R2*值预估子宫内膜样腺癌病理分级的价值
田士峰
刘爱连LIU Ailian
李 烨LI Ye
陈丽华CHEN Lihua
汪禾青WANG Heqing
王逸敏WANG Yimin
韩 铮HAN Zheng
宋清伟SONG Qingwei
R2*值预估子宫内膜样腺癌病理分级的价值
田士峰TIAN Shifeng
刘爱连LIU Ailian
李 烨LI Ye
陈丽华CHEN Lihua
汪禾青WANG Heqing
王逸敏WANG Yimin
韩 铮HAN Zheng
宋清伟SONG Qingwei
中国医学影像学杂志
2016年 第24卷 第11期:864-867
Chinese Journal of Medical Imaging 2016 Volume 24 (11): 864-867
目的探讨增强T2*加权血管成像(ESWAN)序列的R2*值预估子宫内膜样腺癌(EA)病理分级的价值,以期准确判断EA分级,指导临床治疗。资料与方法回顾性分析在1.5T MRI行ESWAN序列检查并经手术病理证实为EA的82例患者,按照病理分级分为3组,其中高分化组37例,中分化组28例,低分化组17例。由2位观察者分别测量各组EA病灶实质区的R2*值,检验2位观察者测量数据的一致性,分析R2*值与EA病理级别的相关性,对不同级别EA的 R2*值进行组间两两比较,评估R2*值预估不同病理级别组EA的效能,并找出相应界值。结果2位观察者测量各组数据的一致性较高(ICC>0.75)。R2*值与EA病理级别呈弱相关(r=0.464,P<0.001),高、中、低分化组EA的R2*值分别为(12.54±2.75)Hz、(13.08±2.92)Hz、(18.71±3.80)Hz,高、低分化组间及中、低分化组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),高、中分化组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。R2*值预估低分化EA的曲线下面积为0.893,R2*值≥16.17 Hz为其界值,敏感度82.4%,特异度87.7%。结论R2*值可以作为非强化方式预估低分化EA的定量指标,有很好的应用前景。
子宫内膜肿瘤;腺癌;磁共振成像;磁敏感加权成像;病理学,外科;女(雌)性
子宫内膜癌是常见的女性生殖系统恶性肿瘤,发病率位居恶性肿瘤前十位[1],其最主要的病理类型是子宫内膜样腺癌(endometrial adenocarcinoma,EA)。不同分化程度的EA生物学行为不同,高、中分化EA因侵袭性弱而较少存在肿瘤淋巴管间隙浸润(lymph vascular space invasion,LVSI),而低分化的EA常侵及深肌层且广泛存在LVSI[2]。LVSI是导致EA复发、影响预后及治疗方案制定的重要因素[3]。术前通过影像学方法预估EA病理分级尤为重要,目前常用的方法是表观扩散系数(ADC)值[4-6]。由于EA的血供及耗氧情况较正常组织不同,因此血液代谢产物等顺磁性物质的浓度常出现变化,而表观横向弛豫率即R2*值对顺磁性物质浓度的变化极为敏感,是评价局部组织氧含量改变的定量指标[7]。本研究拟探讨R2*值预估EA病理分级的价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象 回顾性分析2013年1月-2016年3月于大连医科大学附属第一医院行MR检查,并经病理证实为EA的患者82例。年龄32~86岁,平均(58±11)岁。绝经前28例,主要临床表现为经期不规律、月经量增多等;绝经后54例,主要临床表现为不规则阴道流血。MRI表现为内膜弥漫性增厚75例,厚度1.0~3.7 cm,其中16例形成肿块填满宫腔;7例表现为息肉状局限性肿块,最大径1.5~5.5 cm。经病理证实并按病理级别将EA患者分为高、中、低分化组,分别为37例、28例、17例。所有患者均无MR检查禁忌证,术前均未接受放、化疗或其他治疗,在MR检查后2周内完成手术。
