基于泄漏电流时频奇异谱和模糊聚类的触电故障诊断
韩晓慧,杜松怀,李 振,孙丽华
基于泄漏电流时频奇异谱和模糊聚类的触电故障诊断
韩晓慧1,杜松怀2,李 振2,孙丽华1
(1. 河北科技大学电气工程学院,石家庄 050018;2. 中国农业大学信息与电气工程学院,北京 100083)
针对实测触电故障信号具有非平稳特性而不易被辨识问题,提出了一种基于泄漏电流时频奇异谱和模糊聚类的触电故障诊断方法。首先,利用平滑伪威格纳-维尔分布(smoothed pseudo wigner-ville distribution, SPWVD)对触电故障信号进行时频分析并依据信号的能量分布特征选择时频区域;然后对选择的时频区域进行奇异谱分析,以获取的局部时频矩阵奇异值作为触电信号的特征量输入FCM,即可实现触电信号的故障诊断。对剩余电流保护装置试验平台上获取的实测触电故障信号的时频矩阵奇异值进行模糊C均值聚类,结果表明该方法识别准确率为97.50%,平均识别时间为0.008 5 s,其中植物和动物触电测试样本识别准确率分别为100%,95.00%,从而验证了基于泄漏电流时频奇异谱和模糊聚类的触电故障诊断方法的有效性,该研究可为研发新一代基于触电故障诊断的剩余电流保护装置提供理论依据和方法参考。
电流检测;电力系统;诊断;触电故障;时频矩阵;奇异值分解;特征量提取;模糊C均值聚类
0 引 言
作为电力系统中重要的保护与控制设备之一,剩余电流保护装置能够及时对生物体触电、电气火灾及电气设备损坏等情况做出防护动作[1]。但是,目前现有的剩余电流在线监测保护装置,其动作可靠性和正确投运率都不太理想,因此学者在剩余电流保护装置方面进行了大量研究[2-7],笔者课题组成员也一直致力寻求剩余电流保护新原理和新算法以设计一种高精度、高可靠性的剩余电流保护装置,如文献[8-10]提出用神经网络建立了触电信号检测模型,能有效从总泄漏电流中检测出触电电流。文献[11]针对神经网络容易陷入局部最优、隐层单元数难以确定等缺点,用最小二乘支持向量机建立了触电信号的检测模型。文献[12]针对如何准确、快速提取生物体触电故障暂态信号中电力参数问题,将局部均值分解用于总泄漏电流信号的瞬时幅值和瞬时频率提取。这些方法虽然在一定程度上提高了剩余电流保护装置的技术性能,但尚不具有对监测到的电流信号自动识别和诊断能力。当触电故障出现时,仅依据人工经验判断触电故障类型,且所需时间长也容易出现误判。为此,文献[13]将量子遗传计算和神经计算有机结合,建立了一种量子遗传模糊神经网络作为触电故障模式分类归属的决策系统。但神经网络仍存在网络训练速度慢等无法克服的缺点,针对这些缺点,本文通过对实时监测总泄漏电流,提出一种新的特征提取及诊断算法,以实现触电故障类型的准确判断。
