安全·生态·健康:绿色城市设计的数字化转型
杨俊宴
章 飙
1 绿色城市设计的数字化新趋势
城市设计作为引导城市健康发展的重要手段之一,能改进人们生存空间的环境质量和生活质量[1],帮助复兴城市经济、彰显城市文化[2],营造合理的社会环境与自由公平的社会秩序,并维护可持续发展的生态环境[3]。同时,在当下新型城镇化发展过程中,能够满足提高城市空间精致化的要求[4],对促进城市高质量发展[5]起到十分关键的作用。纵观现代城市设计的发展历程,其设计种类繁多、内容丰富,对象层次从宏观到微观均有囊括。根据主导价值取向的差异,可分为传统城市设计、现代主义城市设计、绿色城市设计和数字化城市设计4代范型[6];而从技术方法的演变脉络来看,城市设计在发展过程中出现了礼制导向、美学导向、现代主义、社会导向、生态导向以及数字化城市设计等主题性特征。绿色城市设计作为其中的重要板块,主要是在传统城市设计的基础上注入生态学理论与分析方法,以达到城市可持续发展的规划目标。总体看来,生态导向的城市设计寻求的是构建人工环境与自然环境相协调的人居空间场所,对于城镇环境建设的可持续发展具有重大的实践指导作用[7],能够有效改善城市生态环境质量、提高土地利用效益、美化城市空间景观,以及提升能源使用效率等,因此基于生态优先理念的绿色城市设计是当下中国城市设计实践的四大趋势之一[8]。
随着中国城镇化的飞速发展,环境污染、能源短缺、交通拥堵等城市问题纷至沓来,而引入生态学理念与方法的绿色城市设计能够对上述问题做出有效应对,因此相关理论研究越来越受到重视。自20世纪80年代起步以来,我国的生态导向城市设计理论从最初简单案例式的生态城市设计研究,到90年代中期全面提出绿色城市设计理论范式[9],再到21世纪的“4E”模式[10]和柔性设计模式[11]等理念的探索与尝试,都极大地丰富了绿色城市设计的整体理论框架,并有效地指导了城市设计项目的实践。但在绿色城市设计理论越来越完善、越来越受到关注的同时,相应的技术分析方法却跟不上理论的发展速度。在当前我国大规模、高密度、快速化的城镇化过程中,传统的依靠主体决策的绿色城市设计技术方法已经难以形成有效支撑。随着大数据时代的来临,数字技术凭借其能满足大尺度化、高颗粒化、人本量化和经验量化等诸多需求的特性,不仅能够给予绿色城市设计以有效的技术支撑,同时也为其提供了全新的研究视角。
进入21世纪以来,随着大数据分析对城市设计学科的渗透,生态导向的城市设计技术方法呈现出明显的数字化倾向,在当下“万物皆数”的信息时代,对多源大数据资源的采集与分析为诸多新技术方法的应用提供了有力支撑。在城市气候环境优化方面,出现了数字化技术的城市热岛效应模拟研究[12]、山地城市近地层风环境研究[13];在城市绿化景观提升方面,进行了数字化景观环境色彩构成研究[14]等。
总体来说,当前生态导向的数字化绿色城市设计方法存在以下几点不足。
1)数字化技术分析水平仍有待加强。数字化技术的根本就是数据,对海量数据的采集、筛选、清洗、处理、分析和应用是一项技术方法应用的全路径,现阶段大数据以多种多样的形式涌现,如何对多样化、多维度的数据进行分析利用仍有待探索,整体的分析水平也有待提升。
2)偏重个案实践,缺乏共性技术的总结。虽然数字技术对传统技术方法的渗透有快有慢,但整体来看,数字化技术方法体系架构较为完善,而现阶段的研究与实践仍以单一技术方法的个案探索为主,缺乏对技术方法的有效分类和共性技术的总结。
3)与实际需求脱节,缺乏与设计方案的有效互动。部分数字化技术方法仍以研究为主,尚未大规模运用在实际项目的实践过程中,少量的实际运用也以专题形式为主导,缺乏与设计方案的有效互动与深度介入,对设计的支撑力度偏弱。
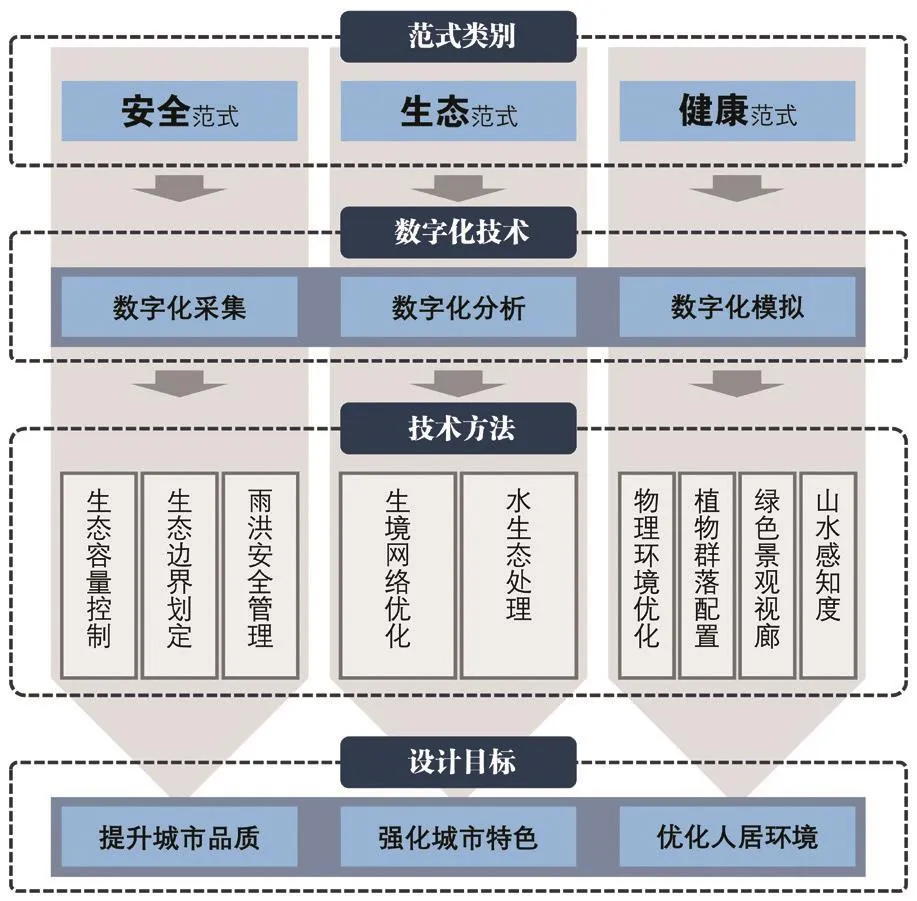
图1 多维需求的绿色城市设计数字化技术方法框架(作者绘)Fig.1 Digital technology system for green urban design with multidimensional demands
因此笔者在理论思考的基础上,通过对近年来承担的南京、郑州、无锡、芜湖和蚌埠等不同城市、不同类型实践项目的总结归纳,对数字化绿色城市设计技术方法予以应用与验证,在此方面积累了大量实践经验与有效数据,并在总结实践反馈的同时,尝试建立数字化绿色城市设计技术方法体系,并对其未来应用进行前瞻。
