侧枝循环对急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓的预后评估
许孝南 戚玉龙 李谆晶 陈旭辉 童晓欣 吴军 胡俊
侧枝循环对急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓的预后评估
许孝南 戚玉龙 李谆晶 陈旭辉 童晓欣 吴军 胡俊
目的探讨Alberta卒中早期CT评分(ASPECTS)评估侧枝循环对急性大脑中动脉供血压梗死静脉溶栓的疗效以及预后。方法选择北京大学深圳医院神经内科自2015年9月~2016年9月接受静脉溶栓治疗的急性大脑中动脉供血压梗死患者39例,依据溶栓前ASPECTS评分分为侧枝良好组及侧枝不良组,比较2组间临床资料及溶栓后90 d的预后差异;再以预后是否良好为因变量进行Logistic回归分析。结果侧枝良好组美国国立卫生研究院卒中量表(National Institute of Health Stroke Scale,NIHSS)评分更低、ONT(onset to needle time)更短,则预后更好。Logistec回归分析显示ASPECTS评分是评估预后是否良好的独立预测因子(OR:39.395,95%CI=1.336~1161.514,P=0.033)。结论ASPECTS可准确评估侧枝循环,对静脉溶栓有明确的指导治疗作用。
侧枝循环 脑梗死 Alberta卒中早期CT评分 静脉溶栓 预后
急性缺血性脑卒中(acute ischemic stroke,AIS)是严重危害我国人民健康最常见的疾病,研究发现良好的侧枝循环可使脑梗死灶体积变小、转归改善[1-2]。其中,Alberta卒中项目早期CT评分(Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score,ASPECTS)是评价AIS患者大脑中动脉供血区早期缺血改变的一种简单、可靠的系统性方法,可间接反映缺血区域的侧枝循环情况,有助于判定溶栓的近期及远期疗效。本研究将运用ASPECTS评分,采用回顾性分析的方法,探讨侧支循环对急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓疗效的影响以及预后的评估。
1 资料与方法
1.1 病例选择
经北京大学深圳医院伦理委员会批准并取得患者同意后选择自2015年9月~2016年9月在北京大学深圳医院神经内科住院并接受阿替普酶(recombinant tissue Plasminogen activator,rt-PA)静脉溶栓的大脑中动脉供血区梗死患者。纳入标准:①年龄≥18岁;②临床确诊的前循环缺血性脑卒中患者(住院后48 h MR明确责任血管);③发病时间<4.5 h;④患者或家属签署知情同意书。排除标准:①预计生存期<90 d;②溶栓前mRs≥1分;余同2016中国急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓指导规范禁忌症[3]。本研究共纳入39例患者,其中男26例,女13例,年龄26~77岁,平均年龄(57±14)岁,其中1例男性患者在住院期间因颅内出血转化死亡。
1.2 分组及相关指标
将ASPECTS≤7分为侧枝不良组,ASPECT>8分为侧枝良好组[4]。比较2组患者年龄、性别、既往史(高血压病、糖尿病、血脂代谢异常、心房颤动)、吸烟、治疗前NIHSS评分、治疗后24 h NIHSS评分、出院时NIHSS评分、发病至治疗时间(onset to needle time,ONT)及治疗前平均动脉压等的差异。
于治疗后90 d用改良Rankin量表(modified Rankin Scale,mRs)进行评分,0~2分定义为预后良好,3~6分定义为预后不良,并进行多因素Logistic回归分析预后的影响因素。
1.3 治疗
采用阿替普酶干粉制剂(50 mg/支),溶栓剂量按照0.9 mg/kg,最大剂量90 mg,10%剂量先于1 min内静脉推注,余剂量60 min持续静脉泵入。
1.4 数据处理
