离心泵平衡孔液体泄漏量试验与分析
刘在伦,陈小昌,王东伟,侯祎华
(1.兰州理工大学能源与动力工程学院,兰州730050; 2.兰州理工大学温州泵阀工程研究院,温州325105)
离心泵平衡孔液体泄漏量试验与分析
刘在伦1,2,陈小昌1,王东伟1,2,侯祎华1
(1.兰州理工大学能源与动力工程学院,兰州730050; 2.兰州理工大学温州泵阀工程研究院,温州325105)
针对离心泵上叶轮平衡孔的实际液体泄漏量难以测量的问题,设计了通过调节平衡腔液体压力来测量平衡孔液体泄漏量的试验装置,在平衡孔直径4、6、8、11 mm条件下对泵性能、平衡孔液体泄漏量和平衡腔液体压力进行了测试及分析,获得了不同直径平衡孔下泵的性能曲线、平衡孔泄漏量系数和轴向力系数与比面积的关系曲线。试验结果表明:加大叶轮平衡孔直径会使泵的扬程降低、输入功率增大和效率降低;平衡孔液体泄漏量系数与比面积关系曲线有明显的规律性,其随着比面积增大而减小,且扬程系数对其有较大的影响;轴向力系数曲线是非线性曲线,在比面积小于2.5时,轴向力系数随比面积增大而急剧减小;比面积大于等于2.5小于等于4.5时,轴向力系数曲线趋于平坦,其均值为0.112;比面积大于4.5时,轴向力系数曲线几乎与横坐标平行,其均值为0.067。该研究为较精确计算平衡孔液体泄漏量与平衡腔区域的轴向力提供了参考。
离心泵;试验;叶轮;平衡孔泄漏量;轴向力
刘在伦,陈小昌,王东伟,侯祎华. 离心泵平衡孔液体泄漏量试验与分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(7):67-74.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.009 http://www.tcsae.org
Liu Zailun, Chen Xiaochang, Wang Dongwei, Hou Yihua. Experiment and analysis of balance hole liquid leakage in centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(7): 67-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.009 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
开平衡孔双密封环叶轮具有能平衡大部分轴向力的特性,至今仍广泛应用于离心泵中[1-4]。平衡孔液体泄漏量对开平衡孔双密封环叶轮平衡轴向力的能力有着决定性的作用,这对泵的容积效率、轮阻损失、泵腔内液体压力分布及轴向力的计算都有较大的影响[5-10],因此研究平衡孔液体泄漏量的测量及计算方法就显的格外必要。
文献[11]基于泵腔液体以叶轮角速度一半作刚体旋转的假设,在密封环正常工作的条件下,推导出了设计工况下平衡孔液体泄漏量理论计算公式,但这一假设与泵腔液体实际流动不符。文献[12]测量出了直径为70 mm、长度为35 mm、径向间隙为0.15 mm的密封环在前后压差在 0~0.7 MPa范围内的泄漏量为 0~4.2×10-4m3/s,该研究为计算离心泵密封环泄漏量提供了试验数据。文献[13]通过测量平衡腔和泵进口的液体压力,给出了不同扬程时平衡孔液体泄漏量与比面积的关系曲线,其不足之处是未测量平衡孔实际泄漏量。基于后密封环径向间隙与平衡孔是通过平衡腔连通的,文献[14]采用封死叶轮进口和外界水泵供压力水的方法来模拟离心泵运行工况,通过测试不同结构形式密封环的泄漏量,获得了密封环间隙泄漏液体的流量系数与泵扬程的关系曲线。上述的研究成果对平衡孔液体泄漏量计算有重要的参考价值。由于离心泵叶轮高速旋转以及泵结构的限制,实测平衡孔液体泄漏量一直是泵研究领域的难题。
本文设计了通过调节平衡腔液体压力来测量平衡孔液体泄漏量的试验装置,采用改变平衡孔直径的方法,通过测试不同直径平衡孔的液体泄漏量、平衡腔液体压力和泵扬程,研究不同直径平衡孔的平衡孔液体泄漏量及泄漏量系数的特性以及其对平衡腔区域轴向力的影响规律。
1 平衡孔液体泄漏量测量方法
1.1 试验装置
试验是在兰州理工大学浮动叶轮离心泵闭式试验台上进行的[15],如图1a所示。被测泵为IS80-50-315型离心泵,其设计参数为:设计流量Qd=25 m3/h,设计扬程Hd=32 m,转速n=1 450 r/min,效率η=52%,叶轮外径D2=316 mm。