2 多维需求的绿色城市设计数字化技术
溯源现代绿色城市设计的根本出发点,无论当下面临的新问题如何涌现,其核心内容始终围绕着提升城市品质、强化城市特色和优化人居环境三大目标。数字化技术是在传统生态健康导向城市设计技术方法基础上的拓展与延伸,能够让设计师获得多样化的新数据与新方法,并以此为基础做出更加理性的分析与判断。数字化技术能更好地掌握人群需求并提供多样化的空间场所,提升城市公共空间品质;能更全面地挖掘城市资源,从整体与节点上强化城市空间特色;能对城市环境数据进行采集、分析和模拟,最大限度地优化人居环境质量。以上述三大核心目标为导向,建构多维需求的绿色城市设计数字化技术方法框架,并划分安全、生态、健康3种维度(图1)。
安全城市设计是以人的安全为目标主体,关注的是物质空间环境中的安全问题,基本内容主要包括心理安全、行为安全、防卫安全和灾害安全4个方面[15],通过城市设计技术方法的运用,优化城市物质空间环境、降低城市公共空间的安全隐患。生态城市设计秉承整体优先、生态优先和可持续发展的准则[9],重点研究生态环境要素,如气候、土壤、植被和水体等的组成、特征及其对城市空间形态要素的影响,形成生态导向的城市设计策略[16]。健康城市设计关注的重点在于如何打造健康的城市物质空间环境、如何改善城市居民的身体健康状况。通过设计研究层面上有机的城市形态塑造、积极的市民行为引导,以及在实施策略层面建立有力的保障机制[17],寻求城市健康发展的有效途径。因此可认为安全、生态、健康导向的城市设计在理论基础、研究内容和技术方法等方面既紧密联系,又各具特色(表1),三者共同构成了生态健康导向城市设计的框架体系。
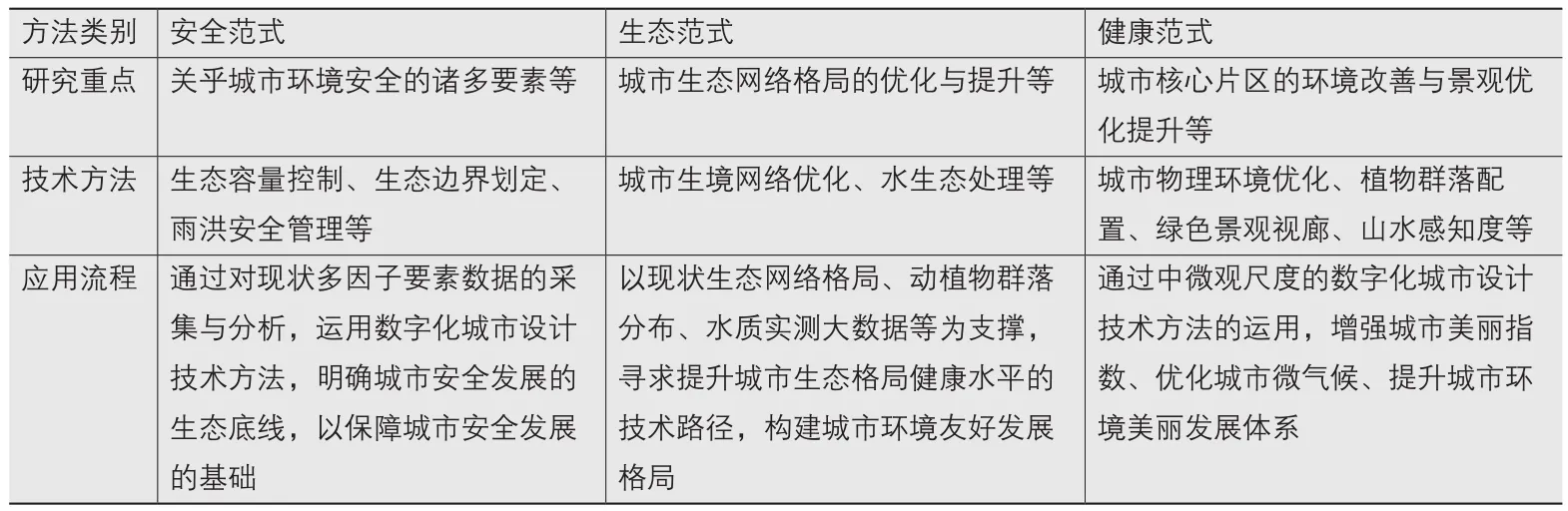
表1 多维度绿色城市设计数字化技术方法类别Tab.1 Multi-dimensional green urban design digital technology category
3 安全范式:保障城市环境安全发展基础
随着数字化采集技术的出现,对特定城市空间数据(如山水格局、绿地系统、道路网络、建筑群落等)的计算机全自动或半自动抓取成为现实,通过对海量数据的抓取构建数字化分析平台,并对数据进行分层化处理,根据要素的影响力强弱对多因子进行赋权叠加,最终明确城市安全发展框架。总体来说,安全范式可分为三方面:开发边界控制、生态容量控制和雨洪安全。开发边界与生态容量控制是从整体视角出发,对城市或片区的开发建设进行全局把控;雨洪安全则是从防灾减灾的角度寻求对雨洪资源的管理与利用。
首先通过对城市山水格局、水绿网络和动植物资源等要素的梳理,采集相应的大数据资源,并对多元要素进行拆解,构建单影响因子群落;再通过对因子的单项分析,获得单因子影响条件下的控制边界;最后利用GIS数据分析平台,对各单因子影响结果进行赋权叠加,得出最终的开发边界与生态容量控制结果,进而有效指导后续城市设计工作的开展。在某总体城市设计实践中,基于城市总体规划中生态红线、生境网络、山水格局以及绿地系统规划等多因子要素的叠加分析,最终划定城市生态边界,并对其进行分类保护与控制,主要分为重点生态保护边界和一般生态保护边界,严格保护城市生态空间。在某滨水地段城市设计项目中,同样采用了基于GIS平台的多因子叠加分析方法,对片区开发容量进行量化模拟。以街区作为研究单元,将会对城市空间容量产生影响的因素分成三大类,即服务支撑、交通支撑和资源支撑要素,并将其细分为城市中心因子、用地布局因子、道路交通因子、区域交通因子、绿地景观因子和滨水景观因子6个支撑因子,在GIS数据分析平台中进行无权重叠加运算,从而得到片区空间容量的等级分区(图2)。

图2 多因子叠加模拟量化开发容量Fig.2 Multi-factor superposition simulation to quantify development capacity

图3 城市生境网络四要素规划对策Fig.3 Four elements planning countermeasures for urban habitat network
