振动声激发超声导波评估皮质骨厚度的研究
刘珍黎,徐峰,他得安
振动声激发超声导波评估皮质骨厚度的研究
刘珍黎,徐峰,他得安
(复旦大学电子工程系,上海 200433)

长骨皮质骨;超声导波;振动声激发;厚度估计
0 引言

1 基本原理
1.1 板状超声导波理论

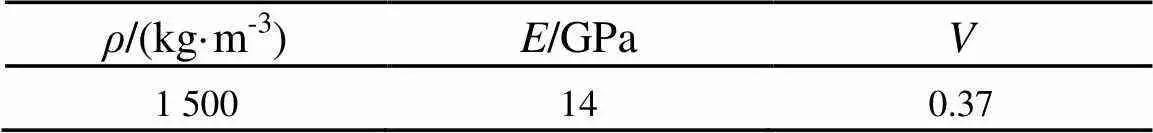
表1 牛胫骨的材料参数[14]


图 1 牛胫骨板的相速度频散曲线图
1.2 振动声原理
在超声波的激励下,组织受到的声辐射力可表示为[15]

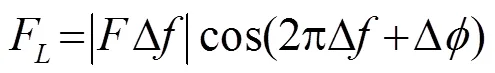
低频声波经骨板上下表面的反射、折射以及横纵波耦合后,最终形成可稳定传播的导波信号。
2 方法

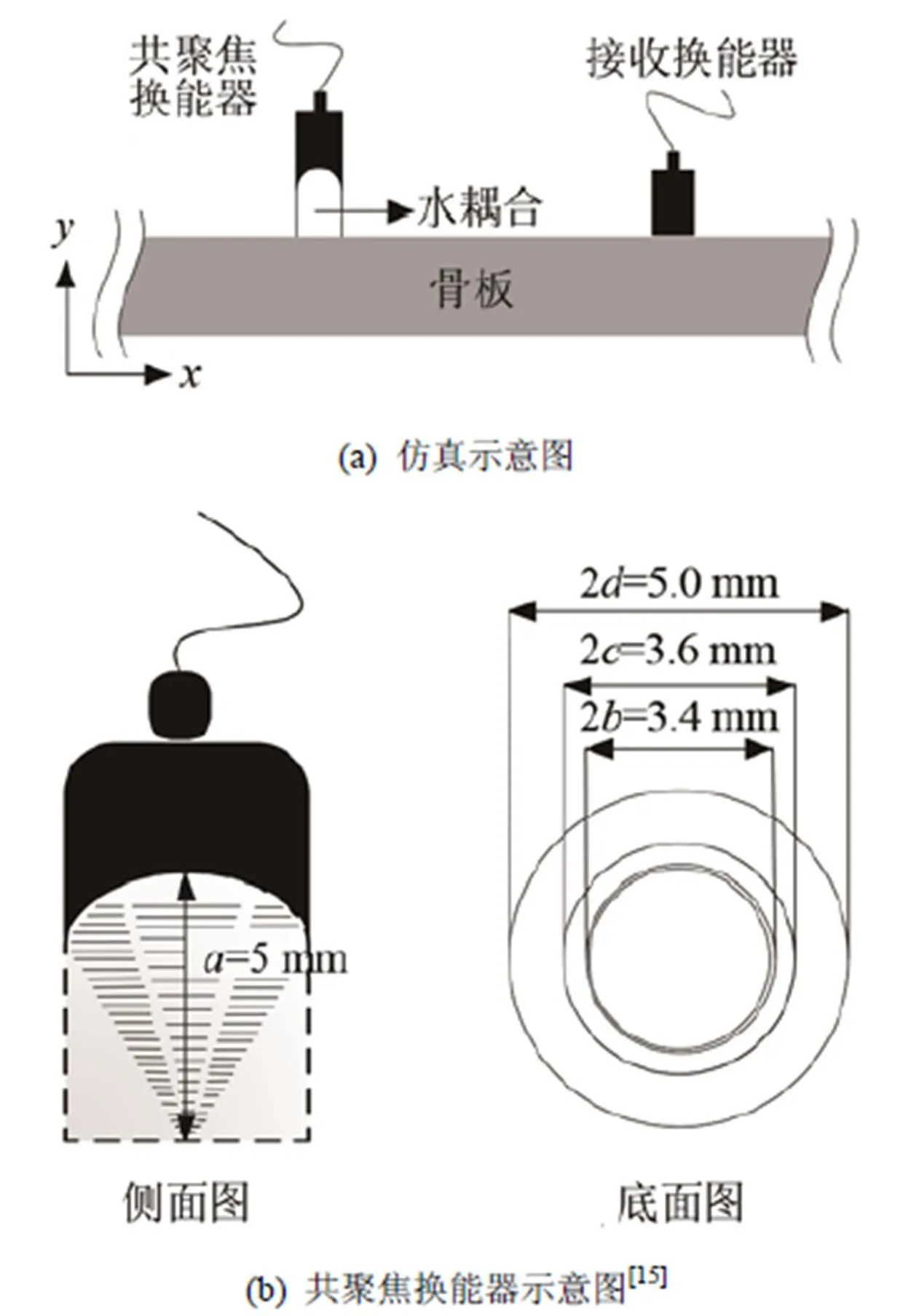
图 2 骨板厚度评估的仿真实验模型
本文以3 mm为步长,记录传播距离为100~121 mm范围内的接收信号。仿真材料选用牛胫骨板,具体的材料参数如表1所示,骨板厚度设置为2~6 mm。共聚焦换能器的示意图如图2(b)所示,其中、、、分别代表换能器的焦距、内圆半径、圆环内半径和圆环外半径。
两路高频超声激励信号可表达为
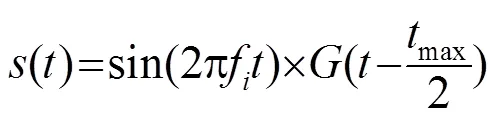
3 结果与讨论