触电故障类型诊断实质上是一个模式识别问题,包括三个环节:信号采集、特征提取及状态识别,其关键在于如何有效提取各触电故障特征。若仅采用单一频域或时域分析方法提取现场获取的非平稳总泄漏电流信号故障特征,并不能全面反映触电信号所包含的频率及其幅值的时变特征信息。而用时域和频域的联合时频分析(time-frequency analysis,TFR)方法来揭示非平稳信号中所包含信息得到了越来越多的应用[14-15]。常用的联合时频分析方法按时频联合函数不同主要分为线性和非线性2种时频分析方法[16]。以线性时频分析方法为例的短时傅里叶变换方法[17]和小波变换方法[18-19]由于受Heisenberg不确定性原理的限制,难以获得理想的时频分辨率。以非线性时频分析方法为例的威格纳-维尔分布(Wigner-Ville distribution,WVD)由于具有较高的时频聚集性被广泛应用于信号分析处理领域,但存在固有的交叉项干扰问题,影响了对WVD分析结果的正确评估[20]。平滑伪威格纳-维尔分布(smoothed pseudo wigner-ville distribution,SPWVD)[21]是一种以WVD为基础的非线性时频分布,通过在时间轴和频率轴方向加窗函数自适应地调节窗口长度,抑制了WVD存在的交叉项干扰问题,能更准确反映信号时频特征,同时还具有时移和频移不变性,因此是分析信号的有效工具。
鉴于此,本文将探索基于SPWVD的触电故障信号时频特征提取与诊断策略。首先,采用SPWVD对发生触电故障时的总泄漏电流时频特性进行表征,并依据信号的能量分布特点选择时频区域;然后,采用奇异谱分析方法对选择的时频区域进行奇异值分解,以获取的该时频矩阵奇异值构成了触电故障信号的特征量;最后,通过模糊C均值聚类算法实现了不同触电故障类型的诊断,并利用该方法对剩余电流保护装置触电物理试验系统平台上获取的触电故障信号进行了有效性验证。
1 平滑伪威格纳-维尔分布
平滑伪威格纳-维尔分布(smoothed pseudo wigner-ville distribution,SPWVD)是反映信号能量的时频分布,其实质是对信号的瞬时相关函数作傅里叶变换时在时域轴和频率轴分别加窗函数进行平滑处理[22]。
信号()经SPWVD分析后的时频矩阵中,其行向量为某一频率随时间变化的分布,列向量为某一时刻随频率变化的分布,某位置上元素的大小就是相应时间和频率处信号SPWVD分析的能量。利用SPWVD时频矩阵可以用时频等值线图来表示信号的时频分布。图1所示为一仿真信号()及其经STFT(short-time Fourier tranformation)、WVD、SPWVD分析后的时频等值线图。仿真信号包括2个频率分量:在采样序列=0~0.8 s之间为一200 Hz的余弦信号,在=0.2~1 s之间又叠加了一个50 Hz的余弦信号。

