Antenna Selection and Power Allocation Design for 5G Massive MIMO Uplink Networks
Hongyuan Gao*,Yumeng SuShibo ZhangMing Diao
1College of Information and Communication Engineering,Harbin Engineering University,Harbin 150001,China
Abstract: Massive MIMO is one of the key technologies in future 5G communications which can satisfy the requirement of high speed and large capacity.This paper considers antenna selection and power allocation design to promote energy conservation then provide good quality of service (QoS) for the whole massive MIMO uplink network.Unlike previous related works,hardware impairment,transmission efficiency,and energy consumption at the circuit and antennas are involved in massive MIMO networks.In order to ensure the QoS,we consider the minimum rate constraint for each user and the system,which increases the complexity of power allocation problem for maximizing energy and spectral efficiency in massive MIMO system.To this end,a quantum-inspired social emotional optimization (QSEO) algorithm is proposed to obtain the optimal power control strategy in massive MIMO uplink networks.Simulation results assess the great advantages of QSEO which previous strategies do not have.
Keywords: 5G;massive MIMO;antenna selection;power allocation;quantum-inspired social emotional optimization
I.INTRODUCTION
With the increasing demands of high-speed communication and rapid development of wireless networks,the carbon emissions and operating costs caused by wireless communication are increasing day by day [1].Nowadays,promoting energy conservation then building intensive community has become a heated research topic [2-4].Therefore,careful planning and deployment of the base station (BS) infrastructure is necessary to decrease the energy consumption in line with green objectives [5-7].As a key technology of 5G communication system,massive MIMO has received substantial attention in both academic and industry domain since 2010 [8-12].Compared to traditional communication networks,massive MIMO has great advantages of higher data rate,larger capacity,lower latency and greater throughput [13].
Large number of antennas at the base station is the major characteristic of massive MIMO compared with conventional MIMO technology [14].The promising technology has been studied in many aspects [15-22].Distributed MIMO has been illustrated to be capable of significantly increasing the system capacity [15].In [16],the author studied the sum rate in different signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) conditions and illustrated how dense multiple antenna arrays can be designed in massive MIMO system.In [17],a coordination approach was proposed to reduce the negative
influence of pilot contamination on channel estimation.Importantly,the author demonstrated that the effect of pilot contamination can be completely vanished under certain conditions on the channel covariance.To reduce the computational complexity of channel estimation,[18] decomposed the space of the received signals into three subspaces according to factor analysis,and an interference-free subspace was created to obtain accurate channel estimation.In [19],a joint pilot design and power allocation strategy was considered to mitigate pilot contamination and provide good service in multi-cell massive MIMO system,which can be used as a benchmark for pilot design in ideal or non-ideal hardware scenarios.Due to the high hardware complexity,linear processing methods are widely used in massive MIMO system [20].In [21],a low-complexity hybrid precoding method named phased-ZF (PZF) was proposed to approach the performance of the optimal linear precoding scheme in massive MIMO systems.In [22],two interference-suppressed precoding methods were proposed and significantly suppressed the mutual interference between the users with statistical and imperfect instantaneous channel state information (CSI).Pilot-based channel estimation can be avoided by utilizing statistical CSI.
With the dramatic increase of antenna quantity,antenna selection is an effective technique to decrease the operating cost and the number of radio frequency chains in massive MIMO networks.It's impractical to obtain the optimal antenna selection by exhaustive search because of the high computational complexity.Some researches on suboptimal antenna selection methods are emerged in recent years [23-25].In [23],a successive removal strategy for antenna selection was proposed.The successive elimination strategy was performed according to the received channel coefficients from the previous users.Considering the tradeoff between the performance and computational complexity,a mixed-integer programming approach was proposed to jointly optimize antenna selection and precoding scheme [24].In order to maximize the channel capacity,the author of [25] proposed an antenna selection strategy based on the theory of rectangular maximum volume submatrices.However,this strategy is invalid if a square matrix with maximum-volume is not given.
Due to the growing demand of environmental protection,energy efficiency (EE) and spectral efficiency (SE) have become two important concerns in massive MIMO networks [26-28].Power allocation is an essential technique to enhance the system performance and promote energy conservation.To further exploit the benefits of power allocation,more and more works have been proposed for power allocation in massive MIMO networks [29-32].For maximizing the achievable uplink rate in multi-cell massive MIMO systems,a pilot power allocation strategy was proposed in [29].Considering pilot allocation,hardware impairments and other system parameters,the resource allocation problem for maximizing SE in multi-cell massive MIMO system was discussed in [30].In [31],an approximate power allocation scheme for maximizing EE was proposed in massive MIMO networks.The author considered power amplifier efficiency,transmission power and circuit power.To ensure the QoS of the whole massive MIMO system,minimum rate constraint of the system was considered in [32].The paper developed a unified framework for EE optimization and proposed a power allocation method based on fractional programming theory.However,all schemes mentioned above could not guarantee the QoS for each user and the system simultaneously.Especially in more complex conditions,it's hard for mathematical approximation to obtain the optimal solution.
1.1 Motivation and contributions
In this paper,we propose an effective antenna selection and power allocation strategy to optimize the EE and SE in massive MIMO uplink networks.To reduce the computation complexity and satisfy the changing requirements of the practical system in real time,an effective antenna selection strategy is designed to select a group of antennas from the available ones at the BS.For promoting energy conservation,we assume that the unselected antennas do not consume any energy.Besides,hardware impairment,transmission efficiency,energy consumed at active antennas and circuit energy consumption are considered in massive MIMO system.Different from former articles,minimum rate constraints of each user and the system are satisfied to guarantee the QoS for each user and the whole system,which highly increase the complexity of the power allocation problem.A quantum-inspired social emotional optimization (QSEO) algorithm is designed to obtain the optimal power allocation result in massive MIMO uplink networks.The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows:
·An effective antenna selection strategy is proposed to reduce the radio frequency chains and promote energy conservation in massive MIMO uplink networks.The number of selected antennas varies according to the variation of system requirements in real time.Larger amount of antennas are selected when higher transmission rate is required in practical system.
·Exact expressions for EE and SE are given considering the hardware impairment,transmission efficiency,circuit power consumption and power consumed by active antennas in massive MIMO networks.To optimize the EE and SE while guarantee the QoS in massive MIMO uplink networks,minimum rate constraints of each user and the system are considered in this paper.
·A quantum-inspired social emotional optimization (QSEO) algorithm is proposed to solve the multi-constrained non-convex power allocation problem in massive MIMO uplink networks.Two different quantum evolution rules are designed to improve the diversity of solutions and guarantee the strong searching ability of the algorithm.The interactions among the quantum individuals are fully utilized to obtain the optimal solution of the feasible region,which avoids the local convergence compared with traditional SEO algorithm.Through the simulation results,QSEO has the advantages which previous strategies do not have.
·QSEO combines the advantages of both quantum evolution and social emotional optimization algorithm,with the strong searching ability and fast convergence.Besides,the QSEO algorithm proposed in this paper can not only be used to obtain the optimal power allocation strategy in massive MIMO uplink networks,it's a general algorithm which can also be widely used to solve continuous,discrete and hybrid optimization problems in many engineering domains.
1.2 Organization and notation
Other sections of this paper are organized as follows.The model of the massive MIMO uplink network is shown in the next section.In Section III,we propose an effective antenna selection strategy and derive exact expressions of EE and SE considering the hardware impairment of the BS.Power allocation strategy based on QSEO for maximizing EE and SE are proposed in Section IV.The simulation results are given in Section V and the last section concludes this paper.
Notation:In this paper,matrix and vector are denoted by boldface upper and lower case symbols.Superscripts (.)Tand (.)Hrepresent the transpose and conjugate transpose,respectively.||.|| and |.| denote the Euclidean norm of a vector and a scalar,respectively.diag(b) represents the diagonal matrix with the elements of vectorbon its main diagonal,andE{.} represents the expectation.