1.2 仪器与方法 采用 GE Signa HDxt 1.5T MR超导型扫描仪,体部8通道相控阵线圈。检查前禁食4~6 h减轻肠道蠕动,并于检查前1 h饮水约500 ml。扫描参数:①轴位T1WI序列采用快速扰相梯度回波序列,TR 500 ms,TE 10.0 ms,激励次数2,矩阵320×192,视野(FOV) 40 cm×40 cm,层厚5.0 mm,间隔l.0 mm,扫描时间1 min 40 s。②轴位T2WI序列采用快速自旋回波序列,TR 4000 ms,TE 125 ms,激励次数4.0,矩阵320×192,FOV 40 cm×40 cm,层厚5.0 mm,间隔l.0 mm,扫描时间2 min 23 s。③增强T2*加权血管成像(enhanced T2 star weighted angiography,ESWAN)序列,轴位三维成像,TR 16.5 ms,8个回波,TE 2.1 ms,反转角12°激励次数0.71,矩阵 256×192,FOV 40 cm×40 cm,层厚2 mm,流动补偿,屏气21 s。④肝脏快速容积成像动态增强扫描,TR 3.7 ms,TE 1.8 ms, IT 7.0 ms,反转角20°,激励次数0.7,矩阵 272×180,FOV 40 cm×40 cm,层厚4.0 mm,层间隔2.0 mm,采集时间3 min 29 s,采用双筒高压注射器经肘静脉注射马根维显(拜耳医药,中国广州),注射剂量0.1 ml/kg,速度2 ml/s。
1.3 图像分析与数据测量 将ESWAN序列图像传至ADW4.6工作站,经Functool软件处理,选取阈值对相位图进行低通滤波过滤,采用多回波幅度平均、相位掩模等对保留回波的相位图及幅度图进行处理,并获得新的相位图、幅度图、R2*图及T2*图。由1名住院医师及1名主治医师采用盲法分析。应用Viewer完成病灶R2*值的测量。方法为选择R2*图病灶横轴位最大截面,在肿瘤实质区放置圆形感兴趣区(ROI),避开坏死、出血、含气及伪影区,取3个平均值(图1)。所得各组R2*值结果的一致性用组内相关系数(intraclass correlation coefficients,ICC)检验,ICC 取值为0~1,<0.4为一致性差,>0.75 为一致性良好。取2位观察者测量结果平均值进行分析。
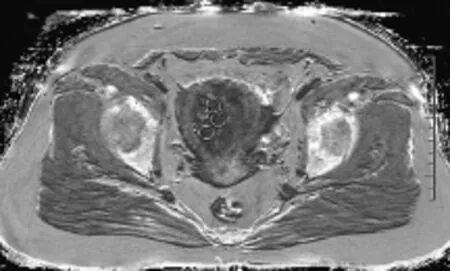
图1 女,55岁,低分化EA。R2*示在病灶最大截面不同区域放置3个ROI,每个ROI面积约1.0 cm2
1.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 17.0软件。R2*值与EA病理级别采用Spearman相关性分析,不同病理级别组EA的R2*值比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采用LSD法,P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。采用受试者工作特性(ROC)曲线评估R2*值对不同病理级别组EA的评判效能,计算曲线下面积(AUC),并根据最大约登指数确定相应界值及其敏感度、特异度。
2 结果
2.1 结果的一致性检验 2位观察者对不同病理级别组EA的R2*值测量结果的一致性均良好,高、中、低分化组测量的ICC值分别为0.894、0.930、0.923,各组测量结果见图2。
2.2 R2*值与EA病理级别的相关性及病理级别组间比较 R2*值与EA病理级别呈弱相关性(r=0.464,P<0.001)。高、中和低分化组EA的R2*值分别为(12.54±2.75)Hz、(13.08±2.92)Hz和(18.71±3.80)Hz(图3~5),高、低分化组EA的R2*值间差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),中、低分化组EA的R2*值间差异有统计学意义(P<0.001),高、中分化组EA的R2*值组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.3 R2*值预估低分化EA的效能 R2*值预估低分化EA的AUC为0.893(图6),R2*值≥16.17 Hz为其界值,灵敏度82.4%,特异度87.7%。
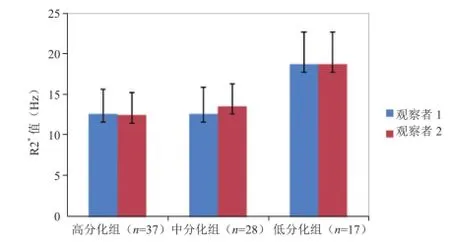
图2 不同病理级别组EA的R2*值

图3 女,56岁,高分化EA(箭)。R2*值为12.17 Hz
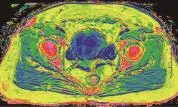
