一种基于多重距离聚类的多源侦察结果融合算法
徐 英
(中国人民解放军电子工程学院 304教研室,合肥 230037)
【信息科学与控制工程】
一种基于多重距离聚类的多源侦察结果融合算法
徐英
(中国人民解放军电子工程学院 304教研室,合肥230037)
由于来自不同传感器的侦察图像获取和传输的非实时性以及图像情报分析结果的非连续性,反侦察监视裁决需要对来自不同传感器的侦察结果进行空间和属性综合聚类,合并属于同一目标的侦察结果。考虑空间位置和多个非空间属性的相似性,提出了基于空间和属性多重距离的空间聚类算法MDBSC(Multiple Distance Based Spatial Clustering),用于多源侦察结果的关联融合,给出了算法步骤和实例。
多重距离; 空间聚类; 多源融合; 关联融合
复杂电磁环境下的作战训练向电磁对抗和体系对抗延伸[1],开展复杂电磁环境下的对抗演习和对抗裁决是信息化条件下战斗力生成和提高的重要保证,反侦察监视裁决是进行对抗裁决的重要组成部分。反侦察监视裁决利用专门设备模拟主要作战对手的侦察卫星和无人机的侦察监视行动,对受训部队重要目标和作战行动进行侦察,检验部队在不同天候、地形条件下实施植被、变形、迷彩等伪装的反侦察效果,从而增强部队隐蔽作战意图的能力,提升战场综合防护水平。
反侦察监视裁决时首先要获得对侦察图像进行人工或自动情报分析后的侦察结果,再将侦察结果与同一时刻实际目标的位置和属性进行比对,若匹配则认为侦察到目标。来自不同图像传感器的侦察结果包括图像中发现和识别的目标位置、目标识别类型、目标属性等信息,由于不同来源的侦察图像获取和传输的时间不同步、数据率不一致,且图像情报分析结果是非实时和非连续的,在进行侦察结果与实际目标位置、属性比对前,需要对来自不同传感器的侦察结果进行关联融合,合并属于同一目标的侦察结果。
侦察目标具有空间位置和非空间属性多重特性,进行多源侦察结果融合的原则是:不同传感器在近似同一时刻时对同一目标的侦察结果既要在空间位置上尽量接近,又要在识别属性上具有最大的相似度。因此,进行多源侦察结果融合时需要进行基于空间位置和非空间属性的多重聚类。
传统的空间聚类方法[2-30]大多仅依据对象的空间位置之间或其他特征属性之间的距离相似度进行聚类,前者忽略了对象的非空间特征属性,后者忽视了空间邻近性。目前能够兼顾空间属性和非空间属性的空间聚类方法主要有分治法和一体化法两类。分治法[31-32]在分别进行空间位置和非空间属性的聚类后综合生成最终聚类结果,如DC(Dual Clustering)算法和DCAD(Dual Clustering Algorithm for Distributed Spatial Databases)算法,这类算法计算量大,输入参数多,可扩展性不好;一体化法[33]将空间位置和非空间属性都视为空间要素的属性数据,使用属性距离函数计算相似度,再结合K均值算法进行聚类。该方法弱化了要素的空间特性,相似度计算权重带有主观性,且随机选取初始聚类中心导致存在聚类不确定性。此外,DDBSC算法[34]提出双重距离的概念,使用染色策略递归检索每个核要素的所有双重距离直接可达或相连的要素,并聚为簇,但是该算法仅考虑了一种非空间属性,且在开始或完成一轮递归搜索后,都要检查所有空间要素是否染色,计算效率较低。本文在DDBSC算法的基础上进行改进,综合考虑空间位置和多个非空间属性的相似性,分别计算空间和多个非空间属性多重距离,并提高算法计算效率,提出了基于多重距离的空间聚类算法MDBSC(Multiple Distance Based Spatial Clustering),用于多源侦察结果的融合。
1 算法原理
设有多源侦察结果构成空间要素集合F={f1(X1,Y1),f2(X2,Y2),…,fn(Xn,Yn)}(n≥2),其中X={x1,x2}为空间位置二维坐标向量,Y={y1,y2,…,ym}为m维非空间属性向量(如目标运动速度,目标发现时间等),则fi到fj(1≤i,j≤n)的空间距离和第k维非空间属性距离分别为DistX(Xi,Xj)和Distyk(yik,yjk),定义为:
(1)
(2)
式中:(xi1,xi2)表示fi的空间位置坐标;yik表示fi的第k维非空间属性。
当两个空间要素空间距离接近,且所有非空间属性距离相似时,可划分为同一类簇。空间上不相邻的空间要素之间可能通过其他要素相连,从而也归为同一类簇。这里引入距离直接可达和距离相连的概念,当且仅当空间和多个非空间属性多重距离直接可达或相连时,空间要素才划分为同一类簇。定义如下:




6) 核:选取一个未归属任何簇的空间要素fc作为新簇的搜索起始点,若至少存在一个要素fd,满足fd↔fc,则要素fc称为核。
7) 簇:每个核要素的所有多重距离直接可达或相连的要素,并聚为簇cluster={fc,∀fi:fi↔fc∪fi~fc}
8) 孤立点:未归属任何簇的要素。
2 算法步骤
在进行目标聚类时,依次搜索各空间要素,判断各要素之间的多重距离是否直接可达或相连,从而获得染色空间要素集,即聚簇结果。定义空间要素的数据结构包括要素的空间位置向量、非空间属性向量、核属性标识bisCore(布尔型)和着色值nColor,当要素为核时标识bisCore为真,当要素尚未着色时nColor值为0。算法过程如下:
1) 按时间先后顺序建立包含所有空间要素的染色队列用于存储要素信息,并设置所有要素的bisCore=FALSE,nColor=0,初始化i=0,C=0;
2) 抽取队列中第i个要素,若已染色,直接转步骤(3),若未染色(nColor=0),令C=C+1,并设置fi的颜色fi.nColor=C,第C个染色要素集FC={fi};

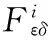

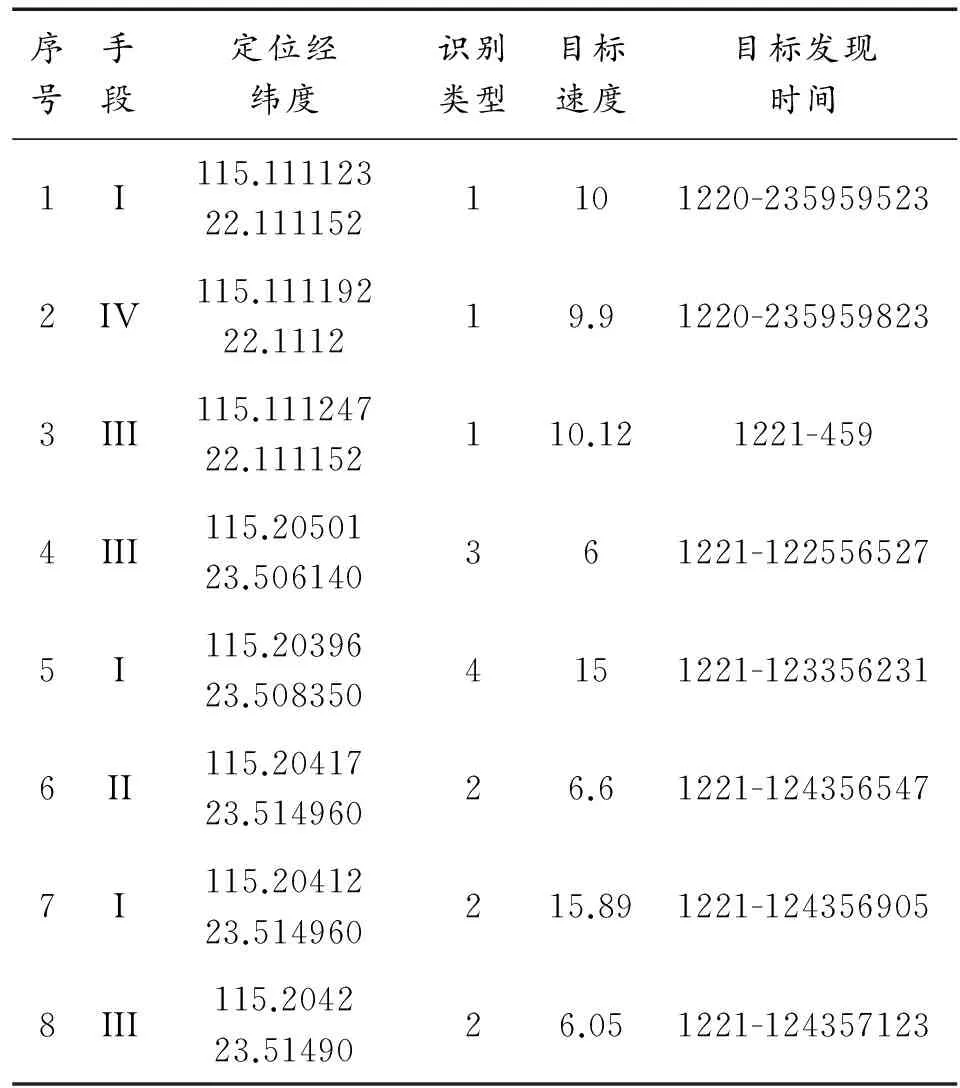