II.SYSTEM MODEL
In this paper,a single-cell multiuser massive MIMO system is considered.One base station equipped withMantennas andKusers with single antenna constitute the system.Bis the bandwidth of the system.To promote energy conservation,there is not necessary to utilize all the antennas at the BS during the period of data transmission.According to the requirements of practical system,we select a part of antennas to participate in communication.The antenna selection strategy is discussed in the following section.Assuming thatMsantennas are selected at the BS,Ms≤M.In massive MIMO uplink system,the CSI matrix from the users to the BS can be expressed by

whereGis anMs×Kmatrix andG=[g1,g2,...,gK],gkdenotes the CSI between thekth (k= 1,2,...,K) user and the BS.His the small-scale fading matrix with the size ofMs×K,whileD=diagis the large-scale fading matrix with the size ofKK× .βkrepresents the shadow and geometric fading between thekth user and the BS,which is shown by the following formula
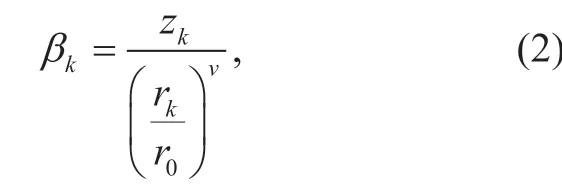
whererkis the distance from userkto the BS,r0denotes the radius of the BS,vrepresents the path loss exponent,andzkis a log-normal distributed variable with zero mean and standard deviation.
During the data transmission phase,each user transmits its signal to the BS while interfering with other users.The signal received at the BS is given by
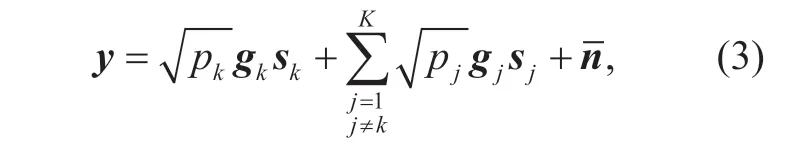
wherepkandpjdenote the transmission power of userkand userj(j=1,...,K,j≠k).skandsjdenote the signal vector of userkand userj,which satisfyE{||sk||2} = 1 andE{||sj||2} = 1,respectively.represents the additive white Gaussian noise vector.
In the case of all CSI can be obtained and maximum ratio combining (MRC) is used for signal processing at the BS,the signal-to-interference-plus- noise ratio (SINR) experienced by userkat the BS is shown as
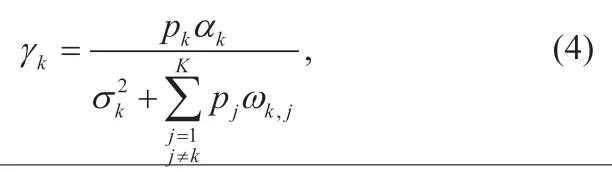
with
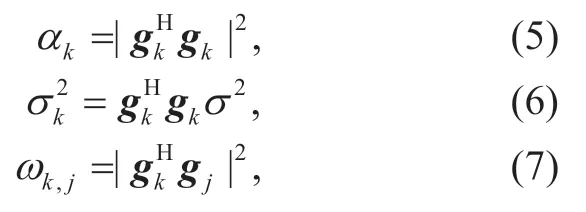
whereαkandωkj,are positive quantities depend on transmission channels,σ2denotes the noise power.In particular,αkis only related to the CSI of userk,while the interference coefficientωkj,depends on the CSI from other users to the base station.
Hardware impairment is inevitable in practical massive MIMO system.The degree of the reduction for the desired signals causing by the hardware impairment is 1-ε2,whereεrepresents the magnitude of error.For simplicity,we assume that the BS is hardware-impaired,andεBSdenotes the impairment magnitude.The SINR experienced by userkat the BS takes the following general form [32]:

with
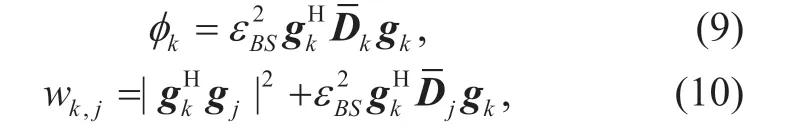
The data transmission rate of userkis given by
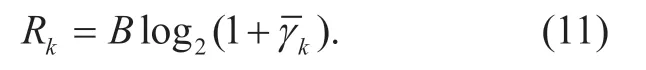
Then,the achievable rate of the massive MIMO uplink system can be expressed as

III.OPTIMIZATION FUNCTIONS IN MASSIVE MIMO UPLINK NETWORKS
In this section,we first propose an effective antenna selection strategy.Then,we derive exact expressions of SE and EE which are two major concerns in massive MIMO system.Considering the impact of various parameters,these expressions provide practical design insights on practical massive MIMO system.
3.1 Antenna selection
According to the requirements of massive MIMO system during the period of data transmission in real time,we selectMs(Ms≤M) antennas out of the availableMones at the BS.The specific expression of the relationship betweenMsandMis shown by
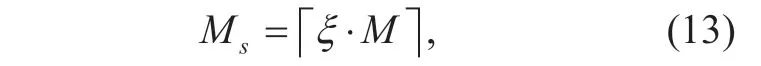
Assuming that the CSI for all antennas is obtained at the BS,the optimal solution for antenna selection can be obtained according to the exhaustive search under a given performance metric.However,with the large amount of antennas in practical system,huge computational cost is inevitable by exhaustive search.It is necessary to design a new strategy since the existing solutions cannot match the practical system in real time.For this reason,an effective antenna selection strategy to reduce the calculation complexity is proposed.
At the stage of antenna selection,we assume that all users have the same transmission power and the antennas at the BS are independent of each other.Then,we calculate the achievable rate from the users to each antenna by (12).Antennas which provide higher sumrate are selected at the BS.
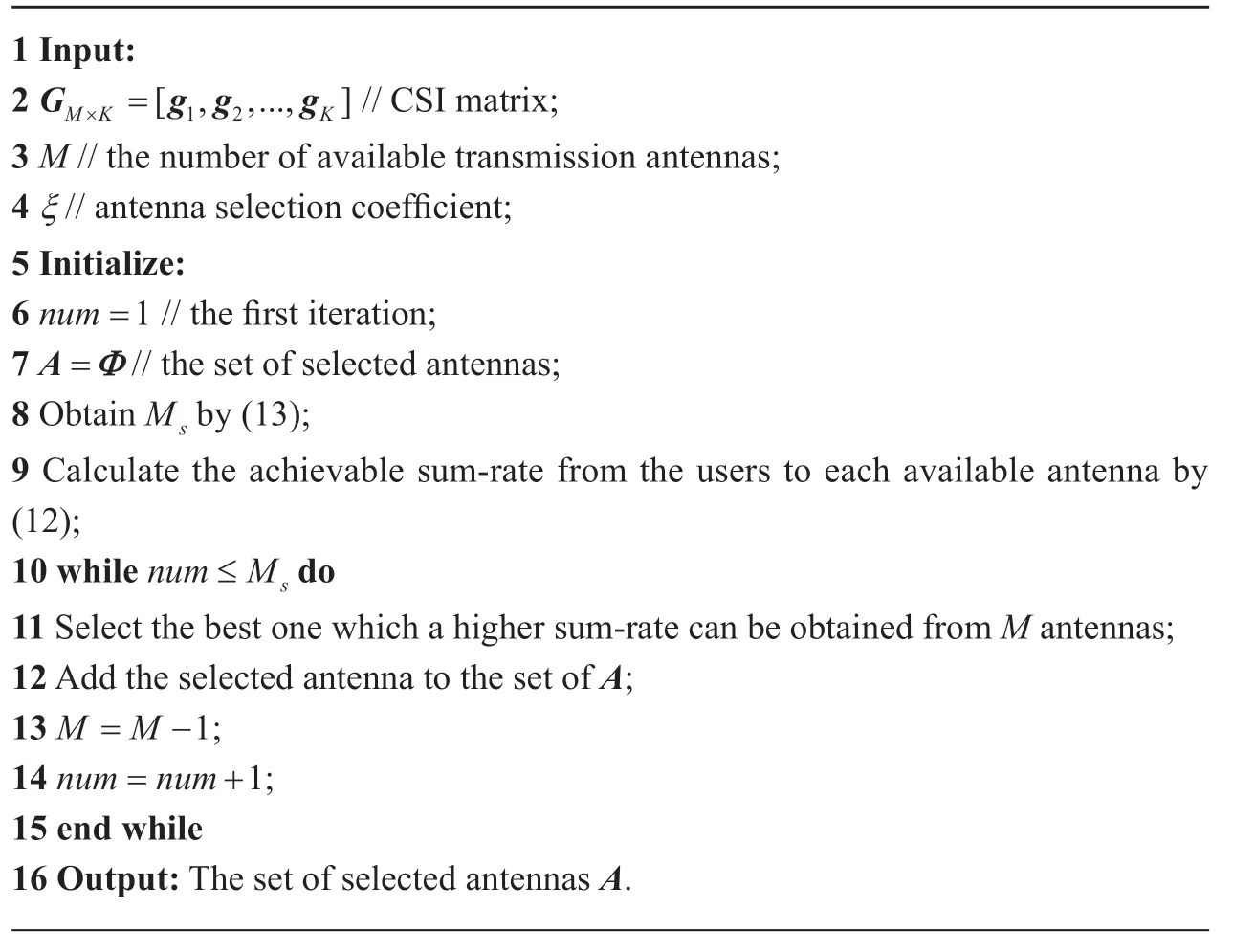
The basic idea of the antenna selection strategy in this paper is to select the bestMsantennas which afford the highest transmission rate.The steps of the antenna selection strategy are summarized in Algorithm 1.
