卧辊式摘穗机构摘穗辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失的影响
陈美舟,孙雪峰,程修沛,贾晓东,李其昀
卧辊式摘穗机构摘穗辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失的影响
陈美舟1,孙雪峰2,程修沛1,贾晓东3,李其昀1※
(1. 山东理工大学农业工程与食品科学学院,淄博 255000; 2.常州东风农机集团有限公司,常州 213000; 3. 山东建筑大学理学院,济南 250000)
针对卧辊式摘穗装置存在的玉米籽粒损失严重、含杂率高等问题,该文通过理论分析和台架试验相结合的方法对摘穗过程中两辊高度差对玉米损伤的影响及趋势进行了分析。单因素试验和方差分析表明,(两辊轴线垂直的平面内,两辊中心连线与水平面的夹角用表示)对玉米籽粒损失率有显著的影响(<0.05)。在24°~30°范围内,玉米平均籽粒损失率呈现明显的下降趋势,在30°时玉米平均籽粒损失率最小,3次试验的平均籽粒损失为0.242%~0.483%;在33°、36°时,籽粒损失率较小,且相差不大。利用高速摄像技术对摘穗过程分析发现,较小时,果穗滞留摘穗辊和“弹跳”现象是造成果穗二次损伤的主要原因;较大时,玉米植株喂入困难,玉米秸秆弯曲严重甚至折断。为此,提出了在低位辊上安装弧形隔板的优化方案,试验验证表明,果穗通过弧形隔板滚动出摘穗区域,避免了低位辊对果穗的损伤,有效降低了玉米果穗的啃伤和籽粒损失率。该研究为卧辊式玉米摘穗装置的优化改进提供了参考。
农业机械;方差分析;试验;卧辊式摘穗装置;高度差;二次损伤;籽粒损失
0 引 言
卧辊式摘穗装置多用于站秆摘穗的机型上,要求两辊的轴线平行或夹角很小且具有约35 mm的高度差[1-2],使被摘下的果穗可以及时进入升运器或相应的收集装置,保证摘下的果穗能迅速脱离摘穗辊而避免掉粒损失。但是由于加工工艺以及装配工艺等原因[3-5],两摘穗辊的高度差得不到保证。高度差过小,被摘下的果穗,会滞留在摘穗辊上,并与旋转的摘穗辊长时间的接触而导致籽粒损失的增加;高度差过大,若两摘辊的中心距不变则会使水平方向投影的间隙减小,尤其会造成摘穗辊前端导锥的引导作用失效,使玉米植株喂入困难,易被推倒或折断,导致漏摘或果穗含杂率增大[6-9]。
国内外对于卧辊式摘穗装置两摘穗辊之间的高度差方面的研究甚少,尤其在对籽粒损失影响方面的研究处于空白。为此本课题组对卧辊式摘穗装置进行了试验研究,分析了两辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失的影响与玉米果穗的运动规律,并结合高速摄像机采集的图像,针对试验过程中发现的玉米果穗二次损伤的问题,对卧辊式摘穗装置进行了优化设计,对比试验表明优化后的摘穗装置可有效降低籽粒损失,改善玉米摘穗质量,为卧辊式摘穗装置的优化设计提供了参考。
1 卧辊式玉米摘穗装置结构及工作原理