6)i=i+1,若i≥n,直接转步骤(7),若i 7) 将第C个融合要素集中所有要素的空间位置进行融合得到第C个目标的融合位置,将所有要素的非空间属性值求平均得到第C个目标的融合属性值,得到融合结果队列。 设有红外(I)、可见光(II)、超光谱(III)、SAR(IV)成像的3类侦察结果(见表1),侦察目标类型用数字1~5代替,以运动速度(m/s)和发现时间(s)作为目标非空间属性。设置距离容差为10m,非空间属性速度容差为1.5 m/s,假设采集时间最小间隔为1 s,只对间隔时间小于1 s内的侦察结果进行融合,即非空间属性目标发现时间容差为1 s。利用本文方法进行多源侦察结果的融合,融合结果见表2,“融合结果”列中“()”内为参与融合的目标序号,以“-”符号连接。 表1 侦察结果中的空间位置和非空间属性 表2 融合结果 由表1可以看出,侦察目标1、2和3在空间位置上相近,目标速度和发现时间属性也近似,对应同一实际目标;侦察目标6、7和8在空间位置上相近,但是由于目标7的速度属性与目标6和8的速度属性差距较大,因此将目标6和8聚类,目标7和目标4、5一样均视为孤立点,最终将来自多源侦察的8个目标聚类后得到5个目标。实验结果表明,本文所提出的MDBSC方法能够根据多源侦察结果在目标位置和非空间属性上的相似性,有效融合多源侦察结果,聚类算法效率高,且结果较为合理。 本文提出了基于空间和属性多重距离的聚类方法用于反侦察监视裁决中的多源侦察结果融合。给出了多重距离直接可达和多重距离相连的概念,当且仅当多重距离直接可达或相连时,空间要素才划分为同一类簇,利用对多源侦察结果的距离直接可达和距离相连的判断,将同一目标的侦察结果聚类融合得到目标的融合情报。通过试验验证了算法的可用性和合理性。 [1]李靖,张坤平,田军.中国陆军复杂电磁环境下训练取得突破性进展[N].解放军画报,2010-02-15. [2]MACQUEEN J.Some Methods for Classification and Analysis of Multivariate Observations [C]//Proceedings of 5-th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability.Berkeley:University of California Press,1967:281-297. [3]KAUFMAN L,ROUSSEEUW P J.Finding Groups in Data:An Introduction to Cluster Analysis[M].New York:John Wiley & Sons,1990. [4]NG R,HAN J.CLARANS:A method for clustering objects for spatial data mining[J].IEEE Trans.Knowledge & Data Engineering,2002,14(5):1003-1016. [5]HOPEENER F,KLAWONN F,KRUSE R.Fuzzy Cluster Analysis:Methods for Classification,Data Analysis and Image Recognition[Z].1999. [6]ZHANG T,RAMAKRISHNAN R,LIVNY M.BIRCH:An Efficient Data Clustering Method for Very Large Databases [C]//Proceeding of the International Conference Management of Data.Montreal:[s.n.],1996:103-114. [7]GUHA S,RASTOGI R,SHIM K.CURE:An Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Large Databases [C]//Proceedings of 1998 ACM-SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD’ 98).New York:ACM,1998:73-84. [8]GUHA S,RASTOGI R,SHIM K.ROCK:A Robust Clustering Algorithm for Categorical Attributes [C]//Proceedings of the International Conference of Data Engineering (ICDE’ 99).Washington:IEEE Computer Society,1999:512-521. [9]KARYPIS G,HAN E H,KUMAR V.CHAMELEON:A hierarchical clustering algorithm using dynamic modeling.Compute[Z].1999:68-75. [10]SUDIPTO G,RASTOGI R,SHIM K.ROCK:A robust clustering algorithm for categorical attributes[C]//Proc.1999 Int’l Conf.Data Engineering(IDCE’ 99).[S.l.]:[s.n.],1999:512-521. [11]ESTER M,KRIEGEL H P,SANDER J,XU X.A Density-based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise [C]//Proceedings of the 2nd the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.