3.2 Spectral efficiency
According to the expression of transmission rate for userkin (11),the achievable SE (in bit/s/ Hz)φkfor userkis defined by
Algorithm 1.Steps of antenna selection strategy.
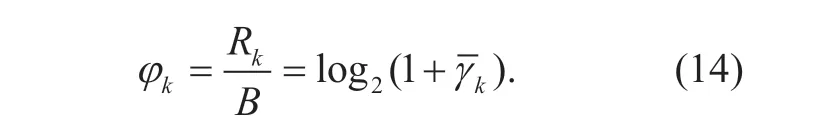
For userk,the following power constraint must be satisfied

wherepkmaxdenotes the maximum transmission power of the userk.To ensure the communication quality of each user,the minimum achievable rate of each user should be satisfied,which is shown by
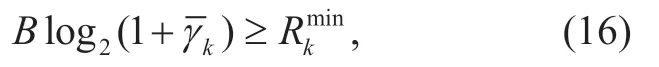
whereRkminis the minimum achievable rate of userk.
In order to ensure the quality of service (QoS) for the massive MIMO system,the following expression needs to be satisfied
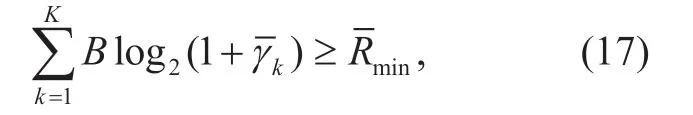
whererepresents the minimum achievable rate of the system.
The total SE (in bit/s/Hz) of the system is given as follows
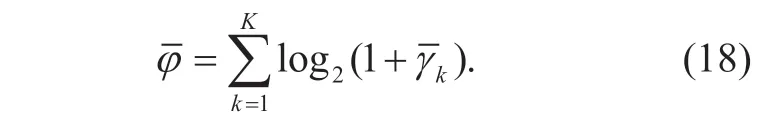
According to (15),(16) and (17),we definePas the feasible set of power allocation results,andp=[p1,p2,...,pK] represents one feasible power allocation result ofP.According to the settings mentioned above,the problem of SE maximization can be denoted as
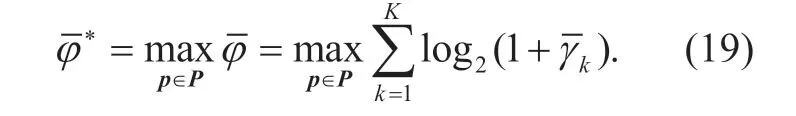
3.3 Energy efficiency
The network EE (in bit/J) is related to the sum-rate and the power consumed in the system,which is defined by the following formula
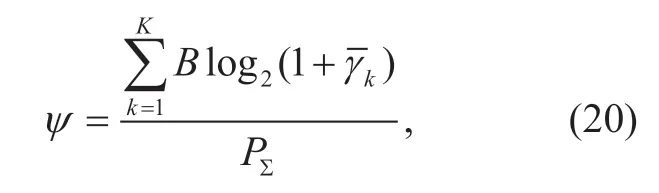
whereP∑represents the total consumption of energy.The circuit power consumption always exists in practical massive MIMO networks.Then we consider the power consumed at the users and the BS respectively.For the perspective of users,the power consumption is larger than total transmission power of each user since the transmission efficiency cannot reach 100%.Active antennas at the BS also consume energy to ensure their works for receiving and processing signals from the users.Thus,the total consumed power is given by
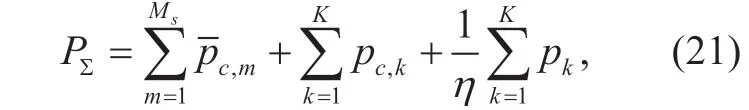
The feasible set of power allocation resultsPis the same as in 3.2 according to the constraints in (15),(16) and (17).The problem of EE maximization can be formulated as follows
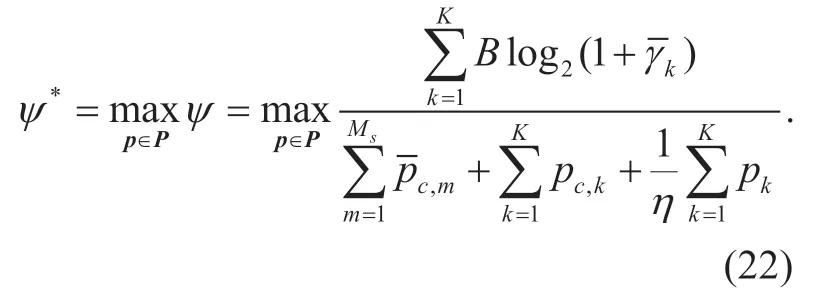
SE and EE are two major concerns in the performance of practical massive MIMO system.In particular,in (18) denotes a variable in proportion to the sum-rate whileψin (20) is the benefit-cost in massive MIMO uplink networks.However,the maximization of SE and EE are two competing goals in massive MIMO system.Both (19) and (22) are non-convex and complicated optimization problems.To tackle the tough problem,an efficient power control strategy is proposed in the next section.
IV.POWER CONTROL STRATEGY IN MASSIVE MIMO UPLINK NETWORKS
As is shown above,the aim of the problems mentioned ahead is to find the optimal power control strategies for maximizing SE and EE in massive MIMO networks.Unfortunately,the feasible region is difficult to determine.Especially in (22),the objective function does not have a concave numerator,and it's difficult to find the optimal solution with affordable complexity.Since the multi-constrains nonlinear optimization problem is difficult to resolve,the existing power allocation method based on fractional programming is hard to find the optimal solution,and the traditional intelligent algorithms cannot be simply applied to the problem because of local convergence.In this section,a quantum-inspired social emotional optimization (QSEO) algorithm is proposed to solve the power allocation problems mentioned before.
4.1 Quantum-inspired social emotional optimization algorithm
QSEO is a discrete optimization algorithm which is inspired from the social emotional optimization (SEO) algorithm [33] and the thought of quantum intelligence computation [34].In theL-dimensional space (Lrepresents the number of dimensions for the optimization problem),there areNquantum individuals in quantum population of QSEO.Thenth (n=1,2,...,N) quantum individual of thetth iteration is defined as
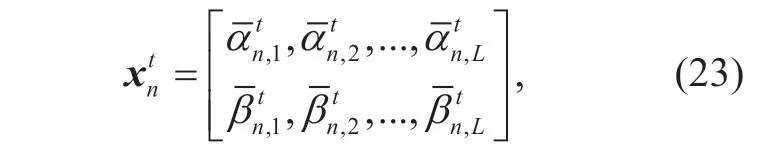
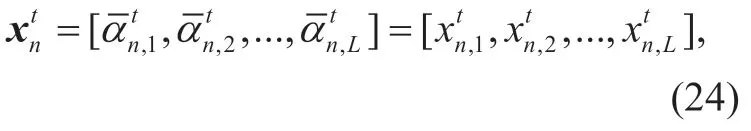
wherel=1,2,...,LandEachdenotes a quantum bit.The measurement stateof thenth quantum individual is gotten by the following rules,which is shown by
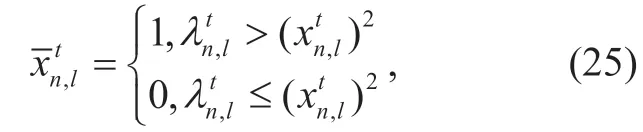
whereis a random number evenly distributed between 0 and 1.
