Kangfuxin Fluid on the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema: a Systematic Review
Si-Yuan Yang, Yuan Jia , Li-Min Guo , Fan-Jie Meng*
1 Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China.
Background
Ulcerative Colitis (UC), a form of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), is a chronic idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by continuous mucosal inflammation that starts in the rectum and extends proximally. UC mainly invades from the rectum, sigmoid colon to the left or right hemicolon, or the terminal ileum.Its clinical manifestations include bloody diarrhea,abdominal pain, urgency and tenesmus [1-2]. The incidence of this disease in developed countries, like Europe and America, is high. With the diet structure,lifestyle and environmental changing, the incidence of ulcerative colitis in China is on the rise in recent years.The prevalence of UC in the world changed by 5.50/10000 to 24.30/10000. Among them, the prevalence rates of UC in developed areas such as North America and Europe were higher, 24.30 / 10000 and 19.2 / 10000,than those in Asia and the Middle East 6.30 / 10000,while the prevalence of UC in mainland China is approximately 11.60 / 10000 [3-6].
The pathogenesis and mechanism of chronic UC have not yet been fully elucidated, and may be related to factors such as infection, abnormal immune response,genetic factors and psychological factors. UC has been listed by the World Health Organization as one of the most refractory diseases because of unclear etiology, long course, high recurrence, ineffective clinical treatment and the possibility of cancer [7]. Present articles about UC treatment, clinical reported methods and efficacy are various. At present, the commonly used drugs are still Amino Salicylic Acids, Glucocorticoids, Antibiotics,Immunosuppressant, which adverse reactions are obvious,so that they should not be used in the long time [8-12].The retention enema of traditional Chinese medicine KFX can avoid this defect. In recent years, the retention enema of traditional Chinese medicine KFX for the treatment of UC has a significant clinical effect. It is necessary that a multifaceted research systematically reviews the high quality randomized controlled trials(RCTs) on the efficacy of KFX in UC with retention enema.
Methods
Search Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies.Randomized controlled trials of KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema were included. The study was restricted to RCTs that compared KFX on the healing was a controlled group, without restriction for single-blind, double-blind or non-blind method. Articles were restricted to English and Chinese.
Types of participants.The study population is in accordance with diagnostic criteria for UC. There was no exclusion based on nationality, age gender, acute or chronic ulcerative colitis
Types of interventions.KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema was assessed as the treatment group.In addition to the basic treatment, other drugs and intervention measures should not be combined with it in the treatment group. There was no exclusion based on other positive drug therapy, treatment or placebo in the control group. The controlled group included in this systematic review included conventional western drugs:Smecta, Gentamycin, Glucocorticoids, Metronidazole,Sulfasalazine, Folic Acid, Lidocaine, Mesalazine, 5 –amino Salicylic Acid as well as the Chinese medicine such as Yunnan Baiyao, Xilei Powder and Berberine.Additional conventional treatment measures and course of treatment were similar in the two groups.
Types of outcome measures.The primary outcome was clinical effectiveness, and score of the quality of life after treatment. The standards of clinical benefit indicators refer to Therapeutic Criteria for Ulcerative Colitis in 2004[13], designed by Anorectal Branch of China Association of Chinese Medicine and Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in 2001 [14], designed by Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Improvements were categorized as following four types: (1) Complete remission: Clinical symptoms and signs disappear, along with that enteroscopy shows that sticky mold lesions return to normal. (2) Significantly effective: Symptoms and signs basically disappear, and the intestinal inflammation of the intestinal mucosa only mildly inflammatory changes. (3)Effective: Symptoms and signs, colonoscopy Lesion lessened. (4) Ineffective: Symptoms, signs, colonoscopy were unchanged
The secondary outcomes included: (1) Mayo disease activity index; (2) Score of diarrhea; (3) Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF); (4) Expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF); (5) Recurrence rate after 3 months treatment.
Assessment of methodological quality of included studies
The methodological quality of the studies was assessed using the Cocharane risk of bias tool. It involves rating trials as high, low and unclear risk of bias: Random sequence generation; Allocation concealment; Blinding;
[2]樊星.汉味小说风格论——方方、池莉合论 [J].华中师范大学学报(哲社版),1994,(1):49-55
Missing data and attrition; Outcome reporting; Other sources of bias. Finally, the funnel plot of Revman5.3 software was performed to determine whether publication bias occurred.
