维生素D受体基因 rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病相关性的meta分析*
石 洁,朱岩昆,郑丹薇,马晓光,王少华,李 辉,邢 进,吴彩霞
河南省疾病预防控制中心 郑州 450016
维生素D受体基因 rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病相关性的meta分析*
石 洁,朱岩昆,郑丹薇,马晓光,王少华,李 辉,邢 进#,吴彩霞
河南省疾病预防控制中心 郑州 450016
#通信作者,女,1966年6月生,硕士,主任医师,研究方向:结核病的防控,E-mail:hncdcxj@163.com
结核病;维生素D受体基因;rs2222570;meta分析
目的:判断维生素D受体(VDR)基因rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病风险的关联性。方法:用关键词“维生素D受体多态性”和“结核病”搜索数据库中相关研究,根据各研究间的异质性,使用随机或固定效应模型进行meta分析。最终有20篇文献纳入研究。对基因型以及合并后产生的遗传模型和等位基因多态性与结核发病的相关性进行分析。结果:F 等位基因携带者结核发病风险降低(OR=0.84,95%CI=0.73~0.95); 显性模型遗传模式降低结核发病风险(OR=0.74,95%CI=0.60~0.92)。结论:VDR基因rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病风险有关。
中国作为结核病高负担国家,每年有100万人发病。结核杆菌携带者中只有十分之一发病[1],这表明结核病的发病情况受到环境和遗传因素交互作用的影响。目前已有很多学者[2-7]对结核病候选基因的多态性进行了研究,尤其是维生素D受体(vitamin D receptor,VDR)基因。人体内维生素D3缺乏会增加结核病易感性[8-9],因为维生素D3的活性代谢物二羟维生素D可帮助单核吞噬细胞抑制胞内结核杆菌的生长[10-11]。而VDR基因遗传因子的改变会对二羟维生素D的细胞学功能产生影响。近年来国内外学者针对VDR基因rs2222570位点与结核病的关系展开了系列研究,但结果存在分歧。因此作者对该位点多态性与结核发病进行了系统综述,以期对VDR基因rs2222570位点多态性与结核易感性之间的关系得出更系统和针对性的结论。
1 材料与方法
1.1 文献检索 英文文献来源为Pubmed数据库、谷歌学术、Springer、Wiley、Elsevier S全文数据库;检索词为tuberculosis、vitamin D、polymorphism、vitamin D receptor,或者 tuberculosis、vitamin D、vitamin D receptor、SNP。中文文献来源为CNKI、万方医学网、维普数据库;检索词为结核病、维生素D、维生素D受体、多态性,或者为结核病、维生素D、维生素D受体、SNP。
1.2 文献纳入和排除标准 纳入标准:①国内外公开发表的关于结核病和VDR基因rs2222570位点多态性的文献。②所有病例均符合WTO结核病诊断标准。③研究设计为病例对照研究。④研究中有等位基因、基因型频率的具体数据。⑤研究对象对照组的基因型频率符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡。排除标准:①综述和评论。②重复发表的文献。③研究类型不属于病例对照研究。④未设立对照组,只针对结核病发病情况的研究。⑤其他位点的研究。⑥资料不完整、数据描述不清楚的文献。⑦对照组基因型不符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡。⑧文献所在杂志级别较低。