The social evaluations of all quantum individuals are calculated by the function of specific problem.The historical optimal solution of thenth quantum individual is expressed byFor the first iteration,the historical optimal solution of each quantum individual is initialized as its measurement state.The quantum individual who gets the highest social evaluation is denoted as the global optimal solutionamongtiterations.We defineϖtas the set of the worst quantum individuals which consists ofN′ (NN′≤ ) quantum individuals with the lowest social evaluations,whererepresents the measurement state of then′th (n′ =1,2,...,N′) quantum individual.
Each quantum individual has different emotions which greatly affect the process of evolution.The emotional index of quantum individualnis a variable between 0 and 1,which is denoted byent.andare two emotional thresholds of three different emotions,that is,upset,calm and enthusiastic.Assuming that,the process of updating the quantum individualnaccording to different emotions can be expressed as follows
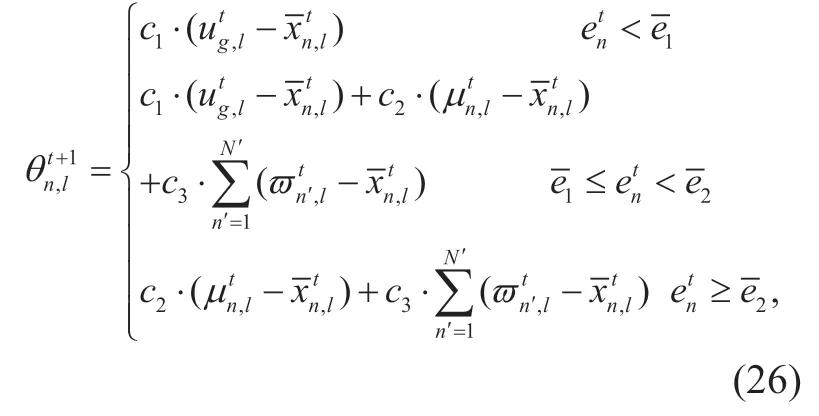
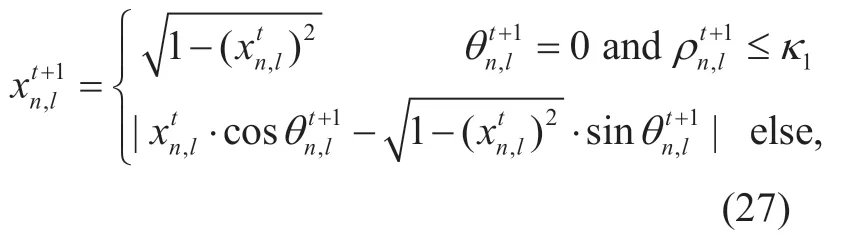
wheredenotes thelth quantum rotation angle of thenth quantum individual;c1,c2,andc3are three constants which represent impact factors of the global optimal solution of the quantum population,the historical optimal solution of thenth quantum individual,and the worst solution set to the quantum individualn,respectively.κ1denotes the mutation probability andis a random variable evenly distributed between 0 and 1.
In particular,for the first iteration,the emotional index of any quantum individualnis set to 1.Each quantum individual obeys the following updating process
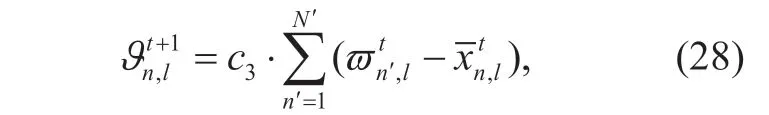
wheredenotes thelth quantum rotation angle of thenth quantum individual.The elements of the quantum individuals are updated by (27),and the corresponding measurement states of the quantum individuals are updated by (25).Then,we calculate the social evaluations of all quantum individuals under the same function of the problem mentioned ahead.To make it easy,the emotional index and the historical optimal solution of each quantum individual are updated by the following
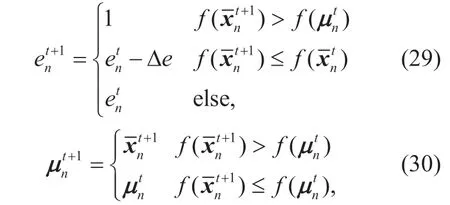
wheref(.) denotes the social evaluation function,Δedenotes the reducing index of emotion.Especially,when<0,we define=0.Then,we update the worst solution set and the global optimal solution of the quantum population.The measurement state of the quantum individual who gets the highest social evaluation value in history is selected as the global optimal solution among all previous iterations.
The process of iteration ends until the algorithm achieves the terminal condition (usually depend on the predetermined number of iteration).
4.2 Computational complexity of the QSEO algorithm
As described in 4.1,the QSEO algorithm needs to update the quantum rotation angles in all dimensions of all quantum individuals at each iteration,which has a computational complexity ofONL( ),whereNis the population size andLis the maximum dimensional number.The quantum individuals are updated by the quantum rotation angles and the measurement states can be obtained by (25),with the computational complexity ofONL(2 ).After the updating process,we calculate the social evaluations of the new quantum individuals with the computational complexity ofO(N).The historical optimal solutions,the emotional indexes of all quantum individuals,the worst solution set and the global optimal solution of the quantum population are updated according to the social evaluations after each iteration.The computational complexity isO( 4N).

Algorithm 2.Power control strategy for SE and EE maximization.
For the termination of the QSEO algorithm after runningtiterations,the computational complexity isO(t(5N+ 3NL)).
4.3 Power allocation strategy based on QSEO
In this subsection,we consider the implementation of power allocation strategy based on QSEO in massive MIMO uplink networks.In order to solve the non-convex continuous optimization problem,we encode the estimated power of the each user bybinary bits.Hence,the dimension of each quantum individual isL=K×.At the stage of initialization,the measurement state of thenth quantum individualis obtained by (25).Since the transmission power of the each user is encoded bybinary bits,the power allocation result can be obtained by the following formula
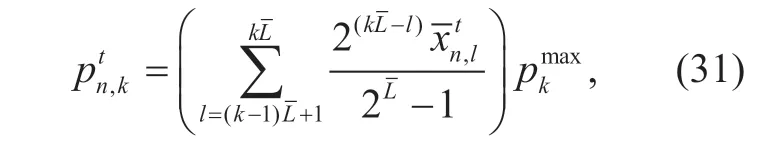
wherek=1,2,...,K,denotes the maximum transmission power of userk,anddenotes thenth feasible power allocation result of userk.The corresponding power allocation result of quantum individualnis denoted by
For the power allocation strategy based on QSEO,(19) and (22) are considered as the social evaluation functions to optimize SE and EE,respectively.The implementation steps of the power control strategy based on QSEO for SE and EE maximization are summarized in Algorithm 2.
V.SIMULATION RESULTS
In this section,the simulation results of different communication scenarios are given to examine the capability of the power control strategy based on QSEO.To this end,we study two major concerns in massive MIMO networks,namely,energy efficiency and spectral efficiency.
5.1 System parameters
We consider the hardware-impaired single-cell multiuser massive MIMO uplink network as depicted in Section II,whereK=3 andM=125.Under the assumption of perfect CSI,MRC is adopted for data recovery.We assume that only the BS is hardware-impaired andεBSrepresents the degree of impairment.Msantennas are selected at the BS,and the antenna selection coefficientξvaries according to the requirements of the practical system.The power of Gaussian white noise isσ2=FBN0.Without loss of generality,assuming that the location of the BS is (0,0)m,the users are distributed in three circles where the centers are located at (125,200)m,(320,0)m,(253,103)m with the radius of 2m,2m,5m,respectively.The parameters in massive MIMO uplink system are shown in table 1.
5.2 Energy efficiency
To make it easy,assuming each antenna consumes the same energy∀min data processing.All users have the same maximum transmission powerpkmax=pmax∀k,the same circuit powerpc,k=pc∀k,and the same minimum achievable rate constraintRkmin=Rmin∀k.For QSEO,all quantum individuals have different emotions and the emotional index of each quantum individual is distributed between 0 and 1.At the stage of initialization,each element of the quantum individual is set to 1/2 and the emotional indexes are set to 1.The other parameters of QSEO are shown in Table II.
For the problem of EE maximization in hardware-impaired massive MIMO networks,the performance of power control strategies based on QSEO,SEO,fractional programming theory,and the maximum power allocation strategy is studied in this section.For comparison purposes,the population size and the iteration number of SEO are the same of QSEO.For SEO,the other parameter settings can refer to [33],while the power control strategy based on fractional programming theory and the maximum power allocation strategy are discussed in [32].All results are the average of 100 simulations.