卧辊式玉米摘穗装置主要由摘穗装置、夹持喂入装置、传动系统、夹角调节装置、高速摄像系统和计算机数据采集系统等组成,如图1所示。
高速摄像机放置在低位摘穗辊一侧,与普通录像机成90°安置,对玉米摘穗过程进行立体图像采集和捕捉,通过观察试验录像对玉米摘穗过程中玉米果穗运动轨迹、籽粒损失以及茎秆折断等现象进行直观分析。夹角调节装置同步调节同一侧的一对挂耳在倾斜耳的上下位置用以实现两辊高度差的调节,如图2所示。
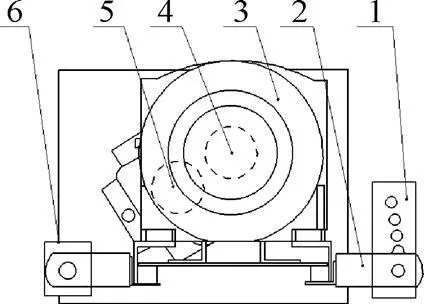
.倾斜调节耳 2.挂耳 3.电磁调速电机 4.高位辊位置 5.低位辊位置 6. 铰接耳
辅助设备:DM6235P数字转速表、JD1A-11型电磁调速电动机控制器、ACS-6型电子计价称等[10-11]。
工作时,玉米植株由夹持喂入装置夹持喂入,经摘穗辊前导锥导入相向旋转的摘穗辊后,玉米茎秆在摘穗段受到两辊上螺旋凸棱的作用力和两辊夹持力的联合作用,玉米茎秆向后向下运动,玉米果穗被高、低位摘穗辊挤下,摘穗完成,秸秆继续被向下拉茎,脱离机器。
2 摘穗装置结构参数
2.1 摘穗辊直径与间隙
摘穗辊应保证能够抓取茎秆但不能抓取果穗[12-14],即
式中1、2分别代表玉米果穗直径与茎秆直径,mm;为摘穗辊间隙,mm;为摘穗辊直径,mm;1与2分别代表对玉米果穗、玉米茎秆的抓取系数,本试验摘穗辊的光辊外表面带螺旋筋条的凸棱,如图3所示,因此取1≈2=1,则
3.41(1–)≥≥3.41(2–) (2)
中国大部分地区种植的玉米植株,其结穗处的秸秆直径一般为18~24 mm[12],玉米果穗大端的直径为45~60 mm[13],摘穗辊间隙=(0.3~0.4)2[14],则设计摘穗辊间隙可调范围为4~12 mm,对摘穗辊的要求是能够抓取最小直径的茎秆而最小果穗不被抓取,则摘穗辊直径大小为
因此本试验摘穗辊直径选取中间范围70 mm,在合理范围之内。摘穗辊间隙根据试验时秸秆的具体情况确定其大小为6 mm[15-16]。
2.2 两辊高度差
本试验设计中两摘穗辊高度差的调节主要通过调节两辊中心连线与水平面的夹角(表示下同)而实现,高度差和之间存在函数关系,即
为了便于两辊高度差调节和试验参数的确定,本文采用代替两辊高度差。玉米收获机两摘穗辊的高度差一般在35 mm左右[17]。因此,高度差选择5个水平分别为36、40、44、48、52 mm,对应的圆整后为24°、27°、30°、33°、36°。与两辊高度差的关系如图4所示。
1.低位辊 2.高位辊
1. Low snapping roller 2. High snapping roller
注:为摘穗辊中心连线与水平面的夹角,(°);为摘穗辊中心的高度差,mm;为两摘穗辊的间隙,mm。
Note:is angle between central line of snapping rollers and horizontal, (°);is height difference of central line of snapping rollers, mm;is gap of snapping rollers, mm.
