一株神舟十号飞船分离少动鞘氨醇单胞菌基因组测序结果及分析
徐 绸,谢 琼,辛冰牧,刘长庭*
(1.中国人民解放军总医院南楼呼吸科,北京100853;2.中国航天员科研训练中心,北京100094)
一株神舟十号飞船分离少动鞘氨醇单胞菌基因组测序结果及分析
徐 绸1,谢 琼2,辛冰牧2,刘长庭1*
(1.中国人民解放军总医院南楼呼吸科,北京100853;2.中国航天员科研训练中心,北京100094)
在神舟十号飞船中检测出一株下行菌,16 S rDNA鉴定后命名为少动鞘氨醇单胞菌LCTSP1。通过对该菌基因组进行二代测序及基因注释,发现该菌包含3884个蛋白编码基因、3个rRNA编码基因和47个tRNA编码基因。通过对该菌基因组进行COG、GO分析及注释,完善了该菌的遗传信息,并建立了该菌的系统发育树。分析发现该菌包含腐蚀相关基因并可适应恶劣的生存环境。通过基因注释发现该菌包含574个毒力相关基因以及57个耐药相关基因,提示该菌存在潜在的致病性。
少动鞘氨醇单胞菌;基因测序;腐蚀性;致病性
1 引言
少动鞘氨醇单胞菌原名少动假单胞菌,广泛存在于水、土壤等自然环境中[1],是一种严格需氧的革兰氏阴性非发酵鞘氨醇单胞菌[2],其氧化酶、过氧化氢酶试验阳性[3]。少动鞘氨醇单胞菌为条件致病菌,也是鞘氨醇单胞菌属中唯一具有重要临床意义的一个种。虽然临床少动鞘氨醇感染病例较少,但近年来发病有增加的趋势,并可导致严重的院内感染甚至爆发感染[4-5]。已有研究证实鞘氨醇单胞菌属可分解阿魏酸[6]、木质素[7]、联苯[8]等材料,我们同期研究发现该株菌还可以分解环氧树脂、酯聚氨酯和醚聚氨酯等多种材料。本研究主要通过对该株少动鞘氨醇单胞菌进行基因组测序及基因组注释,为发现该菌的腐蚀机理提供线索,也为该菌致病性研究及临床防治提供一定依据。
2 材料与方法
2.1 菌种采集
神舟十号飞船于2013年6月11日17时38分发射,2013年6月26日8时07分返回,在轨15天,其中12天与天宫一号组成组合体在太空中飞行。返回后在冷凝水样品中检测分离出一株微生物,通过16S rDNA鉴定、检索文献完善该菌菌种信息,确定为少动鞘氨醇单胞菌[9],命名为LCT-SP1。
2.2 细菌培养和DNA提取
35℃,LB培养基隔夜培养,然后接种于LB琼脂糖培养基。按照Illumina公司试剂盒说明书,用CTAB法提取基因组DNA[10]。
2.3 基因组测序和组装
在上海美吉公司采用Illumina HiSeq2000测序技术对DNA进行paired-end(PE)测序,构建300bp文库。剪切掉原始数据中质量较低的数据以利于后续组装。利用SOAPdenovo(版本号v1.05)拼接软件对优化序列进行多个Kmer参数的拼接,得到最优的组装结果。运用GapCloser软件对组装结果进行局部内洞填充和碱基校正。依据拼接序列的总长、scaffold的数量以及scaffold N50等技术指标,对多个Kmer的组装结果进行综合评定,选择K-mer为31的结果作为最终的组装结果。
2.4 基因预测和功能注释
利用RNAmmer和tRNAscan-SE软件对基因组中包含的rRNA和tRNA进行预测[11-12]。利用Glimmer 3.0软件进行基因预测[13]。将预测基因的蛋白序列与string数据库(版本号v8.3)进行blastp比对,获得基因所对应的同源蛋白簇(Clusters of Orthologous Groups of proteins,COG)注释结果,并根据COG注释结果对蛋白进行功能归类[14]。通过blast2go软件对blast结果进行基因本体论(Gene Ontology,GO)注释分析。自动基因注释是由NCBI原核基因组注释自动路径(PGAAP)完成。用MEGA 5采用NJ(Neighborjoining)法对16S rDNA构建系统发育树[15]。
3 结果
3.1 菌株信息
LCT-SP1鉴定为一株少动鞘氨醇单胞菌(变形菌门,α变形菌纲,鞘脂单胞菌目,鞘脂单胞菌科,鞘脂单胞菌属)。该菌为需氧,非发酵革兰氏阴性短杆菌,无孢子生成,活动缓慢。pH 7.2,35℃,低盐环境(0-1%氯化钠)为该菌最适生长条件。该菌可以利用包括葡萄糖、麦芽糖、蔗糖、乳糖、海藻糖、醋酸、苹果酸、Tween-40等碳源。在有氧条件下,该菌在LB培养基中呈现为边缘整齐的微小黄色菌落。
