3 影响微裂缝发育程度的微观地质因素选取
3 影响微裂缝发育程度的微观地质因素选取
前人研究表明,鄂尔多斯盆地延长组储层微裂缝发育状况是沉积微相带及基底断裂基础上,成岩过程中多期古构造应力场与现今构造应力场共同作用的结果(王瑞飞等,2009),主要发育3种类型裂缝:构造应力缝、层间缝和成岩破裂缝(曾联波等,2007)。鉴于微裂缝发育程度受多种地质因素影响,本次研究综合考虑储层的岩性、物性、沉积微相、微构造以及差异压实等几个方面对微裂缝发育程度的影响,从而定量地表征微裂缝发育程度与各影响因素之间的关系。
(1)岩性是影响储层裂缝发育的内部因素,岩石的脆性很大程度上由岩石的矿物成分所控制(Buller et al.,2010;孟庆峰等,2012;赵金洲等,2013)。在相同应力作用下,储层的天然裂缝在脆性矿物富集位置或脆性矿物附近更发育。
(2)沉积成岩作用对非构造缝形成起控制作用(龙鹏宇等,2011;龙鹏宇等,2012;张顺等,2015)。沉积物颗粒大小在一定程度上反映了沉积过程中水动力条件发生变化,通常岩石粒径中值越小,颗粒越细,微裂缝越发育。
(3)上覆地层压力能在一定程度上反映储层的微构造特征、差异压实作用之间的差异,是裂缝形成的关键因素(王晓波等,2014)。岩石承受的上覆岩层压力越大,压实作用越强烈,势必造成孔隙度的缩小,储层物性越差,岩性越致密,越有利于微裂缝的发育。
(4)均值系数在一定程度上反映储层微观孔隙结构特征的品质好坏。均值系数越大,说明储层物性越差(王瑞飞等,2008),岩性越致密,越有利于微裂缝的发育。
4 应用实例分析
华庆地区地处甘肃省华池县-庆阳县境内,构造位置处于伊陕斜坡的西部(图1);在地质构造上,与区域构造基本一致,总体表现为西倾单斜构造,无断层发育,单斜坡度一般小于1°,平均坡降为7m/ km,局部区域发育数排NW-SE向的小型鼻状隆起(何自新,2003;李建明等,2011;杨友运等,2015)。
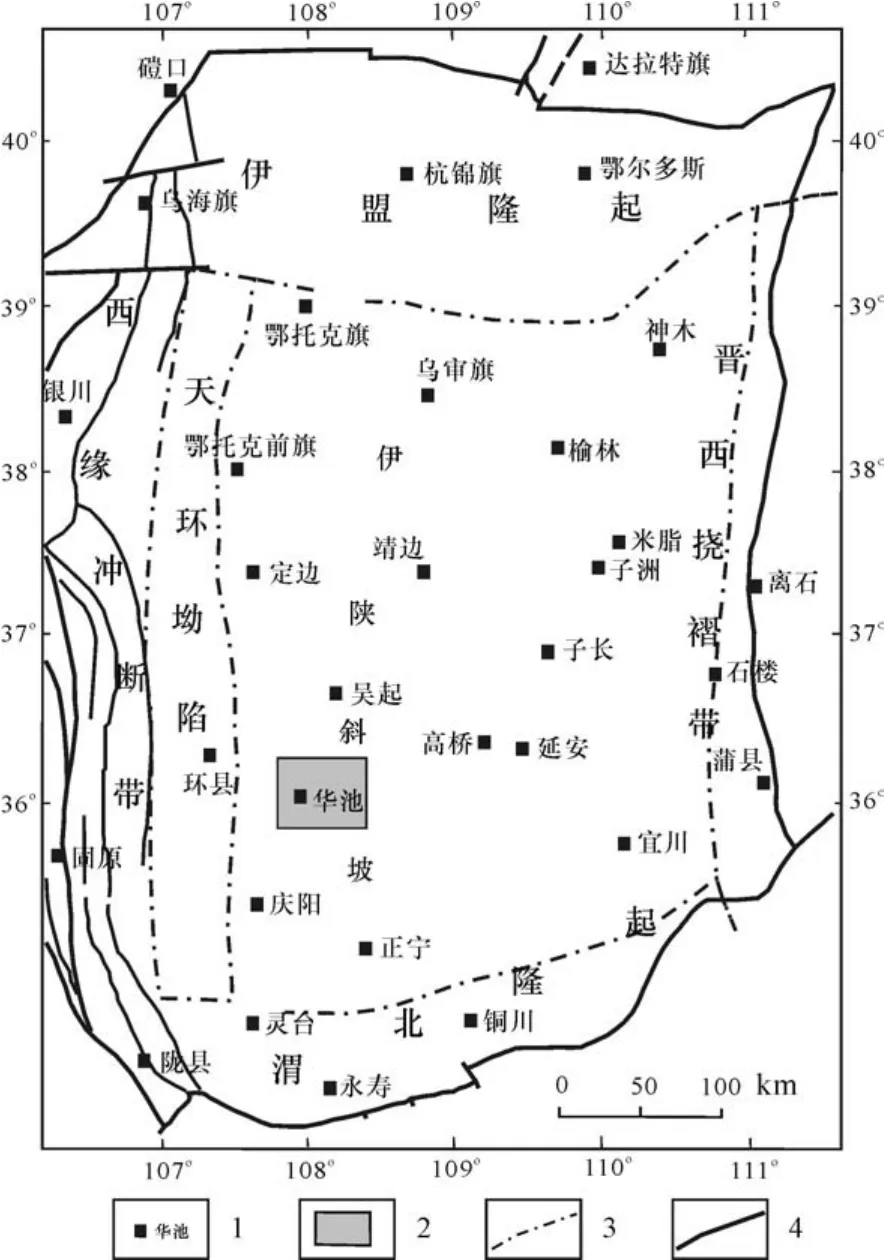
图1 研究区构造位置Fig.1 Tectonic setting of the study area
本次微裂缝发育程度研究应用薄片镜下观测统计技术,通过对研究区9口取心井的岩心样品铸体薄片进行微裂缝统计分析,采用微裂缝线密度(单位长度内垂直于一组给定方位的平行微裂缝所测量的、规则相同的微裂缝条数)这一参数表征微裂缝发育程度,选取脆性矿物总含量、上覆地层压力、孔隙度、粒度中值、均值系数等5个微观地质因素作为评价微裂缝发育程度的指标,其原始数据见表1。
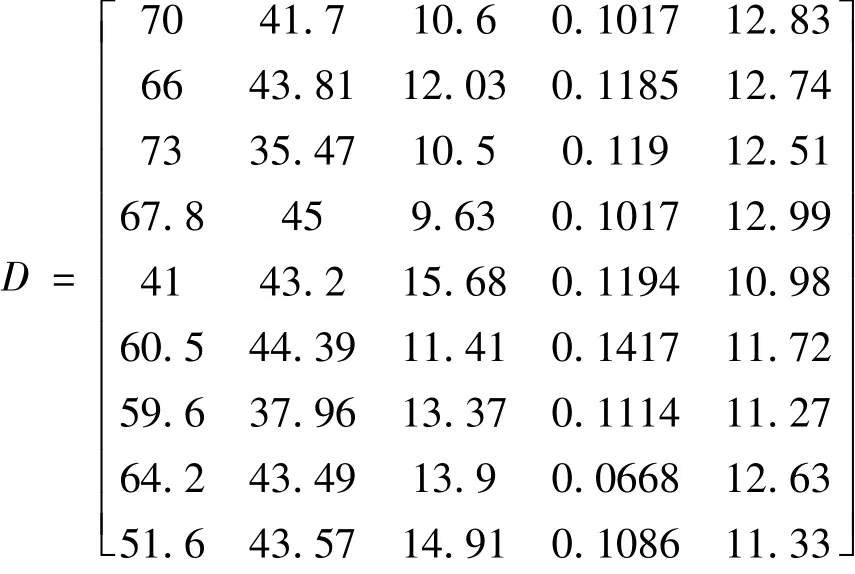
根据表1表征参数各项指标的原始数据,确定微裂缝线密度X0=(7,2.5,3.5,6.5,0.5,2,2,2.5,1)作为评价的参考数列,影响微裂缝发育程度的各微观地质因素的表征参数指标值构成比较数列矩阵D,即:
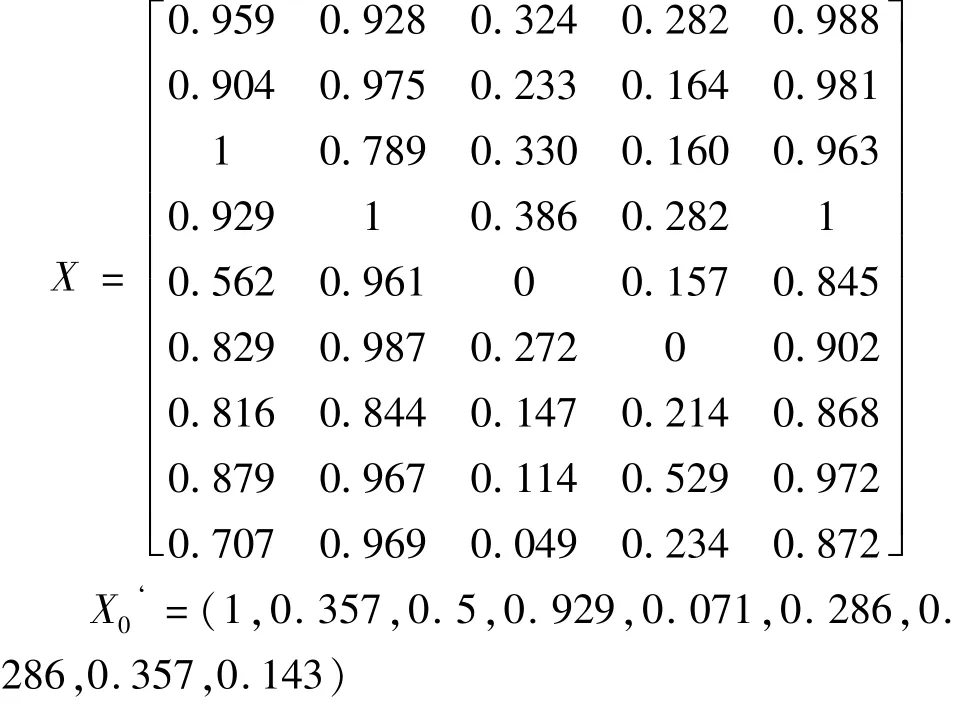
将原始表征微观地质特征的参数矩阵D和参考数列X0=(14,5,7,13,1,4,4,5,2),进行无量纲化处理后可得矩阵X,即:
将无量纲化后的数据代入关联系数计算公式(式3)中可得第k个表征参数的第i时刻与参考数列差的绝对值。即:

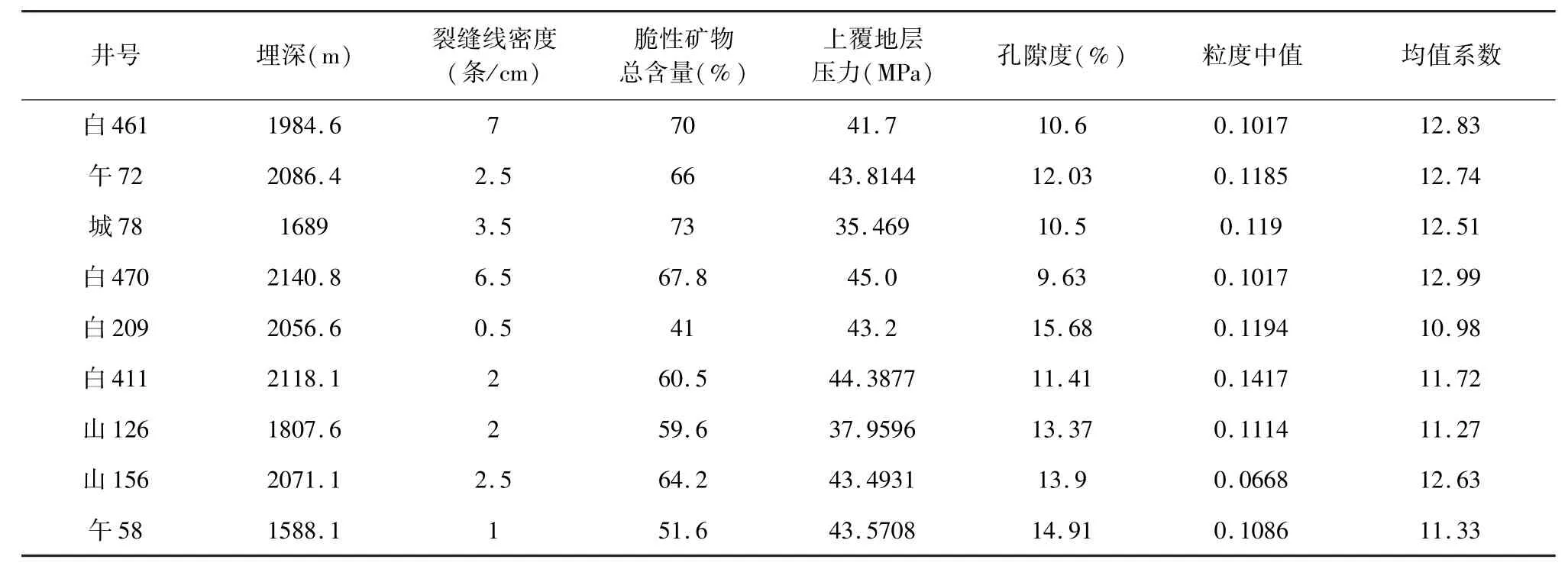
表1 微裂缝发育程度及表征参数各项指标原始数据Table 1 Development degrees ofm icro cracks and raw data of indexes characterizing parameters
然后,根据计算公式(式4、式5、式6、式7)计算出第k个表征微观地质特征的参数的第i时刻与参考数列差的关联系数,即:
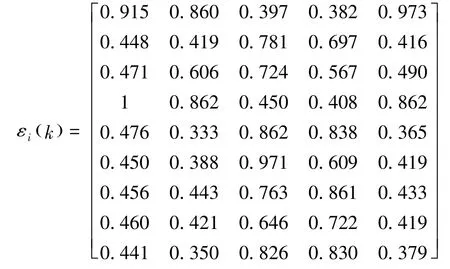
根据公式(式8)算出个评价值指标关联度,如表2所示。
由表2微观地质因素与微裂缝发育程度的关联度可以看出,孔隙度>粒度中值>脆性矿物总含量>均值系数>上覆地层压力。