图4与高度差的关系
Fig.4 Relationship betweenand height difference
2.3 摘穗辊结构
摘穗辊选用多螺旋摘穗辊,光辊外表面带有螺旋筋条的凸棱。凸棱最大高度为12 mm,拉茎筋条呈三角形高12 mm,强制拉茎段长度为120 mm,每条摘穗辊共6根拉茎筋条。
3 玉米摘穗试验
3.1 试验材料
玉米品种为登海605,试验用玉米植株取自山东省淄博市张店区付家镇付家村。正常收获期获得,随机选取30株成熟玉米植株进行测量,结穗处茎秆直径平均值为18.9 mm,籽粒的平均含水率为26.3%。
3.2 评价指标
本试验旨在研究两辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失以及果穗运动规律的影响,降低由两辊高度差造成的玉米籽粒损失。因此选择玉米籽粒损失率作为试验评价指标[18-19],公式如下所示
式中为籽粒损失率,%;1为损失籽粒的质量,g;2为籽粒的总质量,g。
3.3 试验结果与分析
为了研究两辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失的影响规律,试验因素采取单因素试验,两摘穗辊间隙固定在6 mm,喂入速度固定在1.2 m/s,摘穗辊转速固定在800 r/min,对行喂入,每组试验重复3次[20-23],每次随机选取3株玉米,取均值。试验结果如表1所示。
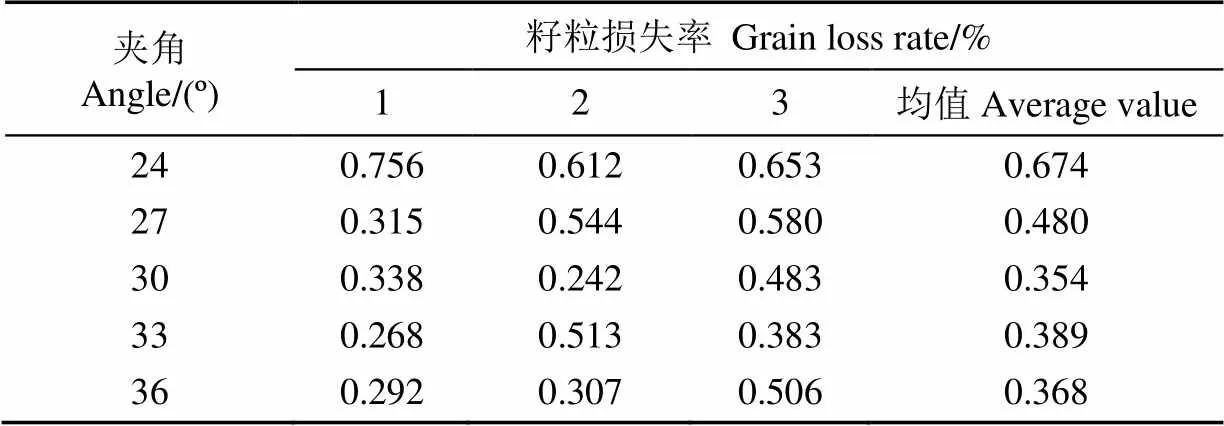
表1 θ对籽粒损失的影响试验结果
注:“1”,“2”,“3”表示试验序号。下同。
Note: “1”, “2” and “3” represent experimental numbers. The same below.
如表1所示,在24°~30°变化时,玉米籽粒损失呈现明显的下降趋势,但各个试验水平的籽粒损失率均小于国家行业标准《NY/T 1355-2007 玉米收获机作业质量》[24]的规定,在30°时籽粒损失率最小,3次试验的平均籽粒损失为0.242%~0.483%。在33°和36°时,籽粒损失率较小,且相差不大。
利用SPSS软件在显著性水平=0.05下,对对进行检验,方差分析如表2所示,输出结果中值小于0.05,因此可以推断在显著性水平=0.05下对籽粒损失率有显著的差异[25-27]。
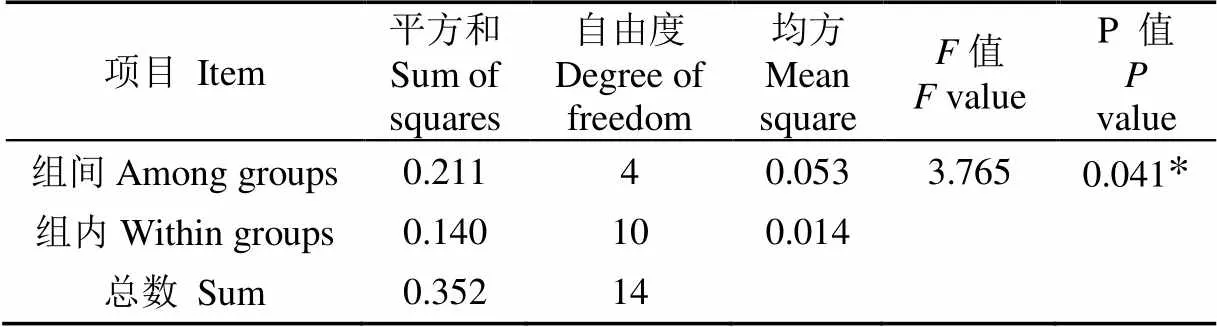
表2 籽粒损失率方差分析
注:“*”表示试验因素对试验结果在0.05水平上有影响显著。
Note: “*” represents the factor has significant effect on test result at 0.05 level.