在雨洪安全方面,主要通过对片区地表径流和淹没模型的分析,运用多情景模拟寻求城市发展的安全场景。采用文献资料查阅、场地实测等方法,对目标范围内整体环境高程、历史水文数据、地形地貌和降雨数据等进行数字化采集。通过SRTM数据分析、GIS空间水文分析对地表径流进行模拟,划定片区排水分区,进而明确潜在易涝区域;通过对不同水位条件下岸线淹没情况进行模拟分析,判断目标地区多情景安全格局,发现潜在的雨洪安全隐患,并指导后续的城市空间布局。如南方某环湖地区城市设计实践中,现状湖体水质良好且划定为二级管控区,在后续城市设计中须落实城市生态红线、湖泊资源生态保护等政策管控要求,以实现环湖地区开发与湖体保护的有效平衡。如何在水环境如此敏感的区域进行城市开发建设?如何保证城市建设基础上的生态安全?规划通过大数据分析,模拟出地区潜在的安全隐患,并提出相应的规划策略:梳──梳理场地高程,充分结合高程管理地表径流;宽──受淹没威胁区加宽滨水绿带宽度,还河流以空间;蓄──低洼处建设绿色海绵设施,提升场地集水储水能力,并将策略思路落实到最终的设计方案之中。
4 生态范式:构建城市环境友好发展格局
生态范式主要的技术方法包括:山水格局分析、生境网络分析和水生态优化等,通过对山水格局的数字化分析,有利于从整体把握城市的山水骨架,并结合都市骨架、人文骨架的分析研究,提炼城市空间特色,通过多要素管控进行空间落实。生境网络是从保护生物多样性的角度出发,对城市生态公园、绿地等绿化开敞空间进行优化调整的技术方法,其重点关注的是城市公园绿地的生态功能,而城市绿地系统规划则更多关注公园绿地的游憩、生态、安全和经济等多方面的综合功效[18]。水生态优化是以目标为导向,通过不同技术方法的应用达到保障水体生态的既定目标,并对城市空间布局形成指导与反馈。
通过对大型生态斑块、绿化廊道、中小型城市公园等的动植物群落的数字化采集,运用文献查阅、数据实测等方法对其现状种类、生存环境、健康状况和迁徙路径等进行综合研究,发现问题并对生境网络进行优化,以改善城市生态环境、提升城市生物多样性。如在中部某城市的总体城市设计实践中,通过对城市范围内的山水格局、湿地公园和生态廊道等现状情况的实地调研,结合文献资料掌握城市鸟类栖息地现状,对现状生境网络问题进行归纳总结。并以问题为导向,分别从生境网络格局指数、生态敏感区保护2个维度建构生境网络评价方法,进而对生境网络及其四要素:核心保护区、生境斑块、廊道结构和跳板结构的规划布局做出指引与优化(图3)。
在水生态优化方面,通过对现状水体的数据采集,掌握水体水质状况,并结合水质保护目标,运用纳污能力与污染负荷计算分析、DHI MIKE模型模拟等相关技术手段,为水体周边区域的用地布局、水系规划等提供依据。如在南方某旅游度假区核心区及周边地段城市设计实践中,湖体作为旅游度假区的核心以及城市备用水源地保护区,是生态敏感性较高的城市片区,如何在保护水体的前提下进行城市开发建设?如何寻求生态保护与城市发展之间的平衡?首先通过对湖体及周边河道的水样进行现场采集、踏勘湖体生态与生物因子,掌握湖体及周边水体的现状水质,建构数字化分析平台与生态健康评价指标体系,分别从水质特征、水文特征、物理形态结构、生态系统指标和湖滨景观五大方面、17个评价指标对湖体进行赋权打分。其次结合现状采集结果,对标湖体规划控制目标,充分考虑未来周边城市建设带来的影响,运用DHI MIKE与ECO Lab软件对湖体流场与水质进行模拟分析,对湖体环境容量与区域污染负荷进行分析测算。并将分析结果反馈至城市设计方案中,对片区总体开发量控制、生态水处理设施空间布局、滨水岸线规划、雨污水收集处理,以及非点源污染处理等方面提出控制引导要求,以实现湖体水生态控制目标,提升片区物种多样性。
5 健康范式:提升城市环境美丽发展体系
健康范式主要包括物理环境模拟与优化、植物群落优化、绿色景观视廊营造、山水感知度分析,以及绿地匹配度优化等数字化技术方法。物理环境模拟与优化主要是从微气候环境提升的角度来优化城市空间布局;绿色景观视廊与山水感知度是从城市景观营造的角度,对城市重要的山水景观点、标志性节点进行空间布局引导;植物群落与绿地匹配度优化是从生物多样性、景观风貌提升和绿地服务半径等角度综合考虑城市绿地的空间布局与植物配置。

