超临界流体萃取技术及其在食品工业中的应用
苗笑雨,谷大海,程志斌,徐志强,王桂瑛,*,普岳红,刘萍,廖国周,*
(1.云南农业大学食品科学技术学院,云南昆明650201;2.云南农业大学云南省畜产品加工工程技术研究中心,云南昆明650201;3.云南泰华食品有限公司,云南昆明 650217)
超临界流体萃取技术是近几年来发展迅速、应用很广的一种新型提取分离技术,该技术利用其流体的高密度、低黏度的双重特性,能够从天然物质中有选择性地提取出有效成分,有效地改善和提高产品的质量[1]。目前,随着人们对“绿色食品”和“天然产物”的追求,传统的提取分离技术已经不能满足高纯优质的产品要求。超临界流体萃取技术的出现可以解决传统提取技术存在的诸多缺陷如:使用有毒的有机溶剂、高能源的使用及低萃取得率等[2]。而且由于食品中大多数的营养成分如维生素、蛋白质等遇热极易发生分解、聚合、氧化等变质反应,因此在使用传统提取技术过程中会造成有效成分的破坏和环境的污染。目前超临界流体萃取技术已广泛应用于食品、药品、生物等各个方面,在食品工业方面,国内外已有数百例通过超临界流体萃取技术进行有害成分去除(加工无咖啡因的咖啡)、有效成分提取(萃取植物精油)等,效果明显且已投入工业化生产[3]。超临界流体萃取技术为食品工业开辟了广泛的应用前景。
1 原理及影响因素
1.1 超临界流体萃取的基本原理
超临界流体萃取技术(supercritical fluid extraction,SFE)是将传统蒸馏技术和有机溶剂萃取相结合,利用超临界流体进行基质与萃取物的有效分离、提取和纯化,其优点为提取效率高、无溶剂残留毒性、天然活性成分和热敏性成分不易被分解破坏,能够最大限度的保持提取物的天然特性且实现选择性分离等特点[4]。超临界流体萃取试验是从19世纪开始的,尤其是近几年逐渐替代了传统的溶剂型萃取技术[5]。Hannay和Hogarth[6]首先发现了超临界流体具有独特溶解现象,在1869年Thomas[7]给出了“临界点”这一概念。这些早期的研究为超临界流体萃取技术的发展提供了方向。超临界流体萃取技术就是利用流体的良好的渗透能力和溶解特性来萃取分离混合物的过程[2]。超临界流体是指当物质超过本身的临界温度和临界压力时,气液两相会混合成为一种均一的流体状态。该流体既具备气体的高渗透能力,也有着类似液体的高溶解能力[3]。通过改变压力和温度来控制流体密度,进而控制超临界流体的溶解能力,将超临界流体与待分离物质充分接触后形成流动相,流动相会受到压力和温度的作用,使被萃取物中的某些组分被超临界流体溶解并携带[8],从而有选择性的依次按溶解能力大小、沸点高低、分子量大小将待分离物质被萃取出来,实现选择性地提取有效成分或去除有害物质[9]。超临界流体的密度和介电常数与压力成正比,且通过压力的不断增加,可以将不同极性的分子逐步萃取出来[10]。但由于其受温度和压力影响较大,萃取风味成分重复性较差,所以不适合定量对食品中的风味成分进行分析[11]。超临界溶剂类型较多,不同的溶剂其临界性质也不同。按非极性溶剂和极性溶剂来划分,主要有二氧化碳、乙烯、丙烯、乙烷、丙烷和甲醇、乙醇、氨、水等[12]。CO2是最为常用的超临界流体,研究最多、应用最广,来源丰富且因其临界压力(7.38 MPa)和临界温度(31.1℃)较低可实现在较低温度下进行分离[13]。而一氧化氮(36.5℃)、乙烷(32.4℃)、丙烷(96.8℃)甲醇(240.5℃)均因临界温度偏高不利于分离,且CO2临界密度(0.47 g/cm3)均比常用超临界溶剂高,因此对有机物溶解能力强,不会对热敏性物质和活性成分造成破坏,安全无毒,无溶剂残留问题,且具有抗氧化灭菌作用,有利于保证和提高天然物产品的质量,广泛应用于食品香料、植物油和生物碱的优良萃取和医药、化妆品等各个领域[14-17]。
1.2 超临界流体萃取的影响因素
在超临界流体萃取过程中,原料的性质即相对分子质量、极性等是影响超临界流体萃取的内部因素,以有效成分的萃取得率和生物学活性来说,溶剂的选择、萃取压力及温度,分离压力及温度,流体流量和萃取时间是外部可控因素[4],其中萃取的压力及温度影响最为明显,可通过试验来进行优化。
1.2.1 原料
原料即溶质、被萃取的样本,超临界流体萃取适用于固体或液体样品,不同的样品萃取过程也稍有不同。当样品为固体时,样品的物理状态对萃取效果有很大的影响[18]。如粉碎粒度会影响传质速率,进而影响萃取得率,因此要选择合适的粉碎粒度来尽可能的增加物料与溶剂的表面接触面积。通常,样品中有一定的水分也会降低萃取得率,选择干样品萃取得率会明显提高。对于液体样品而言,通常采用逆流萃取来增加超临界流体与样品的接触面积。因此不同的样品与超临界流体的接触面以及传质过程都有不同。
1.2.2 溶解度(温度和压力)
在超临界流体萃取过程中萃取的压力和温度对萃取效果影响显著。通过增加萃取压力可以增加溶剂的密度以及溶解度、提高萃取得率。另一方面,当萃取压力一定时,提高萃取温度会降低溶剂密度、但也会促进物料传质的速率。因此,应以目标化合物的萃取得率为指标,确定萃取压力和温度的最佳值。对于天然复杂的样品,需要对多个不同的影响因素以及影响效果进行试验统计,并通过响应曲面分析或正交试验进行萃取工艺参数的优化。
1.2.3 夹带剂的使用
夹带剂、又称为携带剂,在超临界流体萃取过程中,可以与流体溶剂混匀,挥发性介于待萃取物质与超临界组分之间,可以提高溶解度和选择性的一类物质。当超临界流体萃取使用单一气体时,溶解性和选择性往往受到一定程度的限制[8]。如选用最广泛的流体为CO2,因其低极性在某种程度上对极性或亲脂性化合物造成了限制,为了增加其潜在的应用范围,改变溶质的溶解度及超临界流体的选择性,可以在超临界CO2萃取过程中加入夹带剂如甲醇、甲苯、丙酮、乙酸乙酯、水等,一般不超过5%,可以使待萃取物在超临界CO2中的溶解度提高10倍以上[19-20]。但夹带剂的使用也存在一定的负面作用如萃取物中夹带剂的残留问题,因此选择夹带剂要综合考虑夹带剂的性质、被萃取物性质以及避免使用有害物质[21]。
1.2.4 CO2流量
CO2流量的变化对超临界流体萃取也有一定的影响作用[22]。当CO2流量增加时,会造成CO2流体在萃取釜中停留时间短,不利于萃取得率的增加。同时,CO2流量的增大,会增加萃取过程中的传质推动力,增加传质系数,提高萃取得率。而当CO2流量超过一定范围时,CO2溶解能力会急剧下降,因此选择合理的CO2流量可以使得CO2和物料良好的接触且节约资源。
2 应用现状及进展
在食品工业中,超临界流体萃取具有优于传统提取工艺技术的显著特点,即在实现萃取物无残留的基础上,还可以防止热敏性物质的失活变形。第一次应用于工业化生产的是利用超临界流体萃取技术去除咖啡豆中的咖啡因[23]。至今已有近百个食品进行了系统的成分提取和分离研究,且不少产品已走向市场,如生姜精油、无咖啡因的咖啡、小麦胚芽油等。在食品工业中,超临界流体萃取技术主要有两个明显的发展趋势,即去除有害物质和提取有效成分。
2.1 去除有害物质
超临界流体萃取可以对食品中的有害物质进行选择性去除,最广泛的应用为生产无咖啡因的咖啡。西德HAG公司在1978年就开始利用超临界流体脱除咖啡因。目前该技术不仅可以用于咖啡中,还应用于茶叶、中药如伴侣草等[24]。在提取茶叶和伴侣草的过程中,适宜的压力和60℃左右的温度相结合可以提高萃取得率。超临界流体萃取还可以提取酿造啤酒用的啤酒花[25],既去除了硬树脂、农药等有害成分、还保持了啤酒花的香气香味。
