A comparison of lower limb stiffness and mechanical muscle function in ACL-reconstructed,elite,and adolescent alpine ski racers/ski cross athletes
Matthew J.Jordan*,Per Aagaard,Walter Herzog
aCanadian Sport Institute Calgary,Calgary AB T2N 1N4,Canada
bDepartment of Sports Science and Clinical Biomechanics,SDU Muscle Research Cluster,University of Southern Denmark,Odense DK-5230,Denmark
cHuman Performance Laboratory,University of Calgary,Calgary AB T2N 1N4,Canada
Abstract Purpose:The aim of this study was to compare mechanical muscle function in the eccentric/concentric phases of vertical bilateral jumping in anterior cruciate ligament-reconstructed(ACLR),elite(ELITE),and adolescent(ADOL)alpine ski racers and ski cross athletes.Methods:Alpine ski racers/ski crossers(ACLR:n=12,age=26.7±3.8 years;ELITE:n=12,age=23.9±3.0 years;ADOL:n=12,age=17.8±0.7 years;females:n=6 per group,males:n=6 per group)performed 5 maximal countermovement jumps(CMJs)and 5 squat jumps.The ground reaction forces for each limb were analyzed using dual force plate recording to obtain body center of mass(BCM)velocity,displacement,and power.The eccentric deceleration(ECC)and concentric phases were determined from BCM velocity.CMJ net concentric and ECC impulses were calculated(body mass normalized)along with the peak and mean BCM power and maximal vertical jump height.CMJ lower limb stiffness(LLS)was determined by the slope of the ground reaction forces vs.the BCM displacement curve over the ECC phase.Concentric and ECC asymmetry indices were calculated for each leg,and the left vs.right LLS was compared.Outcome measures(reported as mean±SD)calculated as a 5-jump mean were normalized to body mass and compared using an analysis of variance.Results:No between-group differences were found for peak and mean power or jump heights.There were no group differences for LLS or net concentric phase impulse,but the net ECC impulse was lower in the ADOL group compared with ELITE skiers(ADOL:1.33±0.32 Ns/kg;ELITE:1.59±0.16 Ns/kg;p<0.05).Although no group differences were found for ECC asymmetry indices,a group×limb interaction was found for LLS(p<0.01),which was systematically higher in the right vs.the left limb of ADOL skiers(right:54.1±17.9 N/m/kg;left:48.7±15.7 N/m/kg;p<0.01).Conclusion:ADOL skiers demonstrated decreased ECC impulse and systematic right limb dominance in LLS compared with ACLR and ELITE skiers.The implication of these findings for injury and performance are unknown,but further investigation into these potential relationships is warranted.
Keywords:Between-limb asymmetry;Injury prevention;Knee injuries;Muscle power;Vertical jump





Table 1 Subject characteristics(mean±SD).


