遥感卫星
遥感卫星
·编者按·
遥感卫星,是一种利用卫星上所装载的遥感器对地球表面和低层大气进行光学或电子探测以获取有关信息的应用卫星。用卫星作为平台的遥感技术称为卫星遥感。
国际遥感卫星正向高空间分辨率、高时间分辨率、高光谱分辨率、高机动能力和高集成化等方向发展。其中,高分辨率遥感卫星是空间技术发展的一个重要方向,具有十分重要的商业价值与军事意义,对地观测卫星地面分辨率不断提高,目前已发展到0.5 m以内。
按照开发主体的不同,遥感卫星可以分为军用遥感卫星、民用遥感卫星和商用遥感卫星。其中民用遥感卫星主要指不以营利为目的,主要服务于国家政府部门、公众业务等方面的遥感卫星,以国家投资为主;商用遥感卫星主要指以营利为目的,广泛应用于商业市场的遥感卫星,以市场公司投资为主。按照应用领域的不同,遥感卫星可以分为陆地卫星、海洋卫星和气象卫星。
随着卫星数据在各领域的应用越来越广,国内外遥感卫星的数量也越来越多。这些卫星主要应用于国土资源勘查、环境监测与保护、城市规划、农作物估产、防灾减灾和空间科学试验等领域。
本专题得到张永军教授(武汉大学)、黄鹏高级工程师(中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所)、焦伟利副研究员(中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2017年10月13日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“遥感卫星”等为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为2483、4090条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)
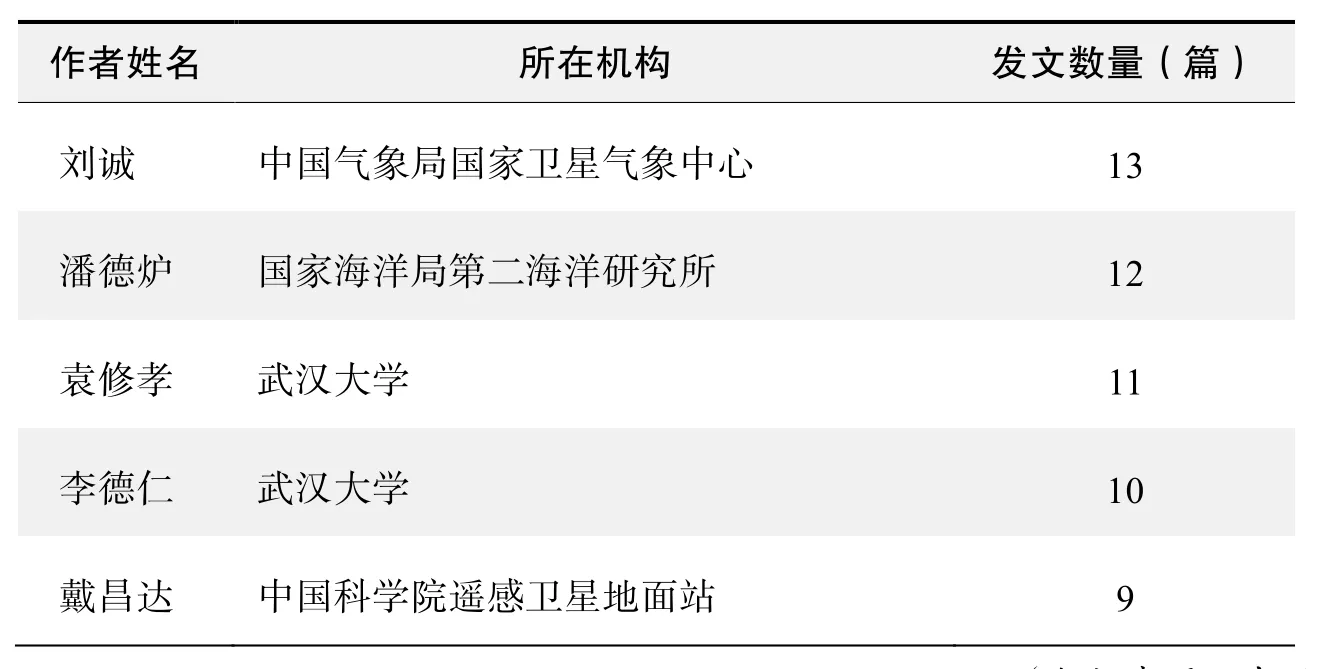
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
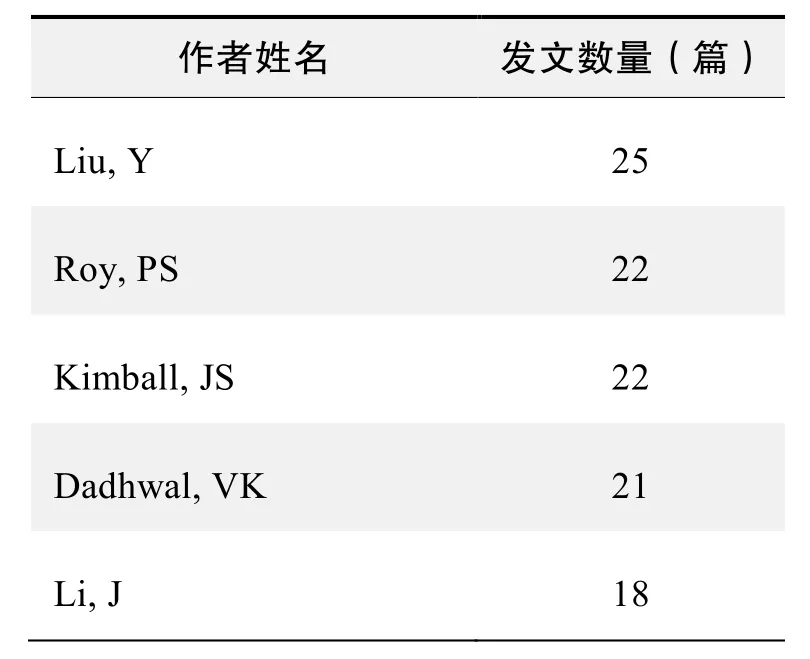
作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
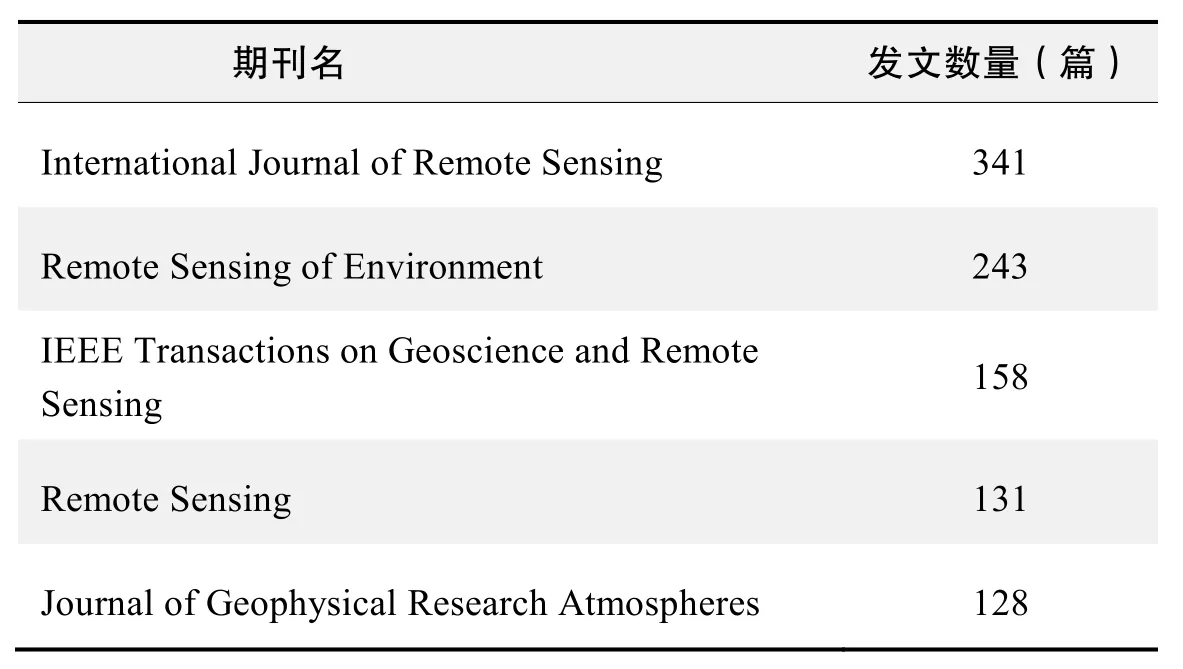