对于食品中存在的一些对健康无益或有害物质如多环芳香烃[26],多氯联苯[27-28],兽药[29-30]等,也可以通过超临界流体萃取技术进行提取。Choi[30]研究了在猪肉中,利用超临界流体萃取技术,通过使用Na4EDTA和海砂并结合80℃、30 MPa的CO2和30%的甲醇,提取氟喹诺酮类抗生素(恩诺沙星、达氟沙星和环丙沙星)效果显著。还有一些有害物质主要来源于农药残留和环境的污染[31],Valverde[32]通过超临界萃取技术对大米、野生水稻和小麦中残留的杀虫剂进行了研究,在萃取压力为20 MPa,萃取温度为50℃,CO2结合甲醇作为夹带剂可以成功提取出农药残留,且效果远比传统使用乙酸乙酯作为提取溶剂效果好。食品中还可能存在几种毒素如霉菌毒素、藻毒素或植物毒素等,在很多情况下,这些毒素大多为大极性化合物,Acorus calamus[33]和 Podophyllum hexandrum rizhomes[34]试验发现相比传统的索氏提取法,利用超临界流体萃取技术更容易成功去除隔离毒素。
在某些食品中存在一些物质,无毒但会降低食品的整体质量。如橄榄油[35]、大豆油[36]、柚子油[37]等中存在的游离脂肪酸,就可以通过逆流超临界流体萃取对提取物进行脱酸处理,与传统的化学提取过程相比,该技术具有很大的优势,即可以得到萃余液中脱酸油、游离脂肪酸的含量以及分离器中挥发性化合物的含量。还有从非活性干酵母中提取一些挥发性化合物[38]。类似的方法也用于精油的分离、精油的回收[39]、农副产品中如小麦胚芽中提取天然维生素E[40]、鲨鱼肝油中提取氧甘油类[41]。
2.2 超临界流体萃取技术在功能性物质提取方面的应用
2.2.1 从植物中提取
应用超临界流体萃取技术最广泛的是从植物中提取功能性成分。植物如小麦胚芽中含有大量亚油酸、天然复合维生素E、蛋白质等,以及8种人体必需氨基酸均可以通过超临界流体萃取出来。武练增[42]等提出了利用超临界二氧化碳技术萃取沙棘油的专利技术,刘军海[43]也对米糠油进行了研究,发现利用超临界二氧化碳萃取率在19.2%~20.4%之间,且油脂色泽和纯度都相对较好。
尤其在过去的十年里,有很多关于利用超临界流体萃取具有生物活性物质如抗氧化活性的研究和报道。芳香植物、水果、豆类和种子是天然抗氧化化合物的主要来源。超临界流体萃取的另一重要应用为从草药中萃取精油。精油传统上用于制作食品、化妆品、清洁产品、香水、除草剂和杀虫剂[44]。精油中包含着几十或数百的复杂成分,特别是碳氢化合物(萜烯、倍半萜烯)和含氧化合物(醇类、醛类、酮类、酸、酚类化合物、氧化物、内酯、缩醛、醚和酯类),除了特有的香味以外,还具有抗菌、抗氧化等生物活性。如于荟等[45]见表1,通过超临界CO2萃取得到牡丹精油,相比传统水蒸气蒸馏提取和有机溶剂提取,花香浓郁,得率最高为0.6%且挥发性物质种类较多,主体香物质为1,3,5-三甲氧基苯、辛烷等。李淑荣等[46]利用超临界CO2萃取烘烤花生中的挥发性成分,确定在萃取压力25MPa,温度55℃,萃取时间120 min时为最佳工艺条件,从萃取率和风味物质提取量来说,超临界CO2萃取技术都优于其他技术。魏贞伟等[47]试验发现在萃取压力25 MPa,萃取温度40℃,CO2流量18 kg/h,萃取时间120 min时,沙棘籽油的出油率为52%,且通过高效液相检测发现精油中的α-VE含量为2.6%,利用超临界萃取后热敏性物质仅损失3.7%。杨万政等[48]也是选择超临界流体萃取技术来提取番茄红素,不仅提取率高93.98%,且保护了番茄红素的活性。
超临界流体萃取过程中还需要根据萃取物的特性进行适当的工艺优化,如Fornari[49]研究了超临界流体萃取精油的影响因素且发现为了更好的萃取出所需要的具有生物活性物质如多酚和萜类化合物,一般会选择加入乙醇或甲醇作为夹带剂以增加萃取得率。其他一些化合物的萃取需要在高压条件下使用少量夹带剂或只以CO2作为流体进行萃取。还有极性较低的化合物如类胡萝卜素也需要在高压条件下萃取。2009年~2016年间以超临界流体萃取技术从植物中提取生物活性成分的相关文献见表1。从表1中可以看出,生物活性成分属于一个广泛的化合物类,包括生育酚[50],药品类[51],脂肪酸类[52],酚类[53]等。通常为了提高化合物提取率,通常以甲醇和乙醇作为夹带剂,含量高达20%左右,对于多酚、萜类化合物的提取乙醇浓度低于2%~5%也被证明是有效的,如表1中利用超临界流体萃取技术从月桂树中提取萜类物质。因此利用超临界流体萃取技术不仅可以提取出植物中具有生物活性的物质,还可以保留植物原有的挥发性风味和热敏性物质。
2.2.2 从动物中提取
超临界流体萃取技术也可用于动物油脂提取、肉类风味研究、海产品即藻类、微藻甲壳类动物、鱼及它们的副产品中提取高价值的化合物[71]。刘俊渤[72]因鹿油中富含饱和脂肪酸、不饱和脂肪酸等多种功能性营养物质,以鹿肉为原料利用超临界流体萃取技术提取鹿油,结果表明超临界萃取出的鹿油酸价低,不饱和脂肪酸含量为41.94%。谢跃杰[73]探讨了超临界流体萃取兔肉腥味物质的条件,发现萃取压力25 MPa,温度40℃,时间3 h时萃取率最高达到97.91%,明确了兔肉腥味物质的组成和成分,为肉类风味成分的研究提供了新的方法。海洋因其生物多样性,可以从藻类、微藻甲壳类动物、鱼及它们的副产品中获得高价值的化合物。鱼油及其副产品可以为人体提供大量所需的多不饱和脂肪酸,包括二十碳五烯酸和二十二碳六烯酸,据报道这些物质可降低心血管疾病的发病率、抗炎、抗血栓和抗心律失常等[74]。鱼油的传统分离方法有有机溶剂萃取、高效液相层析等方法,但这些传统方法存在高温降解和有机溶剂残留等问题。Lopes[75]研究了利用超临界流体萃取南美鸭嘴鲶中的鱼油,该鱼油中含较低(10%)的脂肪酸含量。季晓敏等[76]利用破壁后的雨生红球藻粉,通过超临界萃取技术萃取得到虾青素,并发现虾青素中含有很多不饱和脂肪酸,且与虾青素具有协同抗氧化作用。Hardardottir and Kinsella[77]从虹鳟鱼中萃取脂类,发现在压力(13.8 MPa~34.5 MPa)和温度(40℃~50℃)条件下,加入10%乙醇作为夹带剂萃取得率明显高于以CO2为流体的萃取得率。Sánchez-Camargo[78]和 Fujii K[79]等见表 2 通过研究证明脂类和虾青素的提取过程中加入15%的乙醇作为夹带剂,可以达到最大萃取得率分别为93.8%,65.2%。斋藤正三郎[80]进一步提出了用超临界二氧化碳萃取与尿素包合法相结合,该方法的优点在于可以对不同链长的脂肪酸进行分离,还可以对相同链长但饱和度不同的脂肪酸进行分离,并对鱼油中的多不饱和脂肪酸如EPA和DHA进行分离。国内外利用超临界流体萃取技术对海产品中的生物活性成分提取应用较为广泛见表2。
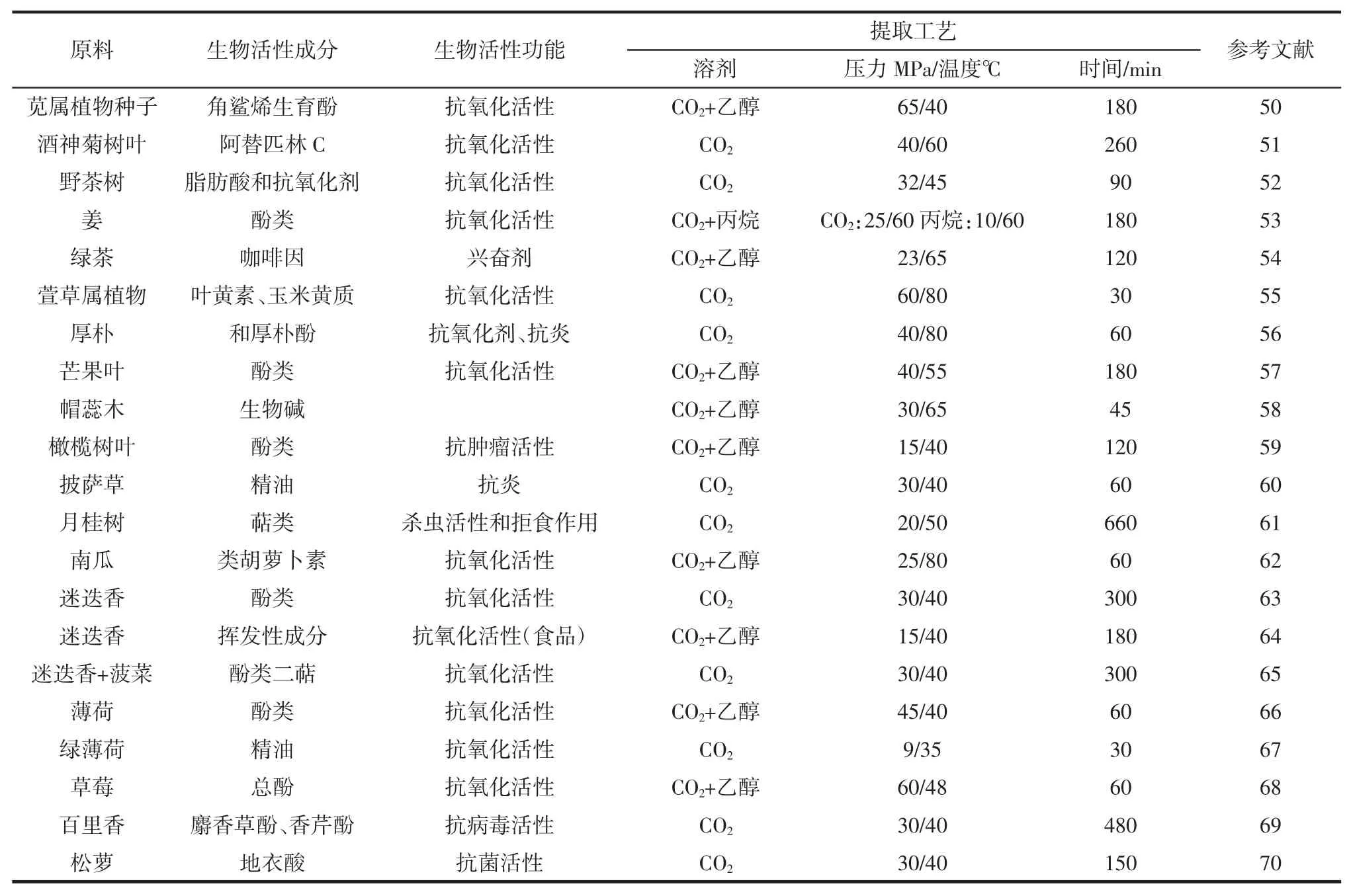
表1 2009年~2016年间以超临界流体萃取技术从植物中提取生物活性成分的相关文献Table 1 Remarkable recent published works(2009-2016)dealing with the use of SFE for the extraction of bioactive components from plants