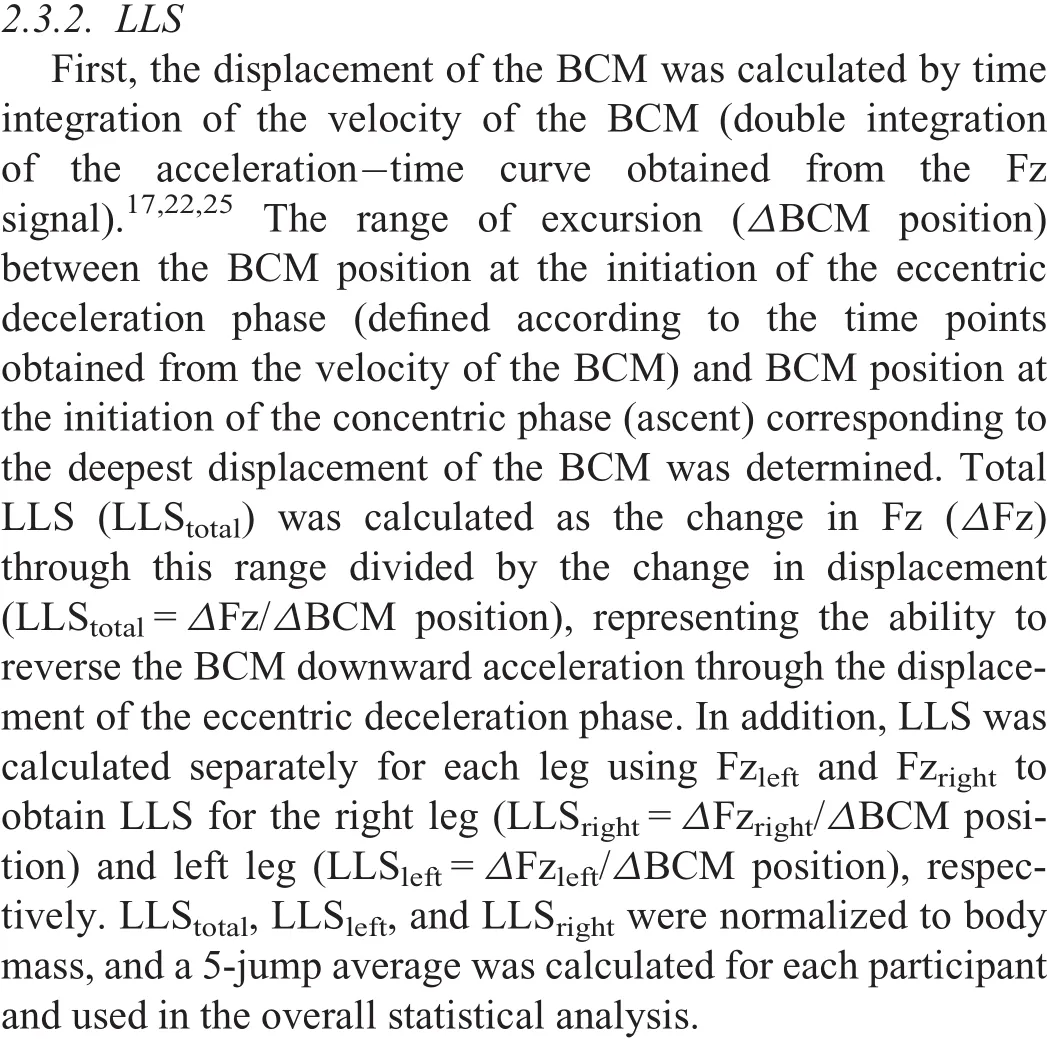
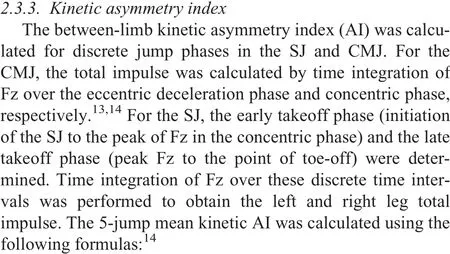
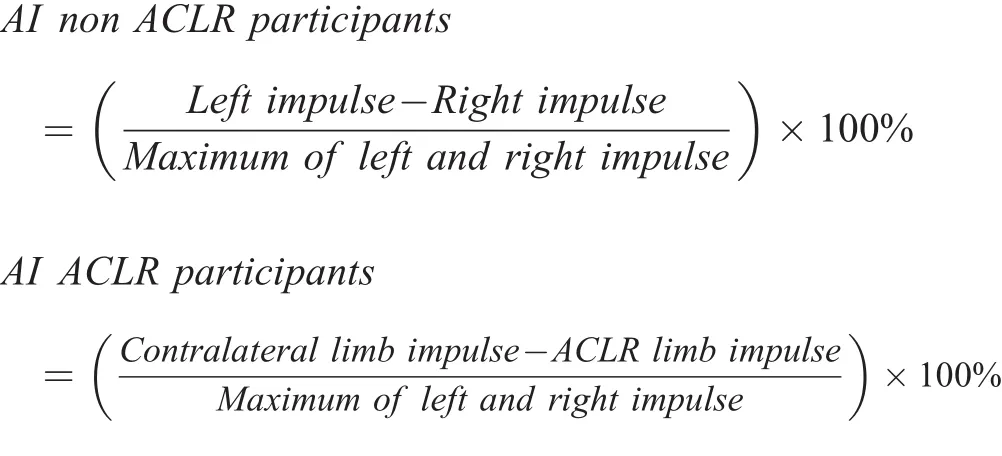