The variation of the system energy efficiency with the number of iterations is shown in figure 1.The results show that: 1) the maximum power allocation strategy causes the lowest EE.The reason is that though the largest energy is obtained for the desired signal,the SINR in (8) is seriously decreased by the strong non-negligible interference between the users.2) For power control strategies based on QSEO,SEO,and fractional programming theory,the EE in massive MIMO uplink networks increases with the number of iterations.3) Compared with other methods,a higher EE is obtained by the power allocation strategy based on QSEO.However,for the power allocation method based on fractional programming theory,a lot of mathematical derivations and Lagrangian constraints are needed for fi nding a suitable power allocation result.It's only applicable to convex optimization problem with equality constraints.For the non-convex power allocation problem with minimum rate constraints in massive MIMO uplink networks,it couldn't get a higher performance,while the resolving method of traditional SEO is easy to get into a local optimum in the early searching stage.In QSEO,two different quantum evolution strategies are designed to guarantee the diversity of solution and the strong searching ability of the algorithm.The designed evolution rules can make full use of the advantages of quantum theory and SEO,and the interactions of quantum individuals are fully utilized to obtain the optimal solution of the feasible region,which avoids the local convergence of traditional algorithms.To sum up,QSEO can overcome the shortcomings of traditional algorithms and show its advantages in convergence speed and convergence accuracy.
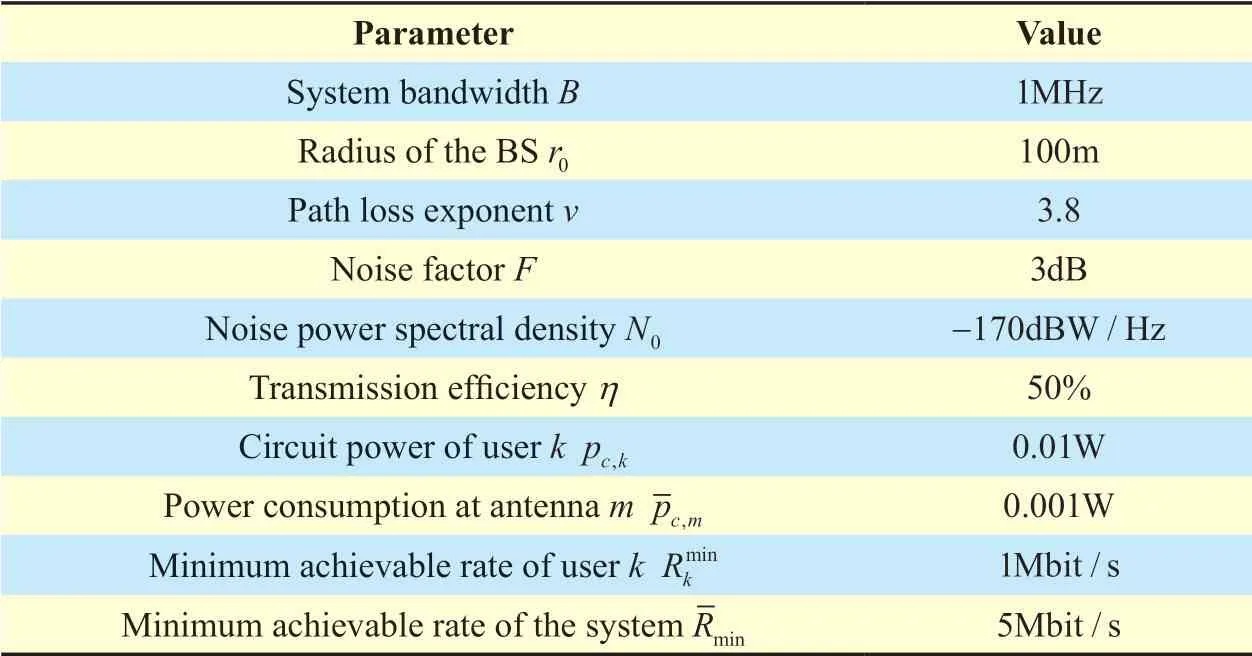
Table I.Parameter settings in massive MIMO system.
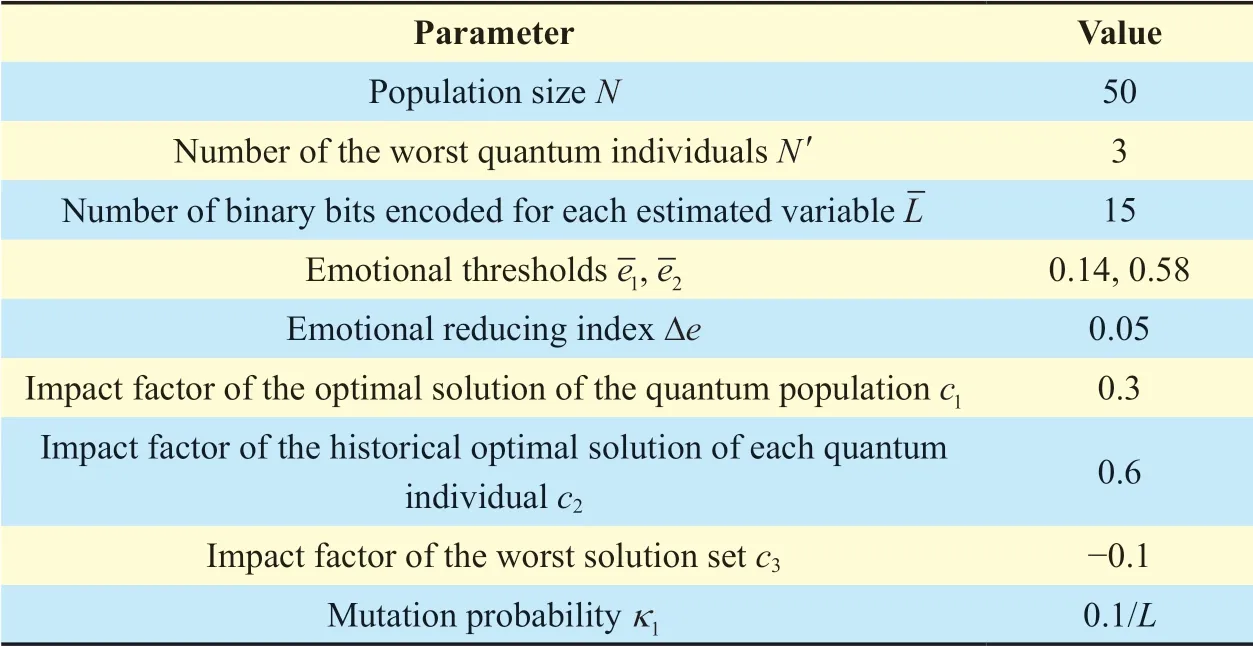
Table II.Parameter settings of QSEO.