2名高年资放射科医师在只知道病灶侧的前提下在CT图像上单独进行ASPECTS评分;对于不一致的评分,由2名医师讨论后达成统一意见。
1.5 统计学处理
2 结 果
2.1 基线资料比较
2组NIHSS评分、ONT、预后良好率有明显差异(P<0.05),其余基线资料无明显差异(P>0.05)(表1)。
2.2 溶栓后90 d影响预后的Logistic回归分析
依据mRs分组,预后良好组27例,预后不良组12例,2组ASPECTS评分有明显差异(P<0.05)(表2)。
3 讨 论
在AIS中侧枝循环良好往往意味着缺血半暗带中低灌注组织和脑梗死体积的相对减少[5],其与影像学的相互演变关系已经得到国内外学者的一致认可。如PROACT II研究显示早期CT演变、临床表现与大脑中动脉栓子位点呈并行关系[6]。Lee等研究发现大脑中动脉近端闭塞的AIS患者,其CTP灌注缺损越大,核心梗死区域越大,预后越差[7]。Christoforidis等[8]的研究则提示溶栓治疗前软脑膜侧枝形成与否是梗死体积、临床结局的强预测因子。
随着科学发展,TCD、CTA、CTP、MR和DSA等新技术可直观地评估侧枝循环,有很高的临床应用价值。对比增强经颅彩色双功能超声(transcranial color-coded duplex sonography,TCCD)可显示脑实质和颅内小动静脉,但由于颅骨肥厚导致经颞超声束穿透不充分及其操作、解释的主观变异性较大,主要用于基层医院的人群筛查[9]。CTA、MRA评估Willis环的解剖结构准确性较高,但分辨率有限,妨碍了其对软脑膜二级侧枝的评估[10-11]。CTP是间接评估侧枝循环的方法,但当上级动脉闭塞时维持灌注的动脉来源是无法证实的。DSA是二、三级侧枝评估的金标准,但其有创、治疗成本高、对远端血管的显示受对比剂的剂量和压力影响,仍需与无创的影像技术互补。综上所述,目前临床上尚无完美评估侧枝循环的方法,而本研究采用的CT-ASPECTS评分能最大限度地缩短DNT[12],既能反映超急性期大脑中动脉闭塞/狭窄后的缺血范围,又能体现侧枝循环的代偿能力。如Tan等[4]对ASPECTS≤5分者的预后行多因素回归分析发现,与年龄(OR0.93,95%CI0.89~0.97,P=0.002)、良好侧枝(基于CTA的ASPECT-collaterals system;OR1.34,95%CI1.15~1.57;P<0.001)呈正相关。Kawiorski等[13]的研究提示ASPECTS评分可作为血管内治疗无效开通的强预测因子,其评分越低,侧枝循环代偿越差,核心梗死区也越大。Yoo等[14]则发现ASPECTS 8~10分者经血管内再通的病死率低,呈下降趋势(P=0.01),而ASPECTS 0~4分的患者经血管内治疗后的出血转化增多(P=0.02),提示ASPECTS评分可作为重度AIS出血转化的预测因子,这与临床上重度AIS患者的早期再灌注不利于临床结局相符。

表1 2组患者基线资料比较
注:与侧枝不良组比较,△P<0.05;*为侧枝不良组15例
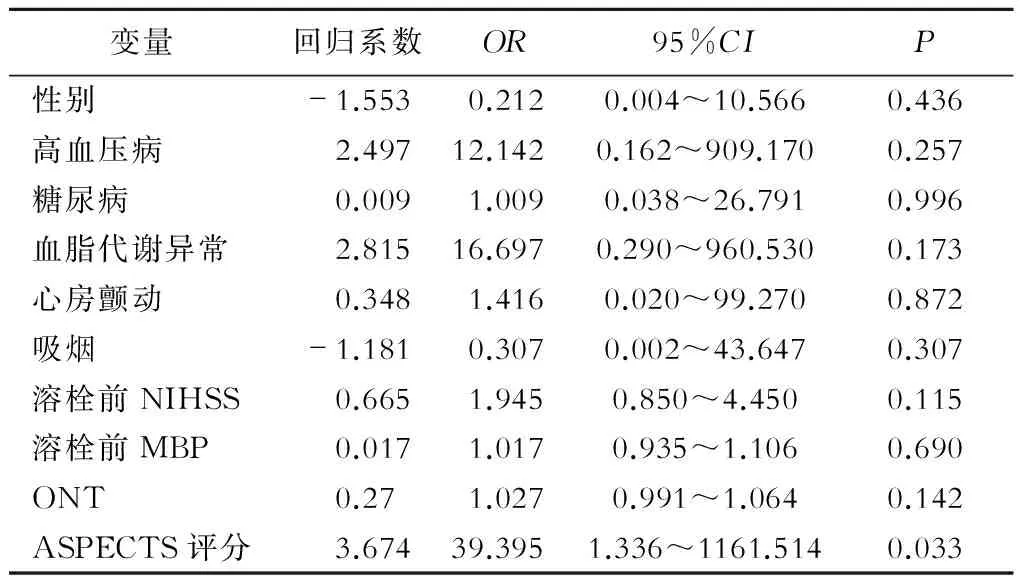
表2 溶栓后90 d影响预后的Logistic回归分析
本研究结果显示ASPECT<8分的患者NIHSS分值偏高、预后不佳,提示ASPEST评分可准确预测病情严重程度。ONT延迟对侧枝循环的建立不利,使CT早期缺血征象早现、扩大,ASPECTS评分随之降低,提示预后不佳,并与上述研究结果类似。既往研究认为高血压病、糖尿病、血脂代谢异常使血管内皮及血管调节能力下降,从而导致三级侧枝代偿不佳、预后不良[15-17],但在本研究结果无明显差异(P>0.05),其原因可能是缺血数天后新生血管才能建立侧枝血流代偿,存在时效偏倚的缘故。
本研究结果显示预后良好率为69%,高于文献报道的26.2%[18]。另一方面,本研究结果提示溶栓前ASPECTS评分是侧枝循环良好的预测因子。综上所述,ASPECTS评分可准确评估侧枝循环,对静脉溶栓有明确的指导治疗作用,目前已有针对ASPECTS≥8分但侧枝代偿良好的超时间窗溶栓研究[19],相信日后将更精确地筛选出更多可获益的AIS超时间窗溶栓患者。
