CYP2C19基因多态性及患者主要临床资料与氯吡格雷药物抵抗的相关性研究
姜金坪,杜晓明,孙亚欣,马淑梅*
CYP2C19基因多态性及患者主要临床资料与氯吡格雷药物抵抗的相关性研究
姜金坪a,杜晓明b,孙亚欣b,马淑梅a*
目的观察药物代谢酶系统中CYP2C19基因多态性及患者主要临床资料与服用氯吡格雷前后血小板聚集率变化(氯吡格雷药物抵抗)的相关性。方法入选拟行冠脉造影检查或支架植入治疗患者35例,根据围手术期应用氯吡格雷前后血小板聚集率变化,将患者分为氯吡格雷抵抗组和非抵抗组。检测CYP2C19基因型,并记录患者年龄、性别、烟酒史、高血压、糖尿病等主要临床资料,分析基因水平及临床水平各因素对血小板聚集及氯吡格雷药物抵抗的影响。结果检测出氯吡格雷抵抗的患者15例,CYP2C19慢代谢基因型患者4例,Logistic回归分析显示,CYP2C19基因型是氯吡格雷抵抗的危险因素(OR=1.236,95%CI:0.273~5.599,P=0.049)。结论CYP2C19基因型在基因水平与氯吡格雷抵抗相关,临床水平资料未见明显相关性。
血小板聚集功能;氯吡格雷抵抗;CYP2C19基因多态性
0 引言
阿司匹林及氯吡格雷双联抗血小板治疗是冠心病心绞痛及急性冠脉综合征住院患者围手术期的常规治疗方法[1]。随着氯吡格雷抵抗及新型ADP P2Y12受体抑制剂(普拉格雷、替格瑞罗)的出现,针对不同患者实施个体化治疗越来越被关注[2-3]。因为CYP2C19基因多态性与支架内血栓及再发心肌梗死密切相关,CYP2C19基因多态性被认为是导致氯吡格雷抵抗在基因水平的影响因素[4-12]。临床可应用ADP诱导血小板聚集来衡量氯吡格雷应用后对血小板聚集功能抑制的有效性,本文于用药前及用药后分别检测血小板聚集功能,根据药物应用前后血小板聚集率变化来定义氯吡格雷抵抗组及非抵抗组。现报道如下。
1 对象与方法
1.1研究对象选取2014年12月至2015年1月入住我院预计接受冠脉造影检查或支架植入治疗患者35例。所有入选患者入院前均未服用过阿司匹林、氯吡格雷等抗血小板治疗药物,患者年龄18~85岁,性别不限,主要临床诊断为冠心病、稳定型心绞痛、急性冠脉综合征均可。入院即检测用药前血小板聚集功能,急诊手术患者给予阿司匹林及氯吡格雷负荷量各300 mg,至少6 h后检测用药后血小板聚集功能;择期手术患者接受阿司匹林100 mg/d、氯吡格雷75 mg/d口服,至少7 h后检测用药后血小板聚集功能。
1.2研究方法
1.2.1血小板聚集功能检测应用南京神州英诺华医疗科技有限公司研发的PL-11自动化血小板聚集功能检测仪测定血小板聚集率。静脉采血,枸橼酸钠1∶9比例抗凝;取全血标本0.5 mL加0.9%生理盐水0.5 mL,放置在试验槽内,10 min后进行测定[13]。Muller[14]定义最大血小板聚集基线水平与服用氯吡格雷后最大血小板聚集率变化<10%为无反应,10%~29%为半反应,>30%为正常反应。本试验将用药前后血小板聚集率变化率<30%定义为氯吡格雷药物抵抗组,变化率≥30%定义为非抵抗组。
