数据不充分情况下的说话人识别
盖晁旭+梁隆恺+何勇军
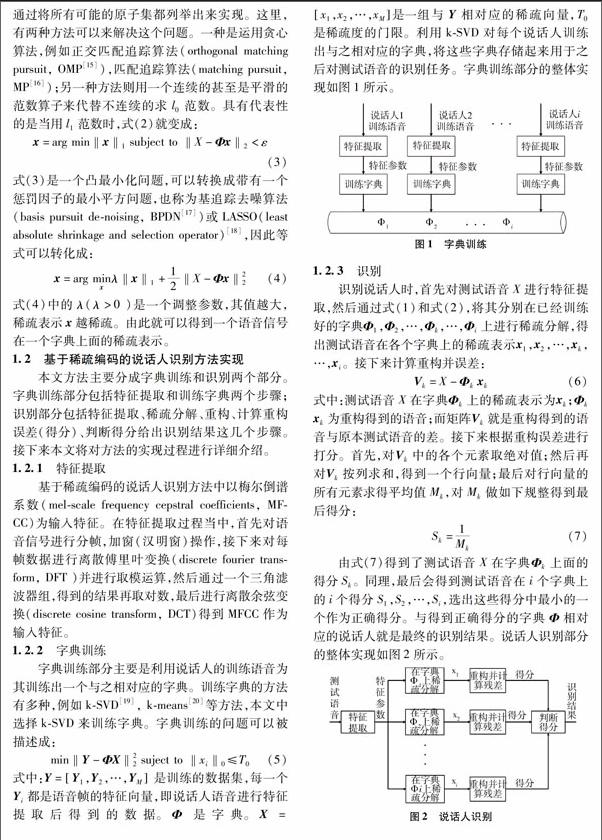
摘 要:在过去的数十年里,研究者们对说话人识别进行了广泛而深入的研究,提出了许多有效的方法。目前主流的说话人识别方法如高斯混合-通用背景模型(Gaussian mixture modelUniversal background model, GMMUBM)和高斯混合-支持向量机模型(Gaussian mixture modelSupport vector machine, GMMSVM),虽然能取得比较理想的识别效果,但都需要充分的训练和测试数据。而这一要求在现实应用中通常难以满足,导致其识别率急剧降低。针对这一问题,提出了一种基于稀疏编码的说话人识别方法。该方法在训练阶段为每个说话人训练一个语音字典;在识别阶段,将测试语音分别表示在每个字典上然后根据重构误差打分。实验表明,在少量无噪的训练和测试语音数据情况下,所提出的方法取得了比GMMUBM和GMMSVM更好的识别效果。
关键词:说话人识别;高斯混合;支持向量机;稀疏编码
DOI:1015938/jjhust201703003
中图分类号: TN9123
文献标志码: A
文章编号: 1007-2683(2017)03-0013-06
Abstract:Speaker recognition has attracted broad and deep research in the past few decades, and many methods have been proposed At present, the popular methods such as the Gaussian mixture modelUniversal background model(GMMUBM) and Gaussian mixture modelSupport vector machine(GMMSVM) have got a better recognition result, but they all need too much training and testing data They will suffer severe performance degradation in practical application, because their data needs always could not be satisfied To solve this problem, a speaker recognition method based on sparse coding is presented In the training stage, the method learns a dictionary for each speaker; and in the recognition stage, it represents test speech over each dictionary sparsely and gets scores from the reconstitution error Experiments show that the proposed method achieves better recognition results than GMMUBM and GMMSVM, when the training and testing data are clean and limited
Keywords:speaker recognition; gaussian mixture model; support vector machine; sparse coding
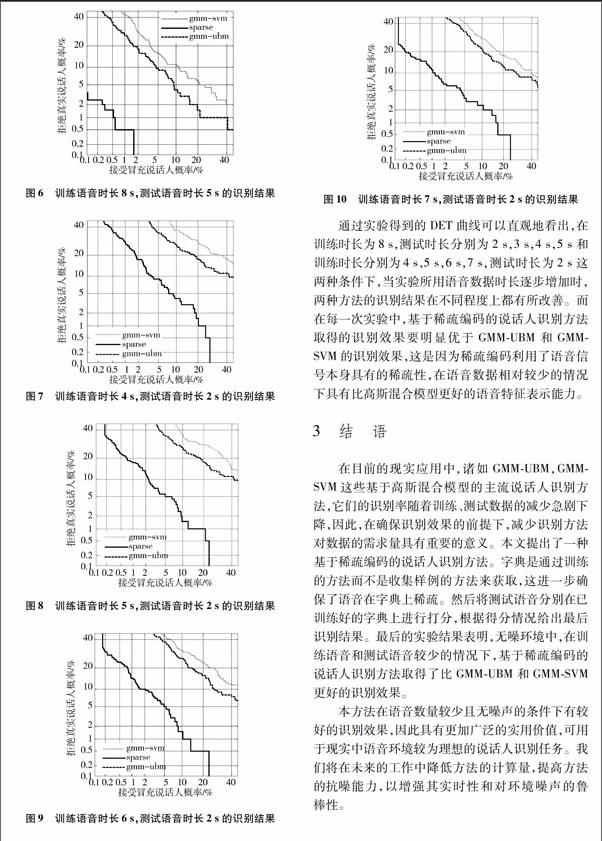
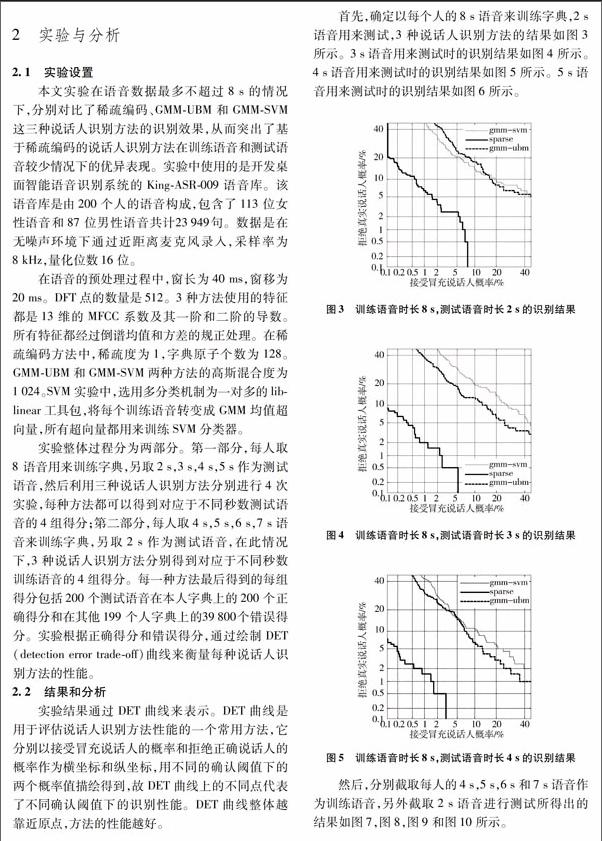
通過实验得到的DET曲线可以直观地看出,在训练时长为8s,测试时长分别为2s,3s,4s,5s和训练时长分别为4s,5s,6s,7s,测试时长为2s这两种条件下,当实验所用语音数据时长逐步增加时,两种方法的识别结果在不同程度上都有所改善。而在每一次实验中,基于稀疏编码的说话人识别方法取得的识别效果要明显优于GMMUBM和GMMSVM的识别效果,这是因为稀疏编码利用了语音信号本身具有的稀疏性,在语音数据相对较少的情况下具有比高斯混合模型更好的语音特征表示能力。