由于孔隙度、粒度中值与微裂缝发育程度的关联度相对较大,因此孔隙度、粒度中值是华庆地区长6低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育的主控因素,脆性矿物总含量、上覆地层压力、均值系数这3个微观地质因素对华庆地区长6低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育也有一定影响,且影响程度相当,但是与孔隙度和粒度中值相比较而言,不是很大。
5 结论
(1)孔隙度、粒度中值是华庆地区长6低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育的主控因素,脆性矿物总含量、上覆地层压力、均值系数这3个微观地质因素是次要因素。孔隙度越低、孔喉半径越细,流体的渗流能力就越差,越不利于流体的交换,易造成压力的积聚形成过剩压力,然而砂岩又属于刚性地层,容易产生微裂缝,使已产生的异常压力破坏,形成相对较高过剩压力区内的低压区。
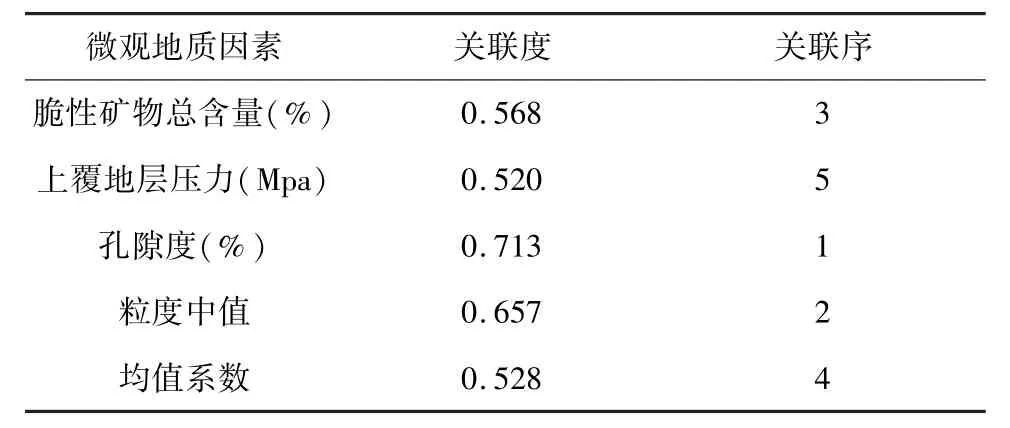
表2 微观地质因素与微裂缝发育程度的关联度及排序Table 2 Correlation and sorting between Micro cracks and Micro geological factors
(2)在系统分析影响低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育程度的微观地质因素的基础上,构建了评价低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育程度指标的分析模型,采用灰色关联分析方法对表征微观地质特征的参数和微裂缝发育程度之间的相关性进行了定量分析评价,使其更有直观性和科学性。
(3)通过应用灰色关联法定量分析微观地质特征的参数和微裂缝发育程度之间关系,发现孔隙度、粒度中值是影响华庆地区长6低渗透致密砂岩储层微裂缝发育程度的主要微观地质敏感参数,为后续研究微观地质表征参数和储层品质参数之间的内在相关性提供了理论上的依据,同时对建立合理的储层微观地质三维表征参数体系具有重要的指导意义。
Buller D,Hughes S,Petre J,Spain D,Odumosu.2010.Petrophysical evaluationfor enhancing hydraulic stimulation in horizon talshale gas wells[C].Proceeding of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition:431-451
He Zi-xin.2003.The evolution and petroleum of Ordos basin[M].Bei-jing:Petroleum Industry Press:1-390(in Chinese)
Li Dao-pin.1997.The development of the low permeability sandstone oilfield[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Ppress:47-48(in Chinese)
Li Jian-ming,Qin Lu,Xu Lun-xun,Wang Xian.2011.Reservoir properties in the6thmember of Yanchang formation in Huaqing area of Ordosbasin[J].Journalof Yangtze University(Nat Sci Edit),8(3): 22-25(in Chinese with English abstract)
Long Peng-yu,Zhang Jin-chuan,JiangWen-li,Nie Hai-kuan,Tang Xuan,Han Shuang-biao,Xing Ya-wen.2012.Analysis on poresforming features and its influence factors of reservoir well Yuye-1[J]. Journal of Central South University(science and technology),43 (10):3954-3963(in Chinese with English abstract)