图4 基于Ecotect软件的热环境分析Fig.4 Heat environment analysis based on Ecotect
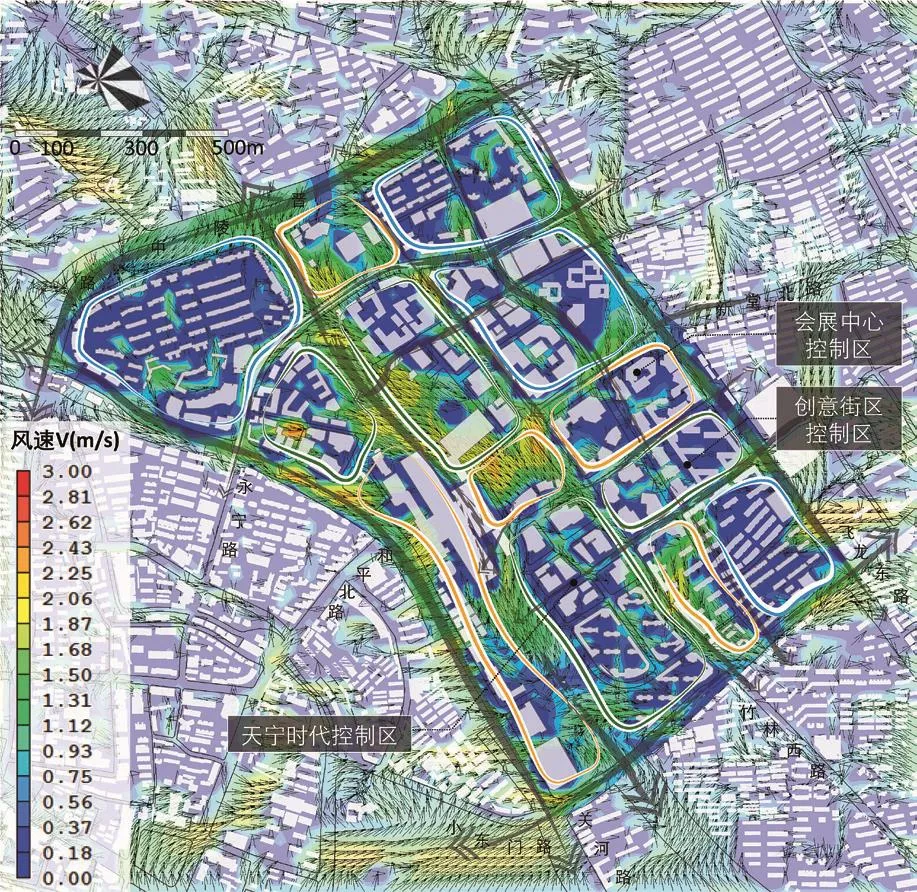
图5 基于Phoenics软件的风环境分析Fig.5 Wind environment analysis based on Phoenics
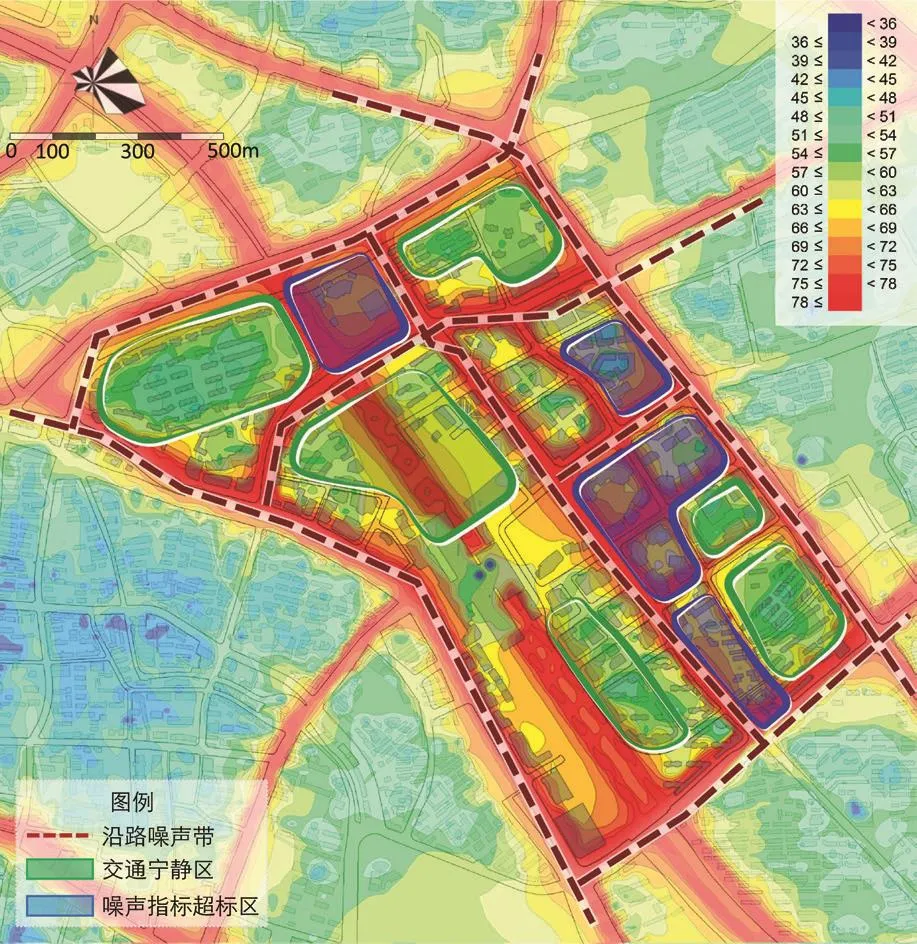
图6 基于Cadna/A软件的声环境分析Fig.6 Sound environment analysis based on Cadna/A
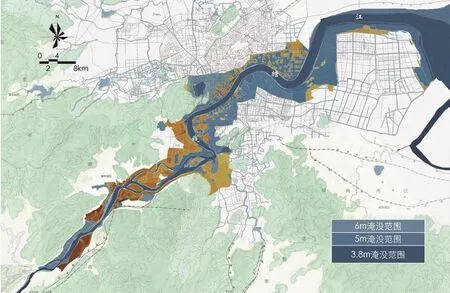
图7 安全策略──钱塘江不同水位下淹没情况模拟分析Fig.7 Security strategy: simulation analysis of flooding situation at different water levels of Qiantang River

图8 生态策略──规划观鸟基地空间布局Fig.8 Ecological strategy: space layout planning the of the bird-watching base
物理环境模拟与优化主要采取模拟与实测相结合的方法,运用卫星遥感技术、Phoenics流体计算软件、SoundPlan软件等对城市或片区的热环境(图4)、风环境(图5)和声环境(图6)进行全范围模拟,分析现状存在的问题,进而提出物理环境提升策略和空间形态管制措施,同时在方案比选阶段对多个方案进行验证和反馈,积极应用于方案深度设计与优化阶段。以声环境分析为例,解析数字化模拟的工作流程。城市中声环境影响最大的是交通噪声,城市声环境模拟分析技术即通过对城市噪声进行实测和模拟,对城市中噪声敏感区进行声学仿真。首先是对空间格栅样本点现状数据进行实际测度,并将实测数据与模拟数据进行校核;其次,将实测数据进行整理并录入Cadna/A软件中,在输入建筑、道路、轨道、三维视角等一系列参数后,对地块进行整体噪声环境模拟计算;最后依据国家及各城市的噪音控制标准进行噪声分区。通过声环境的模拟分析,能够更加直观、清晰地了解整个设计地块的噪声值分布,进而在设计过程中辅助地块环境空间优化,营造交通宁静区,控制交通嘈杂区;同时也能客观评判设计方案的声环境模拟情况,进而优化调整方案布局。
植物群落优化首先通过样方法、文献资料法等手段获取片区植物群落类型、结构与特征等现状基础数据,采用横纵向矩阵对比分析法发现现状植被群落配置的主要问题,再以问题为导向制定相应的生态优化和美化策略,有效指导植物种类配置、空间布局等规划内容。如某滨河地区城市设计中,需要对沿河区域的植被群落进行调查与提升,以达到具有较高知名度的森林生态城市的规划目标。通过选取90个样方点,对面积3.6万m2范围内的约900株植物进行现场调研。调研的空间范围主要包括两大块:沿河区域,以及具有良好地域自然本底的对标区域。选取一处最能体现本土植被群落特征的自然区域作为比较对象,以确定规划区域在植被配置方面的问题与短板。经过数据采集和对比分析,得出以下问题:部分种类与其植物区系不符、植物数量搭配失衡、季相变化片段化、植物种类单调、多样化指数低,以及植物文化主题不突出等。结合规划目标,提出适当增加植物种类、提高多样性指数;增加彩叶植物种类,衔接不同季相、延长季相变化;拓展香味树种数量与种类;增加代表地域植被文化特征的树种数量;大量增加水生植物群落及其多样性等规划策略,并将规划策略与城市设计空间布局相结合等应对措施。
6 生态城市设计样本实证:杭州钱塘江案例
在杭州钱塘江两岸景观提升工程规划实践中,通过多元绿色城市设计数字化技术方法的运用,全面分析了城市山水格局、生境网络、微气候环境、水岸生态、空间特色营造和风貌意向等内容,并在规划设计阶段有针对性地进行优化提升,实现了数字化技术方法簇群的聚合应用。作为滨江地区的城市设计实践,雨洪安全是须首要考虑的内容。研究表明,钱塘江水灾害风险与沿江两岸高程、降雨以及潮汐等情况有着密切联系。通过对降雨频率与月降雨量及钱塘江月水位变化情况等要素的叠加分析,采用计算机模拟技术对沿江两岸在3.8、5.0、6.0m 3种水位状况下的淹没情况(在不考虑江堤的前提下)进行模拟(图7),对可能受淹没区域进行重点设计与监控。
