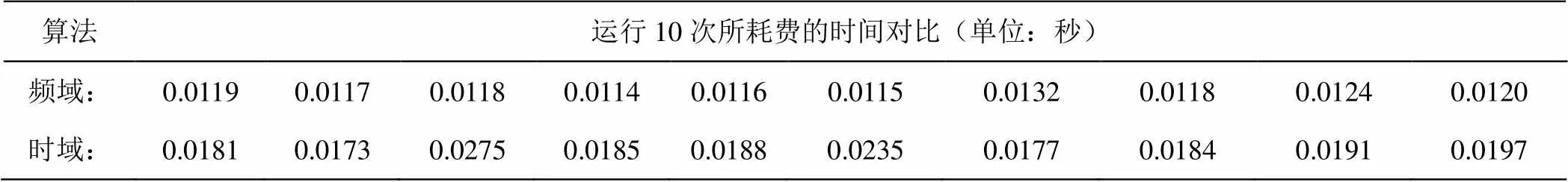
表1 采用频域算法与时域算法运行图1中的程序所耗费的时间对比
4 小结

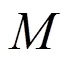
[1] Leigh G M. Fast FIR Algorithms for the Continuous Wavelet Transform From Constrained Least Squares[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1):28-37.
[2] Vrhel M J, Lee C, Unser M. Fast continuous wavelet transform: A least-squares formulation[J]. Signal Processing, 1997,57(2):103-119.
[3] Alotta G, Paola M D, Failla G. A Mellin transform approach to wavelet analysis[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science & Numerical Simulation, 2015,28(1-3):175-193.
[4] 张彤,杨福生. 基于Mellin变换的连续小波变换快速算法[J]. 信号处理, 1996(4):342-349.
[5] 王东伟,应怀樵. 一种基于Mellin变换的连续小波变换快速算法[J]. 信号处理, 1999(3):278-280.
[6] Jones D L, Baraniuk R G. Efficient approximation of continuous wavelet transforms[J]. Electronics Letters, 1991,27(9):748-750.
[7] Torrence C, Compo G P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1998,79(79):61-78.
[8] Lilly J M, Olhede S C. Higher-Order Properties of Analytic Wavelets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009,57(1):146-160.
[9] Mallat S. A wavelet tour of signal processing the sparse way[M]. Academic:Academic press, 2008.
[10] Buckheit J B, Donoho D L. Wavelab and reproducible research[M]. Springer:Springer press, 1995.
[11] 赵元英,袁晓,魏永豪.序列信号连续子波变换的MATLAB方法实现[J].四川大学学报:自然科学版, 2006,43(2):325-329.
[12] Yi H, Chen Z, Cao Y. High Precision Computation of Morlet Wavelet Transform for Multi-period Analysis of Climate Data[J]. Journal of Information and Computational Science, 2014,11(17):6369-6385.
[13] Yi H, Shu H. The improvement of the Morlet wavelet for multi-period analysis of climate data[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2012,344(10):483-497.
[14] Mallat S G. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing[J]. The Sparse Way, 2009,31(3):83-85.
[15] Proakis J G. Digital signal processing: principles, algorithms, and application-3/E[M]. Prentice: Prentice- Hall of India,1996.
[16] Frazier M W. An Introduction to Wavelets Through Linear Algebra[M]. Springer:springer press, 1999.
The Frequency Domain Algorithm of Continuous Wavelet Transform Based on the Discretization of Fourier Transform
YI Hua
(School of Mathematics and Physics, Jinggangshan University, Ji’an, Jiangxi 343009, China)
For a fixed scale, continuous wavelet transform(CWT) is a linear convolution of signal and wavelet function. Because the length of a linear convolution is larger than that of a signal, which part of linear convolution should be chosen as the wavelet coefficients is a question that need an answer. If the Fourier transform of wavelet function has explicit expression, the expression can be exploited to calculate the linear convolution, which method is known as the frequency-domain algorithm of CWT. In this paper, the frequency-domain algorithm of CWT is deduced from the time-domain algorithm of CWT by exploiting the relationship of the discretization of Fourier transform and the discrete Fourier transform. Four results are given. Firstly, the equivalent relation of these two algorithms are proved; Secondly, for time-domain method, the middle coefficients of linear convolution, while for frequency-domain method, the first coefficients of linear convolution are equal, and are the right wavelet coefficients. Thirdly, how to choose the parameter of the frequency domain algorithm is given by the theoretical derivation, which can conquer the boundary effect of frequency-domain method. In the end, the time complexity of the frequency domain algorithm of CWT is lower than that of the time domain algorithm, which is demonstrated by theoretical analysis and numerical experiments.
continuous wavelet transform; Fourier transform; discrete Fourier transform; linear convolution; circular convolution
1674-8085(2019)03-0001-08
O244
A
10.3969/j.issn.1674-8085.2019.03.001
2019-01-18;
2019-03-02
江西省自然科学基金项目(20161BAB201017)
易 华(1973-),男, 湖北松滋人,讲师,博士,主要从事小波分析及其应用研究(E-mail:876145777@qq.com).