3.2 基因组结果
3.2.1 基因组测序、组装及预测结果

表1 LCT-SP1的基因组测序及组装结果Table 1 Genome sequence and assembly results of LCTSP1
该株LCT-SP1少动鞘氨醇单胞菌的基因组测序及组装结果如表1所示。该株LCT-SP1染色体包含4 302 226 bp,其中GC含量为65.66%;基因编码区包含3 772 440 bp,占基因组87.7%,基因编码区基因区GC含量66.2%,平均每个基因大小为958 bp。编码区包含3884个蛋白编码基因,占3934个总预测基因数的98.73%。测序共发现3个rRNA编码基因和47个tRNA编码基因。根据参考基因组使用mavue对细菌草图con-tig进行排序,再采用genomeviz绘制圈图(图1)。该菌的基因组序列已经在GenBank基因库中提交,检索号是KR080483。
3.2.2 COG、GO注释及功能归类
该菌COG注释及功能归类显示,1906个编码蛋白被归类为25个COG中的21个,占总预测基因数的48.45%。在21个同源蛋白簇中,通用功能(211个)比例最高,其他依次为氨基酸转录和代谢(171个),翻译、核糖体结构和生物转化(141个),能量生成和转换(140个),复制、重组和修复(130个),功能未知(124个),转录(115个),无机离子运输和代谢(115个)以及碳水化合物的运输和代谢(109个)等(图2)。该菌的基因产物GO注释及功能归类如图3所示。
3.2.3 系统发育树构建
对该株LCT-SP1少动鞘氨醇单胞菌进行16 S rDNA鉴定并构建系统发育树,发现其同土壤和水中分离的haloaromaticamans单胞菌同源性较为接近(图4)。
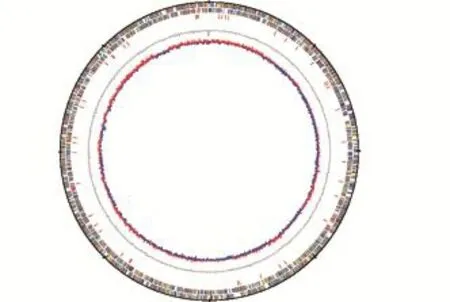
图1 LCT-SP1少动鞘氨醇单胞菌基因组圈图(从外到里分别是cds、t/rRNA、GC含量和GC skew)Fig.1 Circular map of the draft genome of strain LCT-SP1(From outside to the center:cds,t/rRNA genes,GC content,GC skew)
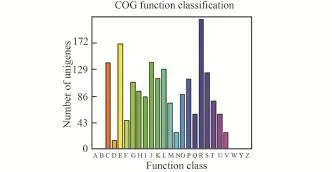
图2 LCT-SP1的COG功能归类图Fig.2 Number of unigenes associated with the COG functional categories
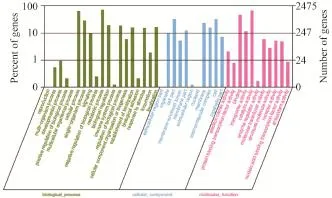
图3 LCT-SP1的GO功能归类图Fig.3 Number of unigenes associated with the GO functional categories
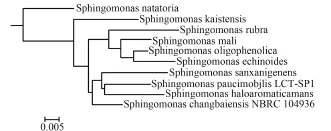
图4 LCT-SP1的系统发育树Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of LCT-SP1
4 讨论
少动鞘氨醇单胞菌可导致社区感染和医院获得性感染,多发生于免疫力低下、体内植入物或抗生素治疗后患者[16]。曾在腹腔感染、腿部溃疡、尿路感染、甚至脑脓肿、脾脓肿等标本中检出。通过基因组分析,发现该菌不含有编码脂多糖的相关基因,印证该菌缺乏这一常见的革兰氏阴性菌重要致病因子,内毒素活性低或许预示该菌较好的预后[17]。但是该菌含有574个毒力相关基因以及57个耐药相关基因(如编码青霉素结合蛋白、多药耐药外排泵、β-内酰胺酶等基因),提示了该菌潜在的致病性及耐药性。航天员在轨过程中受微重力等影响,免疫力下降,增加了该菌的致病风险。目前针对该菌基础研究、临床研究以及流行病调查较少,其致病机理尚不清晰,对航天员健康存在威胁。