图1b为平衡孔液体泄漏量的测试装置。在闷盖上开有6个液体泄漏孔,平衡腔内液体经6个泄漏孔引至外界。为了实现同一个叶轮及后密封环径向间隙下不同直径平衡孔液体泄漏量的测试,叶轮后密封环、平衡孔套可组装在叶轮上,并保证后密封径向间隙b为0.2 mm,叶轮后密封环装配图如图 2所示。该测试装置的主要几何尺寸:后密封间隙长度L1=18 mm,后密封环半径rm=44.5 mm,轮毂半径rh=25 mm,平衡孔套内径(即平衡孔直径)d分别为0、4、6、8、11 mm,不同内径平衡孔套长度(即叶轮平衡孔长度)L为15 mm。通过更换不同内径平衡孔套来改变平衡孔直径。

图1 测试试验台及装置Fig.1 Test bench and device
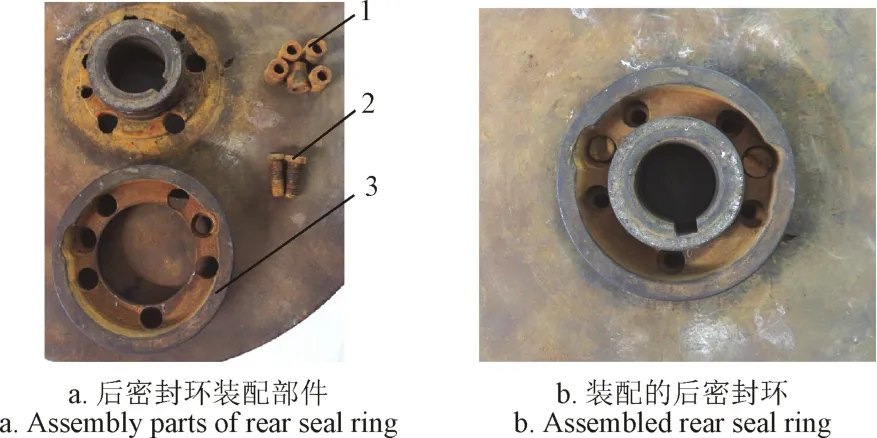
图2 叶轮后密封环装配图Fig.2 Assembly diagram of impeller rear seal ring
1.2 平衡孔液体泄漏量测量原理及方法
在图2b中,叶轮上安装不同内径的平衡孔套,并将6个液体泄漏孔管路上的闸阀关闭,调节泵出口管路上的调节阀,使泵在不同工况下运行,测量出平衡腔液体压力。试验完毕后,将图2b中的叶轮平衡孔堵死,重新启动水泵,首先使 6个液体泄漏孔管路上的闸阀处于关闭状态,调节泵出口管路上的调节阀开度,使泵运行工况与叶轮有平衡孔时运行工况相同。然后分别调节 6个液体泄漏孔管路上的闸阀开度,分别观测平衡腔液体压力和流量计的读数变化情况。据此,反复多次调节泵出口管路上的调节阀开度和 6个液体泄漏孔闸阀的开度,最终使泵运行工况和平衡腔液体压力与叶轮有平衡孔时泵运行工况和平衡腔液体压力相同,则 6个液体泄漏孔流出的液体流量即为对应此泵工况的液体泄漏量。
在堵死叶轮平衡孔时,平衡腔液体经泄漏孔引至外界的储水箱。通过测量Δt时间内流入储水箱液体的体积V就可以得到叶轮平衡孔液体泄漏量qv,其计算公式为

式中qv为平衡孔液体泄漏量,m3/s;V为Δt时间内流入储水箱液体体积,m3;Δt为测量时间,s。
2 试验结果及分析
2.1 平衡孔直径对泵性能的影响
在平衡孔直径d为0、4、6、8、11 mm条件下,对泵性能进行了测试。为使图 3显示清楚,仅给出了平衡孔直径d为0、6、11 mm时泵性能曲线,如图3所示。
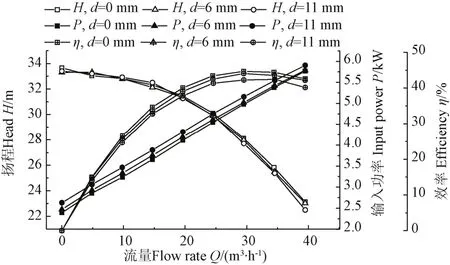
图3 不同平衡孔直径的离心泵性能曲线Fig.3 Performance curves of centrifugal pump with different balance hole diameters
由图 3可知,不同平衡孔直径的泵性能曲线有一定的规律性。以该泵叶轮平衡孔的设计直径d=6 mm时的泵性能为基准,平衡孔直径d=0 mm相对于平衡孔直径d=6 mm下,在0.8Qd即Q=20 m3/h时,扬程增加了0.35%,输入功率减小了2.00%,效率增加了2.44%;在1.0Qd即Q=25m3/h时扬程增加了0.70%,输入功率减小了1.44%,效率增加了2.13%;在1.2Qd即Q=30 m3/h时扬程增加了0.51%,输入功率减小了0.88%,效率增加了1.35%。可见,平衡孔直径0<d<6 mm,其对泵的扬程、输入功率和效率的影响程度较小。
平衡孔直径d=11 mm相对于d=6 mm下,在0.8Qd时扬程降低了0.87%,输入功率增加了2.85%,效率下降了3.20%;在1.0Qd时扬程降低了0.73%,输入功率增加了 3.07%,效率下降了 2.68%;在 1.2Qd时扬程降低了1.67%,输入功率增加了2.68%,效率下降了4.11%。这是因为叶轮存在平衡孔,使叶轮出口的一部分高压流体未能由泵出口处排出而是经叶轮平衡孔又流回到叶轮流道中,从而形成回流。再者从叶轮平衡孔流出的射流流体扰乱了叶轮进口水流的流态,在一定程度上使作用在叶轮上的输入功率增大[16-18]。上述原因导致了泵输入功率增大,效率降低。随着叶轮平衡孔直径的增大,其对泵的扬程、输入功率和效率的影响程度变大。
2.2 平衡孔泄漏量与扬程的关系
在平衡孔直径d为4、6、8、11 mm条件下,分别对平衡孔液体泄漏量qv、泵进口液体压力P1、平衡腔液体压力P2和泵扬程H进行了测试。图4为叶轮有平衡孔且6个液体泄漏孔管路上的闸阀关闭时,平衡腔液体压力与扬程的试验曲线。