表2 2009年~2016年间以超临界流体萃取技术从海产品中提取生物活性成分的相关文献Table 2 Remarkable recent published works(2009-2016)dealing with the use of SFE for the extraction of bioactive components from marine organism
2.2.3 从农业副产品中提取
食品工业加工过程中会产生大量副产品和残次品,造成了一定程度的环境污染和浪费。近期发现利用超临界流体萃取技术可以将副产物和残次品高效利用。如从食品及其副产品中提取的多酚类物质、类胡萝卜素、植物甾醇和精油均具有抗氧化活性,多酚类物质的萃取一般选择10%~20%乙醇作为夹带剂。近期,关于橄榄副产品的加工[96],葡萄[97]及酿酒残留物[98]中多酚类物质的提取也被认为是抗氧化物质的潜在来源。
从食物副产品中提取色素及抗氧化剂最多的研究是类胡萝卜素和番茄红素[99]。超临界流体萃取技术利用废弃的胡萝卜干渣[100]和番茄果皮[101]中提取类胡萝卜素,提取过程中提取温度是影响萃取得率的关键变量,虽然高温可以提高类胡萝卜素的萃取得率,但也会诱导提取物热降解或异构化反应[102]。目前,橄榄[103]、葡萄[104]见表3已被研究表明是多酚等具有高抗氧化性的潜在来源,且通过超临界流体萃取技术从农副产品中研究较多的为类胡萝卜素[105]和番茄红素[106],可以作为色素和抗氧化剂进行开发利用。且提取番茄红素已经从最初的番茄发展到其副产品包括皮、种子等,避免了原料的浪费,实现了有限资源的再利用。
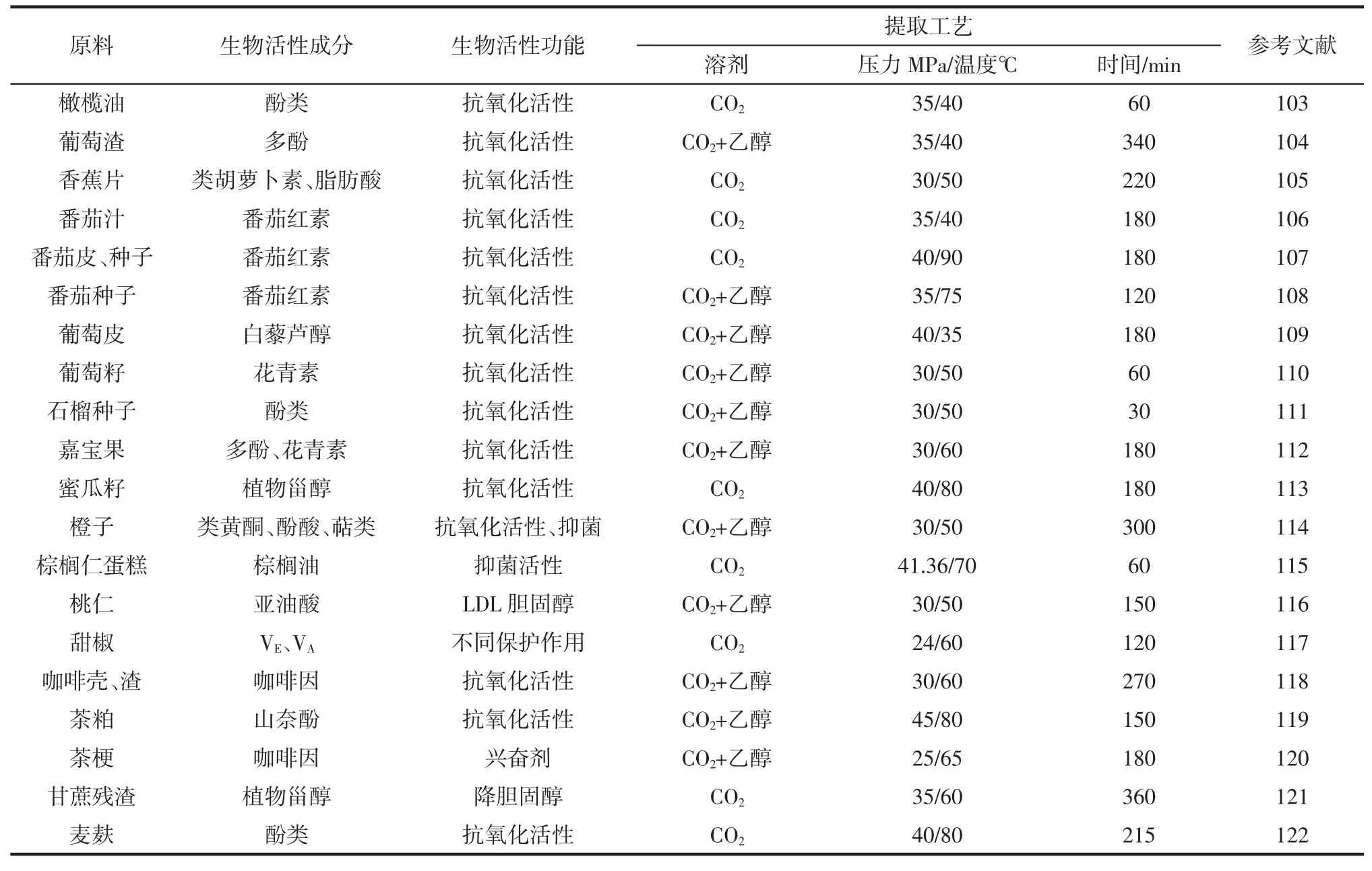
表3 2009年~2016年间以超临界流体萃取技术从食品副产品中提取生物活性成分的相关文献Table 3 Remarkable recent published works(2009-2016)dealing with the use of SFE for the extraction of bioactive components from Agricultural products
3 存在问题及发展方向
超临界流体萃取技术作为一种新型、清洁、高效的绿色提取分离方法,已经受到人们的普遍关注和广泛应用,因其提取物高度浓缩、无溶剂残留等优点不仅在食品工业方面,在药品、化妆品等方面也会有非常广阔的应用前景。在以后的应用方面还可以发展涉及重金属去除、生物农药的生产等方面,该技术的出现,为试验、中试规模提供了一种新的技术手段,如为样品的制备和处理提供了新的方法。目前超临界流体萃取还存在一定的局限性,主要表现为超临界流体萃取设备昂贵,在成本上无法与传统分离技术相比,无法实现大规模的工业化生产等,在以后的发展过程中应着重探讨超临界流体萃取技术工艺的优化,摸索出不同的溶剂如乙烷、甲醚、气体膨胀液体、离子液体、超临界流体之间的使用方法和实际效果。因此将超临界流体萃取技术发展成为可持续性和环保性的技术对我们来讲还有很长的一段路要走。因此在食品工业的应用过程中,应正确了解不同提取方法的优缺点,根据实际情况来选择合适的萃取方法。在今后的发展应用中,应多利用超临界流体萃取技术来提取分离有效成分,开发高品质全新产品,在满足绿色市场需求的同时,提高产品的附加值,并进一步优化工艺参数提高萃取得率,以符合工业化生产的要求,提高生产的可行性。
[1]朱自强.超临界流体技术原理和应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2000
[2]赵春海.超临界流体萃取技术原理及应用研究简述[J].生命科学仪器,2006,4(12):33-35
[3]雷鹏,张青,张滨,等.超临界流体萃取技术的应用与发展[J].河北化工,2010,33(3):25-29
[4]励建荣,夏明.超临界流体萃取技术研究进展[J].食品与发酵工业,2001,27(9):79-83
[5]阎文峰,陈文明.超临界流体技术进展[J].化学通报,1998(4):10-14
[6]Hannay J B,Hogarth J.On the Solubility of Solids in Gases[J].Proc R Soc Lond,1879,29:324-326
[7]Andrews T.The Bakerian Lecture:On the Continuity of the Gaseous and Liquid States of Matter[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London,1869,159:575-590
[8]卢媛媛,魏文挺,胡福良.超临界CO2流体萃取技术在蜂胶提取中的应用[J].食品工业科技,2013,34(19):364-368
[9]SAIRAMP,GHOSH S,JENA S,et al.Supercritical fluids extraction an overview[J].Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2012,2(3):112-120
[10]王莹.超临界萃取在中草药提取中的应用与发展 [J].中医临床研究,2011,3(9):101-106
[11]谢诚,欧昌荣,汤海青,等.食品中挥发性风味成分提取技术研究进展[J].核农学报,2015,29(12):2366-2374
[12]廖传华,黄振仁.超临界CO2流体萃取技术工艺开发及其应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2004
[13]韩玉刚,汪小舟.超临界萃取技术的发展及应用[J].广东化工,2014,14(12):104-105
[14]杨忠林,邵友元,姚创.超临界CO2萃取技术在天然产物中的应用[J].广东化工,2009,36(3):33-35
[15]王勇,魏娜,李洪福,等.海南黑胡椒超临界萃取物中化学成分的GC-MS分析[J].中国试验方剂学杂志,2013,19(12):14-16
[16]毕永贤,蒋丽刚,陆海英.超临界萃取技术在蓝色化妆品活性成分提取分离中的应用进展[J].香料香精化妆品,2014(5):25-29
[17]张红英,颜雪明.超临界萃取技术在中草药研究中的应用[J].盐城工学院学报,2014,27(3):35-38
[18]赵丹,尹洁.超临界流体萃取技术及其应用简介[J].安徽农业科学,2014,42(15):35-39
[19]FORNARIT,VICENTE.Isolation of essential oil from different plants and herbs by Supercritical fluid extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2012,1250(10):34-48
[20]樊文乐,武文洁.超临界萃取中夹带剂的概述[J].食品科技,2005(2):39-42