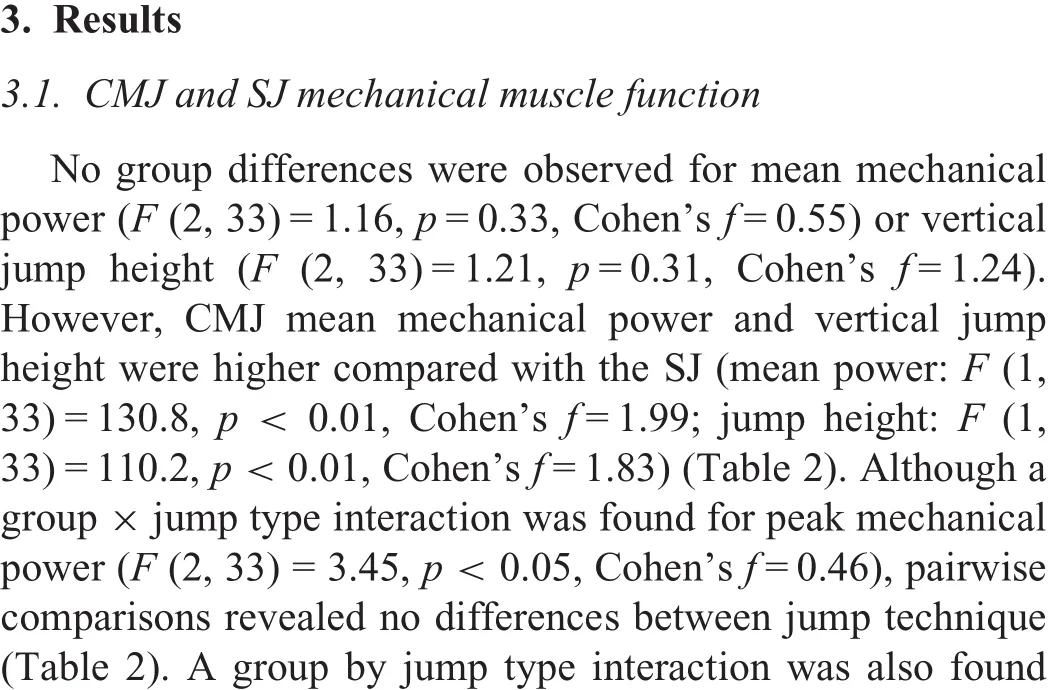


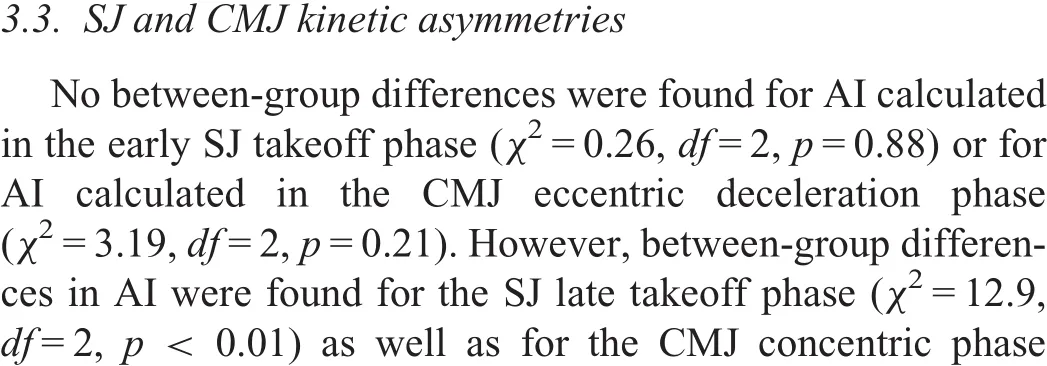
Table 2 Comparison of SJ and CMJ mechanical muscle function measures between groups(mean±SD).

Fig.1.Group comparisons of net eccentric deceleration impulse(A)and net concentric phase impulse(B).*p<0.05.ACLR=anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed;ADOL=adolescent;ELITE=elite.


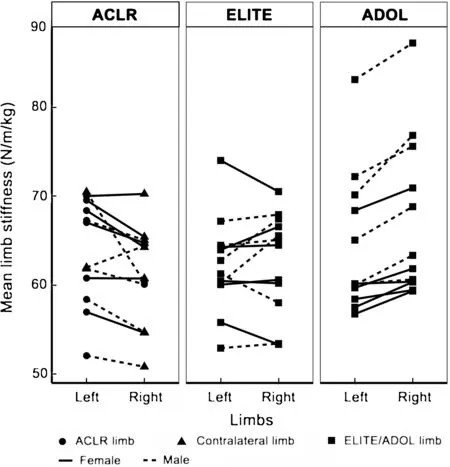
Fig.2.Group comparison of right vs.left limb stiffness for ACLR,ELITE,and ADOL groups.Systematic limb stiffness asymmetry re flecting right limb dominance was found in the ADOL group(p<0.01).ACLR=anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed;ADOL=adolescent;ELITE=elite.

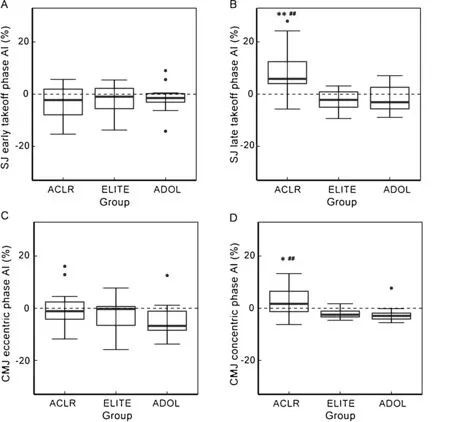
Fig.3.Group comparisons of the SJ early takeoff phase AI(A),SJ late takeoff phase AI(B),CMJ eccentric deceleration phase AI(C),and CMJ concentric phase AI(D).*p<0.05,**p<0.01 compared with ELITE;##p<0.01 compared with ADOL.ACLR=anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed;ADOL=adolescent;AI=asymmetry index;CMJ=countermovement jump;ELITE=elite SJ=squat jump.











 Journal of Sport and Health Science2018年4期
Journal of Sport and Health Science2018年4期
- Journal of Sport and Health Science的其它文章
- Sport participation and vigilance in children:In fluence of different sport expertise
- Pacing and predictors of performance during cross-country skiing races:A systematic review
- he in fluence of physiobiomechanical parameters,technical aspects of shooting,and psychophysiological factors on biathlon performance:A review
- Limb symmetry index in competitive alpine ski racers:Reference values and injury risk identification according to age-related performance levels
- he BRICS Council for Exercise and Sport Science(BRICSCESS)—A new era has dawned
- Battle of the sexes:Which is better for you,high-or low-intensity exercise?
