公司产权性质、经理管理防御与高质量审计需求
张俊民,张 晓,肖志超
(天津财经大学 商学院,天津 300222)
公司产权性质、经理管理防御与高质量审计需求
张俊民,张 晓,肖志超
(天津财经大学 商学院,天津 300222)
以2008-2014年中国上市企业为样本,本文考察不同产权性质下经理管理防御对高质量审计需求的影响。研究发现,在国有企业中,经理管理防御对高质量审计需求具有负向影响;而在民营企业中,经理管理防御则引发了高质量审计需求。进一步发现,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争与外部大股东持股均能显著抑制经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间的负向关系;而在民营企业中,这两种外部治理机制均不具有显著的调节效应。本文提供了不同产权性质企业经理管理防御经济后果的证据,对进一步推进国有企业改革具有借鉴意义。
公司产权性质;经理管理防御;市场约束机制;高质量审计需求
一、引 言
经理管理防御为管理层代理问题的内容之一,是指经理人主动应对公司内外部治理机制以实现自身职位稳固的行为。在我国新兴加转轨的制度背景下,经理管理防御是一项重要的研究议题。现有文献主要研究了公司财务政策领域的经理管理防御行为[1-2],然而,注册会计师审计所具备的鉴证以及信号传递功能也能够对经理人的职位稳固产生影响[3-6];而且,随着管理者权力的日益膨胀,审计师的选聘权也往往掌握在经理人手中[7-8]。在这样的情况下,审计便可能成为经理人进行管理防御的工具。那么,经理人的防御动机将如何影响审计需求呢?进一步,相比于民营企业,市场机制对我国国有企业经理人的约束力较弱,那么,在企业不同的产权性质下,经理管理防御对审计需求的影响相同吗?本文尝试对以上问题做出回答。
以2008-2014年我国A股上市公司为样本,本文分别考察了国有企业和民营企业中,经理管理防御对审计收费以及审计师选择的影响。研究发现,由于市场机制对国有企业经理人的约束力较弱,国有企业经理管理防御与上市公司支付的审计费用以及选择“十大”会计师事务所的概率均呈显著的负相关关系;而在民营企业中,经理管理防御显著增加了上市公司的审计费用水平以及选择“十大”会计师事务所的概率。进一步发现,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争与外部大股东持股具有治理作用,显著降低了经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间的负向关系;而在民营企业中,这一调节效应并不显著。
本文突破了以往研究中股东利益最大化的假定,首次验证了经理人的防御动机对高质量审计需求的影响,丰富了我国经理管理防御经济后果以及审计需求影响因素的相关研究。同时发现,不同于民营企业,在市场机制对经理人约束力较弱的国有企业中,经理的防御动机导致了低质量审计需求,说明进一步推进国有企业经理人约束机制改革的重要性。经研究,本文进一步发现,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争与外部大股东持股对经理人的机会主义行为具有治理作用,说明完善市场机制以及形成有效的公司治理结构有助于减轻经理管理防御对股东利益的损害。
二、文献综述
经理管理防御假说最早由Morck等[9]在发现经理人持股与公司价值之间的非线性关系时提出,当经理人投票权增加到一定程度后,能对公司决策施加较强的影响力,此时经理持股比例的增加会产生防御效应,对公司价值具有负面影响。韩亮亮和李凯[10]发现了我国上市公司中经理人持股比例与公司价值之间的非单调关系,从而证明我国上市公司的经理人处于防御状态。现有关于经理管理防御的相关研究主要涉及公司财务政策领域。例如,Novaes和Zingales[2]研究发现,在资本结构决策中,经理人往往将负债作为防御策略,与股东对资本结构的选择具有很大不同;Farinha[1]对英国公司的研究发现,经理层持股比例与股利支付率之间存在U型关系,当经理层持股比例达到30%后,经理人将通过支付更多的股利以获取私人收益;我国学者袁春生和杨淑娥[11]则指出,管理层的防御动机是导致企业非效率投资的深层次原因。除此之外,王志强等[12]研究发现,公司的高层管理者会通过要求较高的薪酬水平来补偿人力资本破产成本,说明我国上市公司中普遍存在管理层防御现象;李秉祥等[13]则发现,经理人会通过长期资产减值政策选择来进行管理防御。