3 结 语
在目前的现实应用中,诸如GMMUBM,GMMSVM这些基于高斯混合模型的主流说话人识别方法,它们的识别率随着训练、测试数据的减少急剧下降,因此,在确保识别效果的前提下,减少识别方法对数据的需求量具有重要的意义。本文提出了一种基于稀疏编码的说话人识别方法。字典是通过训练的方法而不是收集样例的方法来获取,这进一步确保了语音在字典上稀疏。然后将测试语音分别在已训练好的字典上进行打分,根据得分情况给出最后识别结果。最后的实验结果表明,无噪环境中,在训练语音和测试语音较少的情况下,基于稀疏编码的说话人识别方法取得了比GMMUBM和GMMSVM更好的识别效果。
本方法在语音数量较少且无噪声的条件下有较好的识别效果,因此具有更加广泛的实用价值,可用于现实中语音环境较为理想的说话人识别任务。我们将在未来的工作中降低方法的计算量,提高方法的抗噪能力,以增强其实时性和对环境噪声的鲁棒性。
参 考 文 献:
[1] ALNA B, KAMARAUSKAS J Evaluation of Effectiveness of Different Methods in Speaker Recognition[J]. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika, 2015, 98(2): 67-70
[2] SOONG F K, ROSENBERG / E, RABINER L R, et al A Vector Quantization Approach to Speaker Recognition[C]// Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing(ICASSP),1985: 387-390
[3] FURUI S Cepstral Analysis Technique for Automatic Speaker Verification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics Speech & Signal Processing, 1981, 29(2): 254-272
[4] BENZEGHIBA M F, BOURLARD H Usercustomized Password Speaker Verification Using Multiple Reference and Background Models[J]. Speech Communication, 2006, 48(9): 1200-1213
[5] REYNOLDS D A, ROSE R C Robust Textindependent Speaker Identification Using Gaussian Mixture Speaker Models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech & Audio Processing, 1995, 3(1): 72-83
[6] FARRELL K R, MAMMONE R J, ASSALEH K T Speaker Recognition Using Neural Networks and Conventional Classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Speech & Audio Processing, 1994, 2(1): 194-205
[7] KENNY P, GUPTA V, STAFYLAKIS T, et al Deep Neural Networks for Extracting Baumwelch Statistics for Speaker Recognition[C]//Proc Odyssey,2014: 293-298