图4 女,38岁,中分化EA(箭)。R2*值为14.48 Hz
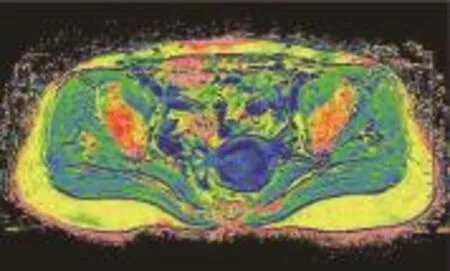
图5 女,67岁,低分化EA(箭)。R2*值为21.40 Hz
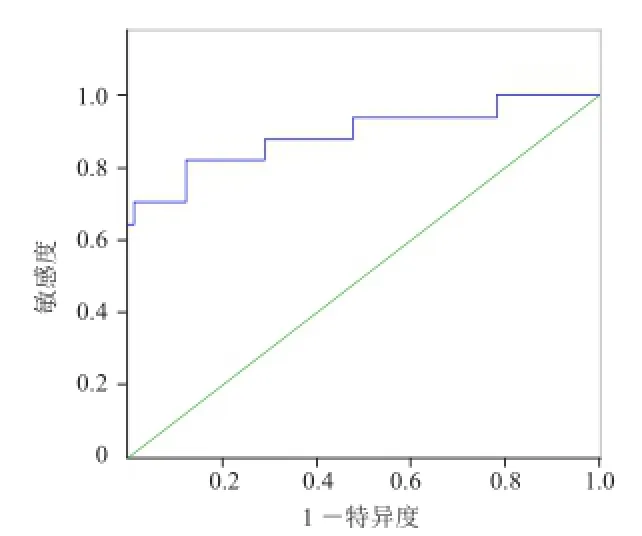
图6 R2*值预估低分化EA的ROC曲线
3 讨论
ESWAN序列扫描可获得多个回波的幅度图及相位图,具有高分辨率、薄层采集、同时获得相位及幅度信息,并获得多个定量参数[8],在定量评估方面颇具优势。R2*值可定量评估局部组织氧含量改变,与组织乏氧、出血等因素密切相关[9],在去氧血红蛋白等顺磁性物质浓度增加等情况下R2*值升高。本研究结果显示,低分化EA的R2*值较高、中分化EA高(P<0.001),可能是EA在肿瘤细胞增殖时,由于血管内皮生长因子等物质的诱导而产生病理性新生血管[10],并在低分化EA中的表达比高、中分化EA强烈,因此低分化EA可生成更多的新生血管[11]。虽然EA新生血管数量增多,但常有形态改变、走行纡曲、管壁基底膜缺陷等异常[12],可导致EA瘤体内微出血、血液循环障碍等,使去氧血红蛋白等顺磁性物质浓度增加,因低分化EA异常血管较多,导致微出血及血液动力学变化更为显著,因此R2*值较高、中分化EA增高。另外,低分化EA较高、中分化EA更高地表达Ki-67抗原,使肿瘤细胞增殖更加活跃,因此耗氧量更高,引起乏氧的程度更为严重,这也会导致R2*值增高[13-14]。Gheytanchi等[15]报道提出血管内皮生长因子与Ki-67可交互促进肿瘤细胞增殖及新生血管生成,使低分化EA的R2*值增高更为显著。此外,低分化EA的肿瘤细胞密度较高、中分化EA大,也会进一步加重缺氧[16]。本研究同时发现R2*值在高、中分化EA间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),其原因可能为两者在异常血供、耗氧等方面无显著差异。本研究中R2*值预估低分化EA的AUC为0.893,效能较高,以R2*值≥16.17 Hz作为判定低分化EA的界值,其敏感度与特异度均较高。本研究的局限性在于放置ROI的肿瘤实质区缺乏病理对照。
总之,R2*值可作为预估低分化EA的定量指标,为MR无创、非强化方式预估EA病理分级提供了一种新的方法,有较好的临床应用前景。
[1] 赫捷, 陈万青. 2012中国肿瘤登记年报. 北京: 军事医学科学出版社, 2012: 10.
[2] Kaloglu S, Guraslan H, Tekirdag AI, et al. Relation of preoperative thrombocytosis between tumor stage and grade in patients with endometrial cancer. Eurasian J Med, 2014, 46(3): 164-168.
[3] 刘剑羽, 周延. MRI在女性生殖系统恶性肿瘤诊断、分期和疗效评价中的价值. 中华放射学杂志, 2015, 49(5): 323-327.
[4] Ippolito D, Cadonici A, BonaffiniPA, et al. Semiquantitative perfusion combined with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in pre-operative evaluation of endometrial carcinoma: results in a group of 57 patients. Magn Reson Imaging, 2014, 32(5): 464-472.
[5] Woo S, Cho JY, Kim SY, et al. Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient map of diffusion-weighted MRI in endometrial cancer: a preliminary correlation study with histological grade. Acta Radiol, 2014, 55(10): 1270-1277.