1.2.2CYP2C19基因型检测应用上海百傲科技有限公司生产的CYP2C19基因检测芯片试剂盒进行CYP2C19基因型多态性检测。静脉采血2 mL,加至EDTA抗凝管中,并充分混匀,血液标本采集后及时检测,操作流程包括样本DNA抽提-PCR扩增-杂交检测等。通过分离外周血淋巴细胞基因组DNA,分别用一对等位基因特异性的反向引物与共用正向引物进行PCR扩增,通过电泳分析对应的PCR产物来判断CYP2C19基因型。CYP2C19等位基因主要是*1、*2、*3型,CYP2C19*2和CYP2C19*3是基因突变的主要类型。野生型(*l/*1)为快代谢型,突变杂合型(*1/*2,*1/*3)为中间代谢型,突变纯合型(*2/*2,*2/*3,*3/*3)为慢代谢型。
1.2.3患者主要临床资料记录所有研究对象性别、年龄、体重指数(BMI)、吸烟及饮酒史、高血压及糖尿病病史、胆固醇、三酰甘油、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白、糖化血红蛋白、血肌酐、血尿酸、血小板计数、纤维蛋白原、D-二聚体等临床资料。

2 结果
2.1CYP2C19基因型分布入选35例患者中,CYP2C19基因型分布为快代谢基因型15例(42.86%),中间代谢基因型16例(45.71%),慢代谢基因型4例(11.43%),见表1。
2.2血小板聚集功能变化率患者用药前血小板最大聚集率为55.94%±15.62%,用药后血小板最大聚集率为34.83%±17.07%;用药前后聚集功能变化率为37.73%±25.15%。其中聚集功能变化率<30%(氯吡格雷药物抵抗)15例(42.86%),变化率≥30%(非抵抗)20例(57.14%)。
2.3主要临床指标统计入选35例患者中,男20例,女15例,年龄26~80岁,平均59岁,两组患者的临床资料见表2。对存在差异项目进行Logistic回归分析,只有CYP2C19基因型(OR=1.236;95%CI:0.273~5.599;P=0.049<0.05)是氯吡格雷抵抗的危险因素,具体见表3。且与*1/*1基因型相比,*1/*2,*1/*3基因型OR=1.846,*2/*2基因型OR=4.846。
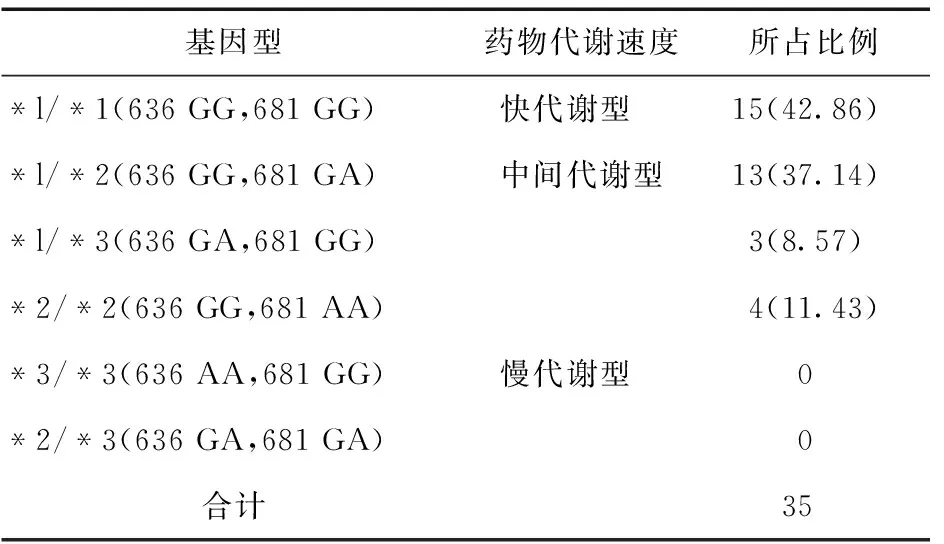
表1 CYP2C19基因型结果统计(例,%)
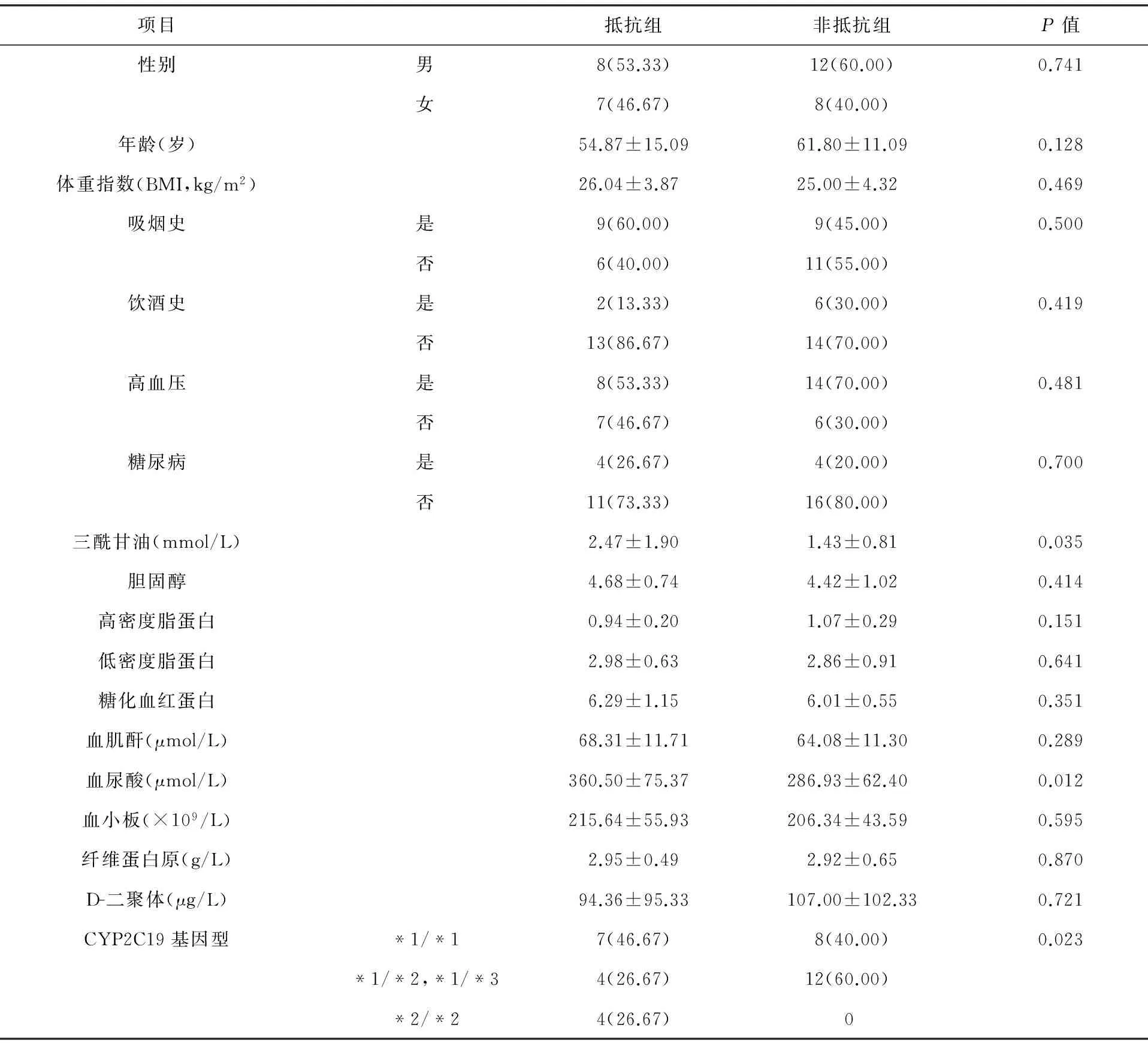
表2 入选患者一般资料(例,%)
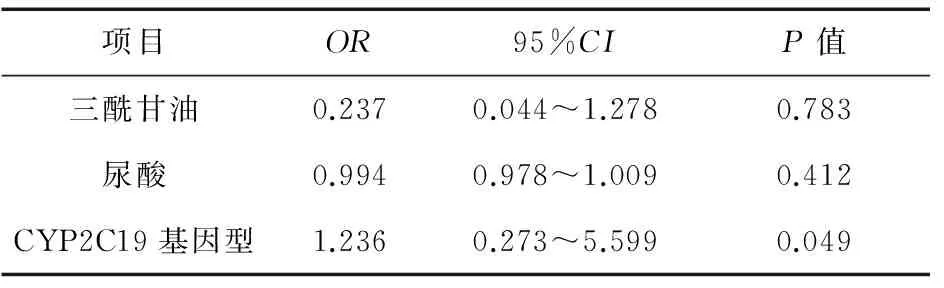
表3 Logistic回归分析
3 讨论
本研究观察了CYP2C19基因多态性及主要临床资料对服用氯吡格雷前后血小板聚集功能变化率(氯吡格雷抵抗)的影响。并通过Logistic回归筛选出CYP2C19基因多态性是氯吡格雷抵抗的高危因素。
