The Study of Higher Vocational English EGP+EOP Teaching Model Reform
Wang Qian
Abstract: The teaching model of English for Occupational Purposes plus English General Purpose (EOP+EGP) meets the needs of the higher vocational English pedagogy in China. This paper analyzes the importance and necessity of the model as well as its specific implementation.
Keywords: higher vocational English, EGP+EOP teaching model
In compliance with the Essential Requirements for Higher Vocational English Teaching (Trial) promulgated by the Ministry of Education in 2000, higher vocational English is offered in China as “a compulsory and fundamental course for students at higher vocational institutions across the country to train highly skilled professionals and meet the needs of the forefront of production, construction, and management sector.” On 26 February 2014, at an executive meeting of the State Council, premier Li Keqiang mapped out a national strategy to gear up China’s modern vocational education. He also pointed out that the vocational education shall cultivate talents for society, and that the government shall work to enhance its attraction, accelerate its system construction, and upgrade its educational quality.On 22 March of 2014, at the China Development Summit, Lu Xin, the former Viceminister of Education, ascertained that vocational education is a key solution to the structural contradiction of employment. Therefore, in the current contexts of the state’s requirement, the reform of English Test in the college entrance examination,and the need of the social markets, vocational English education reform is indeed imperative. Also, unlike disciplinary English courses, the vocational English pedagogy shall cater to the higher vocational learners’ actual needs.
The vocational English course shall be oriented,with timeliness and practicality, to respective sectors and specializations, thus strengthing the graduates’competitiveness and adaptive for prospective jobs requiring English skills. To this end, in the guideline of “service as the mission, employment as the orientation, and development as the specialty,” China is putting into effect overall practice-based and applied educational policies.
1. Reform basis
1.1 Essential requirements of higher vocational education
The higher vocational education is aimed at training developmental, multi-skilled, and innovative skilled and technical talents. Skill-focused and nonacademic, higher vocational education, the relevant English teaching model, shall target vocational communication, give priority to development of vocational competence, upgrade English application capacity, and embody its professionalism and practicality. Meanwhile, in response to the reform and change in the English Test of the college entrance examination, English education is both instrumental and language proficiency specific in the discipline of humanities. The vocational English teaching model shall also be effective in improving the learners’ actual English application competence to meet the needs of talent training objectives and market demands. The vocational English teaching shall aviod singular curriculum designs and shall be based on vocational or industrial needs. Additionally,the higher vocational English teaching features obviously “compulsory + optional courses” toward“professions + sectors,” and the EGP+EOP teaching model is adopted, based on the talent development program for professional core competence through which vocational English skills are designed to complement the mainstay universal language skills education.

English teaching
1.2 Reqirements of market
Reqirements of market refer to the English eligibility for jobs posted at the employing enterprises. With surveys of several enterprises, it is found that the English proficiency required for enterprise can be outlined generally as follows: skills to communicate with foreigners on unsophisticated occasions in everyday English;skills to read English emails from English speaking business partners and compose or answer general emails in English with the aid of a dictionary and spell-checking software; and the skills to understand and use the most common work-related glossary. As it would be very difficult for general English education to achieve this level of proficiency, thus the addition of the EOP module to the current discipline is indispensable.
1.3 Reqirements of students
For the students or their parents, after three years’ junior college study at vocational college,their greatest expectation is to have the graduates find suitable jobs, and make the most of what they have learned in college by effectively applying their knowledge in the workplace. With the additional EOP module to the vocational English teaching, not only can the teaching contents be directly related to their future work, the students’ learning interests can also be greatly inspired. The EOP+EGP teaching model focuses on developing the English learners’competence levels to match their vocational skills,thus preparing them to become qualified and adaptable professionals to better serve themselves and society after graduation.
2. Some thoughts on reform
According to the teaching rules, in line with the Requirements for Higher Vocational English Course Teaching, as well as the principle of professionalism,practicality, pertinency and creativity, a variety of studies shall be conducted to shape such an EGP+EOP teaching model with prioritized general education, supplemented vocational training,and classified teaching teams for corresponding specializations and programs.