1.3 统计学处理 用Revman 5.3软件对数据进行统计处理和分析。效应变量选择OR值。用基于χ2的Q检验统计量和I2进行异质性检验;若存在异质性,使用随机效应模型;若存在较小的异质性,用固定效应模型。绘制漏斗图进行发表偏倚评估,同时对所纳入的数据用Stata 12.0进行Begg's和Egger's线性回归检验。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果 根据检索策略,初步检索到英文文献521篇,中文文献258篇。通过阅读中文题目和摘要,排除720篇,筛选出59篇文献。认真阅读全文按照纳入和排除标准进行审核,排除33篇文献。对纳入的26篇文献的对照组进行Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验,排除6篇,最终纳入20篇文献进行meta分析(表1)。共计包括结核病患者4 896例和健康对照6 057例。

表1 纳入文献基本信息
2.2 基因型分析 结果见表2。VDR基因 rs2222570位点基因型与结核病发病无统计学关联(表2)。Begg's 检验和Egger's检验结果表明不存在明显的发表偏倚。
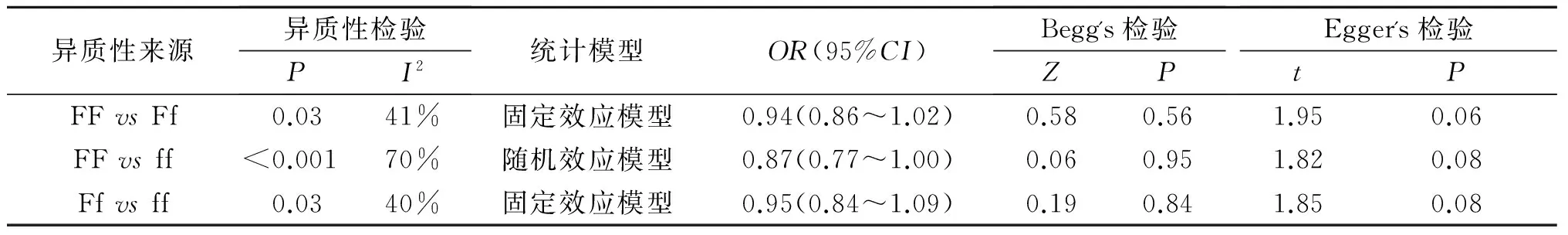
表2 VDR基因 rs2222570位点基因型与结核病发病相关性的meta分析结果
2.3 遗传模型分析 见图1~3、表3。结果表明,显性模型与结核发病有关,Begg's 检验和Egger's检验结果表明不存在明显的发表偏倚。
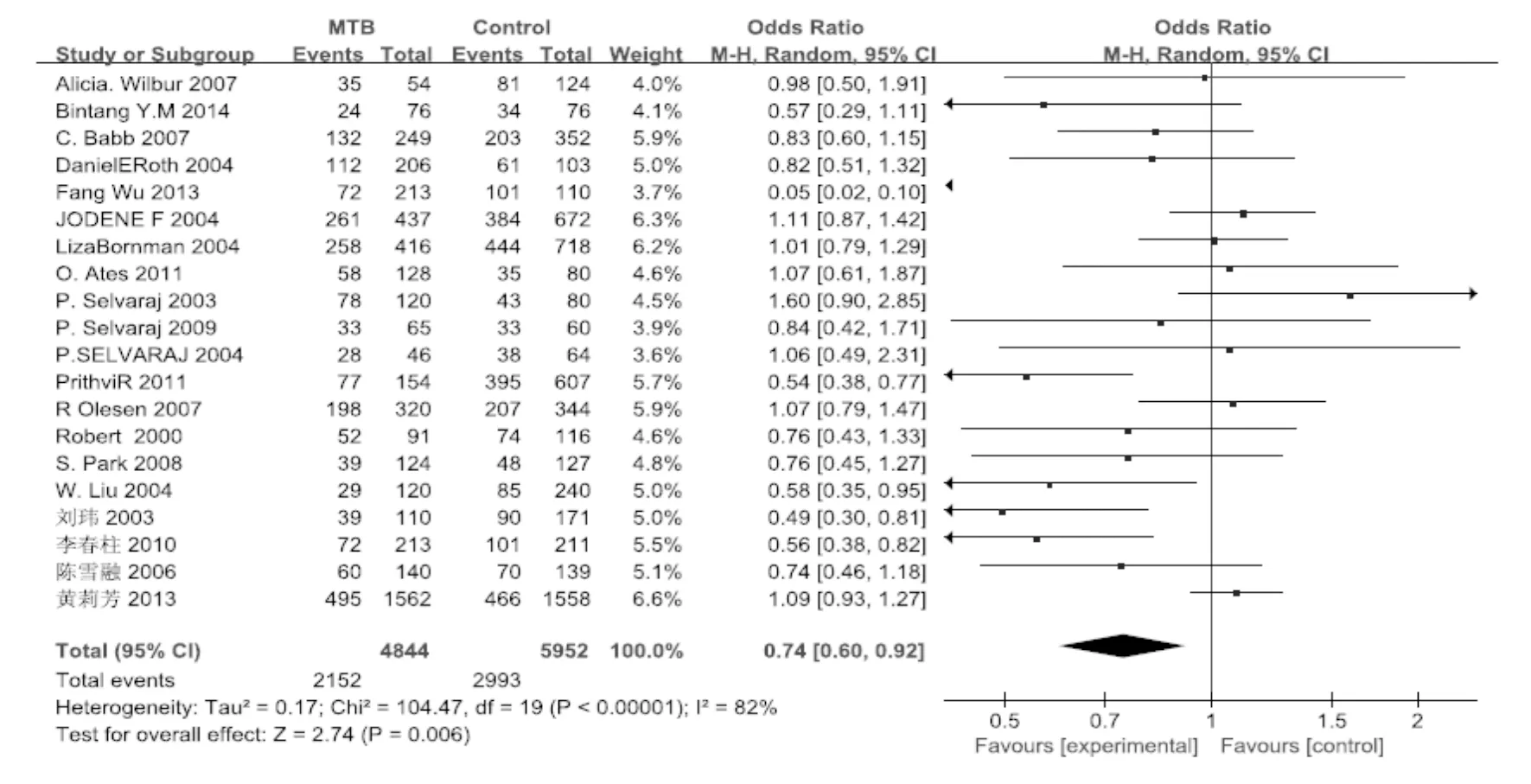
图1 VDR基因 rs2222570位点显性模型与结核发病关联的森林图

图2 VDR基因 rs2222570位点隐性模型与结核发病关联的森林图
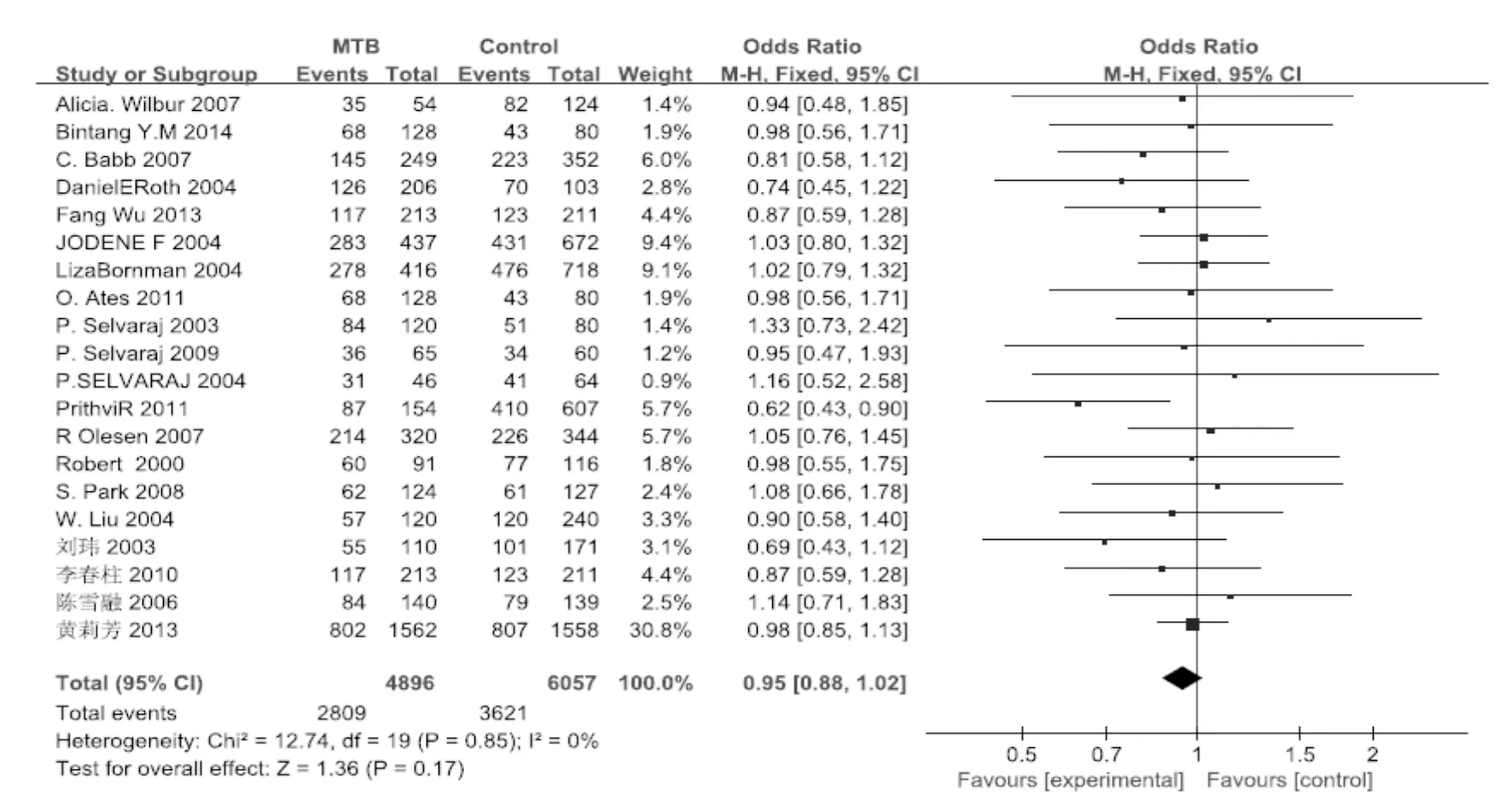
图3 VDR基因 rs2222570位点超显性模型与结核发病关联的森林图表3 VDR基因 rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病相关性的meta分析结果

异质性来源异质性检验PI2统计模型OR(95%CI)Begg's检验ZPEgger's检验tP显性模型<0.00182%随机效应模型0.74(0.60~0.92)0.450.65-1.950.07隐性模型<0.00165%随机效应模型1.28(0.98~1.69)0.060.94-0.850.08超显性模型0.850%固定效应模型0.95(0.88~1.02)0.520.60-0.940.06
2.4 等位基因分析 因存在明显异质性(I2=73%,P<0.001),故采用随机效应模型,森林图见图4。VDR基因 rs2222570位点等位基因F与结核发病有关(OR=0.84,95%CI=0.73~0.95,P=0.007)。结合显性模型的结果说明,F为结核发病的保护因素。Begg's 检验(Z=0.32,P=0.75)和Egger's检验(t=1.90,P=0.07)结果表明不存在明显的发表偏倚。

图4 VDR基因 rs2222570位点等位基因F与结核发病关联的森林图
2.5 敏感性分析 每次去除一个研究,然后计算剩余研究的合并OR值,进行敏感性分析。结果表明去除任一研究均不改变meta分析最终结局,只是对合并OR值大小略有影响,说明表明meta分析结果可靠和稳定。
3 讨论
据WTO统计,目前结核杆菌感染者约占全球总人口的1/3,每天约有8 000人死于结核病,每年约有300万人死于结核病。
作者对VDR受体基因rs2222570位点多态性与结核发病的关系进行了meta分析,结果表明两者存在相关性,该位点的F等位基因为结核发病的保护因素。Selvaraj等[6]2004年的研究也表明该位点FF通过调节维生素D的免疫协调机制增加了VDR受体的表达。在我国,苏倩等[29]对重庆地区人群的研究结果表明Fok I -ff基因型、吸烟及结核病患者接触史在结核发病中存在明显的交互作用。Liu等[13]进行的研究结果表明结核病患者较健康对照存在更高的ff基因型频率。 Wilkinson等[12]研究认为该位点突变为T不会增加结核病的发病风险。Bornman等[20]认为VDR受体FokI RFLP 与结核的发病没有相关性。冯福民等[30]对唐山人群的研究亦未发现VDR基因型与肺结核发病有关。杨本付等[31]对6篇国外文献进行meta分析,结果亦表明尚不能认为VDR基因多态性是肺结核易感性的影响因素。