Statistical analysis
RevMan5.3 software was used to Meta-analysis. The data of clinical efficacy and recurrence rate were dichotomous.The others were continuous. Dichotomous data were expressed as the risk ratio (RR). The continuous outcomes between groups as Mean difference (MD) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), are used a fixed-effects or random-effects model. If the heterogeneity test result is P > 0.1, the fixed effect model is utilized. If P ≤ 0.1,while the random effects model was used. If a critical heterogeneity presented in the literature, there will be a descriptive analysis.
Results
Description of studies
The initial search yielded 141 non-duplicated articles.Based on abstract review, all potential controlled trials and review articles were retrieved for full text review. A total of 18 articles were obtained of which 18 randomized controlled trials were identified by the authors as being eligible for inclusion (See Figure 1). Twenty-eight articles were excluded. Finally,18 references were retrieved for further assessment after reading full text [15-32]. A total of 731 cases were included in the treatment group and 686 cases were included in the control group. A fixed effect model was used in that, there is no statistical heterogeneity amongtrials (Chi2=13.89, I2=0%).
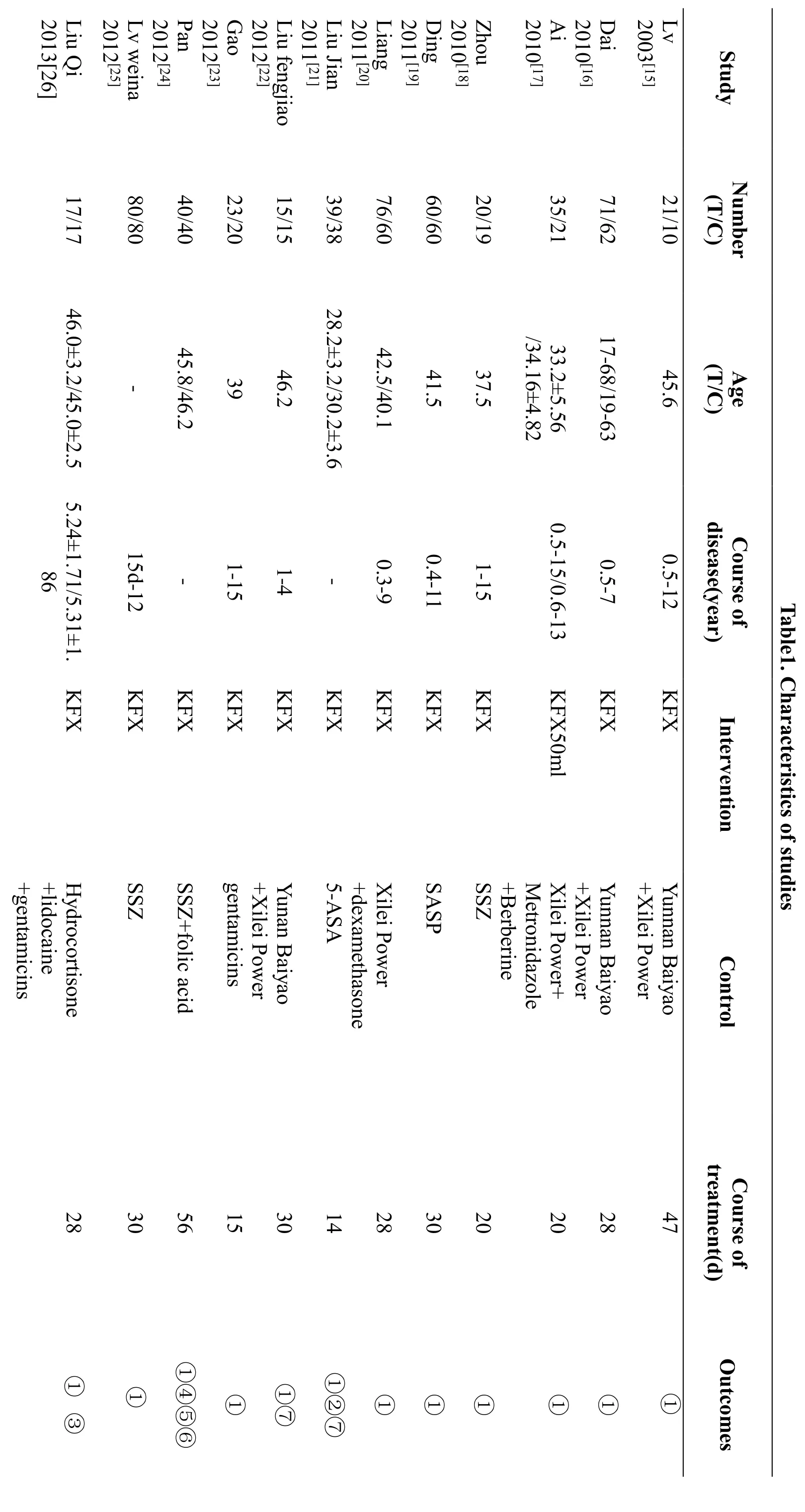
All 18 studies (total of 1417 participants) were carried out in adult patients aged 18 years and over, and in China.Ten trials were compared KFC group with routine treatment of western medicine ,3 of them are taken orally[18,24,29], and the others are with retention enema[19,21,25,27,28,30,32]. Then 4 trials used Yunnan Baiyao and Xilei Powder compared with KFX [15,16,22,27].Only one trial compared KFX against Metronidazole and Berberine [17], and 3 trials compared with Xilei Power,dexamethasone and Gentamicins [20,23,31]. The duration of treatment ranged from 2 weeks to 8 weeks. The basic characteristics of the literature are shown in Table 1.
