射波刀系统射野输出因子测量及对比*
朴俊杰 徐寿平 段学章 曲宝林 徐慧军 王 佳 丁俊强 王东方
射波刀系统射野输出因子测量及对比*
朴俊杰①②徐寿平①*段学章②曲宝林①徐慧军②王 佳②丁俊强②王东方②
目的:通过实际测量和计算机模拟等方法得到射波刀(CyberKnife)各准直器的输出因子,对比分析各方法的结果,从而得到准确的输出因子。方法:采用蒙特卡罗模拟、半导体探测器测量(PTW 60017、PTW 60016)、电离室探测器测量(PTW 31010)和热释光探测器测量(ø1.5 mm、离散度1%)等方法,在相同的参考条件下,源轴距800 mm以及深度15 mm(SAD=800 mm,Depth=15 mm),得到相应的输出因子。结果:在射野较大(≥25 mm)时,各种方法的输出因子差异不大,但是在射野较小(≤20 mm)时,各方法之间的差异较大,尤其是在最小射野(5 mm)的情况下,热释光探测器测量以及蒙特卡罗模拟结果略低于半导体探测器测量,最大误差分别为13%和7%,而电离室探测器测量误差高达37%。结论:输出因子可以通过多种方式获得,而半导体探测器相对于其他探测器,具有更好的灵敏度和稳定性,便于在临床应用中展开,因此可采用半导体探测器测量和热释光探测器测量的方式测量射波刀系统的射野输出因子。
射波刀;输出因子;蒙特卡罗;小射野
射波刀(CyberKnife)系统是全新的立体定向放射治疗设备,拥有12个孔径大小不同的圆形准直器,最小孔径为5 mm,最大孔径为60 mm[1-2]。由于小射野的大量应用提高了靶区的适形性,但是也增加了保证剂量准确性的难度[3]。因此,射野输出因子的准确性对患者的精确治疗尤为重要。
输出因子可以通过多种方式获得,如通过水箱测量(半导体探测器或电离室探测器)、固体水测量(热释光探测器)以及计算机模拟测量(蒙特卡罗模拟)[4]。但是每种方式都有其优势与局限性,因此,如何才能准确有效得到射波刀的输出因子,尤其是小射野的输出因子,成为研究的难题。本研究旨在通过多方法研究得到输出因子,对比其差异性,并分析导致误差的原因,从而为临床剂量学测量提供小射野输出因子测量的参考依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 蒙特卡罗模拟方法
基于BEAM程序建立射波刀的蒙特卡罗模型,并模拟一个均匀的水模体,根据输出因子的测量条件,源轴距800 mm以及深度15 mm(SAD=800 mm,Depth=15 mm),分别读取水模体中相应位置的读数,以60 mm准直器的读数为准,从而得到每个准直器的输出因子(如图1所示)[5-6]。

图1 蒙特卡罗模型
1.2 半导体探测器
采用半导体探测器[7](PTW 60017和PTW 60016)测量时,应用三维水箱(PTW-MP3)测量,将半导体探测器垂直放置于照射野的中心,根据输出因子测量条件(SAD=800 mm,Depth=15 mm),调整探测器位置,连接好静电计(PTW UNIDOS),分别输出100 MU共3次,读取不同尺寸准直器的相应平均读数,得到其相应的输出因子(如图2所示)。
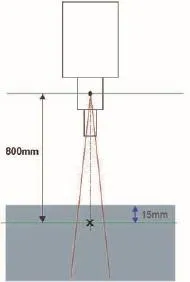
图2 半导体探测器测量方法示意图
1.3 电离室探测器
采用电离室探测器[8](PTW 31010)时,应用水箱测量,将电离室探测器水平放置于照射野的中心,根据输出因子测量条件(SAD=800 mm,Depth=15 mm),调整探测器位置(由于灵敏体积,还要下降0.6 r),连接好静电计(PTW UNIDOS),分别输出100 MU共3次,读取不同尺寸准直器的相应平均读数,得到其相应的输出因子(如图3所示)。

图3 电离室探测器结构示意图
1.4 热释光探测器
采用热释光探测器(ø1.5 mm、离散度1%)时,由于不具有防水性,不能直接放置于水中,故应用固体水模体测量[9]。将热释光探测器放置于照射野的中心,每次放置3~5片,根据输出因子测量条件(SAD=800 mm,Depth=15 mm),调整探测器位置,分别输出100 MU,然后通过读数计分别读取每片的数值,取平均值,得到相应的输出因子(如图4所示)。