传统代理理论下,审计在公司治理中起着监督作用,能够降低企业的代理成本,提高企业市场价值[14]。沿着这一思路,众多学者从公司规模、负债、股权结构以及管理层权力等角度,探讨了代理成本与高质量审计需求之间的关系,发现审计对代理问题具有治理作用[3, 15-19]。然而,尚未有文献研究经理人如何将审计作为其防御工具。尽管如此,一些学者开始关注管理者权力与会计信息质量的关系:黎文靖和卢锐[20]研究发现,我国上市公司中管理者权力对会计信息质量具有显著的负向影响;赵息和徐宁宁[21]认为,管理者权力越大,则越有可能隐瞒公司的内部控制缺陷,并且,相对于非国有企业,这种现象在国有企业中更加显著;周冬华[22]则发现,管理者权力与上市公司盈余管理程度显著正相关。上述研究表明,管理者会通过操纵会计信息来实现个人利益。然而,会计信息质量与审计是紧密联系的,现有文献忽略了经理人的自利动机与审计需求之间的关系研究。基于以上考虑,本文按照公司产权性质区分国有企业样本和非国有企业样本,考察经理管理防御对审计需求的影响。
三、理论分析与研究假设
控制权收益的不可补偿性以及经理失业成本的存在,使得经理具有强烈的防御动机[9]。而经理人的防御行为表现在其对公司经营的各项决策上[1,23-24]。我国公司法规定,股东大会和董事会拥有对会计师事务所选聘和解聘的决策权。然而现实中,随着管理者权力的日益膨胀,往往是经理人决定审计师的选聘[7-8],这为经理人将审计作为防御工具创造了条件。
审计作为公司的一项外部治理机制,从两个方面影响经理人的职位稳固。一方面,审计具有信号传递功能,高质量的审计通过向资本市场传递积极信号,能够增加投资者的信任,有利于提高企业的融资能力以及市场价值,从而降低企业破产清算或被接管的风险[5-6]。因此,在企业经理人受市场机制约束较大的情况下,高质量的审计有利于其职位稳固。另一方面,审计还具有鉴证价值[3-4],高质量审计通过对上市公司披露的财务信息进行鉴证并出具审计意见,能够揭发经理人的自利行为,对其职位产生威胁。因此,当企业经理人受市场机制的约束较小时,低质量审计更有利于其职位稳固。
在我国,国有企业与民营企业对经理人的约束机制具有很大差异。具体而言,一方面相对于民营企业,我国国有企业经理人的聘请多是行政任命,经理人的考核机制也主要关注会计盈余指标[25],经理追求高市场业绩的动机较弱。另一方面,国有企业“所有者缺位”导致其治理机制相对弱化,加剧了经理人的机会主义行为[26];而国有企业经理人的自利行为一旦被高质量审计揭发,经理人不仅面临解雇风险而且还要受到严厉的行政处罚,其失业成本较民营企业经理人更大。因此,在管理防御状态下,国有企业经理人缺乏对高质量审计的需求,甚至倾向于聘用低质量审计师以掩饰自利行为,降低解雇风险。因此,提出如下假设:
H1:国有企业经理管理防御与高质量审计需求呈负相关关系。
对于民营企业,由于其市场化程度相对较高,因业绩不佳而被并购或接管的可能性更大,从而市场绩效对民营企业经理人具有较强的约束;再加上民营企业面临较大的融资约束[27],资金链断裂导致的企业破产风险较高,因而经理人具有强烈的动机聘请高质量审计师以向市场传递积极信号,从而增加投资者的信任,提高融资能力,降低企业破产或被接管的风险。因此,提出如下假设:
H2:民营企业经理管理防御与高质量审计需求呈正相关关系。
四、研究设计
(一)数据来源与样本选择
本文选取2008—2014年沪深两市A股上市公司为研究样本,并在样本选择过程中,进行以下处理:(1)剔除金融行业样本;(2)剔除同时发行B股和H股的样本;(3)剔除相关数据缺失的样本;(4)删除极端异常值并对所有连续变量进行上下1%水平的缩尾处理。最后,本文共计得到18554个非平衡面板观察值,其中:国有企业样本量为8625个;民营企业样本量为9929个。CEO背景特征、公司治理以及财务数据来自国泰安和万德数据库。
(二)变量定义及度量
1.经理管理防御的计量
对经理管理防御的度量一直是学术界关注的问题。由于权力是经理管理防御的基础,在英美股权高度分散的国家,学者通常使用经理人持股比例来衡量其防御水平[9,28]。然而,Finkelstein[29]认为经理权力表现为组织权力、专家权力、所有权权力和声望权力四个维度,所有权并非经理人权力的唯一来源,因此仅从所有权角度衡量经理管理防御水平是不全面的。本文借鉴Chen[30]、Nejla[31]以及Finkelstein[29]的研究,从经理的任期、学历、是否有外部兼职、是否兼任董事长、是否持股等五个维度衡量管理防御水平,赋予各变量相同的权重,计算其算术平均值,得到经理管理防御指数。
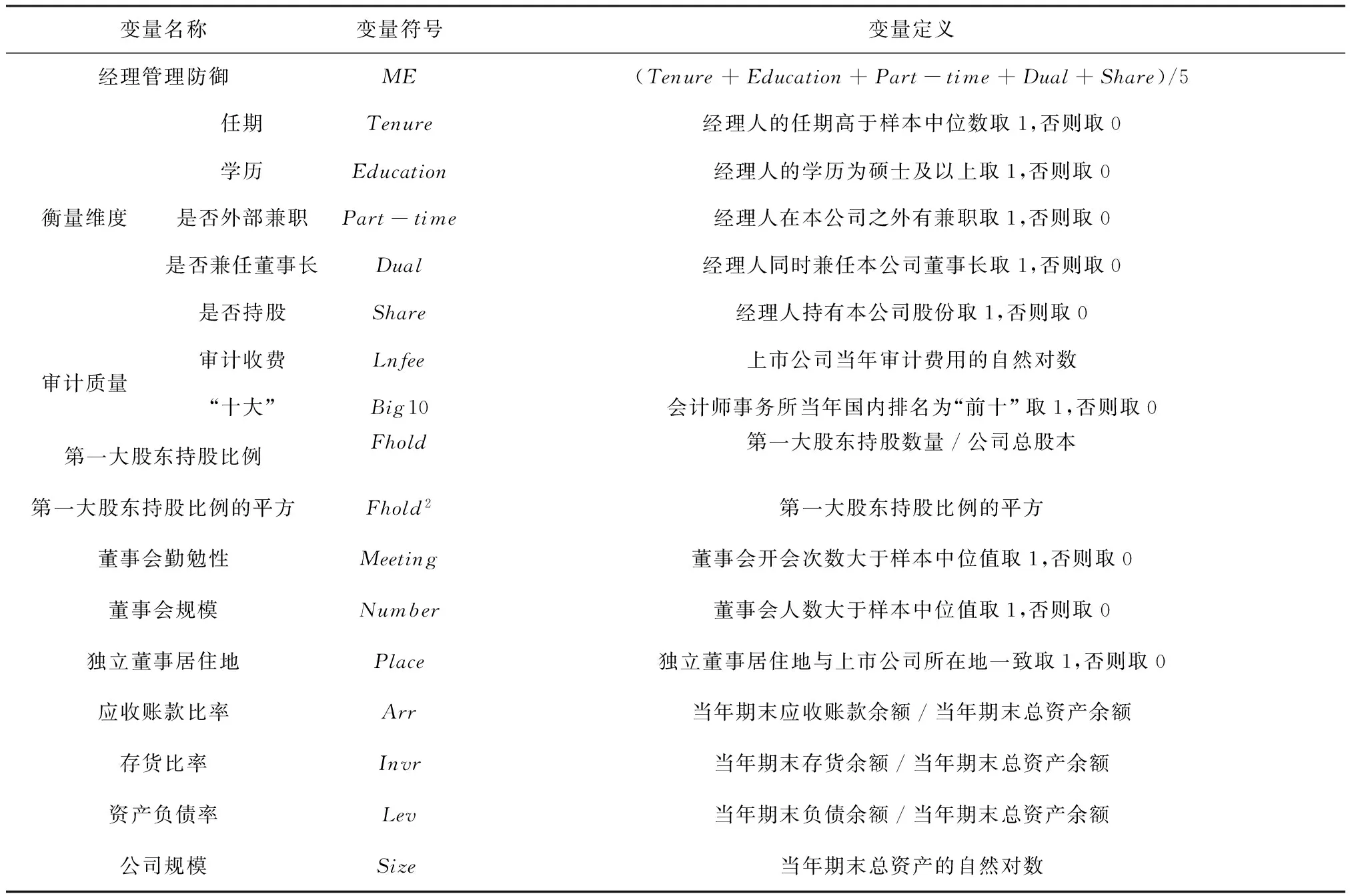
表1 变量定义
2.高质量审计的计量