Long Peng-yu,Zhang Jin-chuan,Tang Xuan,Nie Hai-kuan,Liu Zhujiang,Han Shuang-biao,Zhu Liang-liang.2011.Feature ofmuddy shale fissure and its effect for shale gas exploration and development [J].Natural Gas Geoscience,22(3):525-531(in Chinese with English abstract)
Meng Qing-feng,Hou Gui-ting.2012.Geological controls on shale gas play and potential of shale gas resource in upperYangtze region,China[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,19(1):11-14(in Chinese with English abstract)
Niu Xiao-bing,Hou Gui-ting,Zhang Ju-zeng,Feng Sheng-bin,Zhao Wen-tao,You Yuan,Ju Wei,Wang Fang,Zhang Peng.2014.Assessment criteria formember 6 and 7 tight sand in Ordos basin and its applications[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia,28(3):571-579(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Rui-fei,Chen Ming-qiang,Sun Wei.2008.The research ofmicro -pore structure in super-low permeability sandstone reservoir of the Yanchang Formation in Ordos basin[J].Geological Review,54 (2):270-276(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Xiao-bo,Chen Jian-fa,Li Jian,Wang Dong-liang,Wang Dong-liang,Li Zhi-sheng,Liu Guang-di,Xie Zeng-ye,Sun Ming-liang. 2014.Rock diffusion coefficientmeasuring and its effecting factors of tight gas reservoir under high temperature and high pressure[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum,38(3):25-31(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu Sheng-he,Cai Zheng-qi,Shi Shang-ming.2010.Uranium geology [M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press:283-284(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xie Song-yun,Wang Ying,Xie Yu-bin,Li Hai-bo.2015.Application of grey system theory to determining order of ICA decrypted images [J].Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University,33(1):153 -158(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiong Wei-liang,Pan Zeng-yao,Wang Bin.1999.Distribution of remaining oil and its adjustment in fracture-developed areas of ultralow permeability oilfields[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,26(5):46-48(in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang You-yun,He Kang-ning,Ren Ying-hui.2015.The internal structure pattern analysis of Chang63reservoir of Huaqing area[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,33(2):358-363(in Chinese with English abstract)
Yin Hui,Liu Jin-jun,Guo Jiao-jiao,Ye Jun-hua,Tang Xiao-chuan,Jiang Hong.2014.Application ofwater control and steering hydraulic fracturing technology in high water-cut fractured reservoir-A case study of H1238 well in Huoshaoshan oilfield,eastern Junggar basin[J].Xinjiang Petroleum Geolog,35(3):352-355(in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan Hai-ke,Hao Shi-yan,ZhangWen-zhong.2009.Development regularities of natural fracture of Yanchang formation in Zhidan westarea of Yangchang oilfield[J].Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition),24(5):46-49(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zeng Lian-bo,Li Zhong-xing,Shi Cheng-en,Wang Zheng-guo,Wang Yong-kang.2007.Characteristics and origin of fractures in the extra low-permeability sandstone reservoirs of the upper triassic Yanchang formation in the ordos basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,81 (2):174-180(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Guo-hui,Ren Xiao-juan,Zhang Ning-sheng.2007.Experimental study on the effect