[6] Husby JA, Salvesen ØO, Magnussen IJ, et al. Tumour apparent diffusion coefficient is associated with depth of myometrial invasion and is negatively correlated to tumour volume in endometrial carcinomas. Clin Radiol, 2015, 70(5): 487-494.
[7] Ning N, Zhang L, Gao J, et al. Assessment of iron deposition and white matter maturation in infant brains by using enhanced T2 star weighted angiography (ESWAN): R2*versus phase values. PLoS One, 2014, 9(2): e89888.
[8] 田士峰, 刘爱连. 肾脏疾病MR磁敏感技术的应用进展. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2015, 23(8): 638-640.
[9] Li RK, Palmer SL, Zeng MS, et al. Detection of endogenous Iron reduction during hepatocarcinogenesis at Susceptibility-Weighted MR imaging: value for characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodule in cirrhotic liver. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0142882.
[10] Wang J, Taylor A, Showeil R, et al. Expression profiling and significance of VEGF-A, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and related proteins in endometrial carcinoma. Cytokine, 2014, 68(2): 94-100.
[11] Coenegrachts L, Schrauwen S, Van Bree R, et al. Increased expression of placental growth factor in high-grade endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Rep, 2013, 29(2): 413-418.
[12] Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2011, 10(6): 417-427.
[13] Stefansson IM, Salvesen HB, Immervoll H, et al. Prognostic impact of histological grade and vascular invasion compared with tumour cell proliferation in endometrial carcinoma of endometrioid type. Histopathology, 2004, 44(5): 472-479.
[14] Apostolou G, Apostolou N, Nikolaidou C, et al. Cytodiagnosis of endometrial carcinoma and hyperplasia on imprint smears with additional immunocytochemistry using Ki-67 and p53 biomarkers. Cytopathology, 2014, 25(2): 86-94.
[15] Gheytanchi E, Mehrazma M, Madjd Z. Expression of Ki-67, p53 and VEGF in pediatric neuroblastoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(7): 3065-3070.
[16] Gallego JC, Porta A, Pardo MC, et al. Evaluation of myometrial invasion in endometrial cancer: comparison of diffusionweighted magnetic resonance and intraoperative frozen sections. Abdom Imaging, 2014, 39(5): 1021-1026.
(本文编辑 周立波)
R2*Value in Predicting the Pathologic Grade of Endometrial Adenocarcinoma
Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116011, China
Address Correspondence to:LIU AilianE-mail: cjr.liuailian@vip.163.com
PurposeTo investigate the feasibility of R2*value generated from enhanced T2 star-weighted angiography (ESWAN) sequence in evaluating the pathological grade of endometrial adenocarcinoma (EA), in order to grade the EA accurately and to guide clinical treatment.Materials and MethodsImaging data of 82 EA cases confirmed by pathology were retrospectively analyzed. MRI scan including ESWAN sequence was performed on a 1.5T scanner. The patients were classified into three groups as follows according to the pathological grade: 37 in well differentiated group, 28 in moderately differentiated group, and 17 in poorly differentiated group. The R2*values of EA tumors were measured by two observers, and the consistency of the two observers was tested. The correlation between R2*value and pathological grade was analyzed. The R2*values of different pathological grades were compared. The efficacy of R2*value in predicting the different pathological grade was evaluated to find out the corresponding threshold.ResultsThe consistency of two observers was good (ICC>0.75). The R2*value was weak correlated with the pathological grade of EA (r=0.464,P<0.001). The R2*values of well, moderately, and poorly differentiated groups were (12.54±2.75)Hz, (13.08±2.92)Hz, and (18.71±3.80)Hz, respectively. There was statistic difference of R2*values between well and poorly group as well as moderately and poorly group (P<0.001), while there was no statistic difference of R2*values between well and moderately group (P>0.05). The Area Under Curve of R2*value for diagnosis of poorly differentiated EA was 0.893, and the cut off value was ≥16.17 Hz with sensitivity of 82.4% and the specificity of 87.7%.ConclusionR2*value can be used as a non-enhancement quantitative index for determining the poorly differentiated EA, which has a good application prospect.
Endometrial neoplasms; Adenocarcinoma; Magnetic resonance imaging; Susceptibility-weighted imaging; Pathology, surgical; Female
10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2016.11.016
大连医科大学附属第一医院放射科 辽宁大连 116011
刘爱连
2016-05-27
2016-07-14
R445.2;R711.7