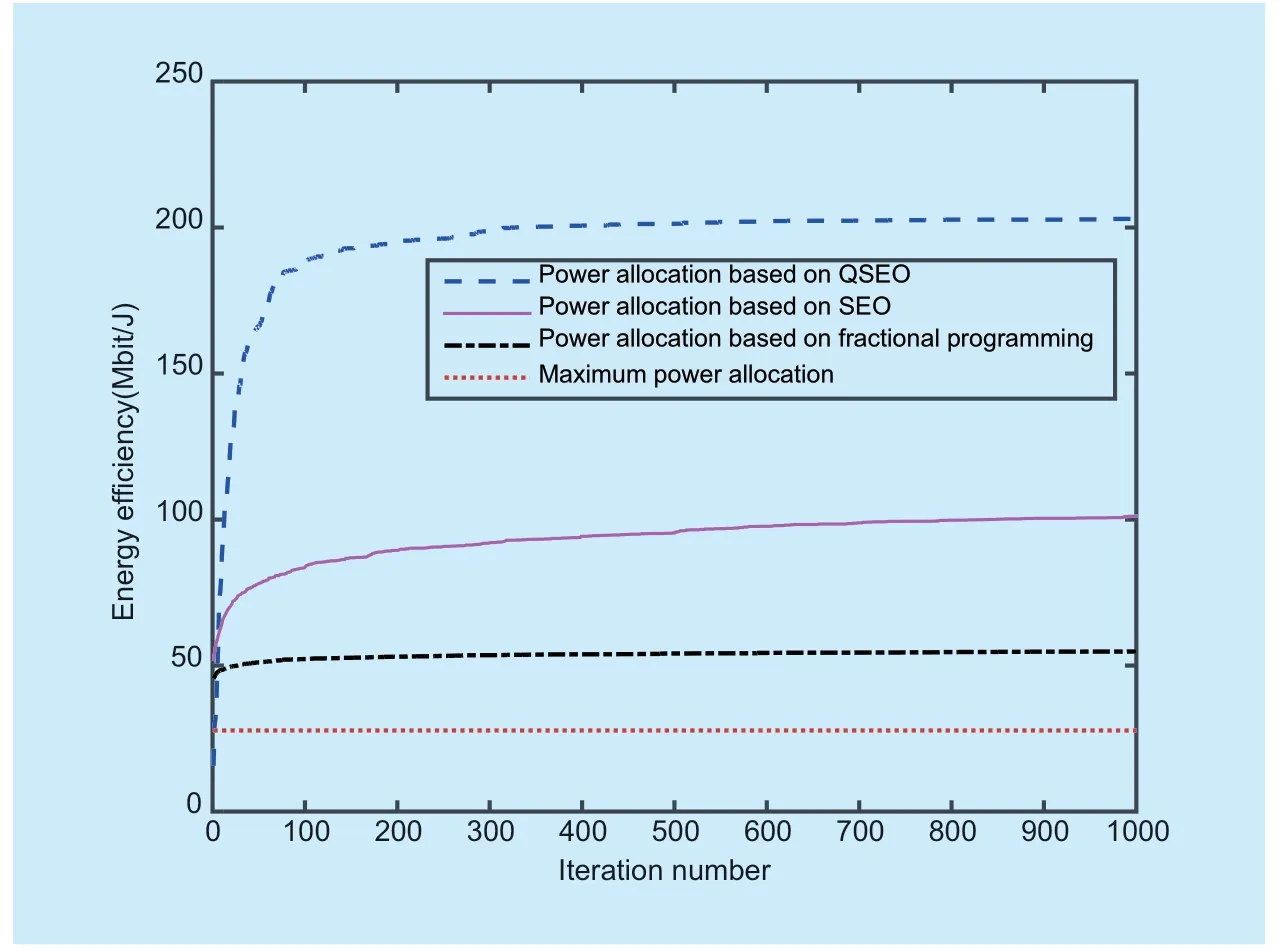
Fig.1.Energy efficiency versus iteration number with ξ=0.7,pmax=-20dBW,εBS=0.
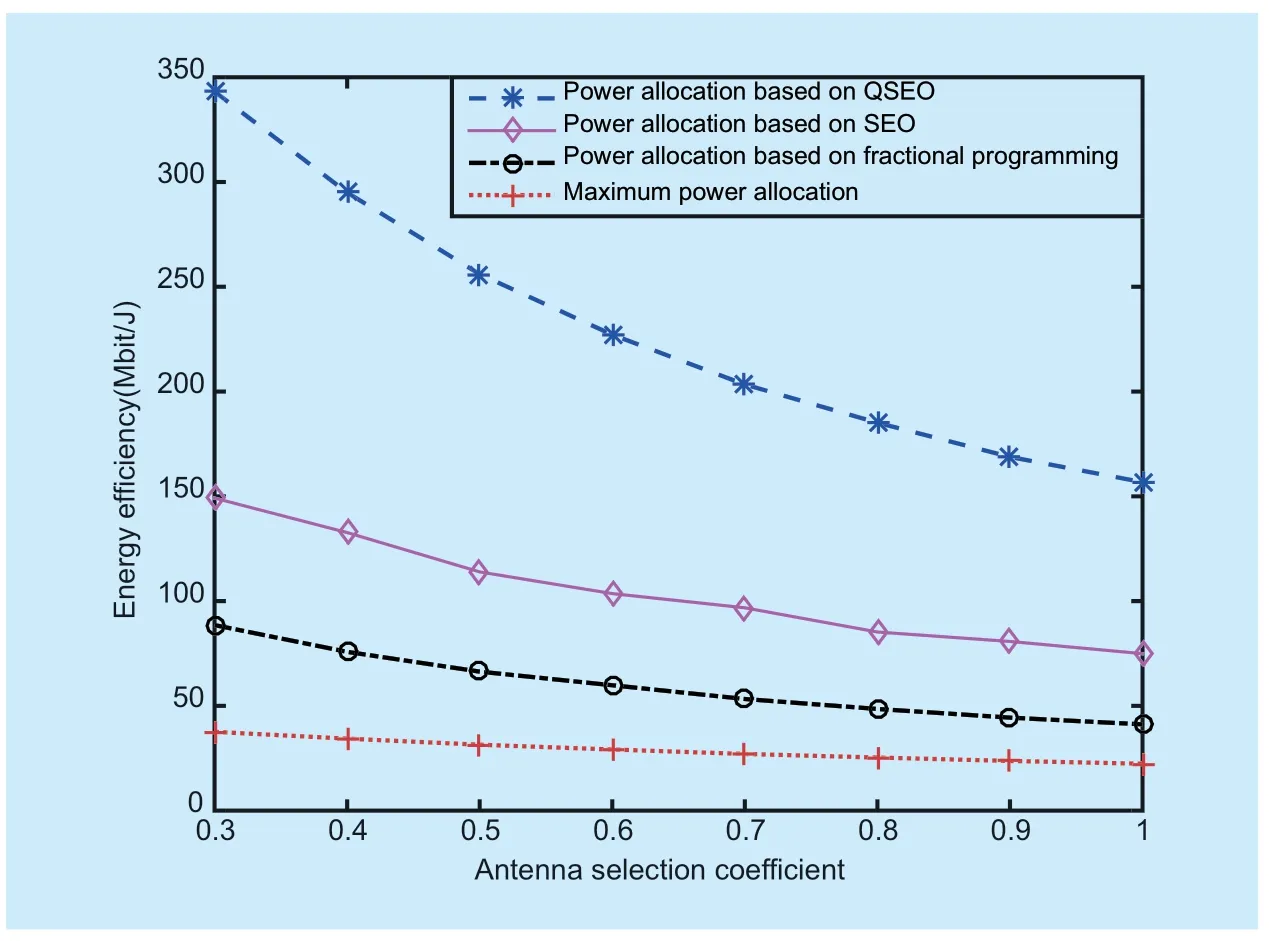
Fig.2.Energy effi ciency as a function of ξ,with pmax=-20dBW,εBS=0.
Fig.2.shows the curves of energy effi ciency for the variation of antenna selection coeffi cientξin no hardware impaired system.The antenna selection coefficient increases as a higher requirement is needed for the communication system.However,the EE decreases with the increase ofξ.The reason is that each antenna consumes energy for data receiving and processing.As the increasing number of selected antennas,the power consumed at the BS increases and the total power consumed in the massive MIMO system goes up.Besides,the increase of achievable rate is far less than energy consumption.Compared with other power control strategies,the power control strategy based on QSEO has the best performance.
Fig.3.shows the variation curves of energy effi ciency with hardware impairment coeffi cient at the BS.εBSis a variable distributed between 0 and 1,whereεBS=0 represents no hardware impairment at the BS andεBS=1 denotes the BS is completely damaged.In order to study the effect of the hardware impairment coefficient on EE,we define dB as the unit ofεBS.We can learn from the curves that EE decreases as the increase of hardware impairment.In particular,whenεBS=0,the EE of all curves goes to zero.That is because the power of the desired signal decreases asεBSincreases.When the BS is totally destroyed,the energy of the desired signal is zero.The power control strategy based on QSEO is more sensitive to hardware impairment and has a better performance than other strategies.
The variation of energy effi ciency with the maximum transmission power of each user is shown in fi gure 4.We observe that the QSEO power allocation strategy has an obvious advantage over the other power control strategies.For the power allocation problem in massive MIMO networks,the solution space expands with the increase of the maximum transmission power.And it's difficult for the strategies based on fractional programming theory and SEO to fi nd the optimal solutions due to their own limitations of randomness and local convergence.But for QSEO,the quantum evolution mechanic and the variety of evolution rules can overcome the disadvantages of traditional SEO algorithm and the approximation method.Hence,the QSEO-based power allocation strategy can get an excellent performance in massive MIMO networks.