ofmicro-fracture on the water displacing oil law in low permeability reservoir[J].Journal of Xi′an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition),22(5):44-47(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Rui-jun,Qiu Ji-wei,Jia Qing-xuan.2014.Multi-objective robust design for reliability based on grey system theory[J].Journalof Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,37(3):23-25 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Shun,Chen Shi-yue,Yan Ji-hua,Tan Ming-you,Zhang Yun-yin,Gong Wen-lei,Wang Guang-zeng.2015.Characteristics of shale lithofacies and reservior space in the3rd and 4thmembers of Shahejie formation,the West of Dongying sag[J].Natural Gas Geoscience,26(2):320-330(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao Jin-zhou,Ren Lan,Hu Yong-quan.2013.Controlling factors of hydraulic fractures extending into Network in shale formations[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(science&technology edition),35(1):1-7(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao Wen-tao,Hou Gui-ting,Zhang Ju-zeng,Feng Sheng-bin,Ju Wei,You Yuan,Yu Xuan,Zhan Yan.2015.Study on the development law of structural fractures of Yanchang Formation in Longdong area,Ordos basin[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,51(6):1047-1058(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao Xiang-yuan,Zeng Lian-bo,Zu Ke-wei,Hu Xiang-yang,Jiao Jun,Zhu Li-feng,Shi Jin-xiong.2016.Brittleness characteristics and its control on natural fractures in tight reservoirs:A case study from Chang 7 tight reservoir in Longdong area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology,37(1):62-71(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou Xin-gui,Zhang Lin-yan,Huang Chen-jun,Wan Xiao-long.2012. Distractionnetwork conceptual model and validity of fractures in Chang 63 low permeable reservoir in Huaqing Area[J].Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition,43(3):689-697(in Chinese with English abstract)