慢代谢基因型氯吡格雷抵抗发生率高,而快代谢基因型中也存在氯吡格雷抵抗,可见CYP2C19基因多态性只是氯吡格雷抵抗基因水平的一个影响因素(其他基因还有ABCB1、PON1),而绝不是唯一影响因素[15-22]。有研究表明,在临床水平糖尿病或糖化血红蛋白影响血小板聚集功能[23-24],而在本研究中未得到证实;在分子水平有药物的相互作用(奥美拉唑)、血小板释放的其他因子(5羟色胺、肾上腺素等)影响氯吡格雷药物抵抗。因此,氯吡格雷抵抗存在基因水平、分子水平、临床水平等多方面影响因素。
目前,临床尚未确定血小板聚集功能检测的金标准,因此,临床上根据服药后血小板聚集率,将患者分为氯吡格雷药物抵抗组及非抵抗组并不合理,而本研究通过用药前后血小板聚集率的变化率进行分组,更加准确地反映出个体对氯吡格雷药物的反应性。但本实验因需测量服药前后两次血小板聚集功能,操作起来相对困难,研究对象偏少,实验数据可能存在偏倚。随着大家对氯吡格雷抵抗研究的深入,以及血小板聚集功能检测方法的增加,相信氯吡格雷抵抗在分子水平方面的研究将有更广阔的空间。
[1]王焕群,刘潇然,王巍巍,等.阿司匹林和氯吡格雷对大鼠血小板聚集的影响[J].沈阳医学院学报,2012,14(3):145-146.
[2]Wallentin L,Becker RC,Budaj A,et al.Ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes[J].N Engl J Med,2009,361(11):1045-1057.
[3]Park KW,Park BE,Kang SH,et al.The harmonizing optimal strategy for treatment of coronary artery stenosis-safety & effectiveness of drug-elcting stents & antiplatelet regimen(HOST-ASSURE)trial:study protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J].Trials,2012,13(1):29.
[4]Snoep JD,Hovens MM,Eikenboom JC,et al.Clopidogrel nonresponsiveness in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with stenting:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Am Heart,2007,154:221-231
[5]Mao L,Jian C,Changzhi L,et al.Cytochrome CYP2C19 polymorphism and risk of adverse clinical events in clopidogrel-treated patients:a meta-analysis based on 23,035 subjects[J].Arch Cardiovasc Dis,2013,106(10):517-527.