图1 信号源s(t)及其经STFT、WVD、SPWVD分析的时频等值线图
由图1可以看出,图1b中由于STFT采用固定的窗函数使其在整体上呈现较低的时频分辨率;图1c中WVD存在严重的交叉项干扰项,难以确定信号的频率成分;图1d中SPWVD通过时频域窗函数的平滑作用,抑制了WVD的交叉项干扰,较好地反映了该信号频率成分随时间变化的分布情况。
综上所述,本文选取的SPWVD时频分析方法,具有较好的时频聚焦性,可尝试将其应用到触电故障信号处理中。
2 SPWVD时频奇异谱特征提取
2.1 时频矩阵奇异谱分析
奇异谱分析是一种通过对信号进行奇异值分解以获取其内在复杂特征的信号分析方法。依据奇异值分解理论[23],对于由SPWVD获得时频分布矩阵×n,求正交矩阵×m、×n和对角矩阵×n使其满足

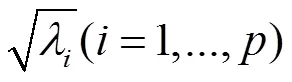
由于×n是一对角矩阵,奇异值分解也可表示为将矩阵×n分解为个秩为1的×阶矩阵的加权和,各子矩阵由特征向量=(1,2,···,w)与=(1,2,···,h)及相应的权值相乘得到
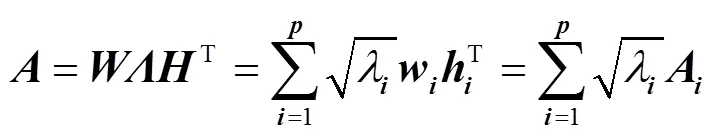
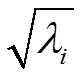
由于矩阵奇异值还具有相对稳定性、比例不变性、位移不变性及旋转不变性[24-25],当矩阵中有一定的干扰和分散性存在时,矩阵的奇异值是相对稳定的代数特征参量,故矩阵奇异值在模式识别中常用于信号特征量的提取。
2.2 SPWVD时频矩阵奇异値特征提取
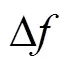
3 FCM聚类算法
模糊C均值(fuzzy C-means,FCM)聚类作为一种非监督动态聚类,利用隶属度表征数据的相对归属性,对数据实现柔性模糊划分。与硬分类K-means聚类相比,FCM对初始聚类中心要求较低,当数据维数较大时FCM可以得到更合理的分类结果[27-28]。
FCM聚类实质是通过若干次迭代求取各样本到聚类中心的距离平方和最小值得到给定分类数下的聚类结果。对于给定数据集={1,2,···,x},每个样本为维向量,即=(x1,x2,···,x)T,其中=1,2,…,,FCM算法的数学模型为[29]

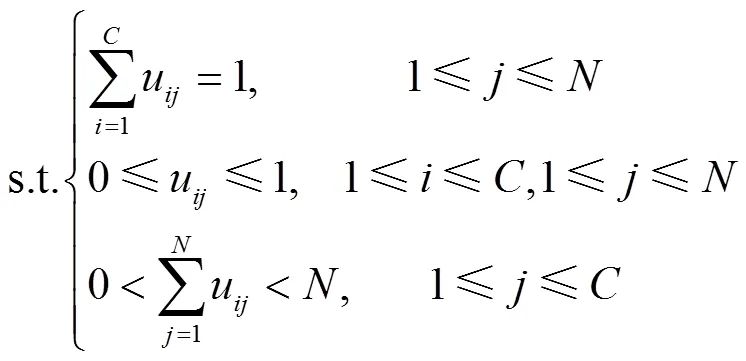
式中fcm为FCM的目标函数,使得样本与聚类中心之间的差异度最小;为隶属度矩阵;为聚类中心;为聚类数;为控制分类矩阵的模糊权重指数(>1,一般取值范围为1.5~2.5);u表示第个样本隶属于第类的程度;d=||−||表示第个样本与第类中心的欧氏距离。FCM的详细算法流程详见文献[30],本文不予重述。