[附中文参考文献]
何自新.2003.鄂尔多斯盆地演化与油气[M].北京:石油工业出版社:1-390
李道品.1997.低渗透砂岩油田开发[M].北京:石油工业出版社:47 -48
李建明,秦璐,徐论勋,汪 弦.2011.鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长63储层物性特征及其影响因素分析[J].长江大学学报(自然科学版),8(3):22-25
龙鹏宇,张金川,姜文利,聂海宽,唐 玄,韩双彪,邢雅文.2012.渝页1井储层孔隙发育特征及其影响因素分析[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版),43(10):3954-3963
龙鹏宇,张金川,唐 玄,聂海宽,刘珠江,韩双彪,朱亮亮.2011.泥页岩裂缝发育特征及其对页岩气勘探和开发的影响[J].天然气地球科学,22(3):525-531
孟庆峰,侯贵廷.2012.页岩气成藏地质条件及中国上扬子区页岩气潜力[J].油气地质及采收率,19(1):11-14
牛小兵,侯贵廷,张居增,冯胜斌,赵文韬,尤 源,鞠 玮,王芳,张 鹏.2014.鄂尔多斯盆地长6-长7段致密砂岩岩心裂缝评价标准及应用[J].大地构造与成矿学,28(3):571-579
王瑞飞,陈明强,孙 卫.2008.鄂尔多斯盆地延长组超低渗透砂岩储微观孔隙结构特征研究[J].地质论评,54(2):270-276
王晓波,陈践发,李 剑,王东良,李志生,柳广弟,谢增业,孙明亮.2014.高温高压致密气藏岩石扩散系数测定及影响因素[J].中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),38(3):25-31
吴胜和,蔡正旗,施尚明.2010.油矿地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社:283-284
谢松云,王 颖,谢玉斌,李海波.2015.利用灰色系统理论确定ICA解密图像的顺序[J].西北工业大学学报,33(1):153 -158
熊维亮,潘增耀,王 斌.1999.特低渗透裂缝发育区剩余油分布及调整技术[J].石油勘探与开发,26(5):46-48
杨友运,何康宁,任颖惠.2015.华庆地区长63储层内部建筑结构模式分析[J].沉积学报,33(2):358-363
尹 辉,刘进军,郭娇娇,叶俊华,唐晓川,江 洪.2014.控水转向压裂技术在高含水裂缝性油藏开发中的应用—以火烧山油田H1238井为例[J].新疆石油地质,35(3):352-355
袁海科,郝世彦,张文忠.2009.延长油田志丹西区延长组天然裂缝发育规律研究.西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),24(5):46 -49
曾联波,李忠兴,史成恩,王正国,赵继勇,王永康.2007.鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝特征及成因[J].地质学报,81(2):174-180
张国辉,任晓娟,张宁生.2007.微裂缝对低渗储层水驱油渗流规律的影响[J].西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),22(5):44 -47
张瑞军,邱继伟,贾庆轩.2014.灰色系统理论的多目标可靠性稳健设计[J].北京邮电大学学报,37(3):23-25
张 顺,陈世悦,鄢继华,谭明友,张云银,龚文磊,王光增.2015.东营凹陷西部沙三下亚段—沙四上亚段泥页岩岩相及储层特征[J].天然气地球科学,26(2):320-330