本研究也存在一定局限性。首先,样本为单中心回顾性资料,样本量较小;其次,远期随访只有90 d一个时间节点,APSECTS评分与远期预后的关系仍需进一步论证。因此,下一步将联合多中心进行长期随访,以期获取更精确的预测指标。
[1] Demchuk AM,Hill MD,Barber PA,et al.Importance of early ischemic computed tomography changes using ASPECTS in NINDS rtPA stroke study[J].Stroke,2005,36(10):2110-2115.
[2] Yeo L,Paliwal P,Teoh HL,et al.Assessment of intracranial collaterals on CT angiography in anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke[J].American Journal of Neuroradiology,2015,36(2):289-294.
[3] 国家卫生计生委脑卒中防治工程委员会,中国急性缺血性脑卒中静脉溶栓指导规范2016[Z],2016.由国家脑防卫发布.
[4] Tan BY,Wan-Yee K,Paliwal PA,et al.Good intracranial collaterals trump poor ASPECTS (Alberta stroke program early CT score) for intravenous thrombolysis in anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke[J].Stroke,2016,47(9):2292-2298.
[5] Bang OY,Saver JL,Buck BH,et al.Impact of collateral flow on tissue fate in acute ischaemic stroke[J].J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,2008,79(6):625-629.
[6] Roberts HC,Dillon WP,Furlan AJ,et al.Computed tomographic findings in patients undergoing intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke due to middle cerebral artery occlusion - Results from the PROACT II trial[J].Stroke,2002,33(6):1557-1565.
[7] Lee KH,Cho SJ,Byun HS,et al.Triphasic perfusion computed tomography in acute middle cerebral artery stroke - A correlation with angiographic findings[J].Arch Neurol,2000,57(7):990-999.
[8] Christoforidis GA,Mohammad Y,Kehagias D,et al.Angiographic assessment of pial collaterals as a prognostic indicator following intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke[J].AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2005,26(7):1789-1797.