4 实测触电信号故障诊断
4.1 触电信号采集与SPWVD时频分析
本文所使用的触电故障信号来自于剩余电流保护装置试验平台上获取的总泄漏电流信号,试验原理详见文献[11]。在10 kHz的采样频率下,采集了400组动植物触电总泄漏电流数据,其中包含了200组植物触电和200组动物触电数据。对采集的信号进一步分析发现,可以用触电前一周期和触电后一周期的数据共0.04 s时长的信号作为待分析触电故障信号,图2、图3所示为上述2种触电类型场景下的具有代表性的总泄漏电流时域波形及SPWVD时频等值线图和三维图谱。

图2 植物触电总泄漏电流及SPWVD时频等值线图和三维图谱
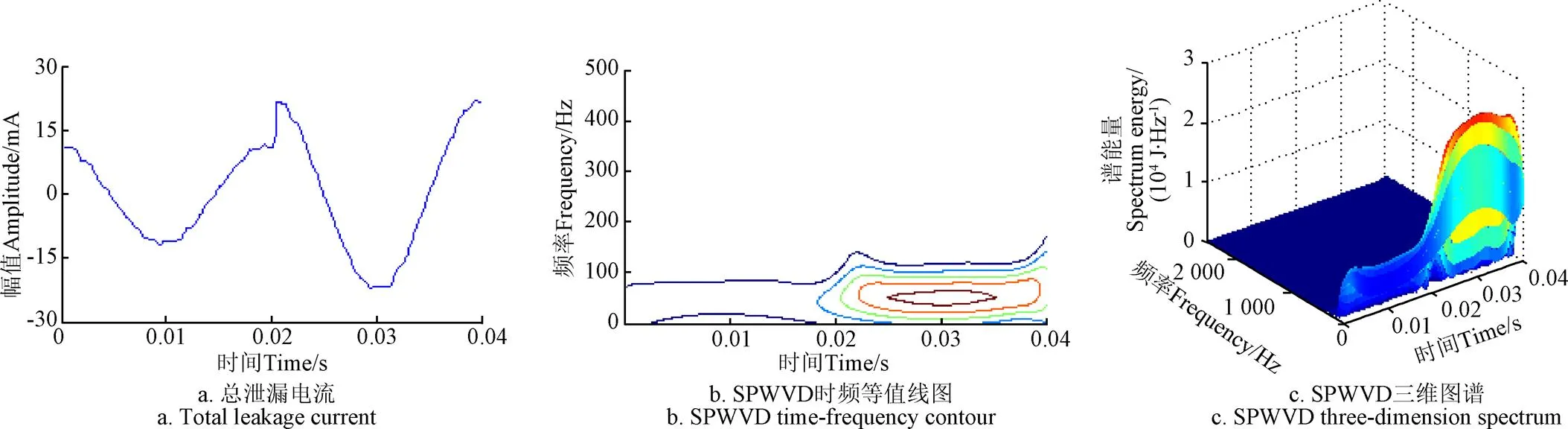
图3 动物触电总泄漏电流及SPWVD时频等值线图和三维图谱
由图2和图3的SPWVD分析结果可以看出,动植物触电总泄漏电流能量主要集中在频率0~150 Hz之间。因此,考虑利用总泄漏电流在频率0~150 Hz之间的时频区域奇异值作为动物触电与植物触电模式识别特征量。
4.2 基于SPWVD时频矩阵奇异谱分析的触电故障信号特征量提取
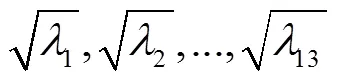
4.3 基于FCM聚类的触电模式诊断
对上述2种触电情况下总泄漏信号各取140组作为已知触电故障类型样本数据,再各取60组数据作为待验触电故障类型样本数据。其中第1~140个采样样本为植物触电故障样本;第141~280为动物触电故障样本;第281~340为待验植物触电故障样本,第341~400为待验动物触电故障样本。
依据4.2节触电故障信号特征提取步骤,求取这400组触电样本数据的时频矩阵奇异值,构造出总泄漏电流特征向量矩阵,将特征向量矩阵作为FCM聚类的输入,求得植物触电模式和动物触电模式的聚类中心分别为
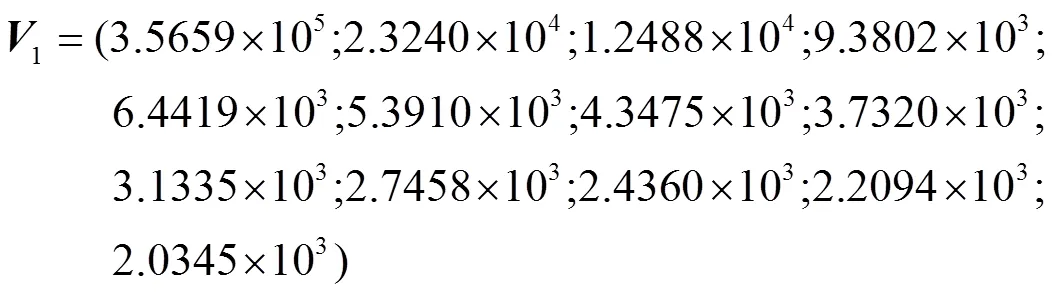
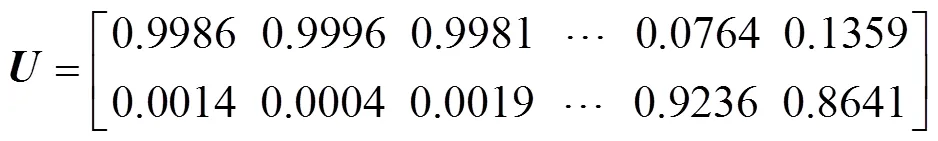
式中的行号与列号分别与触电故障类型与样本编号对应,第1、2行分别对应植物触电故障和动物触电故障,第1~5列分别对应样本编号1~5。由隶属度矩阵可得到植物触电模式和动物触电模式的隶属度划分矩阵分别如图4a、4b所示。
注: 隶属度值越大,代表隶属于对应的触电类型程度越高。
Note: The greater the membership value, the higher the degree of representation of the samples attached to belonging to the corresponding type of electric shock.