表1 各准直器输出因子

图4 热释光探测器测量方法示意图
2 结果
以60 mm准直器的读数为基准,得到其他准直器的输出因子。以上各方法所得输出因子见表1,并得到图5所示输出因子对比图。在射野较大(≥25 mm)时几个方法的输出因子差异不大;但是在射野较小(≤20 mm)时各方法之间的差异较大,尤其是在最小射野(5 mm)的情况下,热释光以及蒙特卡罗模拟结果略低于半导体,最大误差分别为13%和7%,而电离室与半导体的误差高达37%。

图5 各方法测量所得的输出因子示图
3 讨论
Laura等[10]进行了一个多中心的研究,利用半导体探测器(PTW 600019)和塑料闪烁探测器(W1)分别测得射波刀的12个准直器的输出因子,并与蒙特卡罗修正的输出因子进行比对,两种探测器所得结果与标准的蒙特卡罗修正的结果误差在1.5%以内;Senerella等[11]利用最新的半导体探测器(PTW 600019)测量射波刀两套准直器的输出因子(固定准直器Fixed与可变准直器Iris),与蒙特卡罗修正的输出因子比对,固定准直器(Fixed)的误差在0.6%以内,可变准直器的误差在1%以内。陈上河等[12]应用BEAM建立射波刀模型,所得输出因子与实际测量相差在2%以内,但是未模拟出所有准直器大小,尤其是小射野的模型。
蒙特卡罗模拟的优点是能够逼真地描述具有随机性质的事物的特点及物理实验过程[13];缺点是收敛慢,准确性依赖于数据量的样本数,也就是粒子数,但是粒子数的增加又会提高运算时间,误差具有概率性,且建模阶段的准确性要求高,直接影响后续的准确性。
半导体探测器的优点是具有良好的灵敏度,极佳的位置分辨率,很高的能量分辨率,能量线性好,响应时间快,体积小,抗磁场性能好[14];缺点是对辐射损伤比较敏感,辐射损伤与辐射种类、剂量率、照射时间和条件有关,受强辐射后性能变差。
电离室探测器的优点是稳定性好,响应时间快[15];缺点是吸收效率低,且具有一定的灵敏体积,本研究所采用PTW 31010电离室探测器,具有0.125 cc灵敏体积,当射野较小时难以涵盖全部灵敏体积,故无法达到电子平衡,因此导致其读数不准。
热释光探测器能量响应好,灵敏度高,但抗干扰能力较差,在测量中容易引入本底及退火情况等干扰,且测量时的摆位等容易产生误差,热释光片直径ø1.5 mm,测量时要放置在射野中心,尤其是小射野时,中心与边缘的读数差距较大[16]。此外,对读片机的准确性要求很高,当超量程时,可采用滤片。
输出因子可以通过多种方式获得,但每种方法都有其优势与局限性,通过以上几种方法得到的数据来看,半导体探测器相对于其他探测器而言,具有更好的灵敏度以及稳定性,并且便于实际临床应用中的展开,因此建议采用以半导体为主、热释光等多种测量手段为辅的模式进行临床比对参考。
[1]Adler JR,Jr Chang SD,Murphy MJ,et al.The Cyberknife:a frameless robotic system for radiosurgery[J].Stereotact Funct Neurosurg,1997,69(1-4Pt 2):124-128.
[2]朴俊杰,徐寿平,王金媛,等.CyberKnife利用等中心及非等中心立体定向治疗计划质量及效率评价[J].实用癌症杂志,2016,31(5):747-751.
[3]朴俊杰,徐寿平,巩汉顺,等.CyberKnife系统技术评估和临床应用评价[J].医疗卫生装备,2016,37(3):114-117.
[4]Bassinet C,Huet C,Derreumaux S,et al.Small fields output factors measurements and correction factors determination for several detectors for a CyberKnife® and linear accelerators equipped with microMLC and circular cones[J].Med Phys,2013,40(7):071725.
[5]Araki F.Monte Carlo study of a Cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery system[J].Med Phys,2006,33(8):2955-2963.
[6]Xiaoqing D,Wenyun LUO,Kun YUE,et al.Monte carlo study on 6 MV photon beams of a CyberKnife stereotactic radiosurgery system[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques,2010,21(1):16-19.
[7]朱奇,康静波,李建国,等.体部伽玛刀的治疗原理及质量保证探讨[J].中国医学装备,2015,12(2):95-97.
[8]Agostinelli S,Garelli S,Piergentili M,et al.Response to high-energy photons of PTW31014 PinPoint ion chamber with a central aluminum electrode[J]. Med Phys,2008,35(7):3293-3301.
[9]Benmakhlouf H,Fransson A,Andreo P.Influence of phantom materials on the energy dependence of LiF:Mg,Ti thermoluminescent dosimeters exposed to 20-300 kV narrow X-ray spectra,137Cs and60Co photons[J].Phys Med Biol,2014,59(15):4149-4166.
[10]Laura M,Serenella R,Paolo F,et al.CyberKnife beam output factor measurements: A multisite and multi-detector study[J].Physica Medica,2016,32(12):1637-1643.
[11]Serenella R,Laura M,Paolo F,et al.Multicenter evaluation of a synthetic single-crystal diamond detector for CyberKnife small field size output factors[J].Physica Medica,2016,32(4):575-581.
[12]陈上河,王石,吴朝霞,等.基于蒙特卡罗模拟的CyberKnife病人治疗计划剂量验证[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2015,32(4):451-457.
[13]Chetty IJ,Curran B,Cygler JE,et al.Report of the AAPM Task Group No.105:Issues associated with clinical implementation of Monte Carlo-based photon and electron external beam treatment planning[J].Med Phys,2007,34(12):4818-4853.