通过基因组测序发现该菌同可耐受恶劣环境(高紫外线、高矿化度、高pH值、干燥和极端的温差)的少动鞘氨醇单胞菌S17的基因高度相符[18],提示该菌具有顽强的生命力,也预示严峻的灭菌难题。LCT-SP1同样具有编码NhaA(具有Na+/H+逆向转运功能)及多亚基阳离子逆向转运体的基因,说明该菌可以适应碱性及高盐环境,并可通过改变pH值造成材料的腐蚀[19]。该菌顽强的生存能力以及对有机材料较强的腐蚀、分解特性,如运用于环境工程或可有治理污染的广大前景。
5 结论
1)少动鞘氨醇单胞菌LCT-SP1包含腐蚀相关基因并可适应恶劣的生存环境。
2)少动鞘氨醇单胞菌LCT-SP1包含574个毒力相关基因以及57个耐药相关基因,存在潜在的致病性。
(References)
[1]Reina J,Bassa A,Llompart I,et al.Infections with Pseudomonas paucimobilis:report of four cases and review[J].Reviews of Infectious Diseases,1991,13(6):1072-6.
[2]Yabuuchi E,Yano I,Oyaizu H,et al.Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen.nov.and comb.nov.,Sphingomonasparapaucimobilissp.nov.,Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp.nov.,Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp.nov.,Sphingomonas capsulata comb.nov.,and two genospecies of the genus Sphingomonas[J].Microbiology and Immunology,1990,34(2):99-119.
[3]Von G A.Acinetobacter,Alcaligenes,Moraxella,and other nonfermentative gram-negative bacteria[M]//Murray P,Barron E,Pfaller M.Manual of clinicalmicrobiology.6th ed.Washington,DC:American Society for Microbiology;1995:520-532.
[4]Kilic A,Senses Z,Kurekci AE,et al.Nosocomial outbreak of Sphingomonas paucimobilis bacteremia in a hemato/oncology unit[J].Japanese Journal of Infectious Diseases,2007,60(6):394-396.
[5]Maragakis L L,Chaiwarith R,Srinivasan A,et al.Sphingomonas paucimobilis bloodstream infections associated with contaminated intravenous fentanyl[J].Emerging Infectious Diseases,2009,15(1):12-19.
[6]Masai E,Harada K,Peng X,et al.Cloning and characterization of the ferulic acid catabolic genes of Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(9):4416-24.
[7]Nishikawa S,Sonoki T,Kasahara T,et al.Cloning and sequencing of the Sphingomonas(Pseudomonas)paucimobilis gene essential for the O demethylation of vanillate and syringate[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1998,64(3):836-42.