图4 隶属度划分矩阵
Fig.4 Division matrix of membership degree
图4a、4b中每个元素分别代表第(=1,2,3,…,400)个采样样本隶属于植物触电和动物触电的程度,第个采样样本的最大值所在的类即为该样本对应的触电类型状态。因此利用隶属度矩阵及其划分矩阵可识别触电类型状态。
由隶属度矩阵可知,第281~340列(待验样本)的隶属度最大值分别为0.999 7,0.999 9,0.999 9,…,0.999 7,0.999 8出现在第1行,判定待验样本与样本1~140属于同一触电类型样本,即待验样本为植物触电故障类型样本,与实际类型一致;另外,从图4a中也可明显看出第281~340采样样本的隶属度最大值均出现在植物触电划分矩阵中,由此也可判定待验样本为植物触电故障类型样本。第341~373、375~379、381~386、388~389列(待验样本)的隶属度最大值分别为0.951 5,0.912 1,0.954 4,…,0.923 6,0.864 1出现在第2行,判定待验样本与样本141~280属于同一触电类型样本,即待验样本为动物触电故障类型样本,与实际类型一致,但第374、380、387列的最大值分别为0.551 8、0.605 6、0.594 6出现在第1行,判定待验样本为植物触电故障类型样本,与实际类型不一致;同样,从图4a、4b中也可看出第281~340采样样本中除有3个采样样本的隶属度值大于0.5出现在植物触电划分矩阵中,其余采样样本的隶属度最大值均出现在动物触电划分矩阵中,由此判定有3个待验样本为植物触电故障类型样本与实际故障类型不一致,其余待验样本为动物触电故障类型样本。
由以上识别结果可以看出,120组测试样本中有3组样本识别错误,识别准确率为97.50%,其中植物触电测试样本识别准确率为100%,动物触电测试样本中有3组样本识别错误,识别准确率为95.00%,取得了较好的检测效果。平均识别时间为0.008 5 s,少于文献[13]中量子遗传模糊神经网络触电故障诊断算法所需迭代1 156次的训练时间,克服了神经网络训练速度慢的问题,提高了识别效率,从而验证了用所提取的总泄漏电流信号的特征量诊断触电故障信号类型状态的正确性和有效性。
5 结 论
本文针对触电故障信号的诊断问题,提出了一种基于平滑伪威格纳-维尔分布(smoothed pseudo wigner-ville distribution,SPWVD)时频奇异谱特征提取和模糊C均值(fuzzy C-means,FCM)聚类的触电故障信号的诊断方法。
1)采用SPWVD对触电故障时刻的总泄漏电流进行时频分析,时频等值线图和三维图谱表明,不同触电故障类型信号具有相互区别的时频分布特征,说明了利用SPWVD分析触电故障信号的可行性;
2)引入奇异谱分析方法对触电故障信号0~150 Hz频率范围内13个子频带形成的局部时频矩阵进行奇异值分解,得到各子频带奇异值构成的13维向量作为触电故障信号的特征量;
3)通过对120组触电故障信号特征量进行FCM聚类测试,结果表明该方法识别准确率为97.50%,平均识别时间为0.008 5 s,其中植物和动物触电测试样本识别准确率分别为100%,95.00%,由此验证了SPWVD时频矩阵奇异谱特征提取和触电信号故障诊断的有效性,为触电故障信号的诊断提供了有效手段。
[1] 杜松怀,张筱慧.电力系统接地技术[M]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2011.