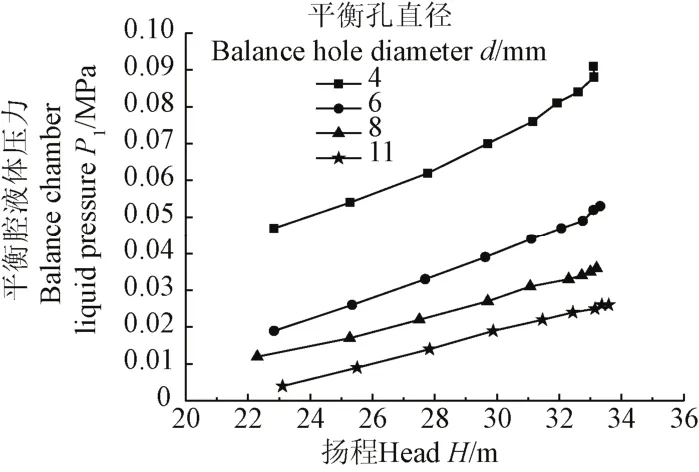
图4 不同平衡孔直径的平衡腔液体压力与扬程的试验曲线Fig.4 Test curves of balance chamber liquid pressure and head with different balance hole diameters
依据图 4试验结果,在叶轮平衡孔堵死条件下,同时调节泵出口管路上的调节阀和 6个液体泄漏孔管路上的闸阀开度,使泵运行工况和平衡腔液体压力与叶轮有平衡孔时泵运行工况和平衡腔液体压力相同时,实测得到不同平衡孔直径的泵进口液体压力和平衡孔液体泄漏量与扬程的试验曲线,如图5所示。
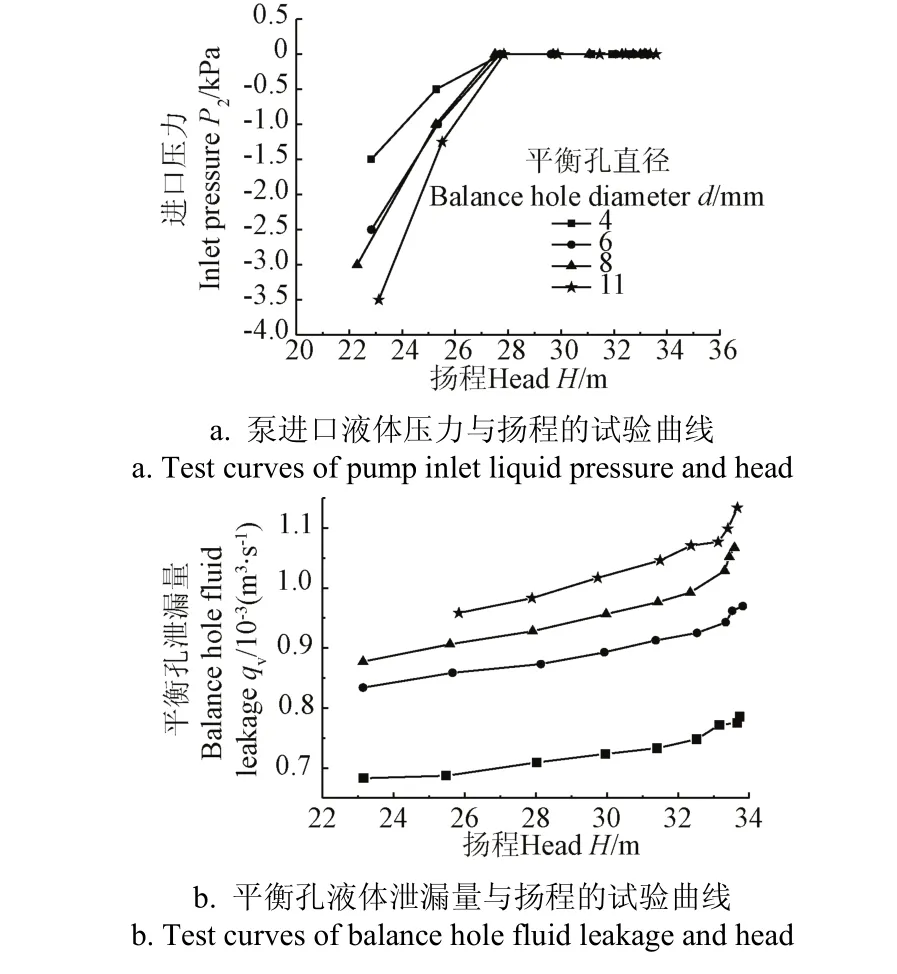
图5 不同平衡孔直径的泵进口液体压力和平衡孔液体泄漏量与扬程的试验曲线Fig.5 Test curves of head and pump inlet liquid pressure and balance hole fluid leakage with different balance hole diameters
从图5a可知,在相同平衡孔直径条件下,随着扬程降低,泵进口液体压力在先保持一段零压力后急剧降低;在相同扬程条件下,不同平衡孔直径的泵进口液体压力之间最大差值仅为2.12 kPa,说明平衡孔直径的变化对泵进口液体压力影响较小。
从图4和图5b中看出,从图4和图5b中看出,在不同直径平衡孔下,平衡孔液体泄漏量和平衡腔液体压力与扬程的曲线的变化趋势近似一条倾斜的直线,即平衡孔液体泄漏量和平衡腔液体压力随扬程增大而增大;在相同的扬程下,平衡孔直径增大其液体泄漏量明显增大而平衡腔液体压力明显降低。其原因是,在泵工况和后密封环间隙b不变条件下,当泵工况一定时,因叶轮进口液体压力和泵腔进口液体压力基本不变,增大叶轮平衡孔直径,平衡孔的过流能力及液体泄漏量增大,会引起平衡腔液体压力降低,这样就降低了平衡腔区域液体压力差值,进一步验证了加大平衡孔直径有明显平衡轴向力效果[19-22]。
2.3 平衡孔泄漏量系数与比面积的关系
文献[23]对平衡腔液体压力分布的数值计算表明,不同直径平衡孔的平衡腔液体压力沿着径向方向逐渐增大,但沿着轴向和切向方向基本保持不变。平衡腔体径向和轴向尺寸一般都较小,为了研究问题方便,认为平衡腔液体压力和泵进口液体压力都沿着径向方向均匀分布[24]。试验泵的平衡孔的长径比1.5≤L/d<4,所以液体流经叶轮平衡孔的泄漏量可按短壁孔口出流来计算[25-26],其泄漏量qv为
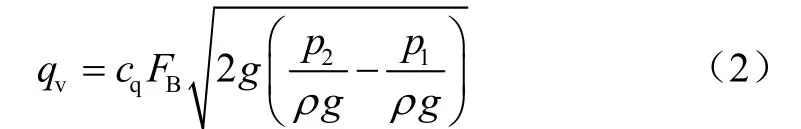
式中cq为平衡孔泄漏量系数;FB为平衡孔总面积,FB=πd2z/4,m2;d为平衡孔直径,m;z为平衡孔数量,z=5;p2为平衡腔液体压力,Pa;p1为泵进口液体压力,Pa;ρ为液体密度,kg/m3;g为重力加速度,m/s2。
为了计算相似泵的平衡孔液体泄漏量及泄漏量系数,引入泵扬程系数ψ、比面积K,其中比面积K为平衡孔总面积与后密封环间隙断面面积的比值,其计算公式分别为

式中H为泵扬程,m;u2为叶轮出口圆周速度,u2=πD2n/60,m/s;n为泵转速,r/min;D2为叶轮直径,m。

式中FB为平衡孔总面积,FB=d2πz/4,m2;Fm为叶轮后密封环间隙断面面积,Fm=2πrmb,m2;d为平衡孔直径,m;z为平衡孔数量,z=5;rm为后密封环半径,m;b为后密封环径向间隙,m。
在图5b中,取不同的扬程值,可获得多组的平衡孔直径值及其对应的泄漏量值。本文选取了扬程分别为24、26、28、30、32 m,并代入式(3)可得扬程系数分别为0.409、0.443、0.477、0.511、0.545。平衡孔直径d为4、6、8、11 mm时,由式(4)计算出的比面积分别为1.12、2.53、4.49、8.50,并结合式(2),从而获得不同扬程系数的平衡孔液体泄漏量、平衡孔泄漏量系数与比面积K的关系曲线,如图6所示。

图6 不同扬程系数的平衡孔液体泄漏量及其系数与比面积的关系曲线Fig.6 Curves of balance hole liquid leakage and its coefficient and specific area with different head coefficients