Meta分析中异质性产生的原因主要有临床异质性、方法学异质性和统计学异质性。此次Meta分析显示个别研究存在较大异质性。入选文献涉及的地域、 种族差异较大,性别和年龄分布不同,这些因素均能解释异质性较大的问题。今后可对地域和种族进行分层, 对性别和年龄进行校正后进一步分析。
发表偏倚是影响meta分析质量的一个很重要的因素。虽然VDR受体基因rs2222570位点的FF和ff、Ff和ff以及隐性基因模型存在发表偏倚,但在显性模型和等位基因与结核病的相关性方面发表偏倚并不明显。
此外,该研究仍存在以下局限性:①筛选的文章均为中英文发表的原始文献,未纳入其他语种,存在语言上的局限性。②纳入文献的基因检测方法不完全一致,可能导致实验结果存在偏倚。③纳入的原始文献数量有限,样本量偏小。
综上所述,该研究结果表明,VDR基因rs2222570位点F等位基因是结核发病的保护因素。
[1]WHO.Global Tuberculosis Control Report 2010:summary[J].Cent Eur J Public Health,2010,18(4):237
[2]FERNANDO SL,SAUNDERS BM,SLUYTER RA,et al.A polymorphism in the P2X(7) gene increases susceptibility to extrapulmonary tuberculosis[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2007,175(4):360
[3]BELLAMY R,RUWENDE C,CORRAH T,et al.Tuberculosis and chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Africans and variation in the vitamin D receptor gene[J].J Infect Dis,1999,179(3):721
[4]LEWIS S,BAKER I,DAVEY SMITH G,et al.Meta-analysis of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and pulmonary tuberculosis risk[J].Int J Tuberc Lung Dis,2005,9(10):1174
[5]ROTH DE,SOTO G,ARENAS F,et al.Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and response to treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis[J].J Infect Dis,2004,190(5):920
[6]SELVARAJ P,CHANDRA G,JAWAHAR MS,et al.Regulatory role of vitamin D receptor gene variants of Bsm I, Apa I, Taq I, and Fok I polymorphisms on macrophage phagocytosis and lymphoproliferative response to mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen in pulmonary tuberculosis[J].J Clin Immunol,2004,24(5):523