[2] 曹国臣,蔡国伟,王海军. 继电保护整定计算方法存在的问题与解决对策[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2003,23(10):51-57.
Cao Guochen, Cai Guowei, Wang Haijun. Problems and solutions in relay setting and coordination[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2003, 23(10): 51‒57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Luo Xiang, Du Y, Wang X H, et al. Tripping characteristics of residual current devices under nonsinusoidal currents[J].IEEETransactions on Industry Applications2011, 47(3):1515-1521.
[4] Czapp S. Elimination of the negative effect of earth fault current higher frequency on tripping of residual current devices[J]. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika, 2009(3): 85-88.
[5] Czapp S. The impact of DC earth fault current shape on tripping of residual current devices[J]. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika, 2015(4): 9-12.
[6] Liew A C. Nuisance trippings of residual-current circuit breakers or ground fault protectors of power sources connected to computer and electronic loads[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 1990, 20(1): 23-30.
[7] 陈义刚,李浩,范康林,等. 考虑相角特征的无死区新型触/漏电保护技术[J]. 四川电力技术,2013(2):35-39,72.
Chen Yigang, Li Hao, Fan Kanglin, et al. The new touch/leakage current protection technology eliminating dead-zone that considering the phase angle characteristics[J]. Sichuan Electric Power Technology, 2013(2): 35-39, 72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李春兰,苏娟,杜松怀,等. 基于小波分析和 BP 神经网络的触电信号检测模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2010,26(2):130-134.
Li Chunlan, Su Juan, Du Songhuai, et al. Detecting model of electric shock signal based on wavelet analysis and BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(2): 130-134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 关海鸥,杜松怀,李春兰,等. 基于有限脉冲反应和径向基神经网络的触电信号识别[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(8):187-194.
Guan Haiou, Du Songhuai, Li Chunlan, et al. Recognition of electric shock signal based on FIR filtering and RBF neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(8): 187-194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 关海鸥,杜松怀,苏娟,等. 一种触电信号的自动快速检测模型[J]. 电网技术,2013,37(8):2328-2335.
Guan Haiou, Du Songhuai, Su Juan, et al. An automatic and quick detection model of electric shock signals[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(8): 2328-2335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 韩晓慧,杜松怀,苏娟,等. 基于参数优化的最小二乘支持向量机触电电流检测方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(23):238-245.
Han Xiaohui, Du Songhuai, Su Juan, et al. Determination method of electric shock current based on parameter-optimized least squares support vector machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(23): 238-245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 韩晓慧,杜松怀,苏娟,等. 基于局部均值分解的触电故障信号瞬时参数提取[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(17):221-227.
Han Xiaohui, Du Songhuai, Su Juan, et al. Extraction of biological electric shock signal instantaneous amplitude and frequency based on local mean decomposition[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(17): 221-227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 王金丽,刘永梅,杜松坏,等. 基于剩余电流固有模态能量特征的生物触电故障诊断模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(21):202-208.
Wang Jinli, Liu Yongmei, Du Songhuai, et al. Fault diagnosis model for biological electric shock based on residual current intrinsic mode function energy features[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(21): 202-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] Jardine A K S, Lin D, Banjevic D. A review on machinery diagnostics and prognostics implementing condition-based maintenance[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006, 20(7): 1483-1510.
[15] Heng A, Zhang S, Tan A C, et al. Rotating machinery prognostics: State of the art, challenges and opportunities[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 23(3): 724-739.
[16] 章立军,刘博,张彬,等. 基于时频图像融合的轴承性能退化特征提取方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2013,49(22):53-58.
