在Android中设计和实现简单的计算能力测试系统
欧阳桂秀
摘 要
介绍了Android中Intent类的一个构造方法,使用这个构造方法来创建Intent类的对象,实现同一个应用程序中多个Activity对象的切换,从而实现更多的功能。
【关键词】计算 测试 Android Activity Intent
1 引言
一个应用程序可以包含若干个Activity。可以让某个Activity对象使用Intent对象来启动其它的Activity对象。
2 Intent类的一个构造方法
Intent(Context packgeContext ,Class <?> cls):该构造方法的参数packgeContext是当前应用程序所在的上下文,参数cls是打算启动的Activity对象的类的名字。
例如:
假设,已经有如下类的声明:
class Calculator extends Activity
class MainCalculator extends Activity
那么,下面这条语句
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MainCalculator.class);
作用是:当前类的对象(Calculator类的当前对象this),打算启动的Activity对象的类的名字是MainCalculator。
接下来的语句
startActivity(intent);
作用是:实现两个Activity之间的切换。从当前的Activity,启动另外一个Activity,即 MainCalculator。
3 一个Activity对象使用Intent对象来启动另一个Activity对象的实例
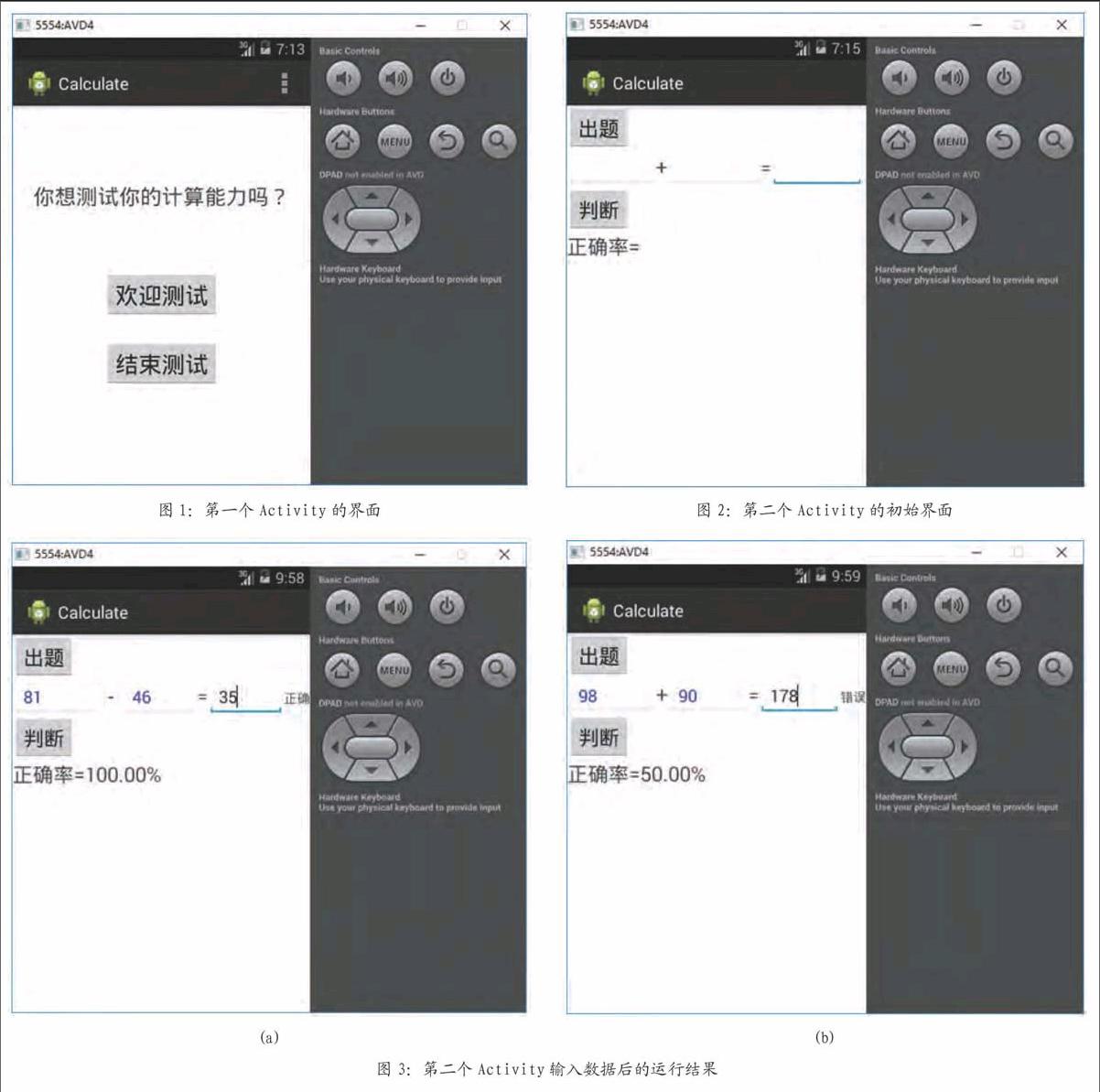
【例1】在Android中实现简单的计算能力测试系统。计算随机给出的两位数的加减法算术题,要求用户回答,答对的提示“正确”,答错的提示“错误”。随时给出答题的正确率。
(1)第一个Activity的相关程序,文件Calculator.java:
package com.example.calculate;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.ActivityNotFoundException;
import android.view.View;
import android.content.Intent; //加
public class Calculator extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.welcome);
}
public void display(View view){
Intent intent=new Intent(this,MainCalculator.class);
try {
startActivity(intent);
}
catch(ActivityNotFoundException exp) {
AlertDialog.Builder build=new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
AlertDialog dialog = build.create();
dialog.setTitle("can not find activity!");
dialog.show();
}
}
public void endTest(View view){
System.exit(0);
}
}
(2)第二个Activity的相关程序,文件MainCalculator.java:
package com.example.calculate;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.*;
public class MainCalculator extends Activity {
EditText texta,textb,textc;
TextView labela,label3,label4;
Button problem,judge;
int a,b,right_answer,answer,op,temp;
float p,right,total;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.test);