In order to see the relationship of two different parameters,we show the simulation results in another way.The simulation result which is related to the variation of two system parameters,hardware impairment coefficient at the BSεBSand the maximum transmission powerpmaxis shown in figure 5.It is clear to see the impact ofεBSandpmaxon energy efficiency based on QSEO power allocation strategy.A higherpmaxand a lower hardware impairment coeffi cient are good for improving the EE in massive MIMO networks.
5.3 Spectral effi ciency
The simulation results for SE maximization in hardware-impaired massive MIMO networks are presented in this part.To make it easy,the parameter settings of power control strategies based on QSEO,SEO,fractional programming theory,and the maximum power allocation strategy are the same of 5.2 in this section.
Fig.6.shows the variation of the system spectral efficiency with the number of iterations under different power control strategies.The simulation results show that SE increases with the iteration number.The trend of the curves is similar to the curves in figure 1.Compared with power allocation strategies based on SEO,fractional programming theory and the maximum power allocation method,the proposed power allocation strategy based on QSEO can get a better performance for the SE maximization in massive MIMO networks.

Fig.3.Energy effi ciency as a function of εBS,with pmax=-20dBW,ξ=0.7.
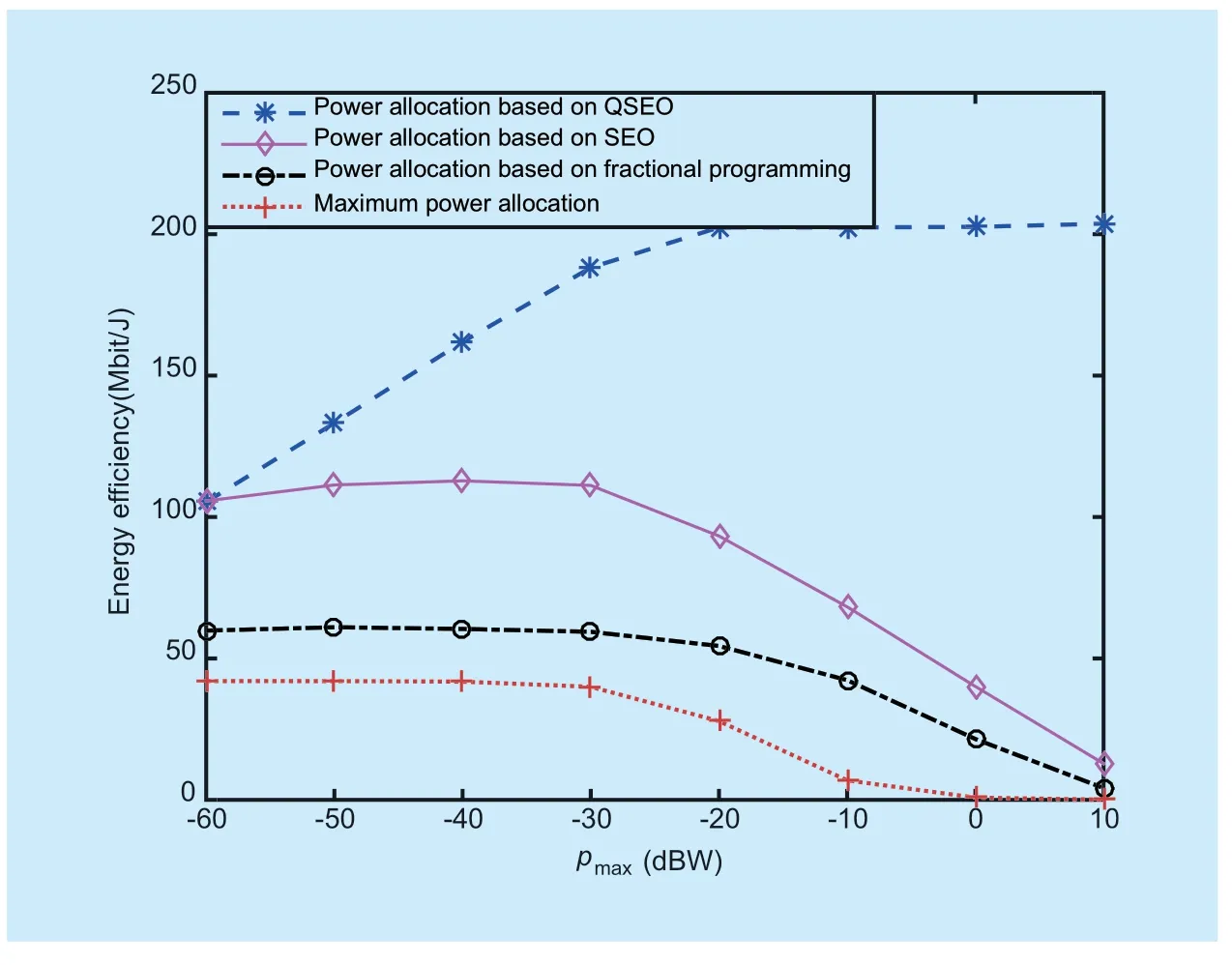
Fig.4.Energy effi ciency as a function of pmax,with εBS=0,ξ=0.7.
Fig.7.shows the variation curves of spectral efficiency with the hardware impairment coefficient.Same as in figure 2,εBSdenotes the degree of hardware impairment at the BS with the unit of dB.We can learn from the curves that SE decreases with the increase of hardware impairment coefficient.When the BS is totally destroyed,εBS=0,the SE of all power allocation strategies goes to zero.The power control strategy based on QSEO is more sensitive to hardware impairment and has a higher SE than other strategies under the condition of BS is not paralyzed.
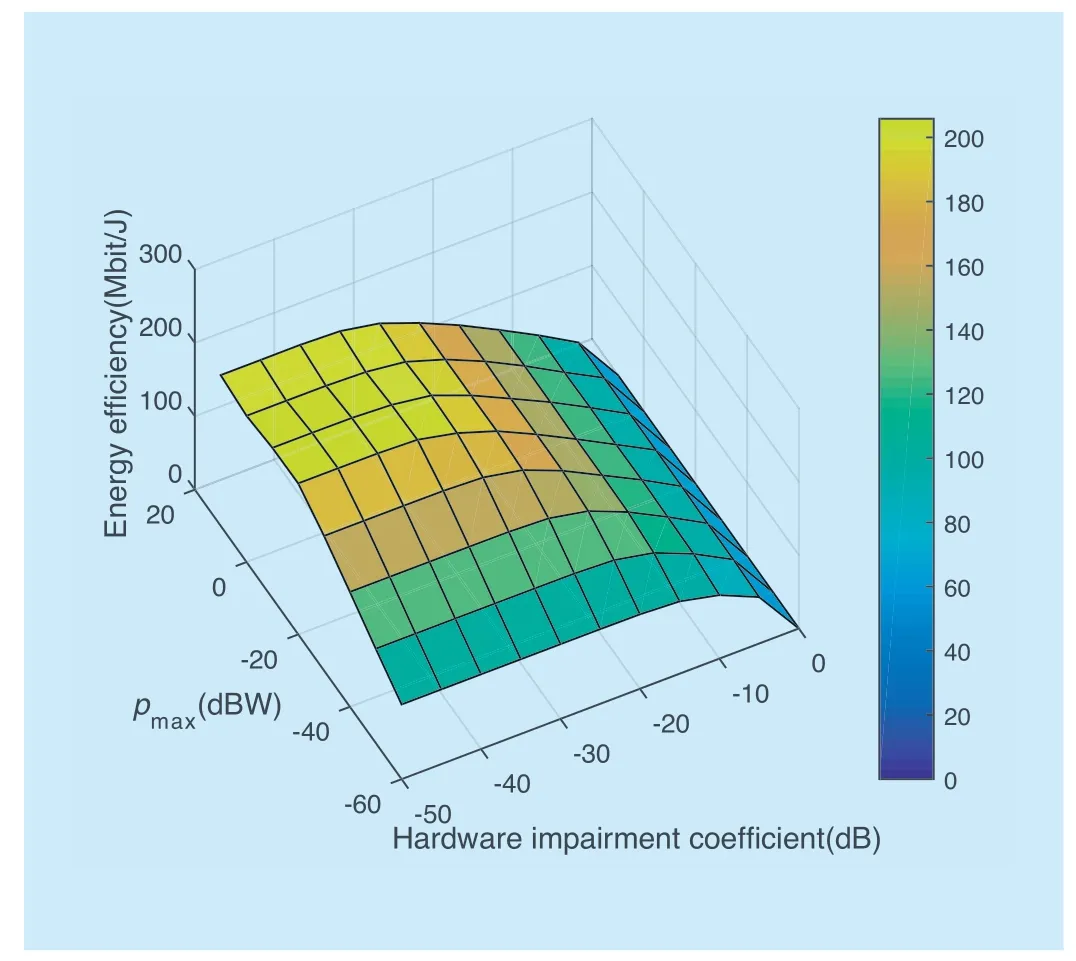
Fig.5.Energy effi ciency as a function of pmax and εBS,with ξ=0.7.