Zhang Lijun, Liu Bo, Zhang Bin, et al.Feature extraction method of bearing performance degradation based on time-frequency image fusion[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(22): 53-58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 徐永海,赵燕. 基于短时傅里叶变换的电能质量扰动识别与采用奇异值分解的扰动时间定位[J]. 电网技术,2011,35(8):174-179.
Xu Yonghai, Zhao Yan. Identification of power quality disturbance based on short-term Fourier transform and disturbance time orientation by singular value decomposition[J]. Power System Technology, 2011, 35(8): 174-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Pillay P, Bhattacharjee A. Application of wavelets to model short-term power system disturbances[J]. IEEE Trans on Power System, 1996, 11(4): 2031-2037.
[19] 冯浩,周雒维,刘毅. 基于复小波变换的暂态电能质量扰动检测与分类[J]. 电网技术,2010,34(3):91-95.
Feng Hao, Zhou Luowei, Liu Yi. Detection and classification of transient power quality disturbances based on complex wavelet transform[J]. Power System Technology, 2010, 34(3): 91-95. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张贤达. 现代信号处理[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2002.
[21] 林勇,周晓军,杨先勇,等. 基于 SPWVD 识别的滚动轴承智能检测方法[J]. 振动与冲击,2009,28(9):86-90.
Lin Yong, Zhou Xiaojun, Yang Xianyong, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis methods of rolling bearing based on SPWVD and AIN[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2009, 28(9): 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 臧怀刚,王石云,李玉奎. EMD和平滑伪 Wigner-Ville 谱熵的轴承故障诊断[J]. 噪声与振动控制,2014,34(5):145-149.
Zang Huaigang, Wang Shiyun, Li Yukui. Bearing fault diagnosis based on EMD and smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville spectrum entropy[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2014, 34(5): 145-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张贤达. 矩阵分析与应用[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2004.
[24] 杜林,戴斌,陆国俊,等. 基于S变换局部奇异值分解的过电压特征提取[J]. 电工技术学报,2010,25(12):147-153.
Du Lin, Dai Bin, Lu Guojun, et al. Overvoltage features extraction based on S transform and local singular value decomposition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2010, 25(12): 147-153. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 郭谋发,徐丽兰,缪希仁,等. 采用时频矩阵奇异值分解的配电开关振动信号特征量提取方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2014,34(28):4990-4997.
Guo Moufa, Xu Lilan, Miao Xiren, et al. A vibration signal feature extraction method for distribution switches based on singular value decomposition of time-frequency matrix[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(28): 4990-4997. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Tian Y, Tang T, Wang Y H, et al. Do singular value contain adequate information for face recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2003, 36(6): 649-655.
[27] 王淳,高元海. 采用最优模糊C均值聚类和改进化学反应算法的配电网络动态重构[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2014,34(10):1682-1691.
Wang Chun, Gao Yuanhai. Dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network based on optimal fuzzy C-means clustering and Improved chemical reaction optimization[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(10): 1682-1691. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 宋易阳,李存斌,祁之强. 基于云模型和模糊聚类的电力负荷模式提取方法[J]. 电网技术,2014,38(12):3378-3383.
Song Yiyang, Li Cunbin, Qi Zhiqiang. Extraction of power load patterns based on cloud model and fuzzy clustering[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(12): 3378-3383. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 汪可,廖瑞金,王季宇,等. 局部放电 UHF 脉冲的时频特征提取与聚类分析[J]. 电工技术学报,2015,30(2):211-219.
Wang Ke, Liao Ruijin, Wang Jiyu, et al. Time-frequency features extraction and clustering analysis of partial discharge UHF pulses[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(2): 211-219. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 高新波. 模糊聚类分析及其应用[M]. 西安:西安电子科技大学出版社,2004.