由于审计质量的不可观测性,学者们为寻找审计质量的替代变量展开了大量研究。DeAngelo[32]采用事务所规模作为审计质量的替代变量,认为规模较大的事务所维护其品牌声誉的内在动机更为强烈,因而会提供较高质量的审计服务。O’Sullivan[33]则指出,审计质量高的事务所具有更高的审计收费溢价,因此采用了审计费用来衡量审计质量。国内研究也大多按照这两种思路对审计质量进行度量[34-38]。因此,本文使用“十大”以及审计费用的自然对数作为审计质量的替代变量。
3.其他控制变量
借鉴Carcello等[39]和Gul等[40]的研究,本文选取董事会会议次数、董事会人数、独立董事的办公地点与上市公司所在地是否一致、大股东持股比例、大股东持股比例的平方、存货比率、应收账款比率、公司规模、资产负债率等变量作为控制变量,并设置了行业和年度哑变量以控制行业和年度效应。
以上变量的具体定义见表1。
(三)模型设计
为了检验经理管理防御对高质量审计需求的影响,本文建立以下两个基础模型:
Lnfee=α0+α1ME+α2Fhold+α3Fhold2+α4Meeting+α5Number+α6Place+α7Arr+α8Invr+α9Lev+α10Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(1)
Big10=β0+β1ME+β2Fhold+β3Fhold2+β4Meeting+β5Number+β6Place+β7Arr+β8Invr+β9Lev+β10Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(2)
在检验过程中,我们对模型(1)采用最小二乘法进行检验分析,对模型(2)采用Logistic估计方法进行回归分析。根据本文假设,我们预测在国有企业样本组,α1和β1显著为负,说明经理管理防御对高质量审计需求具有负向影响;而在民营企业样本组,α1和β1显著为正,说明经理管理防御能够产生高质量审计需求。
(四)描述性统计
各变量的描述性统计结果见表2。可以看出,国有企业审计费用自然对数的均值为13.431,大于民营企业的13.272,这可能是因为国有企业的规模较民营企业更大。国有企业选择“十大”会计师事务所的比例为58.9%,略低于民营企业的59.5%。国有企业的经理管理防御指数均值为0.363,中位值为0.4,均远低于民营企业。具体而言,国有企业经理人除了受教育程度高于民营企业外,其他特征均远低于民营企业。其他控制变量的情况详见表2。
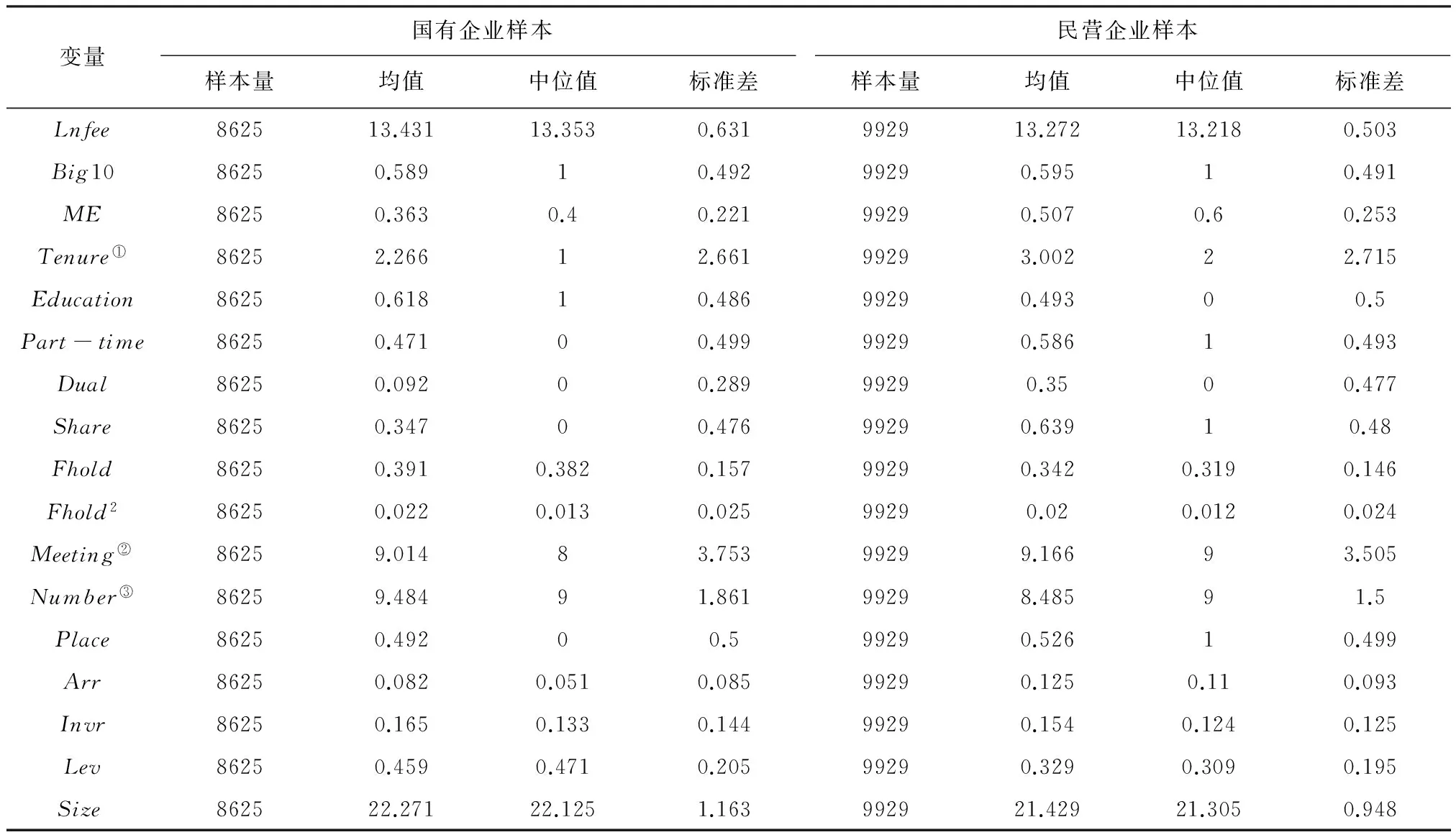
表2 主要变量描述性统计
由于国有企业和民营企业的产权性质不同,二者之间存在较大差异。为了进一步分析主要变量的差异是否显著,本文对国有企业样本和民营企业样本的均值进行了检验,如表3所示。可以发现,国有企业和民营企业的审计收费以及经理管理防御指数都存在显著差异,初步说明在两组样本中,经理管理防御可能会对高质量审计需求产生不同的影响。
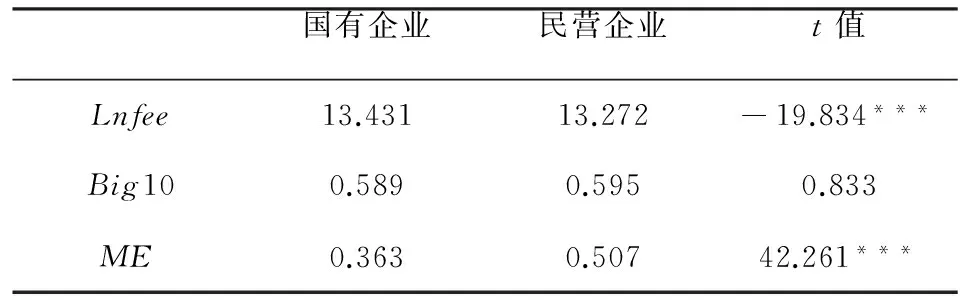
表3 主要变量的均值检验
五、实证结果分析与讨论
(一)模型回归结果
表4的一、三两列报告了国有企业样本的回归结果。其中,模型(1)的被解释变量为审计费用,模型(2)的被解释变量为“十大”。模型(1)中,ME的回归系数在1%水平上显著负相关,这说明经理管理防御水平越高,上市公司支付的审计费用越低;模型(2)中,ME的回归系数同样在1%水平上负向显著,说明经理管理防御水平越高,上市公司聘请“十大”会计师事务所的概率越大。以上结果说明,在国有企业中,出于防御动机的经理人缺乏对高质量审计的需求,甚至会聘用低质量审计师以掩盖其败德行为,对上市公司信息披露质量产生负面影响。
表4的二、四两列报告了民营企业样本的检验结果。可以发现,模型(1)中ME的回归系数在1%水平上显著正相关,这说明随着经理管理防御水平的提高,上市公司支付了更多的审计费用;模型(2)中ME的系数也在1%水平上正向显著,说明上市公司经理管理防御水平越高,越会聘请“十大”会计师事务所。以上结果表明,在民营企业中,经理人为了维护控制权地位,更倾向于聘请高质量审计师以向市场传递积极信号,对上市公司信息披露质量具有正面效应。
(二)进一步分析
上述结果表明,在国有企业相对较弱的公司治理环境下,市场机制的约束力有限,经理人出于防御动机往往会选择低质量审计师,对上市公司的信息披露质量产生负面影响。然而,公司其他外部治理机制是否能够改善这一状况呢?借鉴Kim等[41]的研究,本文选择产品市场竞争和外部大股东持股两种外部治理机制,进一步分析它们对我国上市公司经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的影响。