3.4 试验现象分析
试验过程中,利用高速摄像机快速捕捉不同角度时的试验现象,并对此进行分析。
为24°时,如图5所示,果穗因滞留在摘穗辊间而造成二次损伤。右侧图像显示,低位辊凸棱不断的对果穗顶端撞击,应是过小时籽粒损失较大的主要原因。如图6所示,部分果穗出现了“弹跳”现象,左侧图像为刚摘下时果穗开始弹跳,右侧图像为果穗落下时碰到高位辊产生二次损伤,圈中亮点为碰撞后损失的籽粒,与之较近的果穗上有明显的凹痕。
为27°和30°时,部分果穗偶尔会出现上述问题,果穗被摘下后滞留在摘穗辊上的时间较短。为30°时,果穗直接跳出摘穗辊,因此,在设计玉米收获机时,应重视摘穗辊到升运器之间的衔接及材料。
为33°和36°时,如图7所示,果穗滞留在摘穗辊上的几率明显减少,但由于增大,摘穗辊中心距不变,使得摘穗辊水平面投影间隙缩小,造成玉米植株喂入困难,即使喂入实现也易造成玉米秸秆弯曲过度弯曲甚至折断,影响正常摘穗。因此,采用较大的时,需要进一步调整高低两摘穗辊之间的间隙,或设计成后端角度大,前端角度小的两条轴线不平行辊子,以保证玉米植株的喂入和正常摘穗。
另外,两辊间隙调节部件只调节了摘穗辊前端的间隙,摘穗辊后部(靠近齿轮的一侧)变化相对较小。高低位两摘穗辊的间隙是否合理,直接影响玉米果穗的籽粒损失以及茎秆的喂入情况。高低位两摘穗辊的间隙过大,一方面会降低两辊夹持力增加茎秆在高低辊间打滑的几率,影响拉茎(摘穗)效果及秸秆向后输送的能力,秸秆易滞留甚至堵塞,另一方面由于间隙过大,增加了果穗与摘穗辊的接触面积,使得玉米果穗的籽粒损失率增高,较小的果穗可能会出现“咬穗”现象。高低位两摘穗辊的间隙过小,茎秆容易被夹断或拉断,导致果穗含杂率的增高,也会出现堵塞的情况。
4 结构优化及验证
针对玉米摘穗试验中出现的“二次损伤”和“弹跳”等造成籽粒损失等问题,课题组设计了在低位辊上加装弧形隔板的解决方案,果穗被摘下后从弧形隔板滑到护板上,避免二次损伤,降低籽粒的损失。优化后的结构及尺寸如图8所示,其中弧形隔板与低位辊凸棱的间隙为2~5 mm[28-30],实物图如图9所示。
对优化后的卧辊式玉米摘穗装置进行验证试验,试验条件保持不变,试验结果如表3所示。
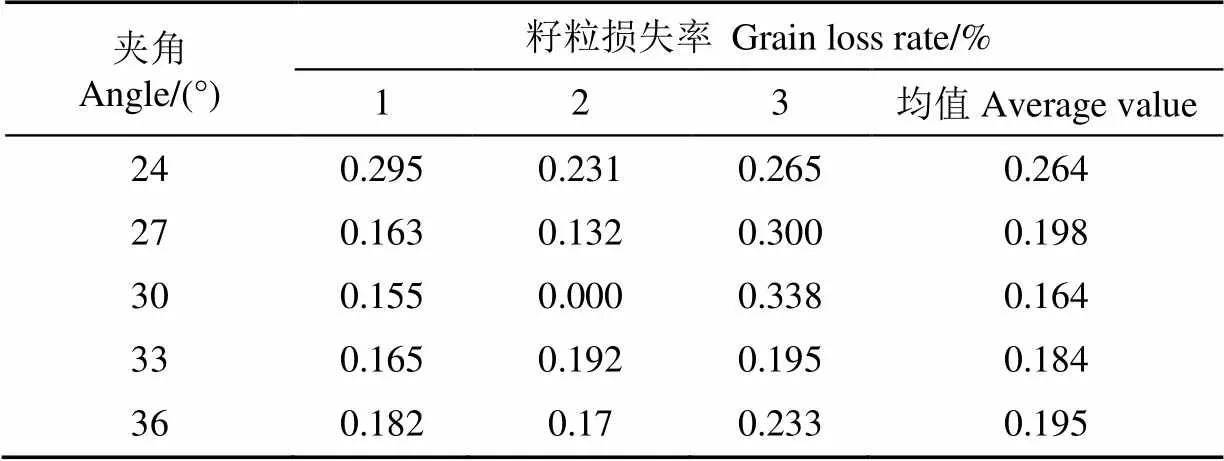
表3 带隔板后θ对籽粒损失率影响的试验结果
优化后,在24°~30°变化时,玉米籽粒的损失比优化前明显减少,且仍呈下降趋势。为24°时,玉米籽粒损失率的平均值从0.674%降低到0.264%,效果最为显著。为30°时,玉米籽粒损失率最小,损失范围在0~0.338%。优化前后,对玉米籽粒损失的影响趋势对比,如图10所示。
与无弧形隔板时相比,果穗通过弧形隔板滚动出摘穗区域,避免了低位摘穗辊对果穗造成的二次损伤。但在低位摘穗辊上方加装弧形隔板后,高位摘穗辊与弧形隔板间的高度差变小,不利于果穗滑出摘穗区域,如图11所示。若果穗滞留在摘穗区域上,会被后面的玉米植株带入高位摘穗辊与弧形隔板的间隙而造成损伤。因此,为30°时较24°和27°时的摘穗效果更好。
5 结 论
1)通过课题组前期对卧辊式摘穗装置的两辊高度差(或在两辊轴线垂直的截面内,两辊中心连线与水平线的夹角表示)对籽粒损失影响的试验研究,在24°~30°时,玉米籽粒损失率呈现明显的下降趋势,在30°时籽粒损失率最小,3次试验的平均籽粒损失为0.242%~0.483%;在33°、36°时,籽粒损失率较小,且相差不大。
2)结合高速摄像机采集的图像发现,果穗滞留摘穗辊上并被旋转的低位摘穗辊啃伤和“弹跳”是造成果穗二次损伤的主要原因,过大时玉米植株喂入困难,使得玉米秸秆弯曲严重甚至折断,也会造成玉米籽粒损失和较高的含杂率。
3)优化卧辊式摘穗装置并进行验证试验,低位辊安装弧形隔板能够有效的避免果穗因低位摘穗辊撞击而产生的二次损伤,玉米籽粒损失显著降低,为30°时,玉米籽粒损失最小,仅为0.164%。
[1] 朱纪春,陈金环. 国内外玉米收获机械现状和技术特点分析[J]. 农业技术与装备,2010(4):23-24,26.
Zhu Jichun, Chen Jinhuan. Present situation and technical characteristics analysis of com combine harvester in home and abroad[J]. Agricultural Technology & Equipment, 2010(4): 23-24, 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 郝付平,陈志. 国内外玉米收获机械研究现状及思考[J]. 农机化研究,2007(10):206-208.