[s.l.]:AAAI Press,1996:226-231. [12]ANKERST M,BREUNIG M,KRIEGEL H P,etal.OPTICS:Ordering Points to Identify the Clustering Structure [C]//Proceedings of the 1999 ACM-SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (DIGMOD’ 99).New York:ACM,1999:49-60. [13]HINNEBURG A,KEIM D A.An Efficient Approach to Clustering in Large Multimedia Databases with Noise [C]// Proceedings of the 1998 International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’98).New York:AAAI Press,1998:58-65. [14]WANG W,YANG J,MUNTZ R.STING:A Statistical Information Grid Approach to Spatial Data Mining [C]// Proceedings of the 1997 International Conference on Very Large Data Bases (VLDB’97).San Francisco:Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc,1997:186-195. [15]SHEIKHOLESLAMI G,CHATTERJEE S,ZHANG A.WaveCluster:A Multi-resolution Clustering Approach for Very Large Spatial Databases [C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Very Large Database.New York:Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc,1998:428-439. [16]AGRAWAL R,GEHRKE J,GUNOPULOS D,et al.Automatic Subspace Clustering of High Dimensional Data for Data Mining Applications[C]//Proceedings of the 1998 ACM-SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data (SIGMOD’98).New York:ACM,1998:94-105. [17]XU X W,ESTER M,KRIEGE H P,et al.A Distribution-based Clustering Algorithm for Mining in Large Spatial Databases [C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE’98).Washington:IEEE Computer Society,1998:324-331. [18]FISHER D.Improving inference through conceptual clustering[C]// Proc.AAAI Conf.Seattle.WA,1987:461-465. [19]CHEESEMAN P,STUTZ J.Bayesian classification (Autoclass):Theory and results.Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining[Z].MA:AAAI/MIT Press,1996:153-180. [21]DAVÉR.Adaptive Fuzzy C-Shells Clustering and Detection of Ellipses [J].IEEE Transaction Neural Network,1992,3(5):643-662. [22]CHERNG J S,LO M J.A Hypergraph Based Clustering Algorithm for Spatial Data Sets [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM’ 01).Washington:IEEE Computer Society,2001:83-90. [23]HARTUV E,SHAMIR R.A Clustering Algorithm Based on Graph Connectivity [J].Information Processing Letters,2000,76 (426):175-181. [24]SHARAN R,SHAMIR R.CLICK:A Clustering Algorithm with Applications to Gene Expression Analysis[C]// Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB).San Diego:AAAI Press,2000:307-316. [25]AMIR B D,ZOHAR Y.Clustering Gene Expression Patterns [J].Journal of Computational Biology,1999,6(324):281-297. [26]SONG G,YING X.GDCIC:A Grid-based Density-Confidence-Interval Clustering Algorithm for Multi-density Dataset in Large Spatial