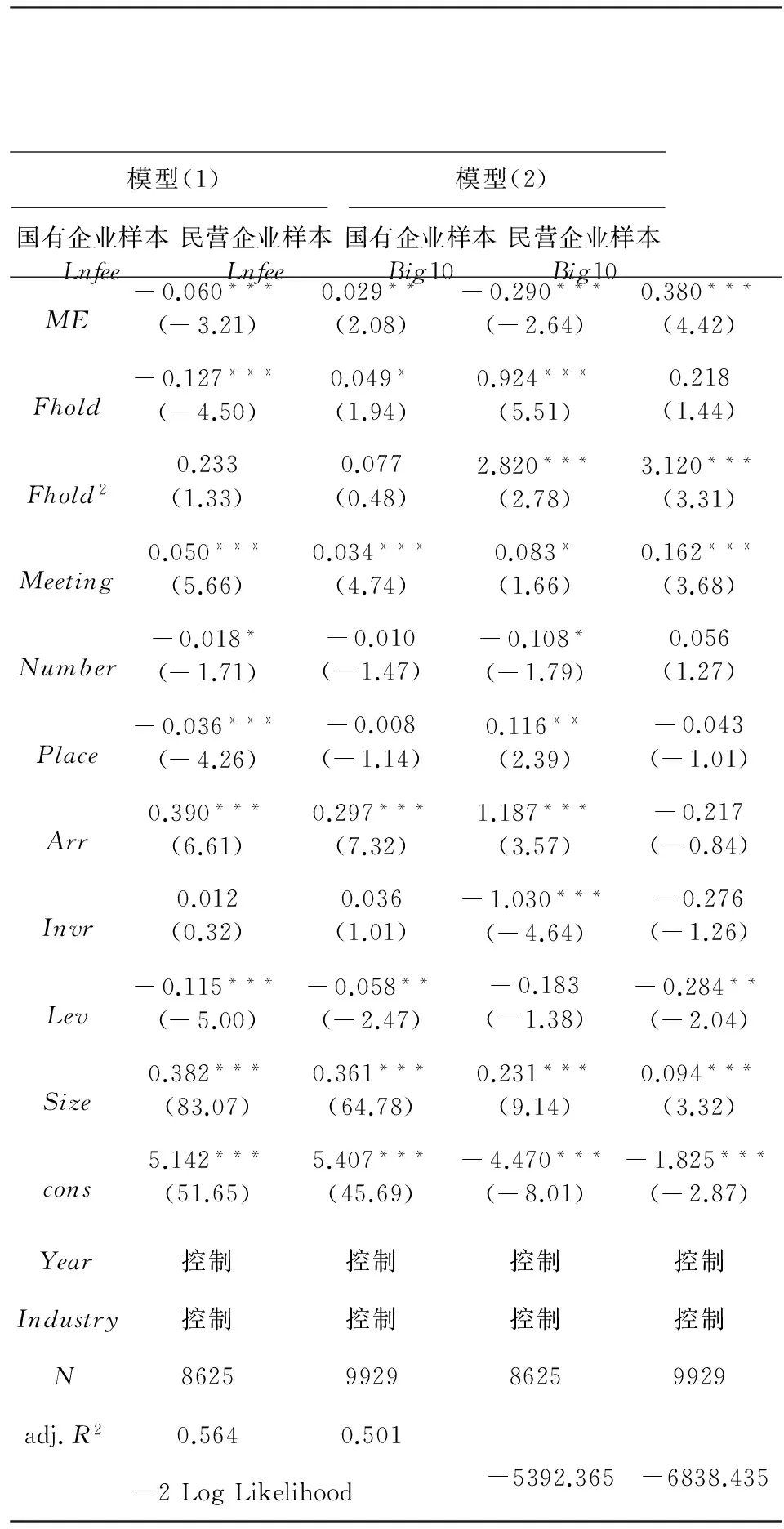
表4 经理管理防御与高质量审计需求的回归结果
1.产品市场竞争与经理管理防御
激烈的产品市场竞争增加了企业破产清算的威胁,给企业和管理者带来极大的财务压力,迫使企业产生较大的外部融资需求[42-44]。在这样的情况下,为了维护控制权地位,经理人必须更加关注企业发展,并努力降低资金供需双方的信息不对称。可见,产品市场竞争作为一种市场约束机制,有利于实现经理人与投资者之间的利益协同,对经理人的机会主义行为具有约束作用。因此,本文认为,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争能够显著抑制经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间的负向关系;而对于民营企业,由于其本身具有较高的市场化水平,因而产品市场竞争的治理效应并不明显。
为了对上述关系进行检验,本文借鉴Kim[41]的研究,采用赫芬达尔指数(HHI)①赫芬达尔指数的计算公式如下:衡量产品市场竞争程度,并构建模型(3)和模型(4):
Lnfee=α0+α1ME+α2HII+α3ME×HII+α4Fhold+α5Fhold2+α6Meeting+α7Number+α8Place+α9Arr+α10Invr+α11Lev+α12Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(3)
Big10=Lnfee=β0+β1ME+β2HII+β3ME×HII+β4Fhold+β5Fhold2+β6Meeting+β7Number+β8Place+β9Arr+β10Invr+β11Lev+β12Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(4)
其中,HHI为赫芬达尔指数的哑变量,若该指数小于样本中位数,取值为1,否则取值为0。两个模型中交叉项ME×HHI的系数α3和β3衡量产品市场竞争对经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的影响,根据本文预测,国有企业样本中α3和β3应正向显著,而民营企业样本中α3和β3不显著。
表5为产品市场竞争对经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的回归结果。可以看出,加入产品市场竞争变量后,两个模型中ME的系数方向在两个样本中均未发生变化,只是在民营企业样本中,模型(3)ME的系数显著性略有不同;两个模型中ME×HHI的系数在国有企业样本中正向显著,而在民营企业样本中则不再显著,与预测一致。
2.外部大股东持股与经理管理防御
相比于分散的小股东,大股东更具有动机和能力去监督管理者[45]。一方面,随着股权集中度的提高,监督管理者能够对大股东产生足够的利益激励;另一方面,他们持有的大量股票能够对现有管理层产生潜在的接管威胁。因此,外部大股东持股对公司治理机制具有替代作用[46]。基于上述分析,本文认为,在治理机制相对弱化的国有企业中,外部大股东HHI=∑(xi/x)2,x=∑xi
其中,Xi为行业内企业i的销售额。当行业内企业数目一定时,该指数越小,表示同一行业内相同规模的企业数量越多,市场竞争越激烈。
持股能够发挥治理作用,有效抑制经理人聘请低质量审计师的防御行为;而在民营企业中,外部大股东相比于内部股东发挥作用的空间较小,因而不具有显著的调节效应。
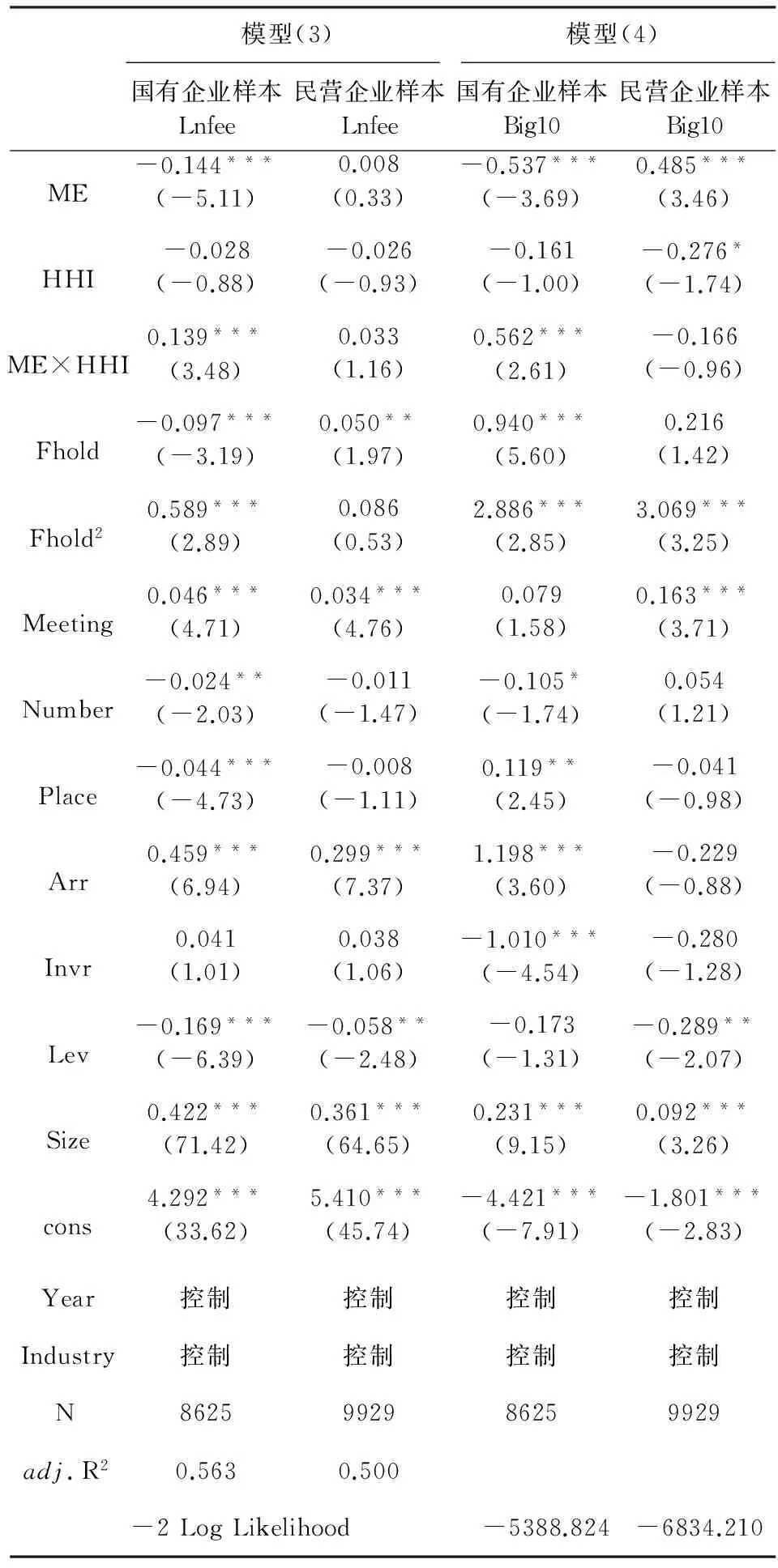
表5 产品市场竞争对经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的回归结果
为了对上述关系进行检验,本文构建模型(5)和模型(6):
Lnfee=α0+α1ME+α2OS+α3ME×OS+α4Fhold+α5Fhold2+α6Meeting+α7Number+α8Place+α9Arr+α10Invr+α11Lev+α12Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(5)
Big10=Lnfee=β0+β1ME+β2OS+β3ME×OS+β4Fhold+β5Fhold2+β6Meeting+β7Number+β8Place+β9Arr+β10Invr+β11Lev+β12Size+∑Year+∑Industry+ε