最终的厚度估计结果如图6所示,其中黑色实线为理论曲线,红色星形点代表估计所得的厚度。可以观察到估计结果与理论曲线非常接近,进一步的计算表明,估计结果的平均误差仅为2.61%,最大误差为8.45%。因此采用振动声激发超声导波的方法可以对骨板的厚度进行有效的评估。
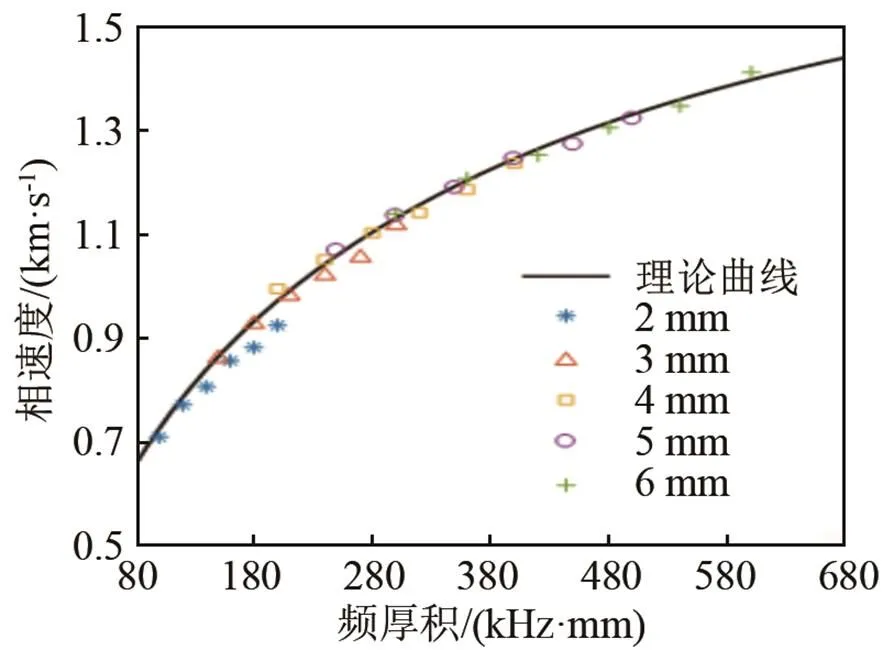
图4 A0模式的相速度随频率与骨板厚度乘积的变化
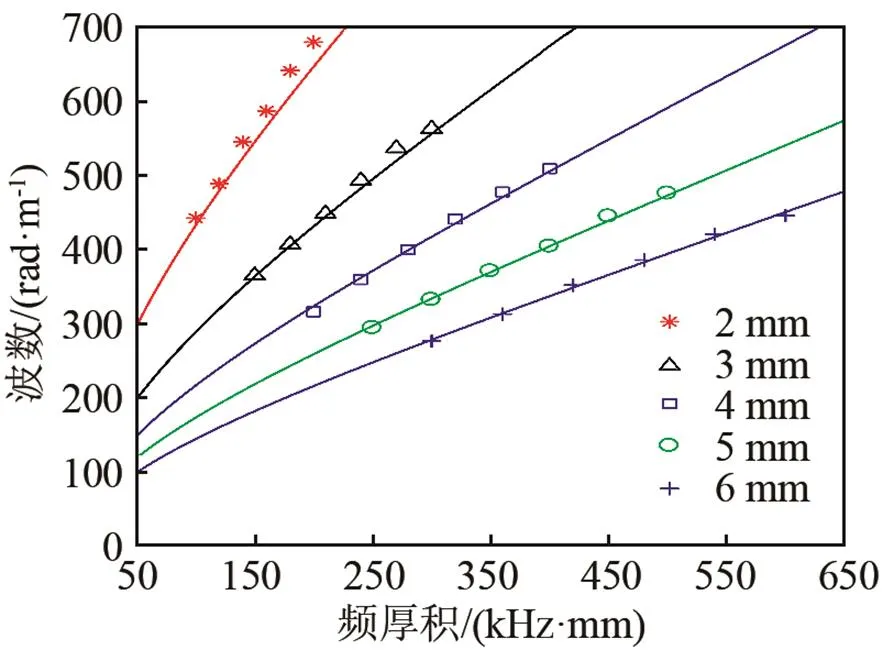
图5 A0模式的波数随频率与骨板厚度乘积的变化