由图6a可知,当比面积K<2.5时,平衡孔液体泄漏量随比面积的增大而急剧增大;当比面积K>2.5时,平衡孔液体泄漏量随比面积的增大而缓慢增大。这表明较小直径的平衡孔的液体泄漏量更易受流动黏性层和叶轮转速的影响,而对于较大直径的平衡孔,其直径的变化对平衡孔的泄漏量同样有影响,但影响相对较小。
从图6b看出,同一扬程系数下,平衡孔液体泄漏系数随比面积的增大而降低;且当比面积K>4.5时,平衡孔液体泄漏系数的降幅减小。同一比面积下,扬程系数越大,平衡孔泄漏量系数越小。
由平衡腔和叶轮平衡孔构成的流道结构简单,但其内液体运动非常复杂。其流道阻力系数取决于其内的流体动力学特性,而流体动力学特性受到其几何结构的影响[27-28]。流道液体阻力系数由进口阻力系数、沿程阻力系数和出口动能损失系数等组成,所有这些因素的影响,难以通过理论计算精确求得。图6b是通过试验测出平衡腔液体压力、泵出口液体压力和平衡孔液体泄漏量,得到的不同扬程系数下平衡孔泄漏量系数与比面积的关系曲线。对相似的开平衡孔的双密封环叶轮离心泵,如已知泵扬程、平衡腔液体压力、泵进口液体压力,由图 6b及式(2)即可方便计算出平衡孔液体泄漏量,这对研究泵的容积效率、轮阻损失、泵腔内液体压力分布及轴向力的计算都有十分重要的意义。
文献[11]给出了这种开平衡孔双密封环叶轮在设计工况下平衡孔液体泄漏量的计算公式,其数学表达式为
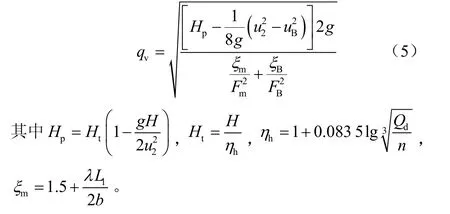
式中Hp为叶轮势扬程,m;ηh为泵水力效率;Qd为泵设计流量,m3/h;uB为平衡孔中心距的圆周速度,m/s;ξm为密封环间隙阻力系数,λ=0.04~0.06;ξB为平衡孔阻力系数;L1为后密封环间隙长度,m。
本文在平衡孔直径d为4、6、8、11 mm条件下,测得泵设计工况的平均流量为 24.63 m3/h,平均扬程为29.84 m。将设计工况的流量扬程的平均值及后密封环几何尺寸代入式(5),并依据文献[11]推荐的λ=0.04,ξB=2,可计算得到平衡孔液体泄漏量的理论曲线。再由图5b查出平均扬程为 29.84 m下不同直径平衡孔的泄漏量试验值,从而获得平衡孔液体泄漏量与比面积的试验和理论曲线,如图7所示。

图7 平衡孔液体泄漏量与比面积的关系曲线Fig.7 Curves of balance hole liquid leakage and specific area
由图7可知,相同比面积时平衡孔液体泄漏量的理论值与实测值相差较大。比面积K>2.5,即平衡孔直径d>6 mm时,平衡孔液体泄漏量的理论曲线几乎为平行横坐标的直线,其原因是,按式(5)计算直径较大的平衡孔液体泄漏量时,变量FB对qv几乎无影响,可见按式(5)校核计算平衡孔液体泄漏量值得商榷。
3 平衡孔直径对轴向力的影响
对于使用开平衡孔双密封环叶轮的单级单吸离心泵,在前后密封环直径相同条件下,其平衡腔区域叶轮盖板前后液体压力差造成的盖板力是叶轮轴向力的主要组成部分[29-35]。平衡腔区域轴向力计算公式为[13,23]

式中F为平衡腔区域轴向力,N。
对试验泵rm=44.5 mm。图8是依据图4和图5a计算得到不同直径平衡孔的平衡腔轴向力与扬程关系曲线。

图8 不同平衡孔直径的平衡腔轴向力与扬程关系曲线Fig.8 Curves of balance chamber axial force and head with different balance hole diameters
从图8中看出,在相同平衡孔直径下,平衡腔区域轴向力随扬程增大而增大。由于在设计流量Qd条件下,不同平衡孔直径的试验泵扬程不同,为定量分析相同扬程下平衡腔区域轴向力与平衡孔直径的变化规律,由图3得到设计流量Qd下,平衡孔直径为0、6、11 mm时试验泵的平均扬程为29.8m,在该扬程下,平衡孔直径d为4、6、8、11 mm较平衡孔直径d=0,平衡腔区域轴向力分别降低了 53.9%、81.9%、87.8%、88.36%。可见,泵工况一定时,随着平衡孔直径的增大,平衡腔区域轴向力明显降低,但会造成平衡孔液体泄漏量增大。
为了计算相似泵的平衡腔区域轴向力,参考文献[11]引入轴向力系数,其定义为
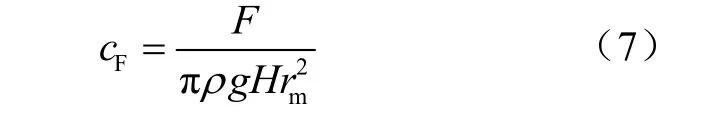
式中cF为轴向力系数。