(6)
其中,OS为外部大股东持股哑变量,若上市公司第二至第十大股东的持股比例之和大于第一大股东的持股比例,则取值为1,否则取值为0。两个模型中交叉项ME×OS的系数α3和β3衡量外部大股东持股对管理者防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的影响,根据本文预测,国有企业样本中α3和β3应正向显著,而民营企业样本中α3和β3不显著。
表6描述了外部大股东持股对经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的回归结果。可以看出,加入外部大股东持股变量后,无论是在国有企业样本还是民营企业样本中,两个模型中ME的系数方向依然与之前一致;而且ME×OS的系数在国有企业样本中正向显著,在民营企业则样本不显著,与预测一致。
以上结果说明,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争与外部大股东持股均具有显著的治理作用,能够有效抑制经理人聘请低质量审计师的防御行为,一定程度上有利于上市公司信息披露质量的提高;而在民营企业中,产品市场竞争与外部大股东持股的治理效应并不明显。
(三)稳健性检验
此外,为验证研究结论的可靠性,本文还进行了如下稳健性检验:(1)重新构建经理管理防御指数。借鉴张海龙和李秉祥[47]的研究,我们在前文用来构建经理管理防御指数的五个变量的基础上,加入年龄变量,计算其算术平均值,得到新的经理管理防御指数并进行回归分析,结果基本一致。(2)变更审计质量替代变量。除了使用审计收费和“十大”衡量审计质量外,很多学者还将“国际四大”作为审计质量的替代变量[18,48],因此我们采用“国际四大”重新衡量审计质量,结果基本一致。由于篇幅限制,文中不再报告回归结果,见附录。
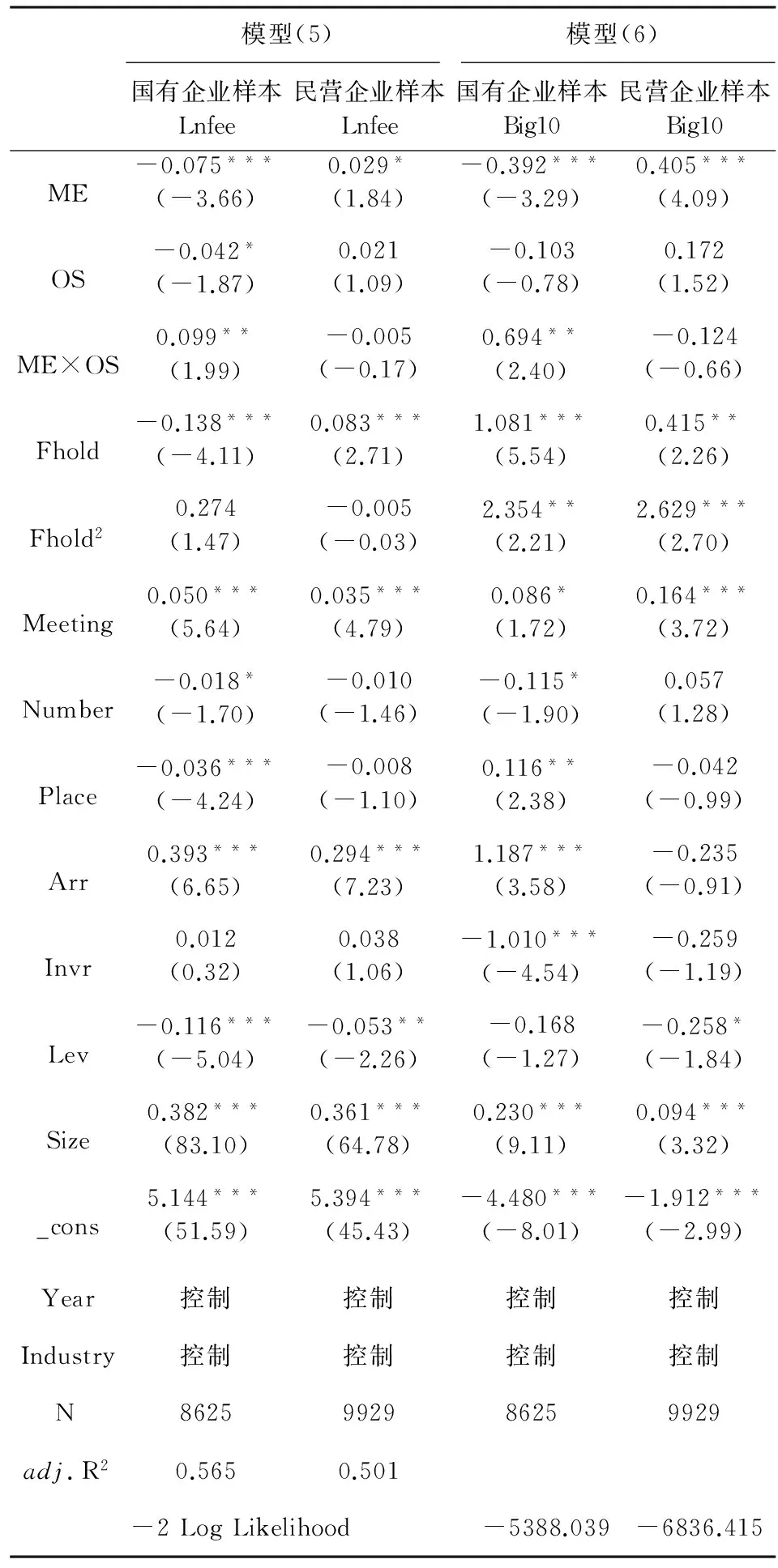
表6 外部大股东持股对经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间关系的回归结果
六、研究结论
随着管理者权力的不断增加,经理管理防御现象日益严重,审计成为经理借以影响信息披露质量进而实现职位稳固的工具。本文以2008年至2014年中国上市企业为样本,区分国有企业和民营企业,研究了上市公司经理管理防御与高质量审计需求之间的关系。研究发现,由于国有企业和民营企业对经理人具有不同的约束机制,在国有企业中,出于防御动机的经理人倾向于选择低质量审计师以掩饰其自利行为,降低解雇风险;而在民营企业中,由于市场机制对经理人具有较大的约束,较高的经理管理防御水平能够引发高质量的审计需求。进一步研究发现,在国有企业中,产品市场竞争和外部大股东持股均能显著抑制出于防御动机的经理人选择低质量审计师的行为;而在民营企业中,这两种外部治理机制并不具有显著的调节效应。以上结论说明,国有企业的市场化改革能够增强市场机制对经理人的约束,有利于实现经理人与投资者之间的利益协同;其次,有效的公司治理结构能够增加对经理人的约束,减轻经理人的防御行为对股东利益的损害。本文的贡献在于:(1)现有文献多基于股东利益最大化假设,将外部审计为缓解代理冲突的公司治理机制,是能够对代理成本施加影响的主体。而本文中,外部审计作为经理人谋求职位稳固的工具,是经理人施加权力影响的客体。本文从第一类代理成本的经济后果入手,试图对管理层权力与外部审计之间关系及影响进行反向解读,是对现有研究范式的重要扩展。(2)本研究表明,不同所有权背景下,经理管理防御动机的差异对审计需求表现出不同的影响特征,为我国特殊制度背景下的审计需求理论提供了更本土化的解释,促使学术界和政策制定者思考如何在制度设计中避免审计机构的选择被管理层干扰,为进一步完善国企公司治理机制提供了借鉴。(3)激烈的市场竞争和权力制衡方的引入,能发挥有效的外部治理作用,提高资本市场运行效率,进一步突出了让市场在资源配置中发挥决定性作用的重大意义。未来的研究中,学术界应尝试关注若将审计作经理防御动机影响的客体,是否会同现有范式下的思路及结论产生冲突,并且应进一步将法制环境、媒体监督等其他外部治理机制的作用纳入考察范围。
[1] Farinha J. Dividend policy, corporate governance and the managerial entrenchment hypothesis: an empirical analysis[J]. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, 2003,30(9-10):1173-1209.