Hao Fuping, Chen Zhi. Actuality of domestic and foreign corn harvester[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2007(10): 206-208. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 范国昌,王惠新,籍俊杰,等. 影响玉米摘穗过程中籽粒破碎和籽粒损失率的因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2002,18(4):72-74. Fan Guochang, Wang Huixin, Ji Junjie, et al. Analysis of influence factor on seed damage rate and loss rate during picking corn-cob[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2002, 18(4): 72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] Johnson E H W, Lamp B J. Principles, Equipment and systems for corn harvesting 1966 agric. consulting associates Wooster, Ohio 360 illus[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1967, 12(2): 171.
[5] Quaye S A, Schertz C E. Corn cob harvest with counter-rotating rollers[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1983, 26(5): 1303-1307.
[6] Shinners K J, Boettcher G C, Hoffman D S, et al. Single-pass harvest of corn grain and stover performance of three harvester configurations[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2009, 52(1): 51-60.
[7] Johnson P C, Clementson C L, Mathanker S K, et al. Cutting energy characteristics of Miscanthus x giganteus stems with varyingoblique angle and cutting speed[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2012(112): 42-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张道林,孙永进. 自走式穗茎兼收型玉米联合收获机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2005,21(1):79-81.
Zhang Daolin, Sun Yongjin. Design and experiment of the self-propelled combine harvester for corn and stalk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2005, 21(1): 79-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 佟金,贺俊林,陈志,等. 玉米摘穗辊试验台的设计和试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2007,38(11):48-51.