All the studies reported the usage of the randomized method. Two of the included trials described the method[17,24], one trial described the method used to generate the allocation sequence by random number table [21], the other used random order [17]. All the studies involving didn’t mention the method that is used to conceal the allocation sequence and blinding of outcome assessment.It was rated as high risk of bias for the incomplete outcome data. The results of risk of bias assessment for every study were revealed in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
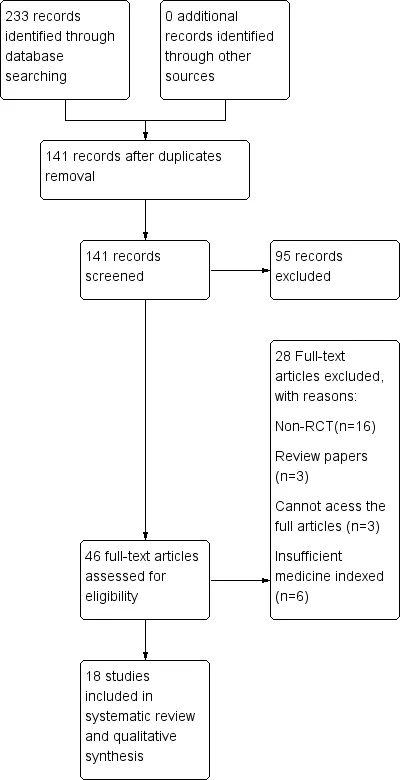
Figure1. Study flow diagram
?



?
Meta-analysis
Total effective rate of KFX retention enema. All of the studies reported the total effective rate of KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema, which involved experimental group 731 cases and control group 686 cases. There was no statistical heterogeneity among the studies (Chi2=13.89, I2=0%), so a fixed effect model was used. And Meta-analysis demonstrated that KDX therapy was superior to control group, total effective rate(RR=1.22 95%CI: [1.16,1.27], Z=8.14, p < 0.00001).(Figure 4)
Quality of life scores of KFX in UC with retention enema.There were 2 trials included 73 patients in the treatment group and 74 patients in control group [21,32],both of them reported the quality of life score after 2weeks treatment. It showed heterogeneity (p = 0.25, I2=25%) with the fixed effect model (MD=11.04,95%CI:[7.40,14.68], Z=5.95, p < 0.00001), then change to Random effect model ,the results were barely changed (MD=11.07, 95%ci:[6.86,15.28], Z=5.15, P <0.00001). Meta-analysis indicated that quality of life score really improved in KFX therapy. (Figure 5)
Recurrence rate of KFX treating the UC with retention enema.Three studies reported the recurrence rate of KFX treating the UC with retention enema after 3 months [21, 22,32]. RR analysis was used to calculate it.The results showed that KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema compared with other drugs in reducing the recurrence rate was not clear [RR = 0.45, 95% CI(0.15, 1.35), Z = 1.43, p=0.15] when using the dichotomous to indicate the recurrence rate. (Figure 6)
Other outcomes. The funnel shape of the plot showed that the trend of the total effective rate of the treatment group and the control group has a publication bias in this review (Figure 7).