Databases [C]// Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications (ISDA’ 06).Washington:IEEE Computer Society,2006:713-717. [27]UNCU O,GRUVER W A,KOTAK D B,etal.GRIDBSCAN:Grid Density-based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise [C]//Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Systems,Man and Cybernetics (ICSMC’ 06).Taipei:[s.n.],2006:2976-2981. [28]TSAI C F,YEN C C.ANGEL:A New Effective and Efficient Hybrid Clustering Technique for Large Databases[M].Berlin:Springer Press,2007. [29]骆剑承,梁怡,周成虎.基于尺度空间的分层聚类方法及其在遥感影像分类中的应用[J].测绘学报,1999,28(4):319-314. [30]骆剑承,周成虎,梁怡.多尺度空间单元区域划分方法[J].地理学报,2002,54(2):167-173. [31]LIN C R,LIU K H,CHEN M S.Dual Clustering:Integrating Data Clustering over Optimization and Constraint Domains[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.Piscataway:IEEE Educational Activities Department,2005:628-637. [32]ZHOU J G,GUAN J H,LI P X.DCAD:A Dual Clustering Algorithm for Distributed Spatial Databases [J].Geo-spatial Information Science,2007,10(2):137-144. [33]李新运,郑新奇,闫弘文.坐标与属性一体化的空间聚类方法研究[J].地理与地理信息科学,2004,20(2):38-40. [34]李光强,邓敏,程涛,等.一种基于双重距离的空间聚类方法[J].测绘学报,2008,37(4):482-488. (责任编辑杨继森) An Algorithm of Multiple Sensor Reconnaissance Results Fusion Based on Multiple Distances Based Spatial Clustering XU Ying (304 Teaching and Research Section, Electronic Engineering Institute of PLA, Hefei 230037, China) During the counter reconnaissance assessment,in order to merge the reconnaissance results belong to the same target, reconnaissance results from different sensor should be clustered based on the spatial position and attributes on account of the non-real time inconstant of the acquisition and transmission of reconnaissance images, and the time non-continuity of image information analysis results. Taking into account of the similitude of the spatial position and multiple non-spatial attributes, MDBSC (Multiple Distances Based Spatial Clustering) algorithm was proposed and used to achieve the reconnaissance results fusion of multi-sensor, and procedure and example of the algorithm were provided. multiple distance; spatial clustering; fusion of multi-sensor; association and fusion 2016-04-16; 2016-04-30 徐英(1979—),女,博士,讲师,主要从事装备电磁环境适应性与评估研究。 10.11809/scbgxb2016.09.020 format:XU Ying.An Algorithm of Multiple Sensor Reconnaissance Results Fusion Based on Multiple Distances Based Spatial Clustering[J].Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering,2016(9):83-86. TP753 A 2096-2304(2016)09-0083-04 本文引用格式:徐英.一种基于多重距离聚类的多源侦察结果融合算法[J].兵器装备工程学报,2016(9):83-86.3 算法实例

4 结论