[7]WILBUR AK,KUBATKO LS,HURTADO AM,et al.Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and susceptibility M.tuberculosis in native Paraguayans[J].Tuberculosis (Edinb),2007,87(4):329
[8]DAVIES PD.Tuberculosis and migration. The Mitchell Lecture 1994[J].J R Coll Physicians Lond,1995,29(2):113
[9]WILKINSON RJ,PASVOL G.Tuberculosis, HIV, hormones and children[J].J R Coll Physicians Lond,1995,29(2):86
[10]ROCKETT KA,BROOKES R,UDALOVA I,et al.1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces nitric oxide synthase and suppresses growth of mycobacterium tuberculosis in a human macrophage-like cell line[J].Infect Immun,1998,66(11):5314
[11]ROOK GA,STEELE J,FRAHER L,et al.Vitamin D3,gamma interferon,and control of proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by human monocytes[J].Immunology,1986,57(1):159
[12]WILKINSON RJ,LLEWELYN M,TOOSSI Z,et al.Influence of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms on tuberculosis among Gujarati Asians in West London:a case-control study[J].Lancet,2000,355(924):618
[13]LIU W,CAO WC,ZHANG CY,et al.VDR and NRAMP1 gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis among the Chinese Han population: a case-control study[J].Int J Tuberc Lung Dis,2004,8(4):428
[14]SELVARAJ P,CHANDRA G,KURIAN SM,et al.Association of vitamin D receptor gene variants of BsmI, ApaI and FokI polymorphisms with susceptibility or resistance to pulmonary tuberculosis[J].Curr Sci,2003,84(12):1564
[15]FITNESS J,FLOYD S,WARNDORFF DK,et al.Large-scale candidate gene study of tuberculosis susceptibility in the Karonga district of northern Malawi[J].Am J Trop Med Hyg,2004,71(3):341
[16]SELVARAJ P,PRABHU ANAND S,HARISHANKAR M,et al.Plasma 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 level and expression of vitamin d receptor and cathelicidin in pulmonary tuberculosis[J].J Clin Immunol,2009,29(4):470