[21]廖传华,黄振仁.夹带剂对超临界CO萃取过程的影响[J].香料香精化妆品,2004(1):34-37
[22]王伟,卢佳.超临界CO2流体萃取技术的研究与分析[J].价值工程,2012,31(13):35-35
[23]刘紫燕,刘政权,李真.超临界CO2脱除绿茶咖啡碱过程中茶叶香气变化研究[J].食品工业科技,2015(19):286-289
[24]刘力萌,欧阳秉春.超临界二氧化碳萃取在食品工业中的应用[J].中国新技术新产品,2010(19):15-16
[25]张侃,刘世斌,郝晓刚,等.超临界CO2萃取啤酒花及其应用[J].太原理工大学学报,2002,33(1):103-105
[26]Bogolte B T,Ehlers G A C,Braun R.Estimation of PAH bioavailability to Lepidium sativum using sequential supercritical fluid extraction-casestudy with industrial contaminated soils[J].European Journal of Soil Biology,2007,43(4):242-250
[27]Kawashima A,Watanabe S,Iwakiri R.Removal of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs from fish oil by countercurrent supercritical CO2extraction and activated carbon treatment[J].Chemosphere,2009,75(6):788-794
[28]Rodil R,Carro A M,Lorenzo R A.Multicriteria optimisation of a simultaneous supercritical fluid extraction and clean-up procedure for the determination of persistent organophosphate pollutants in aquaculture samples[J].Chemosphere,2007,67(7):1453-1462
[29]Mahugo-Santana C,Sosa-Ferrera Z,Torres-Padrón M E.Analytical methodologies for the determination of nitroimidazole residues in biological and environmental liquid samples[J].Analytica Chimica Acta,2010,665(2):113-122
[30]Choi J-H,Mamun M I R.Inert matrix and NaEDTA improve the supercritical fluid extraction efficiency of fluoroquinolones for HPLC determination in pig tissues[J].Talanta,2009,78(2):348-357
[31]刘皓,吕春晖,王立晖.超临界流体萃取技术在农产品加工中的应用[J].农产品加工,2015(16):59-60
[32]Antonio Valverde,Ana Aguilera,Mariano Rodriguez,et al.Evaluation of a multiresidue method for pesticides in cereals using supercritical fluid extraction and gas chromatographic detection[J].Journal of Environmental Science&Health.part.b Pesticides Food Contaminants&Agricultural Wastes,2009,44(3):204-213
[33]Yao Y,Cai W,Yang C.Supercritical fluid CO2extraction of Acorus alamus L.and its contact toxicity to Sitophilus.Natural Product Research,2011,26(16):1498-1503
[34]Gupta D.K,Verma M.K,Lal S.Extraction studies of Podophyllum hexandrum using conventional and nonconventional methods by HPLC-UV-DAD.Journal of Liquid Chromatography&Related Technologies,2013,37(2):259-273
[35]Vázquez L,Hurtado-Benavides A M,Reglero G.Deacidification of olive oil by countercurrent supercritical carbon dioxide extraction:Experimental and thermodynamic modeling[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2009,90(4):463-470
[36]Goyal G,Dwivedi A K.Decolourization and deodourization of soyabean oil[J].Journal of Industrial Pollution Control Paper,2013,29(1):103-110
[37]Terada A,Kitajima N,Machmudah S.Cold-pressed yuzu oil fractionation using countercurrent supercritical CO2extraction column[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2010,71(1):107-113
[38]Arribas M V.Application of Supercritical CO2Extraction for the E-limination of Odorant Volatile Compounds from Winemaking Inactive Dry Yeast Preparation[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(6):3772-3778