Figure4. Effective rate of KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema
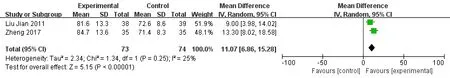
Figure5. Quality of life scores
significant difference statistically to other controlled
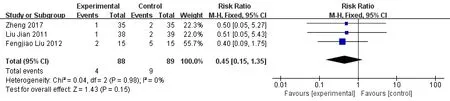
Figure.6 Recurrence rate of Kangfuxin Fluid treating the UC with retention enema
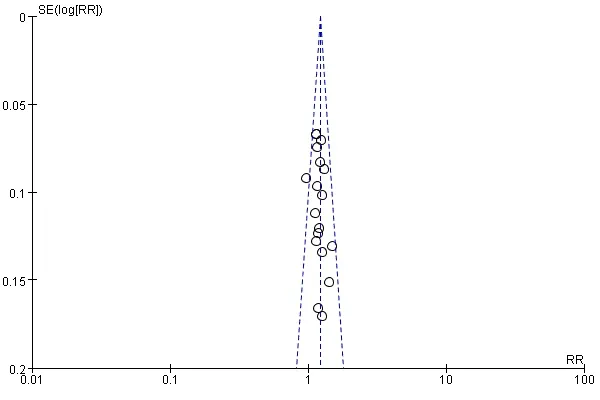
Figure 7. Meta-analysis of inverted funnel plot
Discussion
Evaluation of clinical effect
The etiology of ulcerative colitis has not yet been fully understood. Although ulcerative colitis related colorectal cancer (UCRCC) accounts for only 1% - 2% of all colon cancers, it leads to 15% of the total number of death among patients with colitis. Due to the duration of ulcerative colitis, the longer it is, the more risk cancer also increases.
The controlled group included in this systematic review included conventional western drugs: Smecta,Gentamycin, Glucocorticoids, Metronidazole,Sulfasalazine, Folic Acid, Lidocaine, Mesalazine, 5 –amino salicylic Acid as well as the Chinese medicine such as Yunnan Baiyao, Xilei Powder and Berberine. The Meta-analysis showed that compared with conventional western medicine, KFX on the treatment of UC with retention enema can obviously level up the total effective rate of treatment and better the quality of life of patients with UC after treatment. Furthermore, improve diarrhea,DAI, EGF and HGF expression. KFX treatment is precedent for other control groups. About the recurrence rate, three retrials reported that KFX treatment group has groups on the rate of P < 0.05 [21,22,32]. Meanwhile the Meta-analysis showed P < 0.15. The potential possibilities may be: (1) Although all the patients included suffered UC, UC originated from different parts of the lesion, involving the whole colon, rectum or colon sigmoid , ileum, cecum and colon ascending---invasion of ileum alone, while they did not report types of UC. (2)According to the severity of the disease, UC can be divided into first episode type, chronic recurrence,chronic persistent and fulminant type. The same they did not be clarified. (3) Most trials did not report whether the cleansing enema was advanced prior to the intervention.Moreover, the period or the frequency of coloclyster is not mentioned. (4) Because of the characteristics of recurrent attacks of UC, the treatment time may be slightly shorter in three months. (5) Only 3 trials mentioned to the recurrence rate with low quality and less sample size [21,22,32].
The main component of the KFX is the dried extraction of Periplaneta Americana (Linnaeus), which is one of the blattaria family. Blattaria, commonly known as cockroaches, is a member of the order Arthropoda cockroach, and one of the oldest insect groups.Meanwhile, it is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine,which can be traced back 1800 years ago in Shennong Bencao Jing. After that, "Compendium of Materia Medica" and "Tang Materia Medica" also collected.China's private use of blattaria in the "Compendium of Materia Medica" has long been documented: The blattaria can be captured throughout the year, then burned it with boiling water, next washed and dried [34]. The dried or fresh can be used as medicine, which has a chill of cold flavor, salt, spicy taste, is toxic, while is functional in the liver and kidney meridian. It has the effect of promoting blood circulation for removing blood stasis, and detoxification, also eliminating malnutritional stagnation.In Chinese traditional medicine, ulcerative colitis is similar to the "diarrhea", "dysentery" or "hematochezia’’.The KFX is extracted from the active substance that is called "Epidermal Growth Factor" inside the blattaria via the organic Fluid, main components of which are polyols and peptide, and contains 18 kinds of Amino acid, leading to the function of guiding, releasing and nourishing the"Qi" inside our body, moreover the detoxification and muscle growth [35]. This is consistent with the study of Wang Lu Min, Zheng Wei, Zhang Fujie, Lu Yunmin, Du Wenwen, which showed that KFX can relieve the rats in UC, promote intestinal mucosal recovery, inhibition of inflammation and the pathological changes of the colon[36,37,38,39].