[17]OLESEN R,WEJSE C,VELEZ DR,et al.DC-SIGN (CD209), pentraxin 3 and vitamin D receptor gene variants associate with pulmonary tuberculosis risk in West Africans[J].Genes Immun,2007,8(6):456
[18]SHARMA PR,SINGH S,JENA M,et al.Coding and non-coding polymorphisms in VDR gene and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in tribes, castes and Muslims of Central India[J].Infect Genet Evol,2011,11(6):1456
[19]BABB C,VAN DER MERWE L,BEYERS N,et al.Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and sputum conversion time in pulmonary tuberculosis patients[J].Tuberculosis (Edinb),2007,87(4):295
[20]BORNMAN L,CAMPBELL SJ,FIELDING K,et al.Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to tuberculosis in West Africa: a case-control and family study[J].J Infect Dis,2004,190(9):1631
[21]黄莉芳,姜伟,王群刚,等.维生素D 及其受体基因遗传多态与结核病发病风险的关联研究[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2013,17(10):895
[22]李春柱,彭杰,韩翠英,等.维生素D受体基因多态性与新疆哈萨克族结核病的关联研究[J].石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2010,28(3):330
[23]刘玮,张翠英,田磊,等.中国汉族人群肺结核易感基因的病例对照研究[J].军事医学科学院院刊,2003,27(6):409
[24]陈雪融,冯玉麟,马玙,等.维生素D受体基因多态性与中国藏族结核病的关联研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2006,37(6):847
[25]WU F,ZHANG W,ZHANG L,et al.NRAMP1, VDR, HLA-DRB1, and HLA-DQB1 gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to tuberculosis among the Chinese Kazakh population: a case-control study[J].Biomed Res Int,2013:484535
[26]PARK S,KIM EJ,LEE SH,et al.Vitamin D-receptor polymorphisms and non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease in Korean patients[J].Int J Tuberc Lung Dis,2008,12(6):698
[27]SINAGA YB,AMIN M,SIREGAR Y,et al.Correlation between Vitamin D receptor gene FOKI and BSMI polymorphisms and the susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in an Indonesian Batak-ethnic population[J].Acta Med Indones,2014,46(4):275