在图8中,选取了扬程H为24、26、28、30、32 m,由图 8及式(4)和式(7),计算获得不同扬程系数的轴向力系数与比面积K的关系曲线,如图9所示。
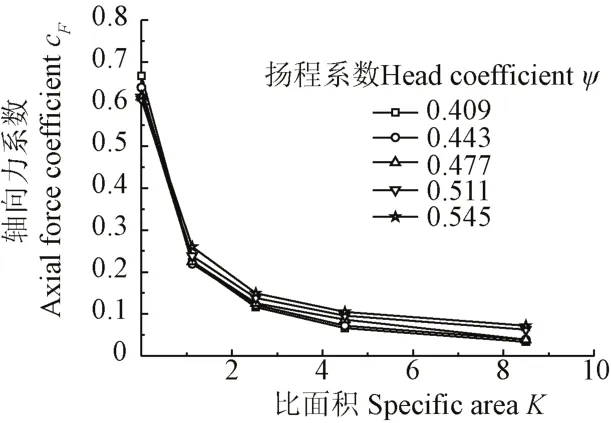
图9 不同扬程系数的轴向力系数与比面积关系曲线Fig.9 Curves of axial force coefficient and specific area with different head coefficients
由图9可知,不同扬程系数的轴向力系数与比面积K的关系曲线都具有明显的相似规律性,0<K<2.5时,轴向力系数随比面积增大而急剧减小;2.5≤K≤4.5,轴向力系数曲线趋于平坦,其均值为0.112;K>4.5时,轴向力系数曲线几乎与横坐标平行,其均值为 0.067,说明K>4.5,即平衡孔直径d>8 mm时,平衡孔平衡轴向力的效果不明显。因此,从减少平衡孔液体泄漏量和轴向力的角度,试验泵的比面积取2.5≤K≤4.5,即平衡孔直径取6~8 mm较为合适。
4 结 论
1)提出了调节平衡腔液体压力来测量平衡孔液体泄漏量装置,解决了长期困扰泵行业离心泵叶轮平衡孔液体泄漏量的测试难题。
2)平衡孔直径增大会影响泵的性能,使其扬程降低,功率增加,效率降低。在设计流量下,相较于平衡孔直径为6 mm时泵的性能,平衡孔直径为0 mm时,其扬程增加了 0.70%,输入功率减小了 1.44%,效率增加了2.13%;平衡孔直径为11 mm时,扬程降低了0.73%,输入功率增加了3.07%,效率下降了2.68%,说明平衡孔直径越大,其对泵性能的影响越明显。
3)平衡孔液体的泄漏量及泄漏量系数与比面积的关系曲线变化具有明显的规律性,比面积小于4.5时,平衡孔泄漏量迅速增大,而平衡孔泄漏量系数快速减小,比面积大于4.5时,平衡孔泄漏量增速减缓,而平衡孔泄漏量系数缓慢降低,但不同扬程系数时平衡孔泄漏量及泄漏量曲线有一定的差别。
4)轴向力系数曲线是非线性曲线,它建立了泵的扬程、平衡孔直径大小及数量和叶轮后密封环直径及间隙的关系。比面积介于2.5到4.5之间时,轴向力系数的均值为 0.112,比面积大于 4.5时,轴向力系数的均值为0.067,其为计算平衡腔区域叶轮盖板前后液体压力差造成的轴向力提供了参考。
[1] Cao Weidong, Dai Xun, Hu Qixiang. Effect of impeller reflux balance holes on pressure and axial force of centrifugal pump[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015(5): 1695-1706.
[2] Budea S. Axial balance in centrifugal pumps-back labyrinth versus dorsal vanes[J]. Hidraulica, 2015, (1): 19-24.
[3] Lefor D, Kowalski J, Kutschelis B, et al. Optimization of axial thrust balancing swirl breakers in a centrifugal pump using stochastic methods[C]// ASME 2014, Joint Us-European Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting Collocated with the ASME 2014, International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, 2014: V01BT10A018.