从城市整体角度看,钱塘江具有重要的生态价值,其不仅是城市重要的生态廊道,也是多个物种的天然栖息地,运用“核斑廊岛”技术方法对钱塘江沿江区域生境网络进行研究,并分别针对四大要素提出相应的优化策略:提升核心保护区、打通生境斑块、延续生态廊道、增添跳板结构。依据鸟类习性,规划将沿江两岸的观鸟基地划分为4种类型:城市园林型、河流湿地型、河漫滩湿地型和农田居民区型,结合现状鸟类栖息地调查和地形地貌特征,共规划14个观鸟基地,展示地区物种多样性(图8)。
在物理环境控制体系方面,主要对风环境、热环境与噪声环境进行了模拟分析,并制定相应对策来提升钱塘江沿线地区的微气候环境。以风环境分析为例,通过运用Phoenics流体计算软件,明确钱塘江两岸存在的弱风段、强风区、静风区以及漩涡风区,并根据每段相应的风环境特征提出针对性的规划策略,重点构建沿江多层级通风廊道。规划顺应城市主导风向建构一级通风廊道,基于切割城市热场、促进空气内部流通的原则建构二级、三级通风廊道(图9)。
在钱塘江的项目实践中,通过对拥有安全、生态、健康策略的数字化技术方法的多维分析与聚合应用,为最终的城市设计方案提供了有力的研究支撑,对方案的空间结构、平面布局、功能组团和景观体系等方面均有较强的指导价值,最终形成“定江湾、联古今、显山水”的空间营造策略,以及多组团、有机网络的整体空间形态(图10)。
7 结语
随着信息化技术的不断渗入,绿色城市设计技术方法也呈现出明显的数字化趋势,笔者通过对近年来开展的规划设计实践的分析总结,从中凝练出安全、生态、健康三大技术范式,并详细阐述了各范式所对应的数字化技术方法,旨在完善绿色城市设计的技术方法体系。多源大数据的支撑为规划实践提供了大量新的数据基础与分析方法,促使规划设计能够沿着更加理性的思路完成推演,但总体来说,数字化技术仍是对既有绿色城市设计技术方法框架的补充与完善。通过对数字化技术方法的总结,试图从中发现未来数字化技术发展的趋势与方向,也为推动数字化方法的实践应用提供一定参考。
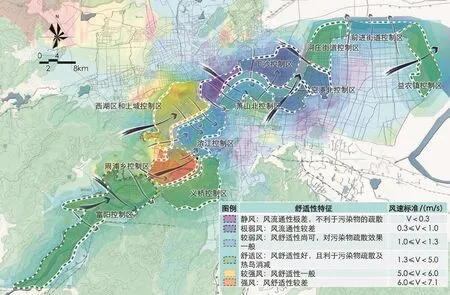
图9 健康策略──钱塘江沿江地区风环境规划引导Fig.9 Health strategy: planning guide of wind environment for the surrounding areas of Qiantang River
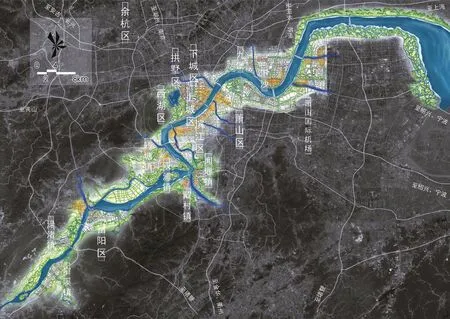
图10 杭州钱塘江两岸景观提升工程规划设计总平面图Fig.10 General plan of the planning of the landscape optimization project on riversides of Qiantang River in Hangzhou
注:文中图片除注明外,均引自杨俊宴工作室既有已完成项目成果文本。
Safety, Ecology, Health: Digital Transformation of Green Urban Design
YANG Junyan, ZHANG Biao
1 New Trend of Digitalization in Green Urban Design
As one of the important means to guide the development of cities, urban design be divided into four generations of traditional urban design,modern urban design, green urban design and digital urban design, from the point of different dominant values.Green urban design, which is one of the four major practice trends in urban design in China, injects ecological theory and analysis methods on the basis of traditional urban design, in order to achieve the goal of sustainable urban development.