[9] Koga M,Kimura K,Minematsu K,et al.Relationship between findings of conventional and contrast-enhanced transcranial color-coded real-time sonography and angiography in patients with basilar artery occlusion[J].American Journal of Neuroradiology,2002,23(4):568-571.
[10] Hoksbergen AW,F lesdi B,Legemate DA,et al.Collateral configuration of the circle of Willis:transcranial color-coded duplex ultrasonography and comparison with postmortem anatomy[J].Stroke,2000,31(6):1346-1351.
[11] Seidel G,Kaps M,Gerriets T.Potential and limitations of transcranial color-coded sonography in stroke patients[J].Stroke,1995,26(11):2061-2066.
[12] Sallustio F,Motta C,Pizzuto S,et al.CT angiography-based collateral flow and time to reperfusion are strong predictors of outcome in endovascular treatment of patients with stroke[J].J Neurointerv Surg,2016.pii:neurintsurg-2016-012628.
[13] Kawiorski MM,Martinez-Sanchez P,Garcia-Pastor A,et al.Alberta stroke program early CT score applied to CT angiography source images is a strong predictor of futile recanalization in acute ischemic stroke[J].Neuroradiology,2016,58(5):487-493.
[14] Yoo AJ,Zaidat OO,Chaudhry ZA,et al.Impact of pretreatment noncontrast CT Alberta stroke program early CT score on clinical outcome after intra arterial stroke therapy[J].Stroke,2014,45(3):746-751.
[15] Omura-Matsuoka E,Yagita Y,Sasaki TA,et al.Hypertension impairs leptomeningeal collateral growth after common carotid artery occlusion:restoration by antihypertensive treatment[J].J Neurosci Res,2011,89(1):108-116.
[16] Iadecola C,Davisson RL.Hypertension and cerebrovascular dysfunction[J].Cell Metab,2008,7(6):476-484.
[17] Van Weel V,De Vries M,Voshol PJ,et al.Hypercholesterolemia reduces collateral artery growth more dominantly than hyperglycemia or insulin resistance in mice[J].Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2006,26(6):1383-1390.
[18] Saver JL,Jahan R,Levy EI,et al.Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci Retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT):a randomised,parallel-group,non-inferiority trial[J].Lancet,2012,380(9849):1241-1249.
[19] Seners P,Turc G,Ma er B,et al.Incidence and predictors of early recanalization after intravenous trombolysis:A systematic review and meta-Analysis[J].Stroke,2016,47(9):2409-2412.
Collateralcirculationinassessingprognosisofpatientswithacutecerebralinfarctionafterintravenousthrombolysis
XuXiaonan,QiYulong,LiZhunjing,etal.
DepartmentofNeurology,PeikingUniversityShenzhenHospital,Shenzhen518036
ObjectiveTo evaluate the role of Alberta stroke program early CT scale (ASPECTS) in predicting collateral circulation of patients with acute middle cerebral artery infarction, and functional outcomes after intravenous thrombolysis.Methods39 patients with acute middle cerebral infarction after intravenous thrombolysis in the department of neurology in Peiking University Shenzhen Hospital were chosen from September 2015 to September 2016. According to ASPECTS, the favorable and unfavorable collateral groups were defined, The clinical data, scores of ASPECTS and Logistic variables were analyzed.ResultsAs compared with patients in the U group, the F group had significantly lower NIHSS scores, shorter ONT and higher functional outcomes(P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that ASPECTS scores (OR:39.395,95%CI=1.336~1161.514,P=0.033) was the independent predictors 90 days after thrombolysis.ConclusionASPECTS could assess collateral circulation accurately, which was of great value in directing intravenous thrombolysis.
Collateral Circulation Stroke Alberta stroke program early CT scale Intravenous thrombolysis Prognosis
R743.3
A
1007-0478(2017)06-0495-04
10.3969/j.issn.1007-0478.2017.06.004
深圳市科创委科研基金(编号为JYC2014031709172271)
518036 深圳,北京大学深圳医院神经内科[许孝南 戚玉龙 李谆晶 陈旭辉 童晓欣 吴军 胡俊(通信作者)]
(2017-01-16收稿)