[14]Geng X,Wu D,Guan Y.Monte Carlo modelling of diode detectors for small field MV photon dosimetry: detector model simplification and the sensitivity of correction factors to source parameterization[J].Physics in Medicine and Biology,2012,57(16):5141-5153.
[15]Baek JG,Jang HS,Kim EC,et al.Evaluation of the applicability of pinpoint ion chambers for SRS dosimetric quality assurance[J].Journal of the Korean Physical Society,2015,66(11):1771-1776.
[16]Eliyahua I,Horowitza YS,Osterc L.Conduction band/valence band kinetic modeling of the LiF:Mg,Ti system incorporating creation of defects in the irradiation stage[J].Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B,2012,293(15):26-34.
Measurement and comparison of output factors of the radiation field for CyberKnife system/
PIAO Jun-jie, XU Shou-ping, DUAN Xue-zhang, et al//
China Medical Equipment, 2017,14(8):17-20.
Objective: To study the output factors of various collimators of CyberKnife system through actual measurement and computer simulation, and to compare and analyze the results of various method so as to obtain the accurate output factors. Methods: In this study, series of tools and methods including Monte Carlo simulation (BEAMnrc), semiconductors (PTW 60017, PTW 60016), ionization chamber (PTW 31010) and thermoluminescence (ø1.5mm, 1% of dispersion) were adopted. Under the same reference conditions, the corresponding output factors of radiation field were obtained when the source axis distance was 800mm and the depth was 15mm (SAD=800 mm, Depth=15 mm). Results: When the range of radiation field was relatively larger (≥25 mm), the difference of output factors among various methods were not obviously, but there were obvious differences among these methods when the range of radiation field was relatively smaller (≤20 mm). Especially under the minimum range of radiation field (5mm), the results of adopting thermoluminescence and Monte Carlo simulation (BEAMnrc) were slightly lower than that of using semiconductors, and in this time, the maximum errors of them were 13% and 7%, respectively. And the error of using ionization chamber has achieved 37%.Conclusion: The output factors could be obtained from various methods, while the semiconductor detector has better sensitivity and stability than other detectors, and it is convenient to be applied in clinical practice. Therefore, the measurement of semiconductor detector and the measurement of thermoluminescent detector should be adopted to measure output factors of radiation field of Cyberknife system.
CyberKnife; Output factor; Monte Carlo; Small radiation fields
Department of Radiotherapy, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Radiotherapy Center of Tumor, 302 Hospital PLA, Beijing 100039, China.
1672-8270(2017)08-0017-04
R812
A
10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2017.08.005

2017-04-17
国家自然科学基金(11275105)“CyberKnife剂量校准与验证的系统研究”
①解放军总医院放射治疗科 北京 100853
②解放军第302医院肿瘤放射治疗中心 北京100039
*通讯作者:shouping_xu@yahoo.com
朴俊杰,男,(1984- ),硕士,工程师。解放军总医院放射治疗科,从事肿瘤放射物理及肿瘤精确治疗的相关工作。