Since the 1980s, green urban design theory in China has evolved from the initial simple casebased study to the mid-1990s' comprehensive theory paradigm, and then to the 21stcentury's"4E" model and the flexible design.These concepts have greatly enriched the theoretical system and effectively guided the practical projects, but the corresponding analysis technology can't keep up with the theory.With the emergence of big data, digital technology provides not only effective technical support but also a new perspective on research.However,the current digital technology of green urban design still has some shortcomings.
Therefore, based on the theoretical thinking and the practical projects, the authors have applied and verified the digital technology of green urban design, accumulated a large amount of practical experience and effective data, summed up the practical feedback, trying to establish a digital green urban design technology system.
2 Green Urban Design Digital Technology with Multidimensional Demands
Digital technology enables designers to obtain diversified new data and new methods for rational analysis and judgment.It can improve the quality of urban public space, strengthen urban spatial characteristics and maximize the quality of the living environment.Guided by these objectives, the article constructs a multi-dimensional green urban design digital technology system, and divides it into three dimensions of safety, ecology and health.
Safety urban design, focusing on safety issues in the material space environment includes the content of psychological safety, behavioral safety,defense safety and disaster safety.Ecological urban design with the criteria of sustainable development,focuses on the elements of ecological environment,forming an ecological oriented strategy.Health urban design attaches a great importance on the design of organic urban form, active guidance of citizen behavior at the research level, and the establishment of a strong guarantee mechanism at the implementation strategy level.Therefore, it can be considered that the safety, ecology and health urban design are closely related but different in terms of theoretical basis, research content and technical methods, which together constitute the system of green urban design.
3 Safety Paradigm: Ensuring the Foundation of Urban Safety Development
With the advent of digital acquisition technology, automatic or semi-automatic capture of specific urban spatial data has become a reality,and through the capture of massive data, digital analysis platforms have been built.Based on these platforms the data is layered, and the multi-factors are weighted and superimposed according to the strength of influence, and finally the system of urban safety development is clarified.In general,the safety paradigm can be divided into three aspects: development boundary control, ecological capacity control and rainfall flood safety.
Firstly, through the clearing of urban landscape pattern, water and green network,animal and plant resources, the corresponding big data resources are collected, and the multiple elements are disassembled to construct a single impact factor community.Then, through the single factor analysis, the control boundary under the influence of the single factor is obtained.Finally, the GIS data analysis is used to weight and overlay the results of each single factor, and the final results of development boundary and ecological capacity control are obtained.