[2] Novaes W, Zingales L. Capital structure choice when managers are in control: entrenchment versus efficiency[Z]. National Bureau of Economic Research, 1995.
[3] Titman S, Trueman B. Information quality and the valuation of new issues[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 1986,8(2):159-172.
[4] Defond M L. The association between changes in client firm agency costs and auditor switching[J]. Auditing, 1992,11(1):16.
[5] Chow C W. The demand for external auditing: size, debt and ownership influences[J]. The Accounting Review, 1982,57(2):272-291.
[6] Watts R L, Zimmerman J L. Agency problems, auditing, and the theory of the firm: some evidence[J]. The Journal of Law & Economics, 1983,26(3):613-633.
[7] 张敏, 李伟, 张胜. 审计师聘任的实际决策者:股东还是高管[J]. 审计研究, 2010(6):86-92.
[8] 张阳, 张立民. 独立性威胁、审计委员会制约有效性:理论分析与实证研究[J]. 会计研究, 2007(10):87-94.
[9] Morck R, Shleifer A, Vishny R W. Management ownership and market valuation: an empirical analysis[J]. Journal of Financial Economics, 1988,20:293-315.
[10] 韩亮亮, 李凯, 宋力. 高管持股与企业价值——基于利益趋同效应与壕沟防守效应的经验研究[J]. 南开管理评论, 2006(4):35-41.
[11] 袁春生, 杨淑娥. 经理管理防御与企业非效率投资[J]. 经济问题, 2006(6):40-42.
[12] 王志强, 张玮婷, 顾劲尔. 资本结构、管理层防御与上市公司高管薪酬水平[J]. 会计研究, 2011(2):72-78.
[13] 陈英, 李秉祥, 李越. 经理人特征、管理层防御与长期资产减值政策选择[J]. 管理评论, 2015(6):140-147.
[14] Jensen M C, Meckling W H. Theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure[J]. Journal of Financial Economics, 1976,3(4):305-360.
[15] Fan J P, Wong T J. Do external auditors perform a corporate governance role in emerging markets? evidence from east Asia[J]. Journal of Accounting Research, 2005,43(1):35-72.
[16] Lennox C S. Managerial ownership and Audit Firm Size[R]. Social Science Electronic Publishing, 2003, http://ssrn.com/abstract=434840.
[17] Simunic D A, Stein M T. Product differentiation in auditing: auditor choice in the market for unseasoned new issues[M]. Canadian Certified General, 1987.
[18] 曾颖, 叶康涛. 股权结构、代理成本与外部审计需求[J]. 会计研究, 2005(10):63-70.
[19] 谢盛纹, 蒋煦涵, 闫焕民. 高质量审计、管理层权力与代理成本[J]. 当代财经, 2015(3):109-118.
[20] 黎文靖, 卢锐. 管理层权力与会计信息质量——来自中国证券市场的经验证据[J]. 山西财经大学学报, 2007 (8):108-115.
[21] 赵息, 许宁宁. 管理层权力、机会主义动机与内部控制缺陷信息披露[J]. 审计研究, 2013 (4):101-109.
[22] 周冬华. CEO权力、董事会稳定性与盈余管理[J]. 财经理论与实践, 2014(6):45-52.
[23] De Jong A, Veld C. An empirical analysis of incremental capital structure decisions under managerial entrenchment[J]. Journal of Banking & Finance, 2001,25(10):1857-1895.
[24] Vishny S A. Managerial entrenchment: the case of manager specific investment[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 1988,25(5):42-67.
[25] 姜付秀, 朱冰, 王运通. 国有企业的经理激励契约更不看重绩效吗?[J]. 管理世界, 2014(9):143-159.
[26] 游家兴, 罗胜强. 政府行为、股权安排与公司治理的有效性——基于盈余质量视角的研究[J]. 南开管理评论, 2008(6):66-73.
[27] Cull R, Xu L C. Institutions, ownership, and finance: the determinants of profit reinvestment among Chinese firms[J]. Journal of Financial Economics, 2005,77(1):117-146.
[28] Fama E F, Jensen M C. Agency problems and residual claims[J]. The Journal of law & Economics, 1983,26(2):327-349.
[29] Finkelstein S. Power in top management teams: dimensions, measurement, and validation[J]. Academy of Management Journal, 1992,35(3):505-538.
[30] Chen S. Managerial entrenchment and loss-shielding in executive compensation[R]. University of Michigan Working Paper 30, 2005.
[31] NejLa N O D. Managerial Entrenchment: modelisation and Impact on the shareholders’Wealth[R]. Ssrn Electronic Journal, 2006, http://ssrn.com/abstract=880703.
[32] DeAngelo L E. Auditor size and audit quality[J]. Journal of Accounting and Economics, 1981,3(3):183-199.
[33] O’Sullivan N. The impact of board composition and ownership on audit quality: evidence from large UK companies[J]. The British Accounting Review, 2000,32(4):397-414.
[34] 陈俊, 陈汉文, 吴东辉. 不确定性风险、治理冲突与审计师选择——来自1998—2004年中国A股IPO市场的经验证据[J]. 浙江大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2010(5):92-103.
[35] 杜兴强, 周泽将. 政治联系与审计师选择[J]. 审计研究, 2010(2):47-53.
[36] 韩洪灵, 陈汉文. 公司治理机制与高质量外部审计需求——来自中国审计市场的经验证据[J]. 财贸经济, 2008(1):61-66.
[37] 肖作平. 公司治理影响审计质量吗?——来自中国资本市场的经验证据[J]. 管理世界, 2006(7):22-33.
[38] 朱小平, 刘西友. 代理理论、审计质量与公司治理——来自中国上市公司的经验证据[J]. 山西财经大学学报, 2009(9):110-117.
[39] Carcello J V, Hermanson D R, Neal T L, et al. Board characteristics and audit fees[J]. Contemporary Accounting Research, 2002,19(3):365-384.
[40] Gul F A, Srinidhi B, Tsui S L. Board diversity and the Demand for Higher Audit Effort[R]. Ssrn Electronic Journal, 2008, http://ssrn.com/abstract=1359450.
[41] Kim E H, Lu Y. CEO ownership, external governance, and risk-taking[J]. Journal of Financial Economics, 2011,102(2):272-292.