图6 厚度估计结果
4 结论
本文采用三维有限元仿真的方法,探讨在骨板中基于振动声激发的超声导波的传播特性,并将其应用于骨板的厚度估计。本文提出的方法通过采用高频共聚焦换能器,实现了在一定低频范围内任意频率超声导波的激发,提高了激励的灵活性。仿真结果表明,采用振动声激发超声导波的方法可以有效地评估骨板的厚度。该方法对长骨皮质骨的厚度估计具有一定的应用价值。下一步的工作将建立长骨的三维管状模型,并探讨将该方法应用于在体测量的可行性。
[1] LI Y, LIU D, XU K, et al. Transverse and oblique long bone fracture evaluation by low order ultrasonic guided waves: a simulation study[J]. BioMed Res Int, 2017, 2017(4): 3083141.
[2] TA D, WANG W, WANG Y Y, et al. Measurement of the dispersion and attenuation of cylindrical ultrasonic guided waves in long bone[J]. Ultrasound med biol, 2009, 35(4): 641-652.
[3] KILAPPA V, XU K, MOILANEN P, et al. Assessment of the fundamental flexural guided wave in cortical bone by an ultrasonic axial-transmission array transducer[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 2013, 39(7): 1223-1232.
[4] MOILANEN P, SALMI A, KILAPPA V, et al. Phased laser diode array permits selective excitation of ultrasonic guided waves in coated bone-mimicking tubes[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122(14): 144901.
[5] FATEMI M, GREENLEAF J F. Ultrasound-stimulated vibro-acoustic spectrography[J]. Science, 1998, 280(5360): 82-85.
[6] ALIZAD A, WHALEY D H, GREENLEAF J F, et al. Potential applications of vibro-acoustography in breast imaging[J]. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment, 2005, 4(2): 151-158.
[7] MITRI F G, KINNICK R R. Vibroacoustography imaging of kidney stones in vitro[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 59(1): 248-54.
[8] ALIZAD A, URBAN M W, MORRIS J C, et al. In vivo, thyroid vibro-acoustography: a pilot study[J]. Bmc Medical Imaging, 2013, 13(1): 12.
[9] MACCABI A, TAYLOR Z, BAJWA N, et al. An examination of the elastic properties of tissue-mimicking phantoms using vibro-acoustography and a muscle motor system[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(2): 341-350.
[10] MOILANEN P. Ultrasonic guided waves in bone[J]. IEEE trans on UFFC, 2008, 55(6): 1277-1286.
[11] XU K, TA D, MOILANEN P, WANG W. Mode separation of Lamb waves based on dispersion compensation method[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 2012, 131(4): 2714-2722.
[12] SU Z, YE L, LU Y. Guided Lamb waves for identification of damage in composite structures: a review[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2006, 295(3-5): 753-780.
[13] VIKTOROV I A. Rayleigh and Lamb waves: physical theory and applications[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1967.
[14] LAUGIER P, HAÏAT G. Bone quantitative ultrasound[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011.
[15] 刘珍黎, 宋亮华, 白亮, 等. 长骨中振动声激发超声导波的方法[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(15):169-176.
LIU Zhenli, SONG Lianghua, BAI Liang, et al. Vibro-acoustic stimulating ultrasonic guided waves in long bone[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2017, 66(15): 169-176.
Estimation of cortical bone thickness by vibro-acoustic excited ultrasonic guided waves
LIU Zhen-li, XU Feng, TA De-an
(Department of Electronic Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China)

long cortical bone; ultrasonic guided wave; vibro-acoustic stimulating; thickness estimation
TB559
A
1000-3630(2018)-05-0442-04
10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2018.05.007
2017-09-30;
2017-11-15
国家自然科学基金项目(11525416、11604054)
刘珍黎(1993-), 女, 重庆人, 硕士, 研究方向为医学超声及超声信号处理。
他得安,E-mail: tda@fudan.edu.cn