[6]Tan DS,Yeo AH,Ho HK,et al.Asian study of clopidogrel(ASCLOP)responsiveness:the contributions of genetic and non-genetic factors[J].Int J Cardiol,2014,171(2):e21-e23.
[7]Lin YJ,Li JW,Zhang MJ,et al.The association between CYP2C19 genotype and of in-stent restenosis among patients with vertebral artery stent treatment[J].CNS Neurosci Ther,2014,20(2):125-130.
[9]Jeong HE,Lee SJ,Cha EY,et al.Development of a multiplex and cost-effective genotype test toward more personalized medicine for the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel[J].Int J Mol Sci,2014,15(5):7699-7710.
[10]Guo B,Tan Q,Guo D,et al.Patients carrying CYP2C19 loss of function alleles have a reduced response to clopidogrel therapy and a greater risk of in-stent restenosis after endovascular treatment of lower extremity peripheral arterial disease[J].J Vasc Surg,2014,60(4):993-1001.
[11]Jeong YH,Abadilla KA,Tantry US,et al.Influence of CYP2C19*2 and *3 loss-of-function alleles on the pharmacodynamic effects of standard- and high-dose clopidogrel in East Asians undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention:the results of the ACCEL-DOUBLE-2N3 study[J].J Thromb Haemost,2013,11(6):1194-1197.