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“遥感卫星”等为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
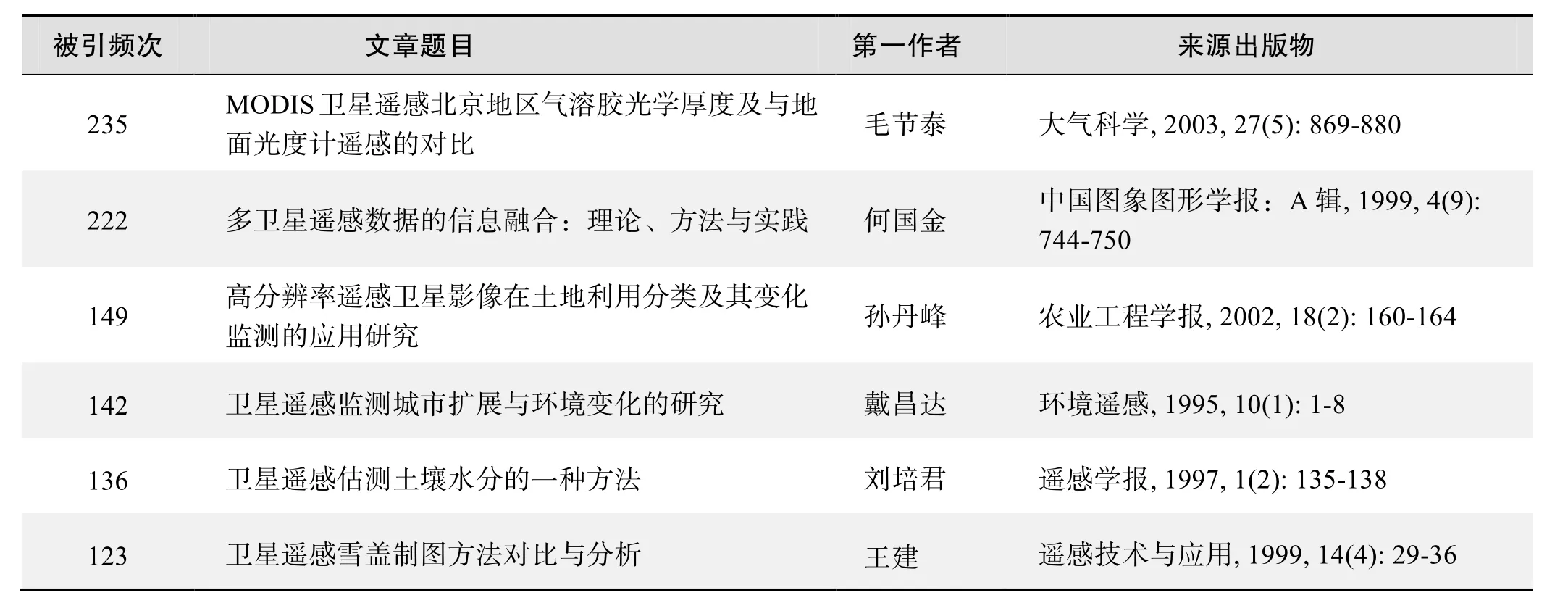
国内数据库高被引论文排行

(续表)
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“遥感卫星”等为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
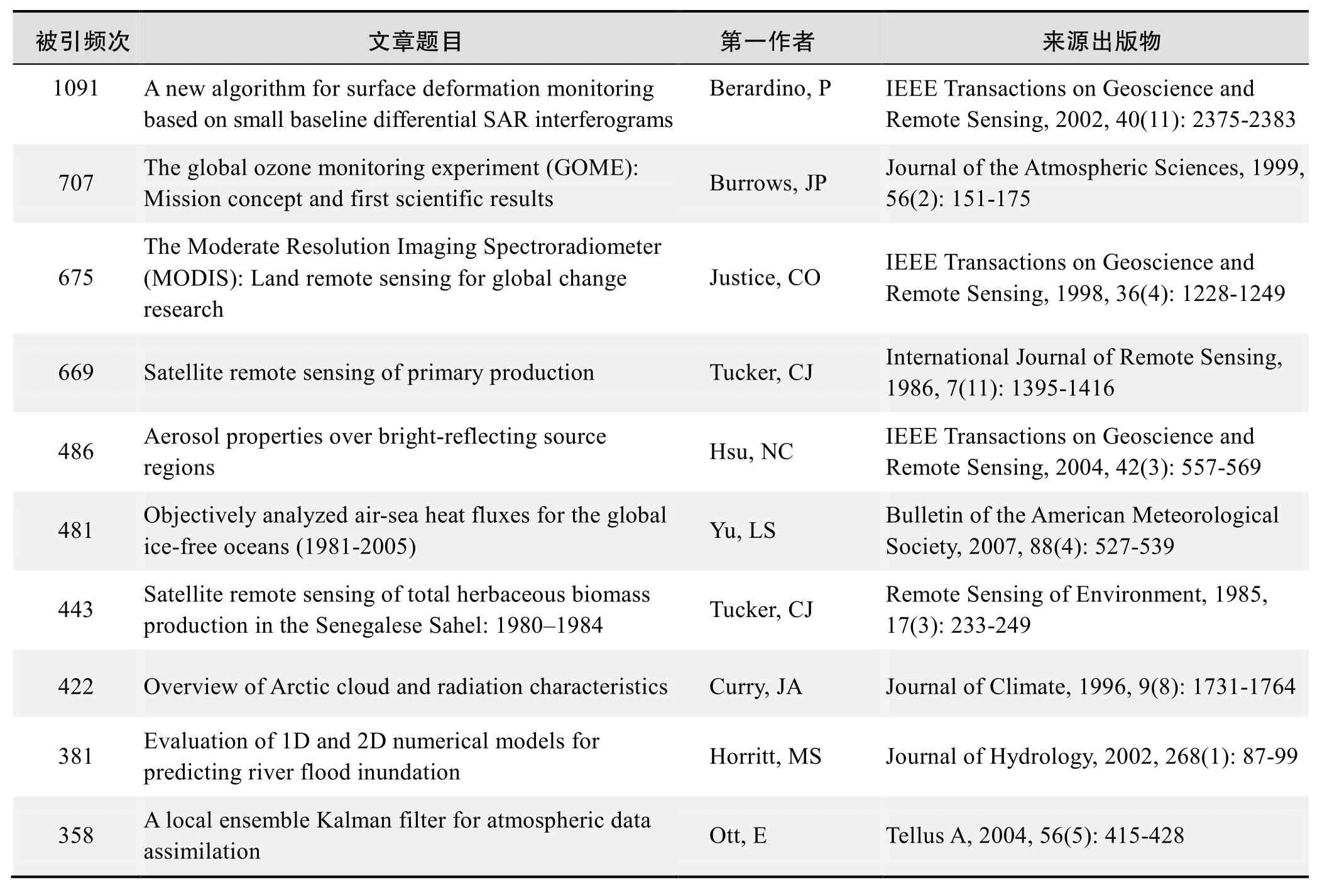
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于 Web of Science检索结果,利用 Histcite软件选取 LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP30文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
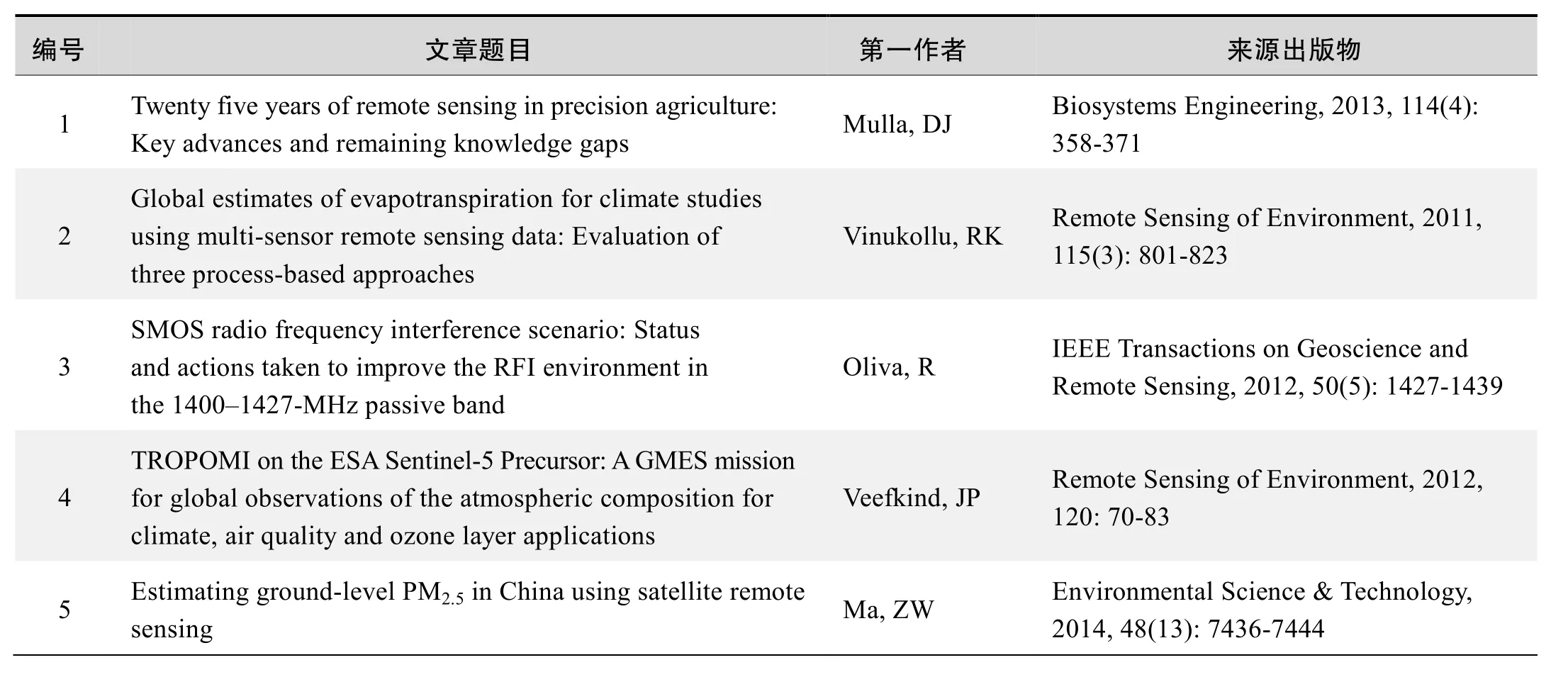
本领域经典文献
来源出版物:Biosystems Engineering,2013,114(4):358-371
Global estimates of evapotranspiration for climate studiesusing multi-sensor remote sensing data:Evaluation of threeprocess-based approaches
Vinukollu, RK; Wood, EF; Ferguson, CR; et al.
Abstract:Three process based models are used to estimate terrestrial heat fluxes and evapotranspiration (ET)at theglobal scale: a single source energy budget model, a Penman–Monteith based approach, and a Priestley–Taylor based approach. All