[39]Gañán N,Brignole E A.Supercritical carbon dioxide fractionation of T.minuta and S.officinalis essential oils:Experiments and process analysis[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2013,78(0):12-20
[40]Ge Y,Ni Y,Yan H,et al.Optimization of the supercritical fluid extraction of natural vitamin E from wheat germ using response surface methodology[J].Journal of Food Science,2002,67(1):239-243
[41]Catchpole O J,Kamp J C V,Grey J B.Extraction of squalene from shark liver oil in a packed column using supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Industrial&Engineering Chemistry Research,1997,36(10):4318-4324
[42]武练增.超临界流体萃取技术在食品工业中的应用[J].食品工程,1996(4):24-31
[43]刘军海.超临界二氧化碳浸出米糠油[J].四川粮油科技,2001(2):18-19
[44]Azmir J,Zaidul I S M,Rahman M M.Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials:A review[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2013,117(4):426-436
[45]于荟,马文平,刘延平,等.顶空-气相色谱-质谱法分析牡丹鲜花精油中的挥发性成分[J].食品科学,2015,36(18):167-171
[46]李淑荣,王丽,宋焕禄,等.超临界CO2萃取烘烤花生中挥发性物质的研究[J].核农学报,2013,27(3):0321-0328
[47]魏贞伟,邵红,王俊国,等.超临界CO2萃取沙棘籽油及热敏性物质分析[J].食品科学,2012,33(24):97-100
[48]杨万政,常华,杜晓鸣,等.超临界二氧化碳萃取番茄红素的研究[J].河北农业大学学报,2009,32(6):114-116
[49]Fornari T,Vicente G,Vázquez E,García-Risco M R,et al.Isolation of essential oil from different plants and herbs by supercritical fluid extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A 2012,1250:34-48.
[50]Kraujalis P,Venskutonis P R.Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of squalene and tocopherols from amaranth and assessment of extracts antioxidant activity[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2013,80:78-85
[51]Martinez-Correa H.A,Cabral F.A.Extracts from the leaves of Baccharis dracunculifolia obtained by a combination of extraction processes with supercritical CO2,ethanol and water[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,63:31-39
[52]Wang Y,Sun D,Chen H.Fatty Acid Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Tea(Camellia sinensis L.)Seed Oil Extracted by Optimized Supercritical Carbon Dioxide[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2011,12(12):7708-7719
[53]Mesomo M.C,Scheer A.d,Perez E.Ginger(Zingiber officinale R.)extracts obtained using supercritical CO2and compressed propane:Kinetics and antioxidant activity evaluation[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,71:102-109
[54]Park H.S,Im N.G,Kim K.H.Extraction behaviors of caffeine and chlorophylls in supercritical decaffeination of green tea leaves[J].Food Science and Technology,2012,45(1):73-78
[55]Hsu Y-W,Tsai C-F,Chen W.Determination of lutein and zeaxanthin and antioxidant capacity of supercritical carbon dioxide extract from daylily[J].Food Chemistry,2011,129(4):1813-1818
[56]Cheah E L C,Heng P W S,Chan L W.Optimization of supercritical fluid extraction and pressurized liquid extraction of active principles from Magnolia officinalis using the Taguchi design[J].Separation and Purification Technology,2010,71(3):293-301
[57]Fernández-Ponce M T,Casas L,Mantell C.Extraction of antioxidant compounds from different varieties of Mangifera indica leaves using green technologies[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,72:168-175