[8] SUN H, LEE K A, MA B A New Study of GMMSVM System for Textdependent Speaker Recognition[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, 2015: 4195-4199
[9] REYNOLDS D A Speaker Verification Using Adapted Gaussian Mixture Models[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2000, 7(1): 19-41
[10]刘明辉 基于GMM和SVM的文本无关的说话人确认方法研究[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学, 2007
[11]DEHAK N, KENNY P, DEHAK R, et al FrontEnd Factor Analysis for Speaker Verification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio Speech & Language Processing, 2011, 19(4): 788-798
[12]张陈昊, 郑方, 王琳琳 基于多音素类模型的文本无关短语音说话人识别[J]. 清华大学学报 (自然科学版), 2013(6):17
[13]林琳, 陈虹, 陈建, 等 基于多核 SVMGMM 的短语音说话人识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013 (2): 504-509
[14]何勇军, 付茂国, 孙广路 语音特征增强方法综述[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2014, 19(2): 19-25
[15]PATI Y C, REZAIIFAR R, KRISHNAPRASAD P S Orthogonal Matching Pursuit: Recursive Function Approximation with Applications to Wavelet Decomposition[C]// in Conference Record of The TwentySeventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers,1995: 1-3
[16]MALLAT S G, ZHANG Z Matching Pursuits with Timefrequency Dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 41(12): 3397-3415
[17]CHEN S S, DONOHO D L, SAUNDERS M A Atomic Decomposition by Basis Pursuit[J]. Siam Review, 1998, 20(1): 129-159
[18]TIBSHIRANI R J Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the LASSO[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 1996, 58:267-288
[19]AHARON M, ELAD M, BRUCKSTEIN A KSVD: An Algorithm for Designing Overcomplete Dictionaries for Sparse Representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311-4322
[20]MACQUEEN J Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations[C]// In 5th Berkeley Symp Math Statist Prob 1967: 281-297
(編辑:温泽宇)