[4] 施卫东,李启锋,陆伟刚,等. 基于CFD的离心泵轴向力计算与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2009,40(1):60-63. Shi Weidong, Li Qifeng, Lu Weigang, et al. Estimation and experiment of axial thrust in centrifugal pump based on CFD[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2009, 40(1): 60-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Florjancic D, Sirok B. Hydraulic axial thrust in multistage pumps-origins and solutions[J]. Journal of Fluids Engineering-transactions of the ASME, 2002, 124(2): 336-341.
[6] 陆伟刚,张金凤,袁寿其. 离心泵叶轮轴向力自动平衡新方法[J]. 中国机械工程,2007,18(17):2037-2040. Lu Weigang, Zhang Jinfeng, Yuan Shouqi. A new method to axial thrust self-balance for centrifugal pump impeller[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 18(17): 2037-2040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 孔繁余,刘建瑞,施卫东,等. 高速磁力泵轴向力平衡计算[J]. 农业工程学报,2005,21(7):69-72. Kong Fanyu, Liu Jianrui, Shi Weidong, et al. Calculation of axial force balance for high-speed magnetic drive pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2005, 21(7): 69-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李伟,施卫东,蒋小平,等. 屏蔽泵轴向力平衡新方法[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(7):86-90. Li Wei, Shi Weidong, Jiang Xiaoping, et al. New method for axial force balance of canned motor pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(7): 86-90. (in Chinese with English abstract )
[9] 汪国庆,王英,王兆兴. 多级离心泵创建压力室平衡轴向力的试验研究[J]. 流体机械,2016(8):10-15. Wang Guoqing, Wang Ying, Wang Zhaoxing. Multistage centrifugal pump to create pressure chamber equilibrium of axial force experiment research[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2016(8): 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张元勋,唐倩,李忠华,等. 基于流体力学泄漏模型的螺杆泵泄漏机理分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(10):326-332. Zhang Yuanxun, Tang Qian, Li Zhonghua, et al. Leakage mechanism of screw pump based on leakage model in fluid mechanics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(10): 326-332. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 关醒凡. 现代泵理论与设计[M]. 北京:中国宇航出版社,2011.