[12]Bennett D,Yan B.Suboptimal response to clopidogrel:a genetic risk factor for recurrent ischaemic stroke[J].J Clin Neurosci,2013,20(6):767-770.
[13]吴小利,李健,向代军.PL-11血小板聚集仪检测全血血小板聚集功能方法学评价及临床意义[J].临床检验杂志,2013,6(2):355-359.
[14]Tanabe K,Serruys PW,Grube E,et al.In-stent restenosis treated with stent-based delivery of paclitaxel incorporated in a slow-release polymer formulation[J].Circulation,2003,107(4):559-640.
[15]Gurbel PA,Antonino MJ,Tantry US.Recent developments in clopidogrel pharmacology and their relation to clinical outcomes[J].Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol,2009,5(8):989-1004.
[16]Gurbel PA,Bliden KP,Hiatt BL,et al.Clopidogrel for coronary stenting:response variability,drug resistance,and the effect of pretreatment platelet reactivity [J].Circulation,2003,107(23):2908-2913.
[17]蔡泓敏,陈珲,赵冠人,等.CYP2C19基因多态性与氯吡格雷抗凝作用的相关性研究[J].中国药物应用与检测,2013,10(5):254-257.
[18]Mega JL,Close SL,Wiviott SD,et al.Cytochrome P-450 polymorphisms and response to clopidogrel[J].N Engl J Med,2009,360(5):354-362.
[19]Small DS,Farid NA,Payne CD,et al.Effects of the proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole on the pharmaeokinetic and phamaeodynamics of prasugrel and clopidogrel[J].J Clin Phamacol,2008,48(4):475-484.
[20]Subraja K,Dkhar SA,Priyadharsini R,et al.Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19 influences the response to clopidogrel in ischemic heart disease patients in the South Indian Tamilian population[J].Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2013,69(3):415-422.
[21]Zhao Q,Liu HL.The association between CYP2C19*2 gene polymorphisms and clopidogrel resistance in the Han population of North China with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease[J].Heart,2012,98:E37.
[22]梁茜,杨希立,张健瑜,等.CYP2C19基因多态性与氯吡格雷治疗后心血管事件发生关系的研究[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(23):3883-3884.
[23]王梅,王春梅,王成钢,等.糖化血红蛋白与直接冠状动脉介入术后氯吡格雷抵抗关系[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2013,27(3):250-252
[24]Liu T,Yin T,Li Y,et al.CYP2C19 polymorphisms and coronary heart disease risk factors synergistically impact clopidogrel response variety after percutaneous coronary intervention[J].Coron Artery Dis,2014,25(5):412-420.
Correlation of CYP2C19 gene polymorphism and major clinical data with clopidogrel drug resistance
JIANG Jin-pinga,DU Xiao-mingb,SUN Ya-xinb,MA Shu-meia*
(a.Department of Cardiology,b.Department of Pharmacy,Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University,Shenyang 110004,China)
ObjectiveTo observe the correlation of CYP2C19 gene polymorphism in drug metabolism enzyme system and main clinical data with the change of platelet aggregation rate before and after taking clopidogrel (clopidogrel drug resistance).MethodsTotally 35 patients with coronary angiography examination or stenting treatment were selected and divided into clopidogrel resistance group (resistance group) and the non-resistance group according to the change of platelet aggregation rate before and after taking clopidogrel.CYP2C19 genotype was tested,and the patients′age,sex,alcohol tobacco history,hypertension,diabetes and other major clinical data were recorded,and the effect of genetic level and clinical level on platelet aggregation and clopidogrel drug resistance were analyzed.ResultsThere were 15 cases with clopidogrel resistance and 4 cases with CYP2C19 genotype slow metabolism.Logistic regression analysis showed that CYP2C19 genotype was a risk factor for clopidogrel resistance (OR=1.236,95%CI:0.273~5.599,P=0.049).ConclusionCYP2C19 gene polymorphisms are associated with clopidogrel resistance at the genetic level,but clinical level shows no obvious correlation.
Platelet aggregation function;Clopidogrel resistance;CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms
2016-01-18
中国医科大学附属盛京医院a.第一心血管内科,b.药学部,沈阳 110004
10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201609010