In terms of rainfall flood safety, the multiscenario simulation is used to seek the safety scene of urban development through the analysis of the surface runoff and submergence models in the area.Through SRTM data analysis and GIS spatial hydrology analysis for the collected digital data, the surface runoff is simulated, the drainage area is defined, and then the potential flood area is identified.Through the simulation analysis of the shoreline flooding conditions under different water levels, the multi-scenario safety pattern in the target area is judged, potential rainfall flood hazards are discovered.
4 Ecological Paradigm: Constructing the Pattern of Urban Friendly Development
The main technology of the ecological paradigm includes landscape pattern analysis,habitat network analysis and water ecological optimization.The landscape pattern analysis is beneficial to grasp the urban landscape framework from the whole and combine the analysis of urban framework and humanistic framework, refining the urban spatial characteristics, and implementing the space through multi-factor management.Habitat network analysis is a kind of technology for optimizing and adjusting greening open spaces.Water ecological optimization applies different technology to achieve the established goals of ensuring water ecology, and to form guidance and feedback on urban spatial layout.
Through the digital collection of animal and plant communities using literature review,data measurement and other methods to comprehensively study the current status, living environment, health status and migration path,problems can be identified and the habitat network can be optimized to improve the urban ecological environment and enhance urban biodiversity.
In the aspect of water ecological optimization, firstly, through the data collection of the current water body, the water quality status is grasped, and then combined with the protection target, the pollution control load calculation, DHI MIKE model simulation and other related technology is used to provide basis for land layout and water system planning.
5 Health Paradigm: Improving the System of Urban Beautiful Development
The health paradigm includes physical environment simulation and optimization, plant community optimization, green landscape view gallery construction, mountain and water perception analysis, and green space suitability optimization and other digital technology methods.The physical environment simulation and optimization is to optimize the urban spatial layout from the perspective of microclimate environment improvement; the green landscape view gallery and the mountain and water landscape perception are to guide the spatial layout of important urban landscape points and landmarks from the perspective of urban landscape construction;the optimization of plant community and green space suitability is to consider the spatial layout and plant configuration of urban green space from the perspectives of biodiversity, landscape improvement and green space service radius.
Physical environment simulation and optimization, combining simulation and measurement, uses satellite remote sensing technology, Phoenics fluid calculation software and SoundPlan software to perform a fullscale simulation of thermal environment, wind environment and acoustic environment.Then it analyzes the existing problems, proposes physical environment improvement strategies and spatial form control measures, and verifies and feeds back multiple scenarios in the program comparison phase.
Plant community optimization is firstly to obtain the basic data of plant community types,structures and characteristics.And then it finds the main problems of the current vegetation community by the method named horizontal and vertical matrix comparison analysis and afterwards the problem-oriented development of the corresponding ecological optimization and beautification strategies are carried out, which effectively guides the planning.
6 Ecological Urban Design Demonstration:Hangzhou Qiantang River
In the planning of landscape optimization project on riversides of Qiantang River in Hangzhou, through the aggregation application of digital technology in green urban design,the urban landscape pattern, habitat network,microclimate environment, waterfront ecology,spatial characteristics and style intentions were comprehensively analyzed and optimized.
As an urban design in the riverside area,rainfall flood safety is a top priority.Due to the fact that the risk of water disasters is closely related to elevations, rainfall, tidal and other conditions,the computer simulation technology is used to simulate the flooding situation under different water levels, in order to focus on the design and monitoring of areas that may be flooded.From the perspective of ecology, the "core,plaque, corridor and island" technology is used to research the habitat network and propose corresponding optimization strategies for the four major elements: enhance the core protection zone, open up habitat patches, continue the ecological corridor, and add springboard structure.According to the habits of birds, the planning sets up 14 bird-watching bases of four types to show regional species diversity.In the control system of physical environment, the wind,heat and noise environment were simulated and analyzed, and corresponding countermeasures were formulated to improve the microclimate environment.For instance, based on the wind environment analysis, the plan proposes targeted strategy to construct the multi-level ventilation corridors along the river.
In the project of Qiantang River, with the strategies of safety, ecology and health, the multidimensional analysis and aggregation application of digital technology strongly guide the final design in terms of the spatial structure, plan layout, functional group and landscape system,and finally form the space construction strategy as well as the overall spatial form.
7 Conclusion
With the continuous infiltration of information technology, the green urban design technology also shows a clear digital trend.The authors analyze and summarize the planning and design carried out in recent years, condense the three technical paradigms of safety, ecology and health, and elaborate the digital technology corresponding to each paradigm, aiming at perfecting the technology system of green urban design.Through the summary of digital technology, the paper tries to find out the trend and direction of digital technology development in the future, and provides some reference for the practical application.
(Editor / LIU Xinya)
Biography:
YANG Junyan, male, born in 1976 in Wuji of Jiangsu Province, Ph.D., Professor, and Doctoral Supervisor of School of Architecture of Southeast University, Associate Dean of Smart City Research Institute of Southeast University, Member of the Urban Design Academic Committee of China Urban Planning Association, research area: digital urban design (Nanjing 210096)
ZHANG Biao, male, born in 1986 in Fuzhou of Jiangxi Province, Ph.D.candidate of School of Architecture of Southeast University,research area: ecological landscape oriented urban design (Nanjing 210096)