[8]Peng X,Masai E,Kitayama H,et al.Characterization of the 5-carboxyvanillate decarboxylase gene and its role in lignin-related biphenyl catabolism in Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2002,68(9):4407-15.
[9]Field D,Garrity G,Gray T,et al.The minimum information about a genome sequence(MIGS)specification[J].Nature Biotechnology,2008,26(5):541-7.
[10]van Embden J D,Cave M D,Crawford J T,et al.Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting:recommendations for a standardized methodology[J].Journal of Clinical Microbiology,1993,31(2):406-9.
[11]Lagesen K,Hallin P,Rodland EA,et al.RNAmmer:consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2007,35(9):3100-8.
[12]Lowe T M,Eddy S R.tRNAscan-SE:a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence[J].Nucleic Acids Research,1997,25(5):955-64.
[13]Delcher A L,Harmon D,Kasif S,et al.Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER[J].Nucleic Acids Research,1999,27(23):4636-41.
[14]Tatusov R L,Galperin M Y,Natale D A,et al.The COG database:a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution[J].Nucleic Acids Research,2000,28(1):33-6.
[15]Tamura K,Peterson D,Peterson N,et al.MEGA5:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood,evolutionary distance,and maximum parsimony methods[J].Molecular Biology and Evolution,2011,28(10):2731-9.
[16]Mohan D,Railey M.Sphingomonas paucimobilis peritonitis:A case report and review of the literature[J].Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation:An Official Publication of the Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation,Saudi Arabia,2015,26(3):567-71.
[17]Kawasaki S,Moriguchi R,Sekiya K,et al.The cell envelope structure of the lipopolysaccharide-lacking gram-negative bacterium Sphingomonas paucimobilis[J].Journal of Bacteriology,1994,176(2):284-90.
[18]Farias ME,Revale S,Mancini E,et al.Genome sequence of Sphingomonas sp.S17,isolated from an alkaline,hyperarsenic,and hypersaline volcano-associated lake at high altitude in the Argentinean Puna[J].Journal of Bacteriology,2011,193(14):3686-7.
[19]Padan E,Tzubery T,Herz K,et al.NhaA of Escherichia coli,as a model of a pH-regulated Na+/H+antiporter[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2004,1658(1-2):2-13.
Genome Sequence Analysis of a Sphingomonas paucimobilis Strain from Shenzhou-10 Spacecraft
XU Chou1,XIE Qiong2,XIN Bingmu2,LIU Changting1*
(1.Nanlou Respiratory Disease Department,the 301th Hospital,Beijing 100853,China;2.China Astronaut Research and Training Center,Beijing 100094,China)
A strain of bacterium,LCT-SP1,was isolated from Shenzhou-10 spacecraft,and identified as Sphingomonas paucimobilis by 16S rDNA sequencing.Its genomic sequence was obtained by the Illumina sequencing platform.After the annotation,3884 protein-coding genes,3 rRNA genes and 47 tRNA genes were found.Based on the COG and GO analysis,the gene-information of the bacteria was obtained.A phylogenetic tree of this bacterium was constructed.The genome analysis shows that the bacterium has corrosion-related genes that might promote its adaptation to the harsh environment.574 virulence associated genes and 57 antibiotic-resistant genes were also found in the genome,which indicated the potential pathogenicity of the bacterium.
Sphingomonas paucimobilis;gene sequence;corrosion;pathogenesis
R856
A
1674-5825(2016)05-0651-04
2015-12-02;
2016-08-13
载人航天预先研究项目(040203);国家重点基础研究发展计划资助(973计划)(2014CB744400);全军医学科研“十二五”课题重点项目(BWS12J046);科技部重大专项项目(空间新药重大创制)(2015ZX09J15102-002)
徐绸(1981-),男,博士,主治医师,研究方向为肺部感染和空间医学。E-mail:xuchou_1018@163.com
刘长庭(1954-),男,硕士,教授,研究方向为空间生命科学。E-mail:changtingliu@sohu.com