Tong Jin, He Junlin, Chen Zhi, et al. Research and development of testing device with snapping rolls for corn harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38(11): 48-51. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 杜岳峰,毛恩荣,朱忠祥,等. 两行玉米收获机械割台设计与实验[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊2):22-26.
Du Yuefeng, Mao Enrong, Zhu Zhongxiang, et al. Design and experiment of two-row corn harvester header[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(Supp.2): 22-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 梁晓军. 纵卧辊式玉米收获机收获损失试验研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2006.
Liang Xiaojun. Experimental Study of Maize Seed Damage during Operating of Harvester with Lengthways-horizontal Rollers[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2007.
[13] 耿爱军,李汝莘,刘双喜,等. 玉米收获机割台性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊2):27-30.
Geng Aijun, Li Ruxin, Liu Shuangxi, et al. Performance experiment of corn harvester header[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(Supp.2): 27-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杜强,贾丽艳. SPSS统计分析从入门到精通[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2009.
[15] 王颉. 试验设计与SPSS应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2007.
[16] 蔡盈盈,李敏,冉翠翠. SPSS在农业试验统计分析中的应用[J]. 河南农业,2009(2):21-21.
[17] 肖信. Origin 8.0实用教程-科技作图与数据分析[M]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2009:68-82.
[18] 任露泉. 试验设计及其优化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2009.
[19] 张道林,孙永进,赵洪光,等. 立辊式玉米摘穗与茎秆切碎装置的设计[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(7):50-52.
Zhang Daolin, Sun Yongjin, Zhao Hongguang, et al. Design of a vertical-roll type of corn picker and stalk chopper[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(7): 50-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 曹彪. 弯曲摘穗式玉米摘穗机构研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2012.
Cao Biao. Study on Corn Snapping Mechanism with Mode of Bending and Breaking[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] Shinners K J, Bennett R G, Hoffman D S. Single-and two-pass corn grain and stover harvesting[J]. Transactions of the ASABE, 2012, 55(2): 341-350.
[22] 张莉. 新型仿生玉米摘穗机构理论分析与仿真研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2015.
Zhang Li. Theoretical Analysis and Simulation Research on Novel Bionic Corn-ear Snapping Mechanism[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 孙雪峰. 卧辊式摘穗机构籽粒损失的试验研究[D]. 淄博:山东理工大学,2015.
Sun Xuefeng. Experimental Research of Corn Grain Loss on Horizontal Snapping Rolls Device[D]. Zibo:Shandong University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] NY/T 1355-2007,玉米收获机作业质量[S].
[25] 张丽萍,李其昀. 仿生玉米掰穗装置掰穗速度与功耗试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(19):9-14.
Zhang Liping, Li Qiyun. Speed of bionic breaking corn ear hand and experiment on power consumption[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(19): 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 张智龙,张东兴,崔涛,等. 玉米梳齿摘穗单体机构设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(20):1-9.
Zhang Zhilong, Zhang Dongxing, Cui Tao, et al. Design and experiment of corn stripping monomer mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(20): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 耿爱军,李汝莘,刘双喜,等. 玉米收获机割台性能试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(增刊2):27-31.Geng Aijun, Li Ruxin, Liu Shuangxi, et al. Performance experiment of corn harvester header[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(Supp.2):
27-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 贺俊林,佟金,胡伟,等. 辊型和作业速度对玉米收获机摘穗性能的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2006,37(3):46-49.
He Junlin, Tong Jin, Hu Wei, et al. Influence of snapping roll type and harvesting speed on 4YWQ corn harvester[J]. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2006, 37(3): 46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 范国昌,王惠新,籍俊杰,等. 影响玉米摘穗过程中籽粒破碎和籽粒损失率的因素分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2002, 18(4):72-74.
Fan Guochang, Wang Huixin, Ji Junjie, et al. Analysis of influence factor on seed damage rate and loss rate during picking corn-cob[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2002, 18(4): 72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] Sokhansanj S, Turhollow A, Cushman J, et al. Engineering aspects of collecting corn stove for bioenergy[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2002, 23(5): 347-355.