The extraction from the cockroach has the function of anti-inflammation and enhance the ability of macrophages to devour [41]. The Arginine inside the KFX enables the non-specific cells to active the immunologic function, allows macrophages to reinforce the capability of swallowing pathogenic cells, enlarges the quantity, tendency and the ability of devouring of neutrophils [42-43]. At the same time, by secreting the active substance, it can be helpful in anti-inflammation and rehabilitation.
Deficiency and suggestions
This study involved 18 articles, 731 cases in the treatment group and 686 cases in the controlled group [15-32]. First of all, because of the systematic evaluation of patients suffering the different severity, so well as the frequency and measures, a good systematic review might be influenced, which increased the heterogeneity and effectiveness between groups. Secondly, the quality of the studies included was not sufficient enough, although both of them mentioned as the randomization, most of the stochastic methods were ambiguous, and even ignored the allocation concealment and blinding. At third, due to the insufficient quality of the referred literature and the limitation of the sample size that there was no objective standard set up. On the other hand, only the effectiveness can be assessed while the safety and adverse reactions of drugs may need to be strengthened after the study. Last but not least, all the studies mentioned in this study are Chinese, which limited the research results.
Conclusion and suggestion
Kangfuxin Fluid on the treatment of UC with retention enema can obviously improve the total effective rate of patients with ulcerative colitis, relieve the clinical symptoms and polish up the quality after treatment. The side effects of the treatment are seldom noted in the literature, which should be worthy of more attention in the future. We wish that more high-quality researches will hit the road with plenty of large-size sample size, multiple measure indicators and pathological examination. And we believe it will be in practice soon.
1. Eugène. C. Ulcerative Colitis practice guideline in adults. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2012, 36:107-109.
2. Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review.Gastroenterol 2012 ,142: 46-54.
3. Ye L, Cao Q, Cheng J. Review of inflammatory bowel disease in China. ScientificWorldJournal 2013,14: 296470.
4. Zheng HB. The Comparation of Global Occurrence of Ulcerative Colitis. Chin J Dig 2001, 21: 242-243.
5. Nundhini, Thukkani, J Lucas, et.al, Incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in Japan:nationwide epidemiological survey during the year 1991. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011, 17: 1333-1337.
6. KT Thia, EV Loftus, WJ Sandborn, et al. An update on the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia. Am J Gastroenterol 2008, 103: 3167-3182.
7. Huang NJ. Chinese Anorectal Disease. 1st ed.Shandong: Shandong Science and Technology Press,1996: 998.
8. Xie ZL, Analysis of treatment of drug enema for ulcerative colitis of 89 Patients. Jilin Med J 2011, 32:6617-6618.
9. Huang XQ. Treatment of Gastrointestinal Diseases.1st ed. Tianjin: Tianjin science and Technology Press, 1996: 674-677.
10. Rui YC. Modern Pharmacology. 1st ed, Beijing:People's Military Medical Publishing House, 1999:780-782.
11. Deng CS, Xia B. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 1st ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House,1998: 265-267.
12. Higgins J P T, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0[M/OL]. (2011-03-01) [2015-05-01] The Coochrane Collaboration, 2011. http: // www.cochrane-handbook. org.
13. China National Chinese medicine anorectal Branch.Therapeutic criteria for ulcerative colitis. J Middle Anorectal Dis 1998, 8: 42.
14 Qin OY, Pan GZ, Wen ZH, Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol 2001, 15: 138-138.
15 Lv W. Observation of Clinical Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema.Chin Compr Clin 2003, 19: 912-913.
16 Dai JH. Observation of Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema. Mod Med Health 2010, 9: 8865-8866.
17 Ai MJ. Observation and Nursing of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema. China Contemp Med 2010 3: 188-189.
18 Zhou CL. Observation and Nursing of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema.Chin General Med 2010, 08: 1474-1475.