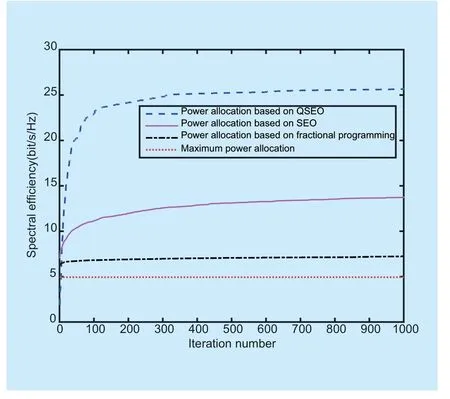
Fig.6.Spectral efficiency versus iteration number with ξ=0.7,pmax=-20dBW,εBS=0.

Fig.7.Spectral effi ciency as a function of εBS,with pmax=-20dBW,ξ=0.7.
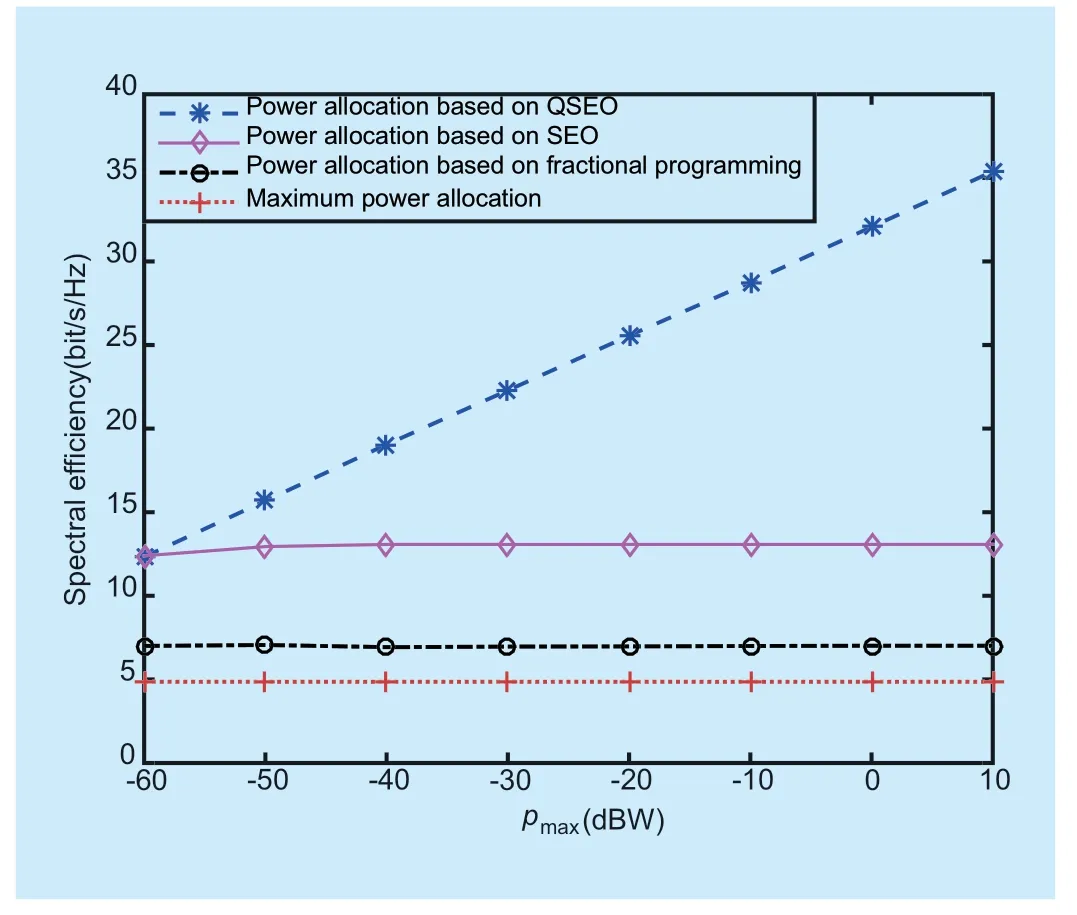
Fig.8.Spectral effi ciency as a function of pmax,with εBS=0,ξ=0.7.
The variation of spectral effi ciency with the maximum transmission power of each user is shown in fi gure 8.The SE of the power control strategy based on QSEO increases with the increase of the maximum transmission power of each user,while other strategies almost no change with the variation ofpmax.Power allocation strategy based on SEO mechanism and fractional programming theory are trapped into the local optimal solution because SEO is vulnerable to local convergence and fractional programming theory is only suitable for the convex optimization problem.For the maximum power allocation strategy,each user transmits signals with the power ofpmax,the SINR in (8) tends to a fi xed value.But for QSEO,the quantum evolution mechanic and the variety of evolution rules can improve the global searching ability and get the optimal power allocation strategy for maximizing SE in massive MIMO networks.
In order to see the effects of two different parameters on the spectral efficiency,we show the simulation results in another way.In figure 9,two system parameters,namely hardware impairment coeffi cient at the BSεBSand the maximum transmission powerpmaxis considered.It is clear to see the impact ofεBSandpmaxon spectral effi ciency based on QSEO power allocation strategy from the simulation results.A higherpmaxand a lower hardware impairment coeffi cient are good for improving the SE of massive MIMO networks.
VI.CONCLUSION
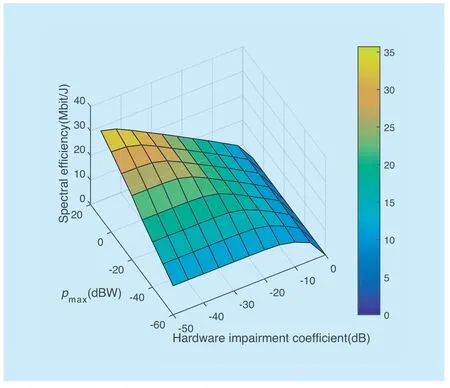
Fig.9.Spectral effi ciency as a function of pmax and εBS,with ξ=0.7.
In this paper,we analyze the EE and SE under the condition of specifi c requirement for data transmission in massive MIMO uplink system.It is assumed that perfect CSI is obtained,and MRC is used for data recovery at the BS.For promoting energy conservation,we select part of antennas at the BS to participate in communication according to the requirements of the system.Hardware impairments,energy consumed at each antenna,circuit power,and the effi ciency of the transmitter are considered in practical systems.To guarantee the QoS in massive MIMO uplink networks,minimum rate constraints of each user and the system are considered in this paper.QSEO algorithm is proposed to solve the non-convex multi-constrained power allocation problem for EE and SE maximization.Simulation results demonstrate the superiority of the QSEO-based power allocation strategy which previous strategies do not have.
Although power control strategy based on QSEO enjoys excellent performance in EE and SE,there are still some certain communication systems which can be investigated.In the future,we will study the application of massive MIMO with imperfect CSI,multi-cell multiuser networks,cognitive radio,heterogeneous networks,and co-time co-frequency full duplex systems.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61571149),the Special China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015T80325),the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HEUCFP201808),the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M530148).
- China Communications的其它文章
- A Bandwidth-Link Resources Cooperative Allocation Strategy of Data Communication in Intelligent Transportation Systems
- UP-TreeRec: Building Dynamic User Profiles Tree for News Recommendation
- A Fuzzy Decision Based WSN Localization Algorithm for Wise Healthcare
- Bistable Stochastic Resonance Enhanced 4-ary PAM Signal Detection under Low SNR
- Tensor Completion for Recovering Multichannel Audio Signal with Missing Data
- A PCA-Based Internet Delay Space Dividing Algorithm