[12] 刘延君,王伟,陆雄. 一种测量微小流量的方法[J]. 甘肃工业大学学报,2001,27(3):44-46. Liu Yanjun, Wang Wei, Lu Xiong. A measuring method of small flow-rate[J]. Journal of Gansu University of Technology, 2001, 27(3): 44-46 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘在伦,王东伟,梁森. 离心泵叶轮平衡孔液体泄漏量特性试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(7):85-88. Liu Zailun, Wang Dongwei, Liang Sen. Fluid leakage characteristic test on balance aperture of centrifugal pump impeller[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(7): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 陈茂庆,陈超. 离心泵密封环泄漏量特性试验[J]. 石油机械,1993,21(1):23-26. Chen Maoqing, Chen Chao. Characteristic test of the leakage ring on centrifugal pump[J]. CPM, 1993, 21(1) :23-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘在伦,孙雨,王东伟,等. 离心泵泵腔流道液体泄漏量试验与计算方法[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(6):97-101. Liu Zailun, Sun Yu, Wang Dongwei, et al. Experiment and calculation method of fluid leakage in flow passage of pump chamber on centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(6): 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 刘在伦,石福翔,王仁忠,等. 叶轮平衡孔直径对离心泵水力性能的影响[J]. 兰州理工大学学报,2016(6):57-61. Liu Zailun, Shi Fuxiang, Wang Renzhong, et al. Influence of impeller balancing hole diameter on hydraulic performance of centrifugal pump[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016(6): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孔繁余,高翠兰,张旭锋,等. PBN65-40-250型屏蔽泵轴向力平衡计算及其试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(5):68-72. Kong Fanyu, Gao Cuilan, Zhang Xufeng, et al. Computation and experiment for axial force balance of canned motor pump PBN65-40-250[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(5): 68-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 严俊峰,陈炜,蒲光荣. 叶轮盖板侧的流动对离心泵泄漏量的影响[J]. 火箭推进,2007,33(3):20-25. Yan Junfeng, Chen Wei, Pu Guangrong. The effect of flow in the impeller shroud on the leakage rate in a centrifugal pump[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion, 2007, 33(3): 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 刘在伦,许立中,贾晓,等. 离心泵浮动叶轮轴向间隙的液体流动分析及轴向力计算[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(12):79-85. Liu Zailun, Xu Lizhong, Jia Xiao, et al. Analysis of liquid flow and axial force calculation in axial clearance for floating impeller of centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(12): 79-85. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 刘在伦,曾继来,邵安灿,等. 离心泵轴向力计算方法研究与试验验证[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2015,33(12):1019-1025. Liu Zailun, Zeng Jilai, Shao Ancan, et al. Calculation method and experimental verification for axial thrust on centrifugalpump[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2015, 33(12): 1019-1025. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 李合,许洪元,张文达,等. 立式屏蔽泵的轴向力及石墨轴承耐磨性试验研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2004,20(1):128-131. Li He, Xu Hongyuan, Zhang Wenda, et al. Experimental research on axial thrust and the wear ability of graphite bearing of a vertical canned motor pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2004, 20(1): 128-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 凌玮,高良凤,沙毅. 比转速185的离心泵研制及平衡孔对泵性能影响的试验研究[J]. 水泵技术,2013(2):20-22.
[23] 董玮,楚武利. 平衡孔直径对离心泵性能及平衡腔压力的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(6):73-77. Dong Wei, Chu Wuli. Influence of balance hole diameter on performance and balance chamber pressure of centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(6): 72-77. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 刘在伦,张森,邵安灿,等. 离心泵泵腔液体压力分布理论计算及验证[J]. 机械工程学报,2016(4):178-184,191. Liu Zailun, Zhang Sen, Shao Ancan, et al. Theoretical computation and verification for fluid static pressure in centrifugal pump side chamber[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016(4): 178-184, 191. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 刘在伦,魏烈江,齐学义,等. 新型轴向力平衡装置间隙泄漏量的计算[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(12):74-76. Liu Zailun, Wei Liejiang, Qi Xueyi, et al. Calculation of gap leakage flow rate in new axial trust device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(12): 74-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陆敏恂,李万莉. 流体力学与液压传动[M]. 上海:同济大学出版社,2006.
[27] 蒋庆磊,戴维平,吴大转,等. 离心泵内泄漏流计算及其对转子振动的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2010,28(3):202-206. Jiang Qinglei, Dai Weiping, Wu Dazhuan, et al. Computation of leakage flow in centrifugal pumps and its effects on rotor's vibration[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2010, 28(3): 202-206. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 刘在伦,王保明,梁森. 浮动叶轮平衡腔内压力的试验分析[J]. 排灌机械,2007,25(5):6-8. Liu Zailun, Wang Baoming, Liang Sen. Experimental study on the pressure in the balance of floating impeller[J]. Drainage and Irrigation Machinery, 2007, 25(5): 6-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 李景悦,严敬,赖喜德,等. 离心叶轮平衡机构轴向力的计算与分析[J]. 西华大学学报:自然科学版,2015(3):73-76. Li Jingyue, Yan Jing, Lai Xide, et al. Calculation and analysis of axial thrust due to balance mechanics of centrifugal impellers[J]. Journal of Xihua University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, (3): 73-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 陆雄,范宗霖,薛建欣. 用改变平衡孔位置改善离心泵轴向力[J]. 水泵技术,1998(6):7-13.