3. Reform content and implementation
3.1 Clarification of teaching objectives
Aimed at developing the students’ competence in actual English applications, the vocational English course shall place emphasis on developing language communication skills in the vocational environment and constantly upgrading their competence in English communications. At the same time, the English course shall enable the students to access effective learning methodologies and strategies, develop their learning interests and independent learning abilities, raise their integrative cultural qualities and cross-cultural awareness, and upgrade their competitiveness for employment and establish the necessary foundation for sustainable development in the future. Depending on the disciplinary diversity, the requirements can be at the basic, general, and most rigid levels.
3.2 Refinement of teaching contents
Teaching involves one curriculum and several course books. Specifically, for teaching the English language, a universal curriculum encompasses the language knowledge (sound, vocabulary, grammar),language skills (listening, speaking, reading,writing, and translation), communicative skills(pragmatics). The EOP teaching contents are crosscultural communicative skills, learning strategies(for development and utilization of independent learning resources), and vocational skills. One universal course book can be selected for language skills training while vocational English skills can be developed through school-compiled handouts.EOP originates from vocational knowledge, with rationally focused module selections, and the teachers’ in-depth explanations and expansions of the modules.
3.3 Creative teaching model
(1) Guidance is classified by such majors as the categories of service and manufacturing technology.
(2)A platform is facilitated for the EGP + EOP model.
EGP is mainly to develop the students’ daily communicative competence and humanities qualities. Contextual reference is necessary for basic language skills and humanities knowledge.The themed contextual assignment may vary from different majors and vocational features may be illustrated with some specialized examples. On the other hand, EOP enables the students to involve spoken and written exchanges related to their future jobs and enhance their employment competitiveness and sustainable development capacity.
4. Updated teaching methodology
For actual teaching with students as subjects and the teacher as director, various approaches are advised, such as situational simulation, roleplay, task-driven method, brainstorming, and initiative discussion. Through application what the students have learned to the settings, the teacher may deploy multi-media devices, the Internet resources, and information technology to create the working scenarios. By doing so,an interactive and coadjutant classroom can be enhanced, and the in-class and after-class learning channels combined.
5. Reform of teaching assessments
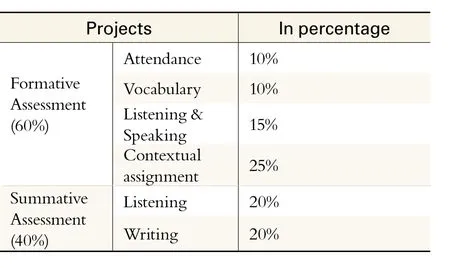
The teaching assessments comprises two major parts, formative and summative, which are scored 60% and 40% respectively.
6. Teaching resources and security conditions
(1) Teachers are recruited from the specialized teacher development educational program. They shall develop experience by teaching 2-3 courses of English for specific purposes with the focus on vocational contents.
(2) Teaching resources include test pools, course books and supplementary materials, handouts, and bands 3-4 training materials.
7. Conclusion
The EGP+EOP higher vocational English teaching model practices the teaching concept of“teach some, learn some, and use some,” in the guideline of “priority to practicability, adequacy as dimension.” It also further refines the scientific higher vocational English teaching system of “social demand satisfaction, employment orientation and application focus” at the junior college level.As it should be, application of the entire model,particularly the EOP model knowledge buildup,requires the vocational English teachers’ self-study and improvement, their presence at enterprises for studies and practice, and development into professional teachers with “dual qualifications.”Only through accumulation of practical experience in the sector, can the teachers better ensure implementation of the model, give expression to the features of modern vocational education, and heighten the students’ employment competitiveness.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2018年6期
Contemporary Social Sciences2018年6期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Lower-Elementary Level School Pupils’ Developmental Trajectories of Chinese Verbal Vocabulary Knowledge and Influential Factors
- On the Farmers’ Role Differentiation and the Effective Implementation of Rural Vitalization Strategy—A Perspective from the Targets, Process and Evaluation of Policy Implementation
- The Overseas Reception of Chinese Science Fiction Works from a Perspective of Western Interpretation Preference—A Case Study of Reader’s Reception of Liu Cixin’s The Three-Body Problem in the USA
- International Communication Theories: Main Development Stages and Reflections
- China’s Process and Action Framework for Transforming to a Manufacturer of Quality
- A Legal and Economic Study of Cooperation among the BRICS Countries under BRI