[28]ATES O,DOLEK B,DALYAN L,et al.The association between BsmI variant of vitamin D receptor gene and susceptibility to tuberculosis[J].Mol Biol Rep,2011,38(4):2633
[29]苏倩,向颍,胡代玉,等.VDR基因多态性、环境因素与重庆地区肺结核病的联系及交互作用研究[J].局解手术学杂志,2012,21(4):361
[30]冯福民,郭梅,郝金奇,等.维生素D受体基因多态性与汉族人肺结核发病的关系[J].山东医药,2009,49(45):4
[31]杨本付,韩长磊.维生素D受体基因多态性与肺结核关系的Meta分析[J].中国热带医学,2006,6(8):1347
(2015-12-09收稿 责任编辑王 曼)
Meta analysis on association between vitamin D receptor gene rs2222570 polymorphisms and tuberculosis risk
SHIJie,ZHUYankun,ZHENGDanwei,MAXiaoguang,WANGShaohua,LIHui,XINGJin,WUCaixia
HenanProvinceCenterforDiseaseControlandPrevention,Zhengzhou450016
tuberculosis;vitamin D receptor gene;rs2222570;meta analysis
Aim: To determine the association of the vitamin D receptor(VDR) gene rs2222570 polymorphisms with the risk of tuberculosis(TB). Methods: We searched for association studies correlating the VDR polymorphisms and TB using pre-established keywords in Database system. Meta analysis was conducted with random effects model or fixed effects model to account for heterogeneity between studies. Twenty studies were included in the VDR gene rs2222570 meta analysis. Data were analyzed in respect to associations between genotypes, alleles, genetic model and TB. Results: The results of meta analysis showed that the risk of TB was decreased in the F allele carriers(OR=0.84,95%CI=0.73~0.95); among Henan population with dominant models, the risk of TB was lower(OR=0.74,95%CI=0.60~0.92).Conclusion: VDR gene rs2222570 polymorphisms may be associated with the risk of TB.
10.13705/j.issn.1671-6825.2016.06.021
*“十二五”科技重大专项课题 2014ZX10003002;河南省科技厅课题
R520.2