[31] 牟介刚,赵锦靖,郑水华,等. 离心泵平衡孔位置对轴向力及外特性的影响[J]. 机械设计与制造,2012,49(6):173-175. Mou Jiegang, Zhao Jinjing, Zheng Shuihua, et al. The influence of balance hole position of centrifugal pump on axial force and external characteristics[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2012, 49(6): 173-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 李彩虹,薛志宽,李红. 叶轮前盖板与泵体轴向间隙对轴向力的影响[J]. 排灌机械工程学报,2016,34(4):295-300. Li Caihong, Xue Zhikuan, Li Hong. Effects of axial clearances between impeller front shroud and pump body on axial force[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2016, 34(4): 295-300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 董玮,楚武利. 离心泵叶轮平衡腔内液体流动特性及圆盘损失分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(4):29-35. Dong Wei, Chu Wuli. Analysis of flow characteristics and disc friction loss in balance chamber of centrifugal pump impeller[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(4): 29-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 刘在伦,王东伟,侯祎华,等. 离心泵泵腔和平衡腔液体压力试验与计算[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(8):42-47,324. Liu Zailun, Wang Dongwei, Hou Yihua, et al. Experiment and calculation of fluid pressure in pump chamber and balance chamber of centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(8): 42-47, 324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 牟介刚,李思,郑水华,等. 多级离心泵叶轮级间泄漏对轴向力的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(7):40-44. Mu Jiegang, Li Si, Zheng Shuihua, et al. Influence of interstage leakage on the axial force of the multistage centrifugal pump[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(7): 40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Experiment and analysis of balance hole liquid leakage in centrifugal pump
Liu Zailun1,2, Chen Xiaochang1, Wang Dongwei1,2, Hou Yihua1
(1.College of Energy and Power Engineering, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou730050,China; 2.Engineering Institute of Wenzhou Pump & Valve, Lanzhou University of Technology, Wenzhou325105, China)
Balancing and reducing the axial force is one of the most significant subjects in the research of the centrifugal pump. The most frequently-used method to balance the axial force is to use the double seal ring impeller with the balance hole the single-stage single-suction centrifugal pump. And the liquid leakage has a decisive role for the ability to balance the axial force of the double seal ring impeller with the balance hole. Therefore, it is indispensable to study the measurement and calculation method of liquid leakage in balance hole of centrifugal pump. Aiming at the problem that the actual liquid leakage of impeller balance hole is difficult to be measured, a special testing apparatus was designed by adjusting the liquid pressure of the balance chamber. Pump performance, balance hole liquid leakage and liquid pressure in the balance chamber was tested and analyzed when the diameters of balance hole were 4, 6, 8 and 11 mm. Some important test curves such as curves of axial force coefficient and specific area in different head coefficient and their variation characteristics were obtained by calculating and analyzing the experimental data. Results showed that when the diameters of balance hole were less than 6 mm, the diameter of balance hole had little change on the head, input power and efficiency of pump. Increasing the diameter of impeller balance hole would reduce the head and efficiency of pump and enlarge the input power. The pump inlet liquid pressure had a sharp reduction after the first stage of zero pressure with decreases of head in the same diameter of balance hole. The maximum difference between the pump inlet liquid pressures of different balance hole diameters were only 2.2 kPa in the same head, which showed that the diameter of balance hole had little effect on the pump inlet liquid pressure. The liquid leakage of the balance hole and the pressure of the balance chamber increased with the increase of the head. The liquid leakage increased significantly and the liquid pressure of balance chamber reduced significantly with increase of the diameter of balance hole in the same head. The axial force of the balance chamber increased with the increase of the head in the same diameter of balance hole. The axial force of the balance chamber reduced obviously with the increase of diameter of the balance hole in the same head, but the decreasing amplitude of axial force of the balance chamber decreased. The relational curves between the liquid leakage of balance hole and the specific area (the ratio of the total area of the balance hole to the clearance area of the rear seal ring) had obvious pattern, the balance hole leakage coefficient decreased with the increase of specific area in the same head coefficient. Under the same specific area, the larger head coefficient, the smaller leakage coefficient of the balance hole. The test curves of axial force coefficient and specific area were the non-linear curves, when the specific area under less than 2.5, the axial force coefficient decreased sharply with the increase of the specific area. When the specific area was between 2.5 and 4.5, the curves tended to be flat, and the mean value of axial force coefficient was 0.112. When the specific area was more than 4.5, the curves of axial force coefficient were almost parallel to the abscissa, and the mean value of axial force coefficient was 0.067. This study provides a new way to calculate accurately liquid leakage amount of the balance hole and axial force in the balance chamber region. It also has a great influence on the volumetric efficiency of the pump, the loss of the wheel resistance, the liquid pressure distribution in the pump chamber and the calculation of the axial force.
centrifugal pumps; experiments; impellers; balance hole leakage; axial force
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.009
TH311
A
1002-6819(2017)-07-0067-08
2016-10-20
2017-03-17
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51269010);甘肃省自然科学基金
资助项目(1508RJYA077);浙江省自然科学基金资助项目(LY12E09002)
刘在伦,男,甘肃景泰人,教授,主要从事流体机械设计理论与测试技术研究。兰州 兰州理工大学能源与动力工程学院,730050。
Email:liuzl88@sina.com