[58]Orio L,Alexandru L,Cravotto G.SFE-CO2and classical methods for the extraction of Mitragyna speciosa leaves[J].Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2012,19(3):591-595
[59]Taamalli A,Arráez-Román D,Barrajón-Catalán E.Use of advanced techniques for the extraction of phenolic compounds from Tunisian olive leaves:Phenolic composition and cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(6),1817-1825
[60]Ocaña-Fuentes A,Arranz-Gutiérrez E,Señorans F J.Supercritical fluid extraction of oregano(Origanum vulgare)essentials oils:Antiinflammatory properties based on cytokine response on THP-1 macrophages[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2010,48(6):1568-1575
[61]Martín L,González-Coloma A,Díaz C E.Supercritical CO2extraction of Persea indica:Effect of extraction parameters,modeling and bioactivity of its extracts[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,57(2):120-128
[62]Shi X,Wu H,Shi J.Effect of modifier on the composition and antioxidant activity of carotenoid extracts from pumpkin(Cucurbita maxima)by supercritical CO2[J].LWT-Food Science and Technology,2013,51(2):433-440
[63]Vicente G,García-Risco M.R,Fornari,T.Supercritical Fractionation of Rosemary Extracts to Improve the Antioxidant Activity[J].Chemical Engineering&Technology,2012,35(1):176-182
[64]Vicente G,Martín D,García-Risco M.Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of antioxidant for rosemary(Rosmarinus officinalis)leaves for use in edible vegetable oils[J].Journal of Oleo Science,2012,61(12):689-697
[65]Vázquez E,García-Risco M R,Jaime L.Simultaneous extraction of rosemary and spinach leaves and its effect on the antioxidant activity of products[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2013,82(82):138-145
[66]Plánder S,Gontaru L,Blazics B.Major antioxidant constituents from Satureja hortensis L.extracts obtained with different solvents[J].European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2012,114(7):772-779
[67]Ansari K,Goodarznia I.Optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of essential oil from spearmint(Mentha spicata L.)leaves by using Taguchi methodology[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,67(7):123-130
[68]Akay S,Alpak I,Yesil-Celiktas O.Effects of process parameters on supercritical CO2extraction of total phenols from strawberry(Arbutus unedo L.)fruits:An 865 optimization study[J].Journal of Separation Science,2011,34(15):1925-1931
[69]Santoyo S,Jaime L,García-Risco M R,et al.Supercritical fluid extraction as an alternative process to obtain antiviral agents from thyme species[J].Industrial Crops and Products 2014,52:475-480
[70]Zizovic I,Ivanovic J,Misic D,et al.SFE as a superior technique for isolation of extracts with strong antibacterial activities from lichen Usnea barbata L.The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,72:7-14
[71]韩玉谦,管华诗.超临界流体萃取技术在海洋生物活性物质提取中的应用[C].全国超临界流体技术学术及应用研讨会,2004:41-44
[72]刘俊渤,王丽,胡耀辉,等.鹿油的超临界二氧化碳萃取工艺及分析[J].华南农业大学学报,2012,10(33):580-584
[73]谢跃杰,贺稚非,李洪军.超临界CO2流体萃取兔肉腥味物质[J].中国农业科学,2016,49(16):3208-3218