赵金洲,任 岚,胡永全.2013.页岩储层压裂缝成网延伸的受控因素分析[J].西南石油大学学报(自然科学版),35(1):1-7
赵文韬,侯贵廷,张居增,冯胜斌,鞠 玮,尤 源,于 璇,詹彦.2015.层厚与岩性控制裂缝发育的力学机理研究—以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组为例[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),51 (6):1047-1058
赵向原,曾联波,祖克威,胡向阳,焦 军,朱利锋,史今雄.2016.致密储层脆性特征及对天然裂缝的控制作用—以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7致密储层为例[J].石油与天然气地质,37 (1):62-71
周新桂,张林炎,黄臣军,万晓龙.2012.华庆地区长63储层裂缝分布模型与裂缝有效性[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版,43(3): 689-697
Correlation Analysis of Microscopic Geological Factors and Micro Cracks Based on Grey Association
DONG Feng-juan1,LU Xue-fei2,LIU Min-yan3,RAO Xin-jiu4
(1.College ofpetroleum engineering,Xi'an Petroleum University,Xi'an,Shaanxi 710065;2.College ofSciences,X i'an Petroleum University,Xi'an,Shaanxi 710065;3.Dingbian Oil Factory,Yanchang Oil Field Corporation,Yulin,Shaanxi 718600;4.Exploration&Development Research Institute ofPetrol china Changqing Oilfield Company,Xi'an,Shaanxi 710018)
This study focuses on complexmicroscopic geological factors that influence development degree ofmicro cracks in tight-sandstone reservoirs.Taking Chang 6 tight sandstone reservoir of the Huaqing area in Ordos Basin as an example,we reveal the relationship between the developmentof micro cracks and various influencing factorsusing themethod of grey association.The results show that thisapproach is applicable for such issues,which allows us to determine themajormicro geologic factors that influence crack development and its degrees.They fairly coincidewith the realmeasurements,and provide a theoretical basis for characterizing themicro cracks in the target reservoirs.
Huaqing region,Chang 6 reservoir,micro cracks,influencing factors,grey association