models adjust the surface resistances or provide ecophysiological constraints to account for changing environmental factors. Evaporation(or sublimation) over snow-covered regions is calculated consistently for all models using a modified Penman equation. Instantaneous fluxes of latent heat computed at the time of satellite overpass are linearly scaled to the equivalent daily evapotranspiration using the computed evaporative fraction and the day-time net radiation. A constant fraction (10% of daytime evaporation) is used to account for the night time evaporation. Interception losses are computed using a simple water budget model. We produce daily evapotranspiration and sensible heat flux for theglobal land surface at 5km spatial resolution for the period2003–2006. With the exception of wind and surface pressure, all model inputs and forcings are obtained from satellite remote sensing. Satellite-based inputs and model outputs were first carefully evaluated at the site scale on a monthly-mean basis, then as a four-year mean against a climatological estimate of ET over26 major basins, and finally in terms of a latitudinal profile on an annual basis.Intercomparison of the monthly model estimates of latent and sensible heat fluxes with12 eddy-covariance towers across the U.S. yielded mean correlation of 0.57 and 0.54,respectively. Satellite-based meteorological datasets of2 m temperature (0.83), humidity (0.70), incident shortwave radiation (0.64), incident longwave radiation (0.67) were found to agree well at the tower scale, while estimates of wind speed correlated poorly (0.17). Comparisons of the four year mean annual ET for26global river basins andglobal latitudinal profiles with a climatologically estimated ET resulted in a Kendall’sτ> 0.70. The seasonal cycle over the continents is well represented in the Hovmöeller plots and the suppression of ET during major droughts in Europe, Australia and the Amazon are well picked up. This study provides the first ever moderate resolution estimates of ET on aglobal scale using only remote sensing based inputs and forcings, and furthermore the first ever multi-model comparison of process-based remote sensing estimates using the same inputs.
来源出版物:Remote Sensing of Environment,2011,115(3):801-823
SMOS radio frequency interference scenario:Status and actions taken to improve the RFI environment in the1400–1427-MHz passive band
Oliva, R; Daganzo-Eusebio, E; Kerr, YH; et al.
Abstract:The European Space Agency’s Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission is perturbed by radio frequency interferences (RFIs) that jeopardize part of its scientific retrieval in certain areas of the world,particularly over continental areas in Europe, Southern Asia, and the Middle East. Areas affected by RFI might experience data loss or underestimation of soil moisture and ocean salinity retrieval values. To alleviate this situation, the SMOS team has put strategies in place that,one year after launch, have already improved the RFI situation in Europe where half of the sources have been successfully localized and switched off.