[74]Aidos I,Padt A V D,Boom R M,et al.Quality of Crude Fish Oil Extracted from Herring Byproducts of Varying States of Freshness[J].Journal of Food Science,2003,68(2):458-465
[75]Lopes B L F,Sánchez-Camargo A P,Ferreira A L K.Selectivity of supercritical carbon dioxide in the fractionation of fish oil with a lower content of EPA+DHA[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,61(51):78-85
[76]季晓敏,王亚男,徐嘉杰,等.扫描电镜和响应面优化雨生红球藻破壁萃取虾青素的工艺研究 [J].核农学报,2014,28(6):1052-1061
[77]Hardardottir I,Kinsella J E.Extraction of Lipid and Cholesterol from Fish Muscle with Supercritical Fluids[J].Journal of Food Science,2010,53(6):1656-1658
[78]Sánchez-Camargo A P,Meireles M Â A,Ferreira A L K.Extraction of ω-3 fatty acids and astaxanthin from Brazilian redspotted shrimp waste using supercritical CO2+ethanol mixtures[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluid,2012,61(12):71-77
[79]Fujii K.Process integration of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and acid treatment for astaxanthin extraction from a vegetative microalga.Food and Bioproducts Processing 2012,90(4):762-766
[80]斋藤正三郎.超临界气体提取及其在食品工业中的应用 [J].食品工业科技,1987(1):58-61
[81]Golmakani M-T,Mendiola J A,Rezaei K.Expanded ethanol with CO2and pressurized ethyl lactate to obtain fractions enriched in γ-Linolenic Acid from Arthrospira platensis(Spirulina)[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,62:109-115
[82]Mezzomo N,Martínez J,Maraschin M,et al.Pink shrimp (P.brasiliensis,and P.paulensis)residue:Supercritical fluid extraction ofcarotenoidfraction[J].JournalofSupercritical Fluids,2013,74(2):22-33
[83]Sánchez-Camargo A P,Martinez-Correa H A,Paviani L C,et al.Supercritical CO2extraction of lipids and astaxanthin from Brazilian redspotted shrimp waste(Farfantepenaeus paulensis)[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2011,56(2):164-173
[84]Ruen-ngam D,Shotipruk A,Pavasant P,et al.Selective Extraction of Lutein from Alcohol Treated Chlorella vulgaris by Supercritical CO2[J].Chemical Engineering&Technology 2012,35(2):255-260
[85]Wang H-M,Pan J-L,Chen C-Y.Identification of anti-lung cancer extract from Chlorella vulgaris C-C by antioxidant property using supercritical carbon dioxide extraction[J].Process Biochemistry,2010,45(12):1865-1872
[86]Rubio-Rodríguez N,de Diego S M,Beltrán S,et al.Supercritical fluid extraction of fish oil from fish by-products:A comparison with other extraction methods[J].Journal of Food Engineering 2012,109(2):238-248
[87]Sahena F,Zaidul I.S.M,Jinap S.Extraction of fish oil from the skin of Indian mackerel using supercritical fluids[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2010,99(1):63-69
[88]Lopes B L F,Sánchez-Camargo A P,Ferreira A L K,et al.Selectivity of supercritical carbon dioxide in the fractionation of fish oil with a lower content of EPA+DHA[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2012,61:78-85
[89]Wang L,Yang B,Yan B,et al.Supercritical fluid extraction of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis and its antioxidant potential in sunflower oil[J].Innovative Food Science&Emerging Technologies,2012,13,120-127.