Diagnosis of electric shock fault based on time-frequency singular value spectrum of leakage current and fuzzy clustering
Han Xiaohui1, Du Songhuai2, Li Zhen2, Sun Lihua1
(1.,,050018,; 2.,,100083,)
Residual current devices (RCDs), a type of protective equipment in low-voltage systems, are widely used to prevent and avoid leakage accident of power grid and protect the safety of life and property. At present, the operation of an RCD is based on sensing the root mean square value of residual current in an electrical circuit. The circuit will be interrupted on the action of a relay when the residual current exceeds a predetermined level (30 mA for human safety), known as the tripping current. Although such devices offer a large degree of protection, they are prone to nuisance tripping or maloperation in the actual operation of the grid due to the lack of the ability to diagnose electric shock type and identify touch current, which reduces the reliability and the rate of proper commissioning for RCDs. Thus, aiming at the problem that the measured electric shock signals are non-stationary and difficult to diagnose the type of electric shock, a new method of fault diagnosis of electric shock signal based on time-frequency singular spectrum of leakage current and fuzzy clustering is proposed. First of all, a simulation signal is used to compare and analyze the time-frequency analysis performance of short-time Fourier transformation (STFT), wigner-ville distribution (WVD) and smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution (SPWVD). The simulation results show that the STFT presents a lower time-frequency resolution because of the fixed window function, the WVD has serious crosstalk terms and it is difficult to determine the frequency components of the signal, and the SPWVD suppresses the crosstalk of WVD and reflects the distribution of signal frequency components with time through the smoothing of time-frequency window function. Therefore, SPWVD is chosen as the time-frequency analysis method in this paper. Then, numerous groups of total leakage current signals were measured using a recorder on the electric shock experiment platform of RCDs. We select a total of 0.04 s of data (one cycle before the electric shock and one cycle after the electric shock) as electric shock sample data. The SPWVD is used to analyze the total leakage current signal to obtain the time-frequency matrix, and the frequency band width of the main spectrum energy is 0-150 Hz, which can be divided into 13 sub-bands. The singular value decomposition (SVD) is adopted to decompose the time-frequency matrix formed by 13 sub-bands, and the singular values corresponding to the respective sub-frequency band are obtained as the feature vectors of the electric shock signal. And then the fuzzy C means (FCM) algorithm is applied to perform the clustering of extracted feature vectors to get the electric shock signal type. Finally, a total of 400 groups of animals and plants shock data are used as the research object. Among them, 140 groups of animal electric shock samples and 140 groups of plant electric shock samples are taken as known samples, and 60 groups of animal electric shock samples and 60 groups of plant electric shock samples are used as test samples. The experimental results show that there are 3 groups of samples in 120 groups of test samples which are wrongly identified and the recognition accuracy rate is 97.50%. Among them, the accuracy rate of plant electric shock test sample is 100%, and there are 3 samples in animal electric shock test samples, which are identified incorrectly and the recognition accuracy rate is 95.00%. The above results verify the correctness and validity of diagnosing the type of the electric shock fault signal by the extracted characteristic value of the total leakage current, which can lay a solid theoretical and technical foundation for developing new generations of adaptive residual current protection devices.
electric current measurement; electric power systems; diagnosis; electric shock fault; time-frequency matrix; singular value decomposition (SVD); feature extraction; fuzzy C-mean (FCM) clustering
2017-07-16
2018-02-01
国家自然科学基金项目(51177165)
韩晓慧,河北石家庄人,讲师,主要研究方向为电力系统继电保护。Email:hanhui854201@126.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.04.026
TM77
A
1002-6819(2018)-04-0217-06
韩晓慧,杜松怀,李 振,孙丽华. 基于泄漏电流时频奇异谱和模糊聚类的触电故障诊断[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(4):217-222.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.04.026 http://www.tcsae.org
Han Xiaohui, Du Songhuai, Li Zhen, Sun Lihua. Diagnosis of electric shock fault based on time-frequency singular value spectrum of leakage current and fuzzy clustering[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(4): 217-222. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.04.026 http://www.tcsae.org