19 Ding Y. 60 Samples of Ulcerative Colitis Treatment by Kangfuxin Fluid. Chin J Integr Tradit Chin Western Med 2011, 19: 129-130.
20 Liang HR. Observation and Nursing of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Retention Enema.Mod Med Health 2011, 27: 2347-2348.
21 Liu J. The Observation of Clinic Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis. Chin Hosp Pharm J 2011,31: 1888-1892.
22 Liu FJ. The Observation of Clinic Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis. Chin Med Guide 2012, 10: 216-217.
23 Gao W. The Understanding of Nursing the Ulcerative Colitis Patient under the Treatment of the Kangfuxin Fluid. J Med Theory Pract 2012, 25: 1509-1510.
24 Pan W. 40 Examples of Treating Ulcerative Colitis by Kangfuxin Fluid. Shanxi Tradi Chin Med 2012,33:1125-1127.
25 Lv WN. The Observation of Clinic Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Enema,Chin Med Guide 2012: 599-599.
26 Li Q. The Observation of Clinic Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Enema. Qinghai Med J 2013,13: 87-87.
27 Li YR. The Observation of Clinic Effect of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis. J Clin Rational Use Drugs 2013, 6: 56-56.
28 Liu Y. The Observing and Nursing 32 Examples under the Treatment of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Enema. China Pharm 2013,22: 106-106.
29 Liu RM. The Observation of Clinic Effect of 40 Ulcerative Colitis Patients under the treatment of Kangfuxin Fluid. Chin Folk Med 2013, 22: 64-64.
30 Wei XX. The Clinic Research of Kangfuxin Fluid on Ulcerative Colitis with Enema. Jilin Med 2013, 34:5388-5389.
31 Kang HJ. The Nursing Understanding of Ulcerative Colitis Patients under the treatment of Kangfuxin Fluid with Enema. Chin Community Doctors 2014,1:138-138.
32 Zheng XX. The Clinic Observation of 70 Ulcerative Colitis Patients under the treatment of Kangfuxin Fluid. Women's Health Res 2017,2: 39-40.
33 Vagefi PA, Longo WE. Colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2005, 4: 313-319.
34 Li SZ. Compendium of Materia Medica. 1st ed.Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2000:1010.
35 Chen XQ, Jin YY. Pharmacology. 14th ed. Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House, 2002: 88.
36 Wang ML, Lu YM, Yu J. Inhibition of cytokine expression in mice with colitis with Kangfuxin Fluid.Chin J Clin Pharm 2006,15: 173-175.
37 Zheng Z, Chen WX. Study on the mechanism of experimental and colitis in acute rats with Kangfuxin Fluid. Gastroenterol 2008,13: 31-34.
38 Zhang FJ. Observation and mechanism of treatment of experimental colitis in rats with Kangfuxin Fluid.Guiyang: Zunyi Medical College, 2011.
39 Lu YM, Jin Y, Chen WX. Study on the Treatment of Experimental Colitis in Mice with Kangfuxin Fluid.Clin med China 2011, 18: 446-449.
40 Du WW. The Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Oxazole to Ulcerative Colitis in Rats with Kangfuxin Fluid. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form 2017,23:126-131.
41 Chen LM. The Clinical and Experimental Research of the Extract AT2 from Cockroach. Chin J Integr Med 1986, 5: 647-650+643.
42 Li SS, Li YG, Peng SZ. The effect of Kangfuxing Fluid on the Rehabilitation of the Rabbit. J clin Exp Med 2006, 5: 730-731.
43 He ZC, Peng F, Song LY, et al. The Research Progress of Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Action of the Extract of the Periplaneta Americana. China J Chin Mater Med 2007, 32: 2326-2631.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2018年3期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2018年3期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Effect of splitting combination of different components of Zhilong Huoxue Tongyu Capsule on vascular remodeling in hypertension
- Pharmacological effects of Paeoniflorin and Albiflorin on IL-3, GM-CSF, IL-6 and TNF-α in the rats of syndrome of stagnation of liver qi and blood deficiency
- Neuroprotective Effect of Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue Extract against High Glucose-induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells
- A novel natural compound Shikonin inhibits YAP function by activating AMPK
- Antioxidative and antiapoptotic effects of (+)-clausenamide on acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in mice
- Immunoregulation and anti-tumor effects of Polyporusus Bellatus:a review of recent research