[42] Aghion P, Dewatripont M, Rey P. Competition, financial discipline and growth[J]. The Review of Economic Studies, 1999,66(4):825-852.
[43] Alchian A A. Uncertainty, evolution, and economic theory[J]. The Journal of Political Economy, 1950,58(3):211-221.
[44] Stigler G J. Economies of scale, [J]. The Journal of Law and Economics, 1958,1:54-71.
[45] Shleifer A, Vishny R W. Large shareholders and corporate control[J]. The Journal of Political Economy, 1986,94(3):461-488.
[46] Lins K V. Equity ownership and firm value in emerging markets[J]. Journal of Financial And Quantitative Analysis, 2003,38(1):159-184.
[47] 张海龙, 李秉祥. 经理管理防御对企业过度投资行为影响的实证研究——来自我国制造业上市公司的经验证据[J]. 管理评论, 2010(7):82-89.
[48] 孙铮, 曹宇. 股权结构与审计需求[J]. 审计研究, 2004(3):7-14.
责任编辑、校对:李斌泉
稳健性检验附录:
(1)重新构建经理管理防御指数。借鉴张海龙和李秉祥的研究,我们在前文用来构建经理管理防御指数的五个变量的基础上,加入年龄变量,计算其算术平均值,得到新的经理管理防御指数并进行回归分析,结果基本一致。

表7 稳健性检验—重新构建经理管理防御指数后的回归结果
(2)变更审计质量替代变量。除了使用审计收费和“十大”衡量审计质量外,很多学者还将“国际四大”作为审计质量的替代变量,因此我们采用“国际四大”重新衡量审计质量,结果基本一致。

表8 稳健性检验—使用“国际四大”衡量审计质量后的回归结果
Market Structure and Loss Ratio: Health Insurance in China from 2004 to 2014
WANG Xiangnan1, BIAN Wenlong2
(1. Institute of Finance and Banking, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 100028, China;2. School of Finance, Guangdong University of Foreign Studies, Guangzhou 510006, China)
The loss ratio of health insurance is relatively low in China. Using the data of prefectural-level cities from 2004 to 2014, this article studies the relation between the market structure and the loss ratio of China’s health insurance market for the first time. Regarding three general market structure indexes, we find that the health insurance loss ratio is positively and significantly related to the number of firms and negatively and significantly related to the market concentration, while the (negative) relation between the loss ratio and inequality of market share is not robust. For the market structure indexes with insurance market feature, we find that the health insurance loss ratio is negatively and significantly related to the market share of nonlife insurers and positively and significantly related to the market share of foreign insurers, while is not significantly related with the insurers’ ages. Those results support the “structure-performance hypothesis” and indicate that, in order to increase health insurance loss ratio, we should carry the “supply side” reform and expand the insurance market openness to domestic and foreign insurers.
Health insurance; Martket structure; Loss ratio; China
Financial Decentralization, Bank Institution Change and Economic Growth—Based on the Empirical Analysis of Inter-provincial Panel Data during 1993~2012
XIE Zongfan1, JIANG Junsong2
(1.School of Public Administration, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410006, China;2. School of Business, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105, China)
Abstract: Chinese decentralization has been seen as one of important reasons to Chinese economic miracle. But the Chinese government delayed the decentralization process in the banking sector, which has been criticized by many scholars with market-oriented view. From the perspective of power, this paper reviews the repeatedly process of financial decentralization and centralization in the process of banking institution change, and analyzes its reasons, then analyzes the performance of banking institution change under the background of financial decentralization by using inter-provincial panel data during 1993~2012. The results find that the higher level of financial decentralization is conducive to improving the performance of the banking institution, and promoting the economic growth, but our country’s financial decentralization level is still at a low level, the government should further construct the market-oriented banking institution on the basis of improving the level of financial decentralization.
Keywords: Financial decentralization; Financial centralization; Bank institution change; Economic growth
How Regional Differences Affect P2P Lending Behavior—Evidence from Renrendai
PENG Hongfeng, YANG Liuming, TAN Xiaoyu
(Economics and Management School, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China)
Abstract: Using lending transaction data from Renrendai, this paper empirically examines the impact of regional differences on the P2P borrowing respectively from four perspectives: the economy level, financial ecological environment, education level and regular financial penetration. The results show that there is a significant discrepancy in the funding success rate among different regions in the domestic P2P lending market. More specifically, borrowers whose provinces enjoy higher economic level, better financial ecological environment, and higher degree of education are more likely to obtain loans; while the degree of regular financial penetration has a negative impact on the funding success rate, and indicate that the P2P network lending is an effective complement to the formal finance. The results presented in this paper have some policy implications on how to further understand the cause of the regional discrimination and how to create a harmonious online lending environment.
Key words:Regional discrimination; P2P network lending; Funding success rate
Regional Differences and Information Transmission in China’s Internet Lending Markets
YANG Hecan1, YANG Xianyue2
(1. School of Economics and Management, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu 241003, China;2. Institute of Applied Economics, Shanghai Academy of Social Science, Shanghai 200020, China)
Abstract: This paper examines regional differences and information transmission of China’s internet lending markets. The rapid development of the network lending markets has surpassed the limitation of time and space, positioning their service for "grassroots" class across the country. However, the difference of interest rates is significant around the country with serious regional segmentation, which is in sharp contrast to changes of interest rates with no regional differences and to free flows of market information. The main reason is that lending platforms have deeply involved in lending transactions and become a similar role of commercial bank credit intermediation, which results in the market pricing confusion. The further development of Internet lending market should aim to enhance market efficiency comprehensively and eliminate market segmentation
Key words:Internet lending; Regional differences; Information transmission
The Join Forces Theory of Economic Development:A Framework for Economic Development Analysis
SHAO Hongwei1,2, JIN Tao1
(1. School of Economics, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China;2. College of Business and Economics, Australian National University, Canberra 2601, Australia)
Abstract: This paper synthesizes former scholars’ insights on economic development and argues that economic development is the result of the join forces produced by the interaction of all parts in the social economic system. This system includes the institution forming the relationship between peoples, namely relation of production and superstructure; science and technology, and productivity forming the relationship between human and nature; the content and structure of economic activity; the platform bearing the economic activity, such as geography, natural resources, infrastructure, fictitious economy, historic background, international environment and so on. Technology and institution interact in the social economic system, technology innovation improves productivity and causes institution change, a favorable institution innovation is beneficial for technology innovation and productivity improvement, technology innovation and institution change decides economic development jointly in their interaction.
Keywords: Economic development; Join forces; Institution; Technology; Structure
Transformation Effect of Public Services on the Urban-Rural Income Disparity:an Empirical Test of Data across the Country
ZHAN Guohui, ZHANG Xinwen, DU Chunlin
(College of Public Administration, Nanjing Agriculture University, Nanjing 210095, China)
Abstract:Income disparity between urban and rural areas is the endogenous structure obstacles of affecting the symbiotic development of the current urban and rural, and then the equalization level of public services has the adverse effect on the urban-rural income disparity, thus effectively straightening out the transformation effect of public service on the urban-rural income disparity is the necessary premise to achieve symbiotic development between urban and rural areas. The paper reviews the existing literature about the urban-rural income disparity, then constructs the smooth transfer model of the public service on urban-rural income disparity. With the aid of the test model of threshold cointegration, this article finds that the transformation effect of development level of public services presents a difference in different level of transfer mechanism. At the same time, by constructing dynamic panel model of the public service and the urban-rural income disparity and using GMM two-step estimation, this article concludes that public service has the significant positively influence on the transformation effect for urban-rural income disparity. To this end, we should make the corresponding path to optimize the public service level, which aims to further narrow the urban-rural income disparity.