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions ongeoscience and Remote Sensing,2012, 50(5):1427-1439
TROPOMI on the ESA Sentinel-5 Precursor: AgMES missionforglobal observations of the atmospheric composition forclimate, air quality and ozone layer applications
Veefkind, JP; Aben, I; McMullan, K; et al.
Abstract:The ESA (European Space Agency) Sentinel-5 Precursor (S-5 P) is a low Earth orbit polar satellite to provide information and services on air quality, climate and the ozone layer in the timeframe2015–2022. The S-5 P mission is part of theglobal Monitoring of the Environment and Security (GMES) Space Component Programme. The payload of the mission is the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) that will measure key atmospheric constituents including ozone, NO2, SO2, CO, CH4, CH2O and aerosol properties.TROPOMI has heritage to both the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) as well as to the SCanning Imaging Absorption spectroMeter for Atmospheric CartograpHY(SCIAMACHY). The S-5 P will extend the data records of these missions as well as be a preparatory mission for the Sentinel-5 mission planned for2020 onward. The mission is pre-operational and is the link between the current scientific and the operational Sentinel-4/-5 missions. This contribution describes the science and mission objectives,the mission and the instrument, and the data products.While building on a solid foundation of the heritage instruments, the S-5P/TROPOMI mission is an exciting step forward with a strong focus on the troposphere. This is achieved by a combination of a high spatial resolution and improved signal-to-noise, as well as dedicated data product development. It is anticipated that the S-5 P mission will make a large contribution to the monitoring of theglobal atmospheric composition, as well as to the scientific knowledge of relevant atmospheric processes.
来源出版物:Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,120:70-83
Estimatingground-level PM2.5 in China using satellite remote sensing
Ma, ZW; Hu, XF; Huang, L; et al.
Abstract:Estimating ground-level PM2.5from satellite-derived aerosol optical depth (AOD) using a spatial statistical model is a promising new method to evaluate the spatial and temporal characteristics of PM2.5exposure in a largegeographic region. However, studies outside North America have been limited due to the lack ofground PM2.5measurements to calibrate the model.Taking advantage of the newly established national monitoring network, we developed a national-scalegeographically weighted regression (GWR) model to estimate daily PM2.5concentrations in China with fused satellite AOD as the primary predictor. The results showed that the meteorological and land use information cangreatly improve model performance. The overall cross-validation (CV)R2is 0.64 and root mean squared prediction error (RMSE) is32.98 μg/m3. The mean prediction error (MPE) of the predicted annual PM2.5is8.28 μg/m3. Our predicted annual PM2.5concentrations indicated that over96% of the Chinese population lives in areas that exceed the Chinese National Ambient Air Quality Standard (CNAAQS) Level2 standard. Our results also confirmed satellite-derived AOD in conjunction with meteorological fields and land use information can be successfully applied to extend theground PM2.5monitoring network in China.
来源出版物:Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(13):7436-7444
Twenty five years of remote sensing in precision agriculture: Key advances and remaining knowledgegaps
Mulla, DJ
Precision agriculture dates back to the middle of the1980’s. Remote sensing applications in precision agriculture began with sensors for soil organic matter, and have quickly diversified to include satellite, aerial, and hand held or tractor mounted sensors. Wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation initially focused on a few key visible or near infrared bands. Today, electromagnetic wavelengths in use range from the ultraviolet to microwave portions of the spectrum, enabling advanced applications such as light detection and ranging (LiDAR),fluorescence spectroscopy, and thermal spectroscopy,along with more traditional applications in the visible and near infrared portions of the spectrum. Spectral bandwidth has decreased dramatically with the advent of hyperspectral remote sensing, allowing improved analysis of specific compounds, molecular interactions, crop stress,and crop biophysical or biochemical characteristics. A variety of spectral indices now exist for various precision agriculture applications, rather than a focus on only normalised difference vegetation indices. Spatial resolution of aerial and satellite remote sensing imagery has improved from100’s of m to sub-metre accuracy,allowing evaluation of soil and crop properties at fine spatial resolution at the expense of increased data storage and processing requirements. Temporal frequency of remote sensing imagery has also improved dramatically.At present there is considerable interest in collecting remote sensing data at multiple times in order to conduct near real time soil, crop and pest management.