[90]Fujii K.Process integration of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and acid treatment for astaxanthin extraction from a vegetative microalga[J].FoodandBioproductsProcessing,2012,90(4):762-766
[91]Liau B-C,Shen C-T,Liang F-P.Supercritical fluids extraction and anti-solvent purification of carotenoids from microalgae and associated bioactivity[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,55(1):169-175
[92]Treyvaud Amiguet V,Kramp K.L,Mao J.Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of polyunsaturated fatty acids from Northern shrimp(Pandalus borealis Kreyer)processing by-products[J].Food Chemistry,2012,130(4):853-858
[93]Macías-Sánchez M D,Fernandez-Sevilla J M,Fernández F G.Supercritical fluid extraction of carotenoids from Scenedesmus almeriensis[J].Food Chemistry,2010,123(3):928-935
[94]Tang S,Qin C,Wang H.Study on supercritical extraction of lipids and enrichment of DHA from oil-rich microalgae[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,57(1):44-49
[95]Aguiar A C,Visentainer J V,Martínez J.Extraction from striped weakfish(Cynoscion striatus)wastes with pressurized CO2:Global yield,composition,kinetics and cost estimation[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,71(11):1-10
[96]Ibanez E,Palacios J,Senorans F J,et al.Isolation and separation of tocopherols from olive by-products with supercritical fluids[J].Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society,2000,77(2):187-190
[97]Yilmaz E.Extraction and identification of proanthocyanidins from grape seed using supercritical carbon dioxide[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,55(3):924-928
[98]Farías-Campomanes A M,Rostagno M A,Meireles M A.Production of polyphenol extracts from grape bagasse using supercritical fluids:Yield,extract composition and economic evaluation[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2013,77(5):70-78
[99]Zaghdoudi K,Framboisier X,Frochot C,et al.Response surface methodologyappliedtoSupercriticalFluidExtraction(SFE)ofcarotenoids fromPersimmon(DiospyroskakiL.)[J].FoodChemistry,2016,208(208):209-219
[100]张学杰,赵永彬,尹明安.胡萝卜干渣中类胡萝卜素的超临界CO2萃取技术研究[J].食品工业科技,2006(2):154-155
[101]惠伯棣,李京,贾宁,等.番茄果皮超临界流体萃取物中类胡萝卜素在大鼠血清中的积累[J].食品科学,2008,29(7):408-411
[102]Mezzomo N,Mileo B R.Supercritical fluid extraction of peach almond oil:Process yield and extract composition[J].Bioresource Technology,2010,101(14):5622-5632
[103]Dermeche S,Nadour M,Larroche C.Olive mill wastes:Biochemical characterizations and valorization strategies[J].Process Biochemistry,2013,48(10):1532-1552
[104]Farías-Campomanes A M,Rostagno M A,Meireles M A A.Produc-tion of polyphenol extracts from grape bagasse using supercritical fluids:Yield,extract composition and economic evaluation.The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 2013,77,70-78
[105]Comim S R R,Madella K,Oliveira J V.Supercritical fluid extraction from dried banana peel(Musa spp.,genomic group AAB):Extraction yield,mathematical modeling,economical analysis and phase equilibria[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,54(1):30-37
[106]Egydio J A,Moraes M.Supercritical fluid extraction of lycopene from tomato juice and characterization of its antioxidation activity[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,54(2):159-164
[107]Machmudah S,Zakaria,Winardi S.Lycopene extraction from tomato peel by-product containing tomato seedusing supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2012,108(2):290-296
[108]Shi J,Yi C,Xue S J,et al.Effects of modifiers on the profile of lycopene extracted from tomato skins by supercritical CO2[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2009,93(4):431-436
[109]Casas L,Mantell C,Rodríguez M.Extraction of resveratrol from the pomace of Palomino fino grapes by supercritical carbon dioxide[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2010,96(2):304-308
[110]Yilmaz E.E,Özvural E B,Vural H.Extraction and identification of proanthocyanidins from grape seed(Vitis Vinifera)using supercritical carbon dioxide[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,55(3):924-928
[111]Castro-Vargas H I,Rodríguez-Varela L I,Ferreira S R S.Extraction of phenolic fraction from guava seeds(Psidium guajava L.)using supercritical carbon dioxide and co-solvents[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,51(3):319-324
[112]Cavalcanti R N,Veggi P C,Meireles M A A.Supercritical fluid extraction with a modifier of antioxidant compounds from jabuticaba(Myrciaria cauliflora)by products:economic viability[J].Procedia Food Science 2011,1:1672-1678
[113]Nyam K L,Tan C P,Lai O M.Optimization of supercritical CO2extraction of phytosterol-enriched oil from Kalahari melon seeds[J].Food and Bioprocess Technology,2009,4(8):1432-1441
[114]Benelli P,Riehl C.A.S,Smânia,A.Bioactive extracts of orange(Citrus sinensis L.Osbeck)pomace obtained by SFE and low pressure techniques:Mathematical modeling and extract composition[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,55(1):132-141
[115]Rahman N N A,Al-Rawi S S,Ibrahim A H.Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of the residual oil from palm kernel cake[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2012,108(1):166-170
[116]Mezzomo N,Mileo B R,Friedrich M T.Supercritical fluid extraction of peach(Prunus persica)almond oil:Process yield and extract composition[J].Bioresource Technology,2010,101(14):5622-5632
[117]Romo-Hualde A,Yetano-Cunchillos A I,González-Ferrero C.Supercritical fluid extraction and microencapsulation of bioactive compounds from red pepper(Capsicum annum L.)by-products[J].Food Chemistry,2012,133(3):1045-1049
[118]Andrade K S,Gonçalvez R.T,Maraschin M.Supercritical fluid extraction from spent coffee grounds and coffee husks:Antioxidant activity and effect of operational variables on extractcomposition[J].Talanta,2012,88:544-552
[119]Li B,Xu Y,Jin Y-X.Response surface optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of kaempferol glycosides from tea seed cake[J].Industrial Cropsand Products,2010,32(2):123-128
[120]I˙çen H,Gürü M.Effect of ethanol content on supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of caffeine from tea stalk and fiber wastes[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2010,55(1):156-160
[121]Prado J M,Prado G H C,Meireles M A A.Scale-up study of supercritical fluid extraction process for clove and sugarcane residue[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2011,56(3):231-237
[122]Rebolleda S,Beltrán S,Sanz M T.Extraction of alkylresorcinols from wheat bran with supercritical CO2[J].Journal of Food Engineering,2013,119(4):814-821