Key words:Public services; The urban-rural income disparity; Transformation effect; Smooth transfer
Do Technological Innovation and Upgrading of Industrial Structure Promote the Development of New-type Urbanization
HE Jianfeng1, WU Hui2
(1. School of Economics and Commerce, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China;2.School of Economics and Management, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China)
Abstract:Using 2005-2014 panel data of China’s provinces, this paper calculated every provinces’ new-type urbanization level through comprehensive index method, and analyzed the effects of the science and technology innovation and the upgrading of the industrial structure by using the panel data model. The results show that: (1) In the past ten years, the new-type urbanization level in eastern China was the highest, the middle took second place, the west was the lowest. The top three provinces were Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin. (2) There was a lagging promotion effect of technological innovation to new-type urbanization. The upgrading of industrial structure had a significant positive effect on the new-type urbanization. (3) The impact of technological innovation on the urbanization of the population was significantly positive, and negative impact on the urbanization of the society. The upgrading of the industrial structure had significantly different degrees of effect on population, economic and social urbanization.
Key words: New-type urbanization; Technological innovation; Upgrading of industrial structure; Panel data
Agricultural Insurance, Agricultural Loan and Per capita Net Income of Rural Households—An Empirical Analysis Based on Provincial Panel Data in China
RUAN Guilin, MENG Weidong
(School of Economics and Business Administration, Chongqing University 400044, China)
Abstract:Based on the panel data of 31 provinces from 2001 to 2013, this paper establishes a PVAR model to investigate the relationship among agricultural insurance, agricultural loan and per capita net income of rural households. The results show that only agricultural insurance of the west area has no positive promoting effect on the per capita net income of rural households; the agricultural loans of every region play positive promoting roles on per capita net income of rural households, but there is a time lag of 1-2 years; The effect of agricultural loan on per capita net income of rural households is greater than that of agricultural insurance. Besides, the interaction between agricultural insurance and agricultural loan has a regional difference.
Key words: Agricultural insurance; Agricultural loan; Per capita net income of rural households; The panel VAR model
How Banking Market Structure Promote Industry Resource Allocation—Based on the Analysis of Heterogeneous Firms Entry and Exit
WU Han1,2, JIA Runsong3,4
(1.Economics School, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China;2.Business School, Durham University, UK, DH1 2HD;3.Postdoctoral Programme of Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China;4.China Banking Regulatory Commission, Beijing, 100140, China)
Abstract:This paper uses Chinese manufacturing firms data to test the promote impact of banking market structure on industry resource allocation, stating that the expansion of the market share of small and medium sized banks can improve the condition of the credit allocation between firms. On the one hand, the development of small and medium-sized banks can supply enough credit to the potential small sized entry firms and promote firm entry, especially for the entry of SMEs; On the other hand, the development of small and medium-sized banks can effectively relief the financial constraints of SMEs and decrease the exit risk of SMEs. While the improvement of banking market structure is beneficial for firm entry and improve the industry resource allocation efficiency.
Key words:Banking market structure; Small and medium-sized banks; Financial dependence; Firm entry; firm exit
Study on the Driving Factors in China’s Energy Intensity Change—Based on LMDI Decomposition Technique
HAN Song1, ZHANG Baosheng1, TANG Xu1, QI Shuai1, MENG Fanyan2
(1. School of Business Administration, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China;2. National Engineering Laboratory for Pipeline Safety, China Petroleum Pipeline Research Institute, Langfang 065000, China)
Abstract:Energy shortage has been the bottleneck of economic and social sustainable development in China. The new task to improve energy efficiency has been put on the agenda of the "13th Five-Year" Plan. Therefore, exploring the driving factors that lead to the change of energy intensity is an important premise to improve the comprehensive energy efficiency in China. The study computes and analyzes the sources of the changes of energy intensity in China during the period 2001-2013 by using the decomposition method. With the logarithmic mean Divisia index technique, the change of energy intensity has been decomposed into four factors: the energy substitution, the technological progress, the changes of industry structure and sector structure. The results show that the technological progress effect is confirmed as the dominant contributor to the decline in energy intensity. Secondly, the energy substitution effect has no significant effect on overall energy intensity. Thirdly, the industry structure increases energy intensity and the structure change effect at the sector level decreases energy intensity.
Key words:Energy intensity; LMDI; Energy substitution; Technology progress; Industry structure; Sector structure
The Influence of Government Funding and Industry-University-Research Cooperation on Innovation Performance of Enterprises: Based on the Empirical Study on Guangdong Province’ Questionnaire Data
HU Junyan1, CHEN Zihong1, ZHOU Mingze2, JIN Yun1
(1. School of Economics and Commerce, South China University of Technology, Guangdong 510006, China;2. School of Business Administration, South China University of Technology, Guangdong 510006, China)
Abstract: The goal of government funding Industry-University-Research (IUR) is to enhance enterprises’ independent innovation ability. To examine whether this expected goal is achieved, this paper divides enterprises’ innovation performance into two types, namely market performance and the performance of research and development (R&D) reserve, and studies the effect of government funding and IUR on these two different innovation performance by using the questionnaire data of IUR in Guangdong province. The empirical results indicate that government funding has a significant positive effect on the performance of R&D reserve and has no significant effect on market performance. And there exists a non-significant positive relationship between IUR interaction and market performance, but a negative significant relationship between IUR interaction and the performance of R&D reserve. That means, it is necessary for the government to finance IUR to achieve the goal of promoting the performance of R&D reserve. However, the function mechanism of IUR interaction in the relationship between government funding and enterprises’ innovation performance is non-liner. Only when a certain threshold is reached, can IUR interaction work. In addition, the performance of R&D reserve has a higher threshold than market performance. And accordingly some policy implications are proposed.
Keywords: Government funding; Industry-University-Research (IUR) interaction; Innovation performance
Study on Managers’ Power Connection with Shareholders and Its Performance Influence in Private Firms
WANG Xinxia1, LIU Chun2
(1. School of Economics and Finance, Xi’an International Studies University, Shaanxi Xi’an 710128, China;2. Jinhe Center for Economic Research, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Shaanxi Xi’an 710049, China)
Abstract: Taking the actual controller as logical starting point, this paper theoretically analyzed managers’ power connection with shareholders and its performance influence in private firms, and discussed the moderating effect of compensation incentive on the performance influence. The empirical tests found that: (1)Managers’ power connection with shareholders has no significant influence on performance in firms with two posts syncretic; (2)In firms with two posts respective, chairman’s power connection with shareholders helps to improve firm performance while CEO’s power connection with shareholders has no significant or adverse impact on firm performance; (3)Compensation incentive is helpful to strengthen the positive influence of managers’ power connection with shareholders and restrain its negative influence.
Keywords: Manager; Power connection with shareholders; Compensation incentive; Performance influence
Company Property Rights, Managerial Entrenchment and the Demand for High Quality Audit
ZHANG Junmin, ZHANG Xiao, XIAO Zhichao
(School of Business, Tianjin University of Finance and Economics, Tianjin 300222, China)
Abstract: Using the data from the Chinese listed companies during the periods 2008-2014, the study examines the effects of managerial entrenchment on the demand for high quality audit among companies with different nature of property rights. The results show that managerial entrenchment has a negative effect on the demand for high quality audit in state-owned companies but in non-state-owned companies it leads to the demand for higher quality audit. The results also show that in state-owned companies both product market competition and ownership of outside blockholders have negative effects on the relationship between managerial entrenchment and the demand for high quality audit. However, none of the two corporate governance mechanism shows obvious effects in non-state-owned companies. The study provides evidence of the economic consequences of managerial entrenchment in the companies with different nature of property rights and has great significance for further promoting the reform of state-owned companies.
Keywords: Company property rights; Managerial entrenchment; The market restraint mechanism; The demand for high quality audit
2016-06-16
国家自然科学基金面上项目“产权视角下的审计师声誉机制及其经济后果研究”(71272189)。
张俊民(1960-),山东省济宁市人,天津财经大学商学院教授,博士生导师,研究方向:会计、审计;张晓(1989-),女,山东省德州市人,天津财经大学商学院博士研究生,研究方向:公司治理、审计;肖志超(1989-),河北省邢台市人,天津财经大学商学院博士研究生,研究方向:会计、审计。
A
1002-2848-2016(05)-0114-10
——基于“关系”的视角