Effect of height difference of horizontal corn snapping rollers device on grain loss
Chen Meizhou1, Sun Xuefeng2, Cheng Xiupei1, Jia Xiaodong3, Li Qiyun1※
(1,,255000,; 2,213000,; 3.,,250000,)
In recent years, corn acreage has became the first place instead of wheat and rice in China.However, corn mechanical harvesting level is low, which has seriously affected the development of corn mechanization. Corn snapping device is a main component of corn harvesting machine, and plays an important role on the quality of harvester. Compared to other kinds of corn ear picking device, horizontal snapping rollers device is easy to cause serious corn grain loss rate and high impurity rate, which has been the choke points of corn harvester development for a long time. Heightdifference of snapping rollers is a significant factor that affects the ability of horizontal snapping rollers device to pick corn ears. If the height difference is too small, corn ears will stick on snapping rollers after picking, and the prolonged exposure increases corn grain loss seriously. When the height difference is too large, the center distance of snapping rollers remains constant that leads to small horizontal projection gap, and triangulardomain shaped by the front cone of the snapping rollers still makes it difficult to feed for corn plant, finally corn plant will bent and broken off, which leads to serious grain impurity rate. Based on the issue of serious gnawing harm and loss of corn ears, experimental research was conducted to analyze the effect of height difference on grain loss. In order to improve the precision for adjustment on the height difference and determine the parameters, the angle between the line of centers of two snapping rollers and the horizontal surface (the angle) was employed to represent the height difference. The horizontal snapping rollers device was built, and the grain loss rate was taken as the index to estimate the effect on height difference. Through the single factor experiment, the impact of the anglewas analyzed. The harvesting process was captured with the high-speed photography, which was helpful to analyze comprehensively in the late period. Through the single factor experiment and the analysis of variance, it was found that the grain loss rate reduced quickly from 24°-30° and changes were small and inconspicuous at 33° and 36°. The average grain loss was the least (0.354%) when the angle was 30°. High-speed cameras were used to collect image datum and analyze the datum. And two phenomena were discerned. It revealed that some corn ears stayed on the snapping rollers after picking, and there was also a “bouncing” phenomenon. Those phenomena caused secondary damage of corn ears and high impurity. In addition, when the anglewas too large, it was more difficult for corn stalk feeding, which made the corn stalk bending seriously and even to break, and even if the corn stalk was fed, it was easy to cause blocking on the snapping region. So if the large angle is employed, the gap between snapping rollers needs to be adjusted or the snapping rollers can be designed not to parallel with large backend and small front-end to ensure corn plant smoothly. For these phenomena, a curved bulkhead was installed above the low snapping roller. The contrast test showed that the solution reduced the chance of secondary damage to the corn ears. The single factor experiment showed that the grain loss rate reduced at each angle variously and grain loss rate was the least(0.164%) when the angle was 30º. The contrast test showed that the solution reduced the chance of secondary damage on the corn ears. It also prevented the snapping rollers from impacting on the corn ears, thereby reducing loss of corn grain. This study provides a reference for optimization and improvement on horizontal snapping rolls device.
agricultural machinery; analysis of variance; experiments; horizontal snapping rollers device; height difference; secondary damage; grain loss
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.009
S225
A
1002-6819(2017)-04-0063-06
2016-05-29
2016-11-10
山东省重点研发计划项目(2015GGX101003);公益性行业(农业)科研专项(200903059-0402);山东省科技发展计划项目(2010GNC10965);山东省自然科学基金专项(ZR2009DL012);山东省自然科学基金项目(2010 ZRE04018);农业科技成果转化资金项目(2014)
陈美舟,女,山东济宁人,博士生,主要从事农业机械的设计与研究。淄博 山东理工大学农业工程与食品科学学院,255000。 Email:chenfeng2830@163.com
李其昀,男,山东淄博人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业机械的设计与研究。淄博 山东理工大学农业工程与食品科学学院,255000。Email:liqiyun@sdut.edu.cn
陈美舟,孙雪峰,程修沛,贾晓东,李其昀. 卧辊式摘穗机构摘穗辊高度差对玉米籽粒损失的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(4):63-68. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.009 http://www.tcsae.org
Chen Meizhou, Sun Xuefeng, Cheng Xiupei, Jia Xiaodong, Li Qiyun. Effect of height difference of horizontal corn snapping rollers device on grain loss[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(4): 63-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.04.009 http://www.tcsae.org