texta = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.texta); //被加数(被减数)
textb= (EditText)findViewById(R.id.textb); //加数(减数)
textc = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.textc); //输入计算结果
labela=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.labela); //运算符“+”或“-”
label3=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.label3); //输出“正确”或“错误”的提示信息
label4=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.label4); //正确率
problem=(Button)findViewById(R.id.problem); //“出题”按钮
judge=(Button)findViewById(R.id.judge); //“判断”按钮
}
public void show(View view){
texta.setText(" ");
textb.setText(" ");
textc.setText(" ");
label3.setText(" ");
a=(int)(Math.random( )*100)+1;
b=(int)(Math.random( )*100)+1;
op=(int)(Math.random( )*2);
if(op<1)
{
labela.setText("+");
texta.setText(String.valueOf(a));
textb.setText(String.valueOf(b));
right_answer=a+b;
}
else
{
labela.setText("-");
if(a { temp=a; a=b; b=temp; } texta.setText(String.valueOf(a)); textb.setText(String.valueOf(b)); right_answer=a-b; } } public void decide(View view){ total++; String s2=" "; s2=textc.getText().toString(); answer=Integer.parseInt(s2.trim()); if (right_answer==answer) { label3.setText("正确"); right++; } else { label3.setText("错误"); } p=(right/total)*100; String s3=String.format("%.2f", p); label4.setText("正确率="+s3+"%"); } } (3)配置文件AndroidManifest.xml,在之前,新增加Activity 语句如下: 第一个Activity的界面如图1所示。 单击图1的“欢迎测试”按钮,出现的第二个Activity的初始界面如图2所示。 第二个Activity,单击“出题”按钮,输入运算结果,然后单击“判断”按钮,运行结果如图3所示。 4 结束语 通过学习Android中Intent类的构造方法,我们可以使用Intent类的构造方法来创建Intent类的对象,实现同一个应用程序中多个Activity对象的切换,从而实现更多的功能。 这个简单的计算能力测试系统的界面welcome.xml和test.xml比较简单,在这里就不介绍了。另外,这个系统还可以扩展,实现乘、除等计算功能。限于篇幅,不再详细讲解了。 参考文献 [1]耿祥义,张跃平.Android手机程序设计实用教程[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2013. [2]李刚.疯狂Android讲义[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2013. [3]明日科技.Android从入门到精通[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2012.
电子技术与软件工程2016